Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Perception
Uploaded by
Samad Sam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views22 pagesBy Samad Sam
Original Title
Perception.pptx
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBy Samad Sam
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views22 pagesPerception
Uploaded by
Samad SamBy Samad Sam
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR
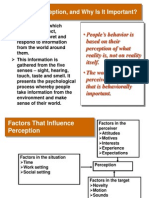
What Is Perception, and Why Is It Important?
Peoples behavior is based on their perception of what reality is, not on reality itself.
The world as it is perceived is the world that is behaviorally important.
Factors That Influence Perception
Person Perception: Making Judgments About Others
Distinctiveness: shows different behaviors in different situations.
Consensus: response is the same as others to same situation. Consistency: responds in the same way over time.
Attribution Theory
Errors and Biases in Attributions
Frequently Used Shortcuts in Judging Others
Frequently Used Shortcuts in Judging Others
Specific Applications in Organizations
Employment Interview Perceptual biases affect the accuracy of interviewers judgments of applicants. Performance Expectations Self-fulfilling prophecy (pygmalion effect): The lower or higher performance of employees reflects preconceived leader expectations about employee capabilities. Performance Evaluations Appraisals are subjective perceptions of performance. Employee Effort Assessment of individual effort is a subjective judgment subject to perceptual distortion and bias.
The Link Between Perceptions and Individual Decision Making
Perceptions of the decision maker
Outcomes
Assumptions of the Rational Decision-Making Model
1. 2. Problem clarity Known options
3.
4. 5. 6.
Clear preferences
Constant preferences No time or cost constraints Maximum payoff
Steps in the Rational DecisionMaking Model
The Three Components of Creativity
How Are Decisions Actually Made in Organizations
How Are Decisions Actually Made in Organizations (contd)
How/Why problems are identified Visibility over importance of problem Attention-catching, high profile problems Desire to solve problems Self-interest (if problem concerns decision maker) Alternative Development Satisficing: seeking the first alternative that solves problem. Engaging in incremental rather than unique problem solving through successive limited comparison of alternatives to the current alternative in effect.
Making Choices
Making Choices
Decision-Style Model
Performance Evaluation
Organizational Constraints on Decision Makers
Evaluation criteria influence the choice of actions.
Reward Systems
Decision makers make action choices that are favored by the organization.
Formal Regulations
Organizational rules and policies limit the alternative choices of decision makers.
System-imposed Time Constraints
Organizations require decisions by specific deadlines.
Historical Precedents
Past decisions influence current decisions.
Cultural Differences in Decision Making
Problems selected Time orientation Importance of logic and rationality Belief in the ability of people to solve problems Preference for collect decision making
Ethics in Decision Making
Ethical Decision Criteria
Utilitarianism
Seeking the greatest good for the greatest number.
Rights
Respecting and protecting basic rights of individuals.
Justice
Imposing and enforcing rules fairly and impartially.
Ethics in Decision Making
Ethics and National Culture
There are no global ethical standards. The ethical principles of global organizations that reflect and respect local cultural norms are necessary for high standards and consistent practices.
You might also like
- Perception: Individual Decision MakingDocument31 pagesPerception: Individual Decision MakingsczameeNo ratings yet
- 5 - Perception & Decision MakingDocument24 pages5 - Perception & Decision MakingAditya MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Perception: DR Sireesha MamidennaDocument24 pagesPerception: DR Sireesha MamidennaAnu GupteNo ratings yet
- Influences On Employee Behavior HRD Slide Set 1Document53 pagesInfluences On Employee Behavior HRD Slide Set 1Asad JuttNo ratings yet
- Perception and Individual Decision MakingDocument20 pagesPerception and Individual Decision MakingM Soban Murad JoyiaNo ratings yet
- Perceptual ProcessesDocument26 pagesPerceptual ProcessesPratyum PradhanNo ratings yet
- Perception Decision MakingDocument16 pagesPerception Decision MakingUmarNo ratings yet
- PerceptionDocument36 pagesPerceptionAditya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Organizational BehaviorDocument12 pagesOrganizational Behaviorศุภธณิศร์ เติมสงวนวงศ์No ratings yet
- Perception and Individual Decision Making - FinalDocument36 pagesPerception and Individual Decision Making - Finaltracxx100% (4)
- OB PerceptionsDocument21 pagesOB PerceptionsFatima AhmadNo ratings yet
- Perception and Individual Decision MakingDocument36 pagesPerception and Individual Decision MakingTayyab NaqviNo ratings yet
- Perception and decision makingDocument29 pagesPerception and decision makingNeggaz D MapeleNo ratings yet
- Attitudes Perception For 25th OctDocument25 pagesAttitudes Perception For 25th OctPratik MehtaNo ratings yet
- Decision Making Models and BiasesDocument16 pagesDecision Making Models and BiasesRohit DeoghareNo ratings yet
- 6 Chap PerceptionDocument26 pages6 Chap PerceptionJahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- 05 Flex HboDocument26 pages05 Flex HboAbegail Mercado PamplonaNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior and Group DynamicsDocument50 pagesOrganizational Behavior and Group Dynamicssystems kmfNo ratings yet
- Perception and Individual Decision MakingDocument48 pagesPerception and Individual Decision MakingSyed Ali XaidiNo ratings yet
- What Is Perception, and Why Is It Important?: - People's Behavior IsDocument28 pagesWhat Is Perception, and Why Is It Important?: - People's Behavior IsRaj PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Perception and Individual Decision Making (Chapter 6Document26 pagesPerception and Individual Decision Making (Chapter 6Phạm Thị Hà Vi 1M-20ACNNo ratings yet
- Lectures 45decision Making-2Document226 pagesLectures 45decision Making-2Andreea AnghelNo ratings yet
- Lectures 45decision MakingDocument37 pagesLectures 45decision MakingAndreea AnghelNo ratings yet
- Perception and Individual Decision MakingDocument36 pagesPerception and Individual Decision MakingAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- DECISION MAKING RULES OF THUMBDocument32 pagesDECISION MAKING RULES OF THUMBPaeng PadrinoNo ratings yet
- Decision Making and Rules of ThumbsDocument32 pagesDecision Making and Rules of ThumbsPaeng PadrinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Key Concepts on Perception, Decision MakingDocument20 pagesChapter 5 Key Concepts on Perception, Decision MakingRonyNo ratings yet
- What makes perception importantDocument16 pagesWhat makes perception importantDeepak DograNo ratings yet
- PERCEPTION AND INDIVIDUAL DECISION MAKINGDocument15 pagesPERCEPTION AND INDIVIDUAL DECISION MAKINGAshraful AlamNo ratings yet
- Perception & DMDocument25 pagesPerception & DMchinmayakumarbisoyi159No ratings yet
- Ob Final LectureDocument14 pagesOb Final LectureBlesszie VillegasNo ratings yet
- PerceptionDocument15 pagesPerceptionशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Perception and Decision MakingDocument22 pagesChapter 5 Perception and Decision MakingDaniyal WarsiNo ratings yet
- Perception and Decision MakingDocument37 pagesPerception and Decision MakingMariamChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Faiza - 72 - 18825 - 1 - Lecture 5 - Perception & Individual Decision MakingDocument17 pagesFaiza - 72 - 18825 - 1 - Lecture 5 - Perception & Individual Decision MakingEsha BhabhaNo ratings yet
- HUMANBEH Chapter 12 Informal and Formal GroupsDocument19 pagesHUMANBEH Chapter 12 Informal and Formal GroupsEugene AguirreNo ratings yet
- MANAGEMENT PERCEPTION DECISIONSDocument16 pagesMANAGEMENT PERCEPTION DECISIONSMahin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Perception What Is Perception?Document7 pagesPerception What Is Perception?Mohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Imp Topics of ObDocument5 pagesImp Topics of ObSyed Farhan RasoolNo ratings yet
- Perception and Decision Making Chapter SummaryDocument3 pagesPerception and Decision Making Chapter SummaryĐặng Trần Thu UyênNo ratings yet
- Decision Making Organisation BehaviourDocument47 pagesDecision Making Organisation BehaviourIpokia OnlineNo ratings yet
- Decision Making 1Document29 pagesDecision Making 1Mehbub Bihan SajinNo ratings yet
- OB PERCEPTION DECISIONDocument25 pagesOB PERCEPTION DECISIONJanaVrsalovićNo ratings yet
- Organizational BehaviorDocument10 pagesOrganizational BehaviorFree MailNo ratings yet
- AttitudesDocument30 pagesAttitudesarindam6666No ratings yet
- 02 Foundation of Individual BehaviorDocument46 pages02 Foundation of Individual BehaviorBui Manh Tuan100% (1)
- Business-Ethics-Ppt-Ch5 SlidesDocument16 pagesBusiness-Ethics-Ppt-Ch5 SlidesKaram AlhajNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics MGT-chapter 6Document16 pagesBusiness Ethics MGT-chapter 6مها الشمريNo ratings yet
- Perception and Individual Decision Making by Niswatun ChairaDocument4 pagesPerception and Individual Decision Making by Niswatun Chairaniswachaira99No ratings yet
- Decision Making (DM) : - Every Manager Strives To Do Making Good DecisionsDocument30 pagesDecision Making (DM) : - Every Manager Strives To Do Making Good DecisionsTommba TommyNo ratings yet
- Ethical Decision Making and Ethical LeadershipDocument16 pagesEthical Decision Making and Ethical LeadershipSofyan AliNo ratings yet
- Organizational BehaviourDocument23 pagesOrganizational Behaviourssbiswal42No ratings yet
- Perception and Decision Making: Key FactorsDocument40 pagesPerception and Decision Making: Key FactorsSaad NaseemNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of OD 1Document25 pagesFundamentals of OD 1api-3741610100% (1)
- Leadership and Social Responsibilities Who Is A Leader: Instructor: Ed SawyerDocument113 pagesLeadership and Social Responsibilities Who Is A Leader: Instructor: Ed Sawyerlulalala8888No ratings yet
- Decision Making by Individuals and GroupsDocument42 pagesDecision Making by Individuals and GroupsLaszlo Foldvari100% (1)
- What Is Perception?: 6-1 Manoj Mathew, RCBSDocument11 pagesWhat Is Perception?: 6-1 Manoj Mathew, RCBSPonni MoluNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking: The Skills and Psychology of Questioning the ObviousFrom EverandCritical Thinking: The Skills and Psychology of Questioning the ObviousRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Critical Thinking: The Concept and Power of Thinking CriticallyFrom EverandCritical Thinking: The Concept and Power of Thinking CriticallyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Managers, Profits, and Markets: Eighth EditionDocument19 pagesManagers, Profits, and Markets: Eighth EditionAnugraha SNo ratings yet
- Success Story of NirmaDocument3 pagesSuccess Story of NirmaSamad Sam100% (1)
- Organizational Behavior Course Model: OB Outcomes: Attitudes and Behaviors Influenced by Managers UsingDocument37 pagesOrganizational Behavior Course Model: OB Outcomes: Attitudes and Behaviors Influenced by Managers UsingpixeldreamNo ratings yet
- Sewai RecipeDocument1 pageSewai RecipeSamad SamNo ratings yet
- Sewai RecipeDocument1 pageSewai RecipeSamad SamNo ratings yet
- Pyaz ParathaDocument1 pagePyaz ParathaSamad SamNo ratings yet
- Instruments or Tools of Commercial PolicyDocument2 pagesInstruments or Tools of Commercial PolicySamad SamNo ratings yet
- FDI in India: Benefits and DrawbacksDocument1 pageFDI in India: Benefits and DrawbacksSamad SamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Test BankDocument38 pagesChapter 1 Test BankLauren WebNo ratings yet
- Decision Support Systems: ITEC 1010 Information and OrganizationsDocument33 pagesDecision Support Systems: ITEC 1010 Information and OrganizationsMeenakshi AnilNo ratings yet
- Lane (2005)Document18 pagesLane (2005)Tshelane Ngoato NkadimengNo ratings yet
- Approach To Political ScienceDocument17 pagesApproach To Political ScienceRandy Raj OrtonNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Growth of Guidance in Nigeria Meaning of GuidanceDocument100 pagesMeaning and Growth of Guidance in Nigeria Meaning of GuidanceMeshach SamuelNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior: Common Biases and Errors in Decision MakingDocument13 pagesOrganizational Behavior: Common Biases and Errors in Decision MakingnikhilNo ratings yet
- Types and Phases of Evaluationin Educational PracticeDocument11 pagesTypes and Phases of Evaluationin Educational Practicefasya mayaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Difficult TransitionsDocument2 pagesCase Study Difficult TransitionsU N D E R D O GNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Accounting Information Systems: An OverviewDocument20 pagesChapter 1 Accounting Information Systems: An OverviewDuyên Đặng Trần ThảoNo ratings yet
- Social Studies - 2020 Colorado Academic StandardsDocument125 pagesSocial Studies - 2020 Colorado Academic StandardsamberNo ratings yet
- Control Inhibitorio y MatematicasDocument15 pagesControl Inhibitorio y MatematicasCa LúNo ratings yet
- Zetter L., Lobbying The Art of Political Persuasion, Petersfield, Hampshire, Royaume-Uni de Grande-Bretagne Et D'irlande Du Nord, Harriman House, 2014, xxx+560 P.Document165 pagesZetter L., Lobbying The Art of Political Persuasion, Petersfield, Hampshire, Royaume-Uni de Grande-Bretagne Et D'irlande Du Nord, Harriman House, 2014, xxx+560 P.Jim BowNo ratings yet
- Zollo 2018Document20 pagesZollo 2018MultazamMansyurAdduryNo ratings yet
- Boost Tax Compliance with Behavioral InsightsDocument26 pagesBoost Tax Compliance with Behavioral InsightsAgus WahyuNo ratings yet
- SITXFIN003 Learner GuideDocument67 pagesSITXFIN003 Learner GuideZHWNo ratings yet
- Educational Reforms in NigeriaDocument42 pagesEducational Reforms in NigeriaJoshua Bature SamboNo ratings yet
- Understanding Organizational Buying BehaviorDocument34 pagesUnderstanding Organizational Buying BehaviorAryan KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Policy Formulation and ImplementationDocument46 pagesPolicy Formulation and ImplementationJeambe RendalNo ratings yet
- Wealth Insight - Jan 2024Document108 pagesWealth Insight - Jan 2024vinodNo ratings yet
- Automotive Consumer Archetypes - India PerspectiveDocument53 pagesAutomotive Consumer Archetypes - India PerspectiveBhaskar BatejaNo ratings yet
- Ringkasan Perilaku OrganisasiDocument41 pagesRingkasan Perilaku OrganisasiMira Alya SafiraNo ratings yet
- Ethics - PPT (Bus1301)Document51 pagesEthics - PPT (Bus1301)shefali1988100% (2)
- Notes - Decision MakingDocument11 pagesNotes - Decision MakingSyamil DzulfidaNo ratings yet
- Using 360 Virtual Reality As A Decision-Making Assessment Tool in SportDocument5 pagesUsing 360 Virtual Reality As A Decision-Making Assessment Tool in SportesrNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN QUẢN TRỊ HỌCtiếng anhDocument16 pagesĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN QUẢN TRỊ HỌCtiếng anhNguyễn Thị Mỹ LinhNo ratings yet
- Anthony Downs-An Economic Theory of Democracy-Harper and Row (1957)Document321 pagesAnthony Downs-An Economic Theory of Democracy-Harper and Row (1957)Rafael Souza100% (12)
- Rational Decision Making Model - Myth or RealityDocument8 pagesRational Decision Making Model - Myth or RealityElizabeth Joy Anor FadriNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy - AIDocument20 pagesMarketing Strategy - AIHossam HashieshNo ratings yet
- The First-Time Manager by Loren B. Belker Jim McCormick Gary S. Topchik)Document322 pagesThe First-Time Manager by Loren B. Belker Jim McCormick Gary S. Topchik)May Chan Myae100% (2)
- ICM Ethische Code EngelsDocument8 pagesICM Ethische Code Engelssaleha sultanaNo ratings yet