Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ch01 01
Uploaded by
Pritam JadhavOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ch01 01
Uploaded by
Pritam JadhavCopyright:
Available Formats
PowerPoint Presentation
for
Instructors Online Learning Center
Thermodynamics
An Engineering Approach
Fourth Edition
Yunus A. engel
Michael A. Boles
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
CHAPTER
1
Basic Concepts
of Thermodynamics
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Mechanical
Engineering
Mechanics
Energy
Systems
Design
The over arching goal is
design of products to
meet societal needs.
General overview
Thermodynamics
A part of the Energy
component of mechanical
engineering.
Governs all energy
consuming and
transforming devices and
system.
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
The engineering framework
THEORY
JUDGMENT
(DESI GN)
DATA
FIGURE 15
Some application areas of
thermodynamics.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
1-1
Diet
Air vents
FIGURE 17
The definition of the force units.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
1-2
1 lbm will have a gravitational force on it of 1 lbf on earth.
Check for dimensional homogeneity!
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Beginning ideas and
concepts...
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Macroscopic vs. microscopic
viewpoints...
A collection of atoms within a container, each with a unique velocity.
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Number of atoms = N
Energy of each atom =
2
2
1
V m e =
Total Energy =
=
= =
N
i
ke V m
N
eN
1
1
2
2
Energy in a microscopic description
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
The energy in both cases
is the same, E. In the
macroscopic description,
atomistic concepts are
disregarded.
How we describe the
system chosen for study
requires careful selection of
properties that are based
on observable, measurable
quantities.
The macroscopic description
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
The macroscopic
viewpoint...
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
State of a
thermodynamic
system.
Enumeration of
all of its
properties.
I n macroscopic thermodynamics,
the properties of system are
assigned to the system as a whole.
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Properties in macroscopic thermodynamics
|
.
|
\
|
A
A
A
=
0
0
m
lim
0
D
e
n
s
i
t
y
,
Molecular and atomic
effects are important
Limit of the macroscopic
model and assumptions.
(m
3
)
0
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
How does the state of
system change?
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
System
Energetic interactions
Surroundings
Energy
Flow
System Boundary
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Basic definitions...
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
System
0 =
dt
dm
Closed
System
Open
System
Mass Flow
Mass Flow
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
System and surroundings
Universe = Systems +Surroundings
Closed System
Surroundings
System Boundary
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
System and surroundings
Open systems have mass flow across
their boundaries.
Open System
( Fixed space or
volume)
Surroundings
Control Surface
Mass flow
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
I nteractions between
system and surroundings...
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Closed system
System
Surroundings
Work
Heat
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Open system
System
Surroundings
Mass Flow
Mass
Flow
Power
Heat
Usually look at rates.
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Example: Piston and cylinder - a closed system
m
Gas at pressure, p
Piston
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Example: The gas turbine engine - an open system
Shaft Work Output
Combustor
Fuel Flow I n
Air Flow I n
Exhaust Gases Out
Compressor Work Out
FIGURE 117
A control volume may involve fixed,
moving, real, and imaginary
boundaries.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
1-5
A control volume is an open system
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Key concepts and terms
Closed System
Open System
System Boundary
Surroundings
Universe
Thermodynamic Properties
Thermodynamic State
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Equilibrium states and
properties
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Properties
Properties:
Temperature
Pressure
Volume
Internal energy
Entropy
System
The system can be either open or
closed. The concept of a property
still applies.
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Classes of properties
Extensive
MASS
VOLUME
ENERGY
ADDITIVE OVER
THE SYSTEM.
Intensive
TEMPERATURE
PRESSURE
DENSITY
NOT ADDITIVE
OVER THE SYSTEM.
Specific Properties
Continuum approach is valid if system is large
compared to distance between molecules
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
State
At a given state, all the properties of the
system have fixed values.
If the value of one property changes, the
state changes.
If no properties are changing, then it is at
equilibrium
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Equilibrium
Thermodynamics deals with equilibrium
states.
No driving forces
Mechanical equilibrium
No change in pressure with time
Thermal equilibrium
Temperature is same throughout system
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Equilibrium
Phase equilibrium
No change in the amounts of different phases
Chemical equilibrium
Chemical composition does not change with
time.
Instructors Visual Aids
Heat Work and Energy. A First Course in Thermodynamics
2002, F. A. Kulacki
Chapter 1 Module 1 Slide #
Energy, Heat and Work
Introduction to Macroscopic Thermodynamics
State Postulate
The state of a simple compressible system
is completely specified by two
independent, intensive properties
Simple compressible system:
Absence of electrical, magnetic, gravitational,
motion and surface tension effects.
Independent if one property can be held
constant while another is varied
You might also like
- ACE AcademyDocument4 pagesACE AcademyPritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Fixing Insufficient Memory Errors - Classic GamingDocument2 pagesFixing Insufficient Memory Errors - Classic GamingPritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Previous GATE Questions & Solutions (ME) (1987 To 2013) : S.No. Name of The Subject Page NoDocument1 pagePrevious GATE Questions & Solutions (ME) (1987 To 2013) : S.No. Name of The Subject Page NoPritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Practice PapersDocument12 pagesPractice PapersPritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Insufficient MemoryDocument6 pagesInsufficient MemoryPritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Ch20Thermodynamics (A)Document30 pagesCh20Thermodynamics (A)Pritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Base - Why Do I Get An - Insufficient Memory To Perform Operation - Error When Gridding DataDocument2 pagesKnowledge Base - Why Do I Get An - Insufficient Memory To Perform Operation - Error When Gridding DataPritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 ThermodynamicsDocument57 pagesChapter 19 ThermodynamicsPritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Memory Optimising - TutorialDocument6 pagesMemory Optimising - TutorialPritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- CH2ch17 1Document11 pagesCH2ch17 1Pritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Installing A IDE - EIDE Hard Drive.Document4 pagesInstalling A IDE - EIDE Hard Drive.Pritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Fundamentals ExplainedDocument19 pagesThermodynamics Fundamentals ExplainedAFSETCADLab100% (1)
- Presentation On Landscape of Automobile Industry in India: Consulting ClubDocument8 pagesPresentation On Landscape of Automobile Industry in India: Consulting ClubNíìlesh Krîshñä GøléNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document60 pagesCH 6Nor Hafiza AhmadNo ratings yet
- ch01 03Document8 pagesch01 03Pritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Autoindus 120223094832 Phpapp01Document24 pagesAutoindus 120223094832 Phpapp01Pritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- CH 15Document73 pagesCH 15Pritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Physics 101: Lecture 27, PG 1Document16 pagesThermodynamics: Physics 101: Lecture 27, PG 1Pritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Physics 101: Lecture 27, PG 1Document16 pagesThermodynamics: Physics 101: Lecture 27, PG 1Pritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- 02-Chapter 11 ThermodynamicsDocument99 pages02-Chapter 11 ThermodynamicsPritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Rajma RecipeDocument2 pagesRajma RecipePritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Rajma MasalaDocument2 pagesRajma MasalaPritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@corn in Red Gravy Recipe - Easy Corn in Red Gravy Recipe - Recipe For Corn in Red Gravy PDFDocument2 pages@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@corn in Red Gravy Recipe - Easy Corn in Red Gravy Recipe - Recipe For Corn in Red Gravy PDFPritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Corn Capsicum Gravy Recipe - TarladalalDocument3 pagesCorn Capsicum Gravy Recipe - TarladalalPritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Punjabi RajmahDocument8 pagesPunjabi RajmahPritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Rajma Rice (Kashmiri Style) : February 11, 2013 4 CommentsDocument6 pagesRajma Rice (Kashmiri Style) : February 11, 2013 4 CommentsPritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Rajma Masala RecipeDocument7 pagesRajma Masala RecipePritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- SeemaDocument1 pageSeemaPritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- Rajma RecipeDocument2 pagesRajma RecipePritam JadhavNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- DCI Assignment Sample 2Document50 pagesDCI Assignment Sample 2james smithNo ratings yet
- Signed Off - Introduction To Philosophy12 - q1 - m2 - Methods of Philosophizing - v3Document25 pagesSigned Off - Introduction To Philosophy12 - q1 - m2 - Methods of Philosophizing - v3Benjamin Fernandez Jr.No ratings yet
- Marketing in 4th Industrial RevolutionDocument8 pagesMarketing in 4th Industrial RevolutionCamille Anne ParacNo ratings yet
- T REC G.650.1 201210 S!Amd1!PDF EDocument16 pagesT REC G.650.1 201210 S!Amd1!PDF EVenâncio Ricardo MendonçaNo ratings yet
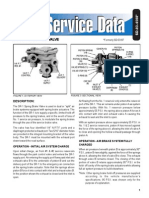
- SR-1 Spring Brake Valve (SD-03-4508)Document8 pagesSR-1 Spring Brake Valve (SD-03-4508)EdvinCastleNo ratings yet
- SS 100-Writing and CommunicationDocument10 pagesSS 100-Writing and CommunicationCool MomNo ratings yet
- BSBWHS308Document40 pagesBSBWHS308Pragati AryalNo ratings yet
- Fan6602r 1122356 PDFDocument20 pagesFan6602r 1122356 PDFGiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaNo ratings yet
- 2280-Motorola Maxtrac 100-300 User ManualDocument37 pages2280-Motorola Maxtrac 100-300 User ManualKo AzaniNo ratings yet
- 2 Oieyqhwgfdewio 9 D 328 eDocument1 page2 Oieyqhwgfdewio 9 D 328 euihgfhjjhghNo ratings yet
- English For Ethiopia: Grade 6Document3 pagesEnglish For Ethiopia: Grade 6Esrom Abebe100% (2)
- Winning Without Losing Preorder Gift BookDocument23 pagesWinning Without Losing Preorder Gift Bookcarlos_645331947No ratings yet
- PVC Water Pumps PDFDocument26 pagesPVC Water Pumps PDFYulidar Wahyu RachmawanNo ratings yet
- NASA Earth and Space Science Fellowship (NESSF) Program - 2009Document11 pagesNASA Earth and Space Science Fellowship (NESSF) Program - 2009Sherman100% (1)
- Mathematical-Olympiads PDFDocument27 pagesMathematical-Olympiads PDFG100% (1)
- Force Field AnalysisDocument4 pagesForce Field AnalysisrishiNo ratings yet
- Data Communications and Networking: Circuit Switching and Packet SwitchingDocument22 pagesData Communications and Networking: Circuit Switching and Packet SwitchingPratibhaNo ratings yet
- Section Analysis: Autodesk Robot Structural Analysis Professional 2012 Author: File: Address: Project: StructureDocument8 pagesSection Analysis: Autodesk Robot Structural Analysis Professional 2012 Author: File: Address: Project: Structureakhmad syibli husniNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 6ES7215-1AG40-0XB0: General InformationDocument10 pagesData Sheet 6ES7215-1AG40-0XB0: General InformationautomaxNo ratings yet
- Geberit Bathroom Collection BrochureDocument125 pagesGeberit Bathroom Collection BrochureThanhNo ratings yet
- Daily Site Inspection ReportDocument2 pagesDaily Site Inspection Reportfreanne_0527No ratings yet
- Top 20 Automation Testing Interview Questions and AnswersDocument36 pagesTop 20 Automation Testing Interview Questions and AnswersBilal Achernan100% (1)
- Image Processing: CSE4019 Project Review-1Document4 pagesImage Processing: CSE4019 Project Review-1Prithviraj N indiNo ratings yet
- ELEC3030 Notes v1Document118 pagesELEC3030 Notes v1kosmos3384No ratings yet
- CaFSET (Antigua) Office Workbook - Sixth Edition - Programming Concepts Sample PagesDocument4 pagesCaFSET (Antigua) Office Workbook - Sixth Edition - Programming Concepts Sample PagescafsetNo ratings yet
- ELT 1000 Y1-03-0259 Rev GDocument62 pagesELT 1000 Y1-03-0259 Rev GKumaraswamy RSNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Problem Solving Through Flowcharts 1Document14 pagesLesson 2: Problem Solving Through Flowcharts 1catherine carreonNo ratings yet
- 4K HDR - What Is It, and What's The Different Between 8,10, and 12-Bit HDRDocument12 pages4K HDR - What Is It, and What's The Different Between 8,10, and 12-Bit HDRArkadiusz StrzeszewskiNo ratings yet
- Outline Medical TerminologyDocument3 pagesOutline Medical TerminologypearlparfaitNo ratings yet
- SWOT and PESTLE analysis of FoodpandaDocument4 pagesSWOT and PESTLE analysis of FoodpandaPui Xin LooNo ratings yet