Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ecgd4122.101 14042009
Uploaded by
Luqman YusofOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ecgd4122.101 14042009
Uploaded by
Luqman YusofCopyright:
Available Formats
ECGD 4122 Foundation Engineering
Lecture 4
Faculty of Applied Engineering and Urban Planning
Civil Engineering Department
2
nd
Semester 2008/2009
Content
Shear Strength
Subsoil Exploration
Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criterion
Total Stresses:
Coulomb approximation for shear stress on the
failure plane:
Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criterion
Shear Strength Measurement
Based on Mohrs circle criteria, two ways are
possible to cause failure:
First:
Increase the normal stress in one direction
Shear Strength Measurement
Second:
Apply shear directly
Shear Strength Measurement
o
3
=0
o
1
Direct Shear
Uniaxial Compression
Shear Strength Measurement
Unconfined compression
test is used when | = 0
assumption is valid
Triaxial compression is a
more generalized version
The soil sample is first
compressed isotropically
and then sheared by axial
loading
o
1
o
3
Triaxial Compression
Shear Strength Measurement
Direct Shear Test
Direct Shear Test
Direct Shear Test
Direct Shear Test
Direct Shear Test
Direct Shear Test
Direct Shear Test
Unconfined Compression Test
For clay soils
Cylindrical specimen
No confining stresses
(i.e. o
3
= 0)
Axial stress
= o
1
o
3
= 0
o
1
Uniaxial Compression
o
3
=0
o
1
Uniaxial Compression
Unconfined Compression Test
Unconfined Compression Test Data
( )
c
c
A
P
A
A
l
l
=
=
A
=
o
c
c
1
0
0
Unconfined Compression Test Data
2
u
u
u
q
Strngth Shear Undrained S
Strength n Compressio Unconf ined q
= =
=
Unconfined Compression Test Data
o
3
=0
o
1
Uniaxial Compression
o
t
o
1
Horiz. plane
Max. shear
plane
Unconfined Compression Test
Unconfined Compression Test
Triaxial Compression Test
Triaxial Compression Test
Triaxial Compression Tests
Unconsolidated Undrained (UU-Test);
Also called Undrained Test
Consolidated Undrained Test (CU-
Test)
Consolidated Drained (CD-Test); Also
called Drained Test
Consolidated Undrained Triaxial Test
for Undisturbed Soils
Shear Strength
in terms of Total Stress
Shear Strength in terms of effective
stress
Shear strength in terms of total
stress
| o tan + = c s
u =
'
o o
| o
' '
+
'
= tan c s
hydrostatic pore pressure
Shear Strength
Total Stress - | = 0 condition
Shear strength in terms of total
stress
For cohesive soils under saturated
conditions, | = 0.
| o tan + = c s
c s
u
=
Shear
Strength,S
Normal Stress, o
C
| = 0
Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criterion
Boring
Sampling
Standard Penetration Test (SPT)
Vane Shear Test
Cone Penetration Test (CPT)
Observation of Water Table
Subsoil Exploration
Boring
Boring Spacing
ASTM Method
Boring
ASTM Method for Calculating Depth of Boring
Boring
Auger
3-5 m deep
Hand-driven
Boring Methods
Boring Methods
Flight Auger
1-3 steps
Tractor
mounted
Boring Methods
Rotary drilling
Wash boring
Standard Split Spoon
The sampler is driven into the soil at the
bottom of the borehole by means of hammer
blows.
Sampling
Common Sampling Methods
Sampling
Sampling
Sampling
Standard Split Spoon
The number of blows required for driving the
sampler through three 152.4 mm (6)
intervals is recorded. The sum of the
number of blows required for driving the last
two 152.4 mm (6 in.) intervals is defined as
the standard penetration number (N).
Sampling
Common Sampling Methods
Standard Penetration Number
Standard Penetration Number
Vane Shear Test
Vane Shear Test
K
T
C
u
=
Vane Shear Test
Measures:
The Cone Resistance
The Frictional Resistance
Cone Penetration Test
Cone Penetration Test
Cone Penetration Test
Cone Penetration Test
Assignment # 1
Determine the effective stress at point X for the
two cases shown below. The drawing is not to
scale. Take
sat
= 19 kN/m
3
.
Assignment # 1
(a) Static condition:
o = (9.81)(0.6) + (19)(1) = 24.89 kPa
u = (0.6 + 1)(9.81) = 15.70 kPa
o = o u = 9.19 kPa
Flow-down condition:
i = Ah/L = 0.6/3.0 = 0.2
o = (9.81)(0.6) + (19)(1) = 24.89 kPa
u = (0.6 + 1)(9.81) - (0.2)(1.0)(9.81) = 13.73 kPa
o = o u = 11.16 kPa
Assignment # 2
A soil deposit is composed of clay with
Sat
= 20
kN/m
3
. The GWT is at the ground surface.
Calculate the shear strength on a horizontal
plane at a depth of 10m, if c = 5 kPa and | = 30.
Assignment # 2
t = c + otan|
o = (20)(10) (9.81)(10) = 101.9 kPa
t = 5 + (101.9)(tan30) = 63.83 kPa
Assignment # 2
A drained direct shear test is performed on a
normally consolidated silty soil. The soil sample
is 75 mm in diameter and 25 mm in height. The
vertical load is 883 N and the shear force at
failure is 618 N. Calculate c and |.
Assignment # 2
Drained test t = c + otan|
Normally consolidated soil c = 0
t = c + otan| t = otan| | = tan
-1
(t/o)
t = S/A = 618/[t(37.510
-3
)
2
]
t = 139.89 kPa
o = N/A = 883/[t(37.510
-3
)
2
]
o = 199.87 kPa
| = tan
-1
(139.89/199.87) ~ 35
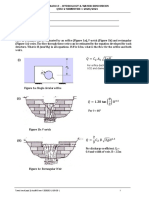
Quiz # 1
Determine the height of
water level (H) above the
surface of gravel, given
that the flow rate (q) is to
be maintained at 40 liters
per second.
Quiz # 1
q
1
= q
2
= q = 4010
-3
m
3
/s
a
1
= a
2
= a = tr
2
= t(0.75)
2
= 1.767 m
2
v
1
= v
2
= v = q/a = 2.26410
-2
m/s
i
1
= v
1
/k
1
= 2.26410
-2
/1010
-2
= 0.2264
i
2
= v
2
/k
2
= 2.26410
-2
/110
-2
= 2.264
i
1
= 0.2264 = Ah
1
/L
1
= (H + 1 z)/(1.0)
i
2
= 2.264 = Ah
2
/L
2
= (z + 1)/(1.0)
Solving the equations for z and H
z = 1.264 m
H = 0.4904 m
Quiz # 1
Quiz # 2
For a clay deposit: C
c
= 0.4 and C
r
= 0.05,
determine the final void ratio for each of the
following loading conditions:
a) Initially o' = 50 kPa, e = 1.2, Finally o' = 90 kPa,
and given that o'
pc
= 100 kPa
b) Initially o' = 50 kPa, e = 1.2, Finally o' = 190
kPa, and given that o'
pc
= 100 kPa
Quiz # 2
C = slope = Ae/Alogo = (e
i
e
f
)/log(o
f
/o
i
)
(a) 0.05 = (1.2 e
f
)/log(90/50)
e
f
= 1.187
(b) Two stages:
0.05 = (1.2 e
fi
)/log(100/50)
e
fi
= 1.185
0.4 = (1.185 e
f
)/log(190/100)
e
f
= 1.073
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- VFTDGNFDGVFDDocument76 pagesVFTDGNFDGVFDLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Kuiz 2 Skaa3613 Sem 1 20202021Document3 pagesKuiz 2 Skaa3613 Sem 1 20202021Luqman YusofNo ratings yet
- 4 VFDBRDocument84 pages4 VFDBRLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Pad Footing DesignDocument19 pagesPad Footing DesignLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- 2 FGSDFVFGDocument19 pages2 FGSDFVFGLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Skab/Skaa3613 - Hydrology & Water Resources Section 01 QUIZ 1 SEMESTER 1 2020/2021Document4 pagesSkab/Skaa3613 - Hydrology & Water Resources Section 01 QUIZ 1 SEMESTER 1 2020/2021Luqman YusofNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- TyhfvwacdsDocument6 pagesTyhfvwacdsLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- HMTHDBRFBDocument21 pagesHMTHDBRFBLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Company Registration FormDocument3 pagesCompany Registration FormLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- FdjkryfkjhdsgDocument14 pagesFdjkryfkjhdsgLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- FdjkryfkjhdsgDocument14 pagesFdjkryfkjhdsgLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- EdgffdDocument80 pagesEdgffdLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- GfmjtdgndesrtgDocument90 pagesGfmjtdgndesrtgLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- DHRSJDSGVEDocument39 pagesDHRSJDSGVELuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- AsdgyfdgjtDocument158 pagesAsdgyfdgjtLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- UlouykrdyhrDocument67 pagesUlouykrdyhrLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- PuhgfhewDocument72 pagesPuhgfhewLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- MsdfvwqefDocument78 pagesMsdfvwqefLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- Road Asset Management SystemDocument214 pagesRoad Asset Management SystemLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- IhjmdhtfdDocument501 pagesIhjmdhtfdLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- FhbftgiujDocument83 pagesFhbftgiujLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- JbniherdyghDocument9 pagesJbniherdyghLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- Wet GHRTDocument144 pagesWet GHRTLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- SahbtgfikghDocument24 pagesSahbtgfikghLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- MsdfvwqefDocument1 pageMsdfvwqefLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- GHJKLDocument67 pagesGHJKLLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- FDHRWSHDocument80 pagesFDHRWSHLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- POIUYDocument61 pagesPOIUYLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- MNVCXZXDocument49 pagesMNVCXZXLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- LKJHGFDocument23 pagesLKJHGFLuqman YusofNo ratings yet
- A275Document6 pagesA275solrac4371No ratings yet
- Venturi, Orifice, RotameterDocument34 pagesVenturi, Orifice, RotameterVinod VadithyaNo ratings yet
- Bearing Dynamic Static Load Carrying Capacity PDFDocument11 pagesBearing Dynamic Static Load Carrying Capacity PDFmanimeczNo ratings yet
- Tests For BricksDocument31 pagesTests For BricksTeddy0% (1)
- FMHM - EEE - Final Exam Important QuestionsDocument5 pagesFMHM - EEE - Final Exam Important QuestionsBhavani Chandra Unique100% (1)
- Biomechanics QuestionsDocument9 pagesBiomechanics QuestionsTrang BuiNo ratings yet
- Ekadhikena Purvena - Mltiplication - Vedic MathsDocument3 pagesEkadhikena Purvena - Mltiplication - Vedic MathsSowmya Srinivasan100% (1)
- Student Lab Manual: Fundamentals of ElectricityDocument9 pagesStudent Lab Manual: Fundamentals of ElectricityAbdisalam A. MohamedNo ratings yet
- Vibration Dampers - An Evolution in AustraliaDocument12 pagesVibration Dampers - An Evolution in Australiaskc3128No ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Boron NitrideDocument62 pagesBoron NitrideSteven SullivanNo ratings yet
- TS8 - Accounting Research (Ho)Document40 pagesTS8 - Accounting Research (Ho)edzateradoNo ratings yet
- 1212441515electricity WorksheetsDocument6 pages1212441515electricity Worksheetsaayush619_com3918No ratings yet
- ch5 6 7Document1 pagech5 6 7Jeff MartinNo ratings yet
- Tides Are The Rise and Fall of Sea Levels Caused by The Combined Effects of Gravitational Forces Exerted by The MoonDocument4 pagesTides Are The Rise and Fall of Sea Levels Caused by The Combined Effects of Gravitational Forces Exerted by The Moonapi-286301523No ratings yet
- Dark Energy DissertationDocument7 pagesDark Energy DissertationBestPaperWritingServiceUK100% (1)
- Apendice 3Document10 pagesApendice 3JazmínARNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Light Source Materials-Modulation of LED-LASER Diodes-Modes and Threshold ConditionsDocument7 pages3.3 Light Source Materials-Modulation of LED-LASER Diodes-Modes and Threshold ConditionsDEEPAK SNo ratings yet
- Steam - Basic Concepts &: FundamentalsDocument11 pagesSteam - Basic Concepts &: FundamentalsermiasNo ratings yet
- Postlab Protein ConcnDocument25 pagesPostlab Protein ConcnMarie Elexis P. RevillezaNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity Worksheet.............Document8 pagesRadioactivity Worksheet.............ashokNo ratings yet
- Determination of Iron With 1,10-PhenanthrolineDocument5 pagesDetermination of Iron With 1,10-PhenanthrolineOmSilence26510% (1)
- Section 6 Magnetism Electromagnetism - UnlockedDocument43 pagesSection 6 Magnetism Electromagnetism - UnlockedgesNo ratings yet
- Gale TransformDocument18 pagesGale TransformPablo Soberón BravoNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra With Applications 2nd Edition Holt Solutions Manual 1Document67 pagesLinear Algebra With Applications 2nd Edition Holt Solutions Manual 1leon100% (50)
- Effect of Drying Conditions On Skinkage and Porosity of Dehydrated Agricultural ProductsDocument12 pagesEffect of Drying Conditions On Skinkage and Porosity of Dehydrated Agricultural ProductsYến Phượng HồNo ratings yet
- Blade Calculations For Water Turbines of The Banki Type: Citation For Published Version (APA)Document24 pagesBlade Calculations For Water Turbines of The Banki Type: Citation For Published Version (APA)Anonymous Hy5Ir9QXNo ratings yet
- Chladni Figures With FG-ModuleDocument1 pageChladni Figures With FG-ModuleJose GalvanNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 3 Waves - Edexcel Physics IGCSEDocument5 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 3 Waves - Edexcel Physics IGCSEVarsha PNo ratings yet
- 2016 Updated Objectives With Answer Key & Topic Wise Numericals With Formulae Physics XI PDFDocument95 pages2016 Updated Objectives With Answer Key & Topic Wise Numericals With Formulae Physics XI PDFSameer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Imperfections in Crystalline SolidsDocument27 pagesImperfections in Crystalline SolidsMvk ChaitanyaNo ratings yet