Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6 - Soil Data in Orcaflex-Y.T.kim
Uploaded by
Youngtae KimOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
6 - Soil Data in Orcaflex-Y.T.kim
Uploaded by
Youngtae KimCopyright:
Available Formats
Soil data in Orcaflex
Prepared by Y.T Kim
Offshore Engineering Lab. Seminar No. 6
1/9
1. API RP 2A-WSD
1. Winklers hypothesis
Most of the theoretical solutions for laterally loaded piles involve the concept of modulus of subgrade
reaction
Modulus of subgrade reaction (the pressure distribution which is the result or reaction of the
subgrade to a load imposed upon the top of a foundation structure)
unit kN/m
2
/m
Because of the limitation of available data and the uncertainty of soil condition, it was also
proposed to use the empirical equations. The following empirical equations (Widjaja, 2008) were
suggested to estimate k value both in clay and sand:
Clay : k = 40 50 su (t/m3)
Sand : k = 70 100 NSPT (t/m3)
Winklers hypothesis-The reaction at any point on the base of the beam in Fig.1 depends only on the
deflection at that point.
The same principle applies to batter piles.
2/9
1. API RP 2A-WSD
1.1 Winklers hypothesis
A series of nonlinear - the force deformation characteristics of the soil.
The springs attached to the blocks of different sizes - reaction increasing with deflection and then
reaching a yield point, or a limiting value that depends on depth.
The taper on the springs a nonlinear variation of load with deflection
The gap btw the pile and the springs the molding away of the soil by repeated loadings
Fig.1
Fig.2
3/9
1. API RP 2A-WSD
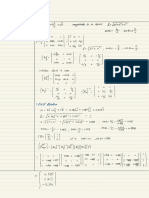
1.2 Lateral bearing capacity for soft clay (API RP 2A 6.8.2)
For static lateral loads, the ultimate unit lateral bearing capacity of soft clay p
u
8c~12c
Cyclic loads cause deterioration of lateral bearing capacity
The following is recommended,
'
tan
f
c t o | = +
=critical shear stress
cohesion
friction angle
f
c
t
|
=
=
3 , 0
u R
cX
p c X J X X
D
= + + s s
9
u R
p c X X = >
4/9
1. API RP 2A-WSD
1.3 Load-deflection (p-y) curves for soft clay (API RP 2A 6.8.3)
Lateral soil resistance-deflection relationships in soft clay non-linear
The p-y curves for short-term static load case as following table:
p/p
u
y/y
c
0.00
0.23
0.33
0.50
0.72
1.00
0.0
0.1
0.3
3.0
8.0
P=actual lateral resistance, psi(kPa)
y=actual lateral deflection, in.(m)
y
c
=2.5
c
D, in.(m)
c
=strain which occurs at one-half the maximum stress on laboratory
unconsolidated undrained compression tests of undisturbed soil
samples.
0
5
10
15
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
y
/
y
c
p/p
u
p-y curves
5/9
2. Orcaflex p-y Models
Model type
One of the following options:
The API RP 2A Soft Clay option uses the load-deflection curves for piles in soft clay under short-term static loading as
specified in API RP 2A (2000).
Similarly, the API RP 2A Sand option uses the API RP 2A (2000) load-deflection curves for sand.
The P-y Table option allows you to specify the load-deflection curves directly in tabular form.
6/9
3. Orcaflex Seabed data
2.1 Linear Model
Treat the seabed as a simple linear spring
Seabed resistance is proportional to the penetration
Normal seabed stiffness-the spring reaction force, per unit are of contact, per unit depth of penetration, (e.g., rock-high but
clay-very low)
Shear seabed stiffness-used by the friction calculation. A value of '~' results in the Normal Seabed Stiffness being used.
The Seabed Damping-a percentage of critical damping. Equals 0 when using the implicit integration scheme.
The normal stiffness reaction force has magnitude = K
n
Ad K
n
= seabed normal stiffness
A = penetrator contact area
d = depth of penetration into the seabed.
7/9
3. Orcaflex Seabed data
2.2 Non-linear Model
Prof. Mark Randolph, University of Western Austrailia
It is a development from earlier models that proposed and used a hyperbolic secant stiffness formulation
Fig.4 Soil model characteristics for different modes
More sophisticated than the linear model
Models the non-linear and hysteretic behavior of seabed soil
including modelling of suction effects.
The non-linear modelling only applies to the seabed normal
direction. Linear modelling of lateral directions
Fig.3 Soil model penetration modes
8/9
Remains of the non-linear seabed modelling of Orcaflex
Seabed stiffness & linear vs. nonlinear modelling parametric study using Orcaflex
and SHEAR7
6. Future Plan
You might also like
- Offshore Mechanics: Structural and Fluid Dynamics for Recent ApplicationsFrom EverandOffshore Mechanics: Structural and Fluid Dynamics for Recent ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Ageing and Life Extension of Offshore Structures: The Challenge of Managing Structural IntegrityFrom EverandAgeing and Life Extension of Offshore Structures: The Challenge of Managing Structural IntegrityNo ratings yet
- Principia DeepLines PresentationDocument45 pagesPrincipia DeepLines Presentationbello imamNo ratings yet
- 23 Mooring Analysis During ShorepullDocument53 pages23 Mooring Analysis During ShorepullNoverdo Saputra100% (1)
- Orcaflex OrcinaDocument40 pagesOrcaflex OrcinaPeggy Jan QorbanNo ratings yet
- Orcaflex Training ScopeDocument3 pagesOrcaflex Training ScopeGodwinNo ratings yet
- Orcina Production Risers GuideDocument135 pagesOrcina Production Risers GuideOkolo Obinna100% (1)
- Moses Mooring Analysis - Introduction - 230903 - 101634Document42 pagesMoses Mooring Analysis - Introduction - 230903 - 101634Hermawan Saini100% (1)
- Case Studies in Pipeline Free Span FatigueDocument10 pagesCase Studies in Pipeline Free Span FatiguejoaogularNo ratings yet
- Flexible Jumper Design PremiseDocument12 pagesFlexible Jumper Design PremiseAgus BudionoNo ratings yet
- OrcaFlex Dynamic Analysis Automation (DynaFlex Tutorial)Document19 pagesOrcaFlex Dynamic Analysis Automation (DynaFlex Tutorial)Abam Joshua100% (1)
- Lazy AssignmentDocument5 pagesLazy Assignmentthefoot39No ratings yet
- J-Tube Pull-In Simulation SetupDocument4 pagesJ-Tube Pull-In Simulation SetupArie Indra MasudiNo ratings yet
- OMAE2012 84121 PresentationDocument16 pagesOMAE2012 84121 PresentationsojanvasudevanNo ratings yet
- Cable On-Bottom Stability Analysis for Zakum Oil Lines Replacement ProjectDocument12 pagesCable On-Bottom Stability Analysis for Zakum Oil Lines Replacement ProjectSourabhNo ratings yet
- Structural Design of Offshore Ships: DNV-OS-C102Document9 pagesStructural Design of Offshore Ships: DNV-OS-C102MinhddNo ratings yet
- Choi 2000 Free Spanning Analysis of Offshore PipelinesDocument14 pagesChoi 2000 Free Spanning Analysis of Offshore Pipelinesbello imamNo ratings yet
- Technical Paper - Modelling Suction Pile Lowering Through The SplashzoneDocument9 pagesTechnical Paper - Modelling Suction Pile Lowering Through The Splashzonecxb07164No ratings yet
- Design of Offshore Pipelines - Shore ApproachDocument60 pagesDesign of Offshore Pipelines - Shore ApproachYoungtae KimNo ratings yet
- Design by AnsysDocument103 pagesDesign by AnsysHoang Tien DungNo ratings yet
- Offshore Pipeline Design, Analys and Methods PDFDocument199 pagesOffshore Pipeline Design, Analys and Methods PDFddaalayamoct313024No ratings yet
- Ultimate Strength PrinciplesDocument105 pagesUltimate Strength PrinciplesSahil Jawa100% (1)
- OPT98 Fatigue Design-DNV-Guideline-Free Spanning PipelinesDocument24 pagesOPT98 Fatigue Design-DNV-Guideline-Free Spanning PipelinesYemi LawalNo ratings yet
- FatFree User ManualDocument41 pagesFatFree User ManualLava Sat100% (1)
- Effective Stiffness of Concrete Coated Line PipeDocument11 pagesEffective Stiffness of Concrete Coated Line PipeKok Jin OoiNo ratings yet
- JEE309 Assignment3 OnBottomStabilityDocument2 pagesJEE309 Assignment3 OnBottomStabilityAnwarul Shafiq AwalludinNo ratings yet
- 14 - NRG - Pipe Installation - Davit LiftDocument16 pages14 - NRG - Pipe Installation - Davit LiftBalanNo ratings yet
- Offpipe Dynamic Analysis InstallationDocument25 pagesOffpipe Dynamic Analysis Installationbello imam100% (2)
- Moses IntroductionDocument170 pagesMoses IntroductionRahim KhanNo ratings yet
- OrcaFlex For PipelayDocument4 pagesOrcaFlex For PipelaySandeep RangapureNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Instation Using Orcaflex Master Thesis 4 PDFDocument144 pagesPipeline Instation Using Orcaflex Master Thesis 4 PDFsamiransmita100% (3)
- On Bottom StabilityDocument25 pagesOn Bottom StabilityhariharanoilgasNo ratings yet
- Offshore TechDocument351 pagesOffshore Techmarkengineer100% (2)
- Shore ApproachDocument5 pagesShore Approachvpandya1981No ratings yet
- Hydro Structure PapersDocument157 pagesHydro Structure PapersChen Chu-yunNo ratings yet
- On-Bottom Analysis ABAQUSDocument206 pagesOn-Bottom Analysis ABAQUSlsatchithananthan100% (1)
- Iors 2013Document35 pagesIors 2013jeedanNo ratings yet
- On-Bottom Stability Check of Wellhead Jacket in Gulf of Thailand - Offshore Structural CornerDocument17 pagesOn-Bottom Stability Check of Wellhead Jacket in Gulf of Thailand - Offshore Structural Cornerthomas1313No ratings yet
- LOTOS SIWZ A1-3 Z12 112996-EnG-RPT-00003 R02 IFC Pipeline Installation AnalysisDocument33 pagesLOTOS SIWZ A1-3 Z12 112996-EnG-RPT-00003 R02 IFC Pipeline Installation AnalysisJP EDSNo ratings yet
- Sec 4BDocument19 pagesSec 4BhatakerobotNo ratings yet
- Sea TransportationDocument8 pagesSea TransportationMark Samsel RohanNo ratings yet
- OrcaFlex Demonstration IIT MadrasDocument11 pagesOrcaFlex Demonstration IIT MadrasvigambetkarNo ratings yet
- Boatlanding and Riser Protecter Design-2Document15 pagesBoatlanding and Riser Protecter Design-2samiransmitaNo ratings yet
- Splash Zone Lifting Analysis of Subsea StructuresDocument11 pagesSplash Zone Lifting Analysis of Subsea StructuresAnonymous PibYPghNo ratings yet
- OrcaFlex ManualDocument429 pagesOrcaFlex Manualviknes07100% (1)
- Quayside Mooring Analysis - Floatel Triumph at Kemaman (P30049-MA-REV 0) (2095)Document35 pagesQuayside Mooring Analysis - Floatel Triumph at Kemaman (P30049-MA-REV 0) (2095)cliff1234No ratings yet
- Lifting Analysis Preview)Document4 pagesLifting Analysis Preview)Faisal AjaNo ratings yet
- OrcaFlex TutorialDocument491 pagesOrcaFlex Tutorialaipk11100% (1)
- Trinidad Metocean Design Data SummaryDocument93 pagesTrinidad Metocean Design Data SummaryLyudmyla BobinaNo ratings yet
- Orca Flex 1Document376 pagesOrca Flex 1autienhaiNo ratings yet
- Offshore Pipeline Design Course ChaptersDocument6 pagesOffshore Pipeline Design Course ChaptersDonald.K100% (1)
- Installation of Anchors For Mooring System of Floating Wind TurbinesDocument134 pagesInstallation of Anchors For Mooring System of Floating Wind Turbines정재영100% (1)
- Above Water Tie inDocument2 pagesAbove Water Tie inZadeh NormanNo ratings yet
- Collapse Analysis 1Document13 pagesCollapse Analysis 1samiransmitaNo ratings yet
- Bonga Pipe in Pipe LayDocument66 pagesBonga Pipe in Pipe LayWilliam O OkolotuNo ratings yet
- MOSES Advanced TrainingDocument4 pagesMOSES Advanced TrainingYudha MeremNo ratings yet
- Master's Thesis on Estimating Pipeline Roll Angle Using Residual Curvature MethodDocument153 pagesMaster's Thesis on Estimating Pipeline Roll Angle Using Residual Curvature MethodPrashanth Talkad Rajagopal100% (1)
- Subsea Rigid Pipelines – Methods of InstallationFrom EverandSubsea Rigid Pipelines – Methods of InstallationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mechanics of Offshore Pipelines, Volume 2: Buckle Propagation and ArrestFrom EverandMechanics of Offshore Pipelines, Volume 2: Buckle Propagation and ArrestNo ratings yet
- 문서1Document7 pages문서1Youngtae KimNo ratings yet
- Homework#3Document3 pagesHomework#3Youngtae KimNo ratings yet
- Check Your English Vocabulary For TOEICDocument81 pagesCheck Your English Vocabulary For TOEICRobby100% (27)
- CalcII Complete PDFDocument377 pagesCalcII Complete PDFfalcon724No ratings yet
- Very Easy Toeic PDFDocument258 pagesVery Easy Toeic PDFChien Tran Ngoc100% (12)
- FE Simulation of PIP Systems With SAGE ProfileDocument8 pagesFE Simulation of PIP Systems With SAGE ProfileGodwinNo ratings yet
- Check Your English Vocabulary For TOEICDocument81 pagesCheck Your English Vocabulary For TOEICRobby100% (27)
- Homewor#2Document4 pagesHomewor#2Youngtae KimNo ratings yet
- Sesam Feature DescriptionDocument207 pagesSesam Feature DescriptionYoungtae KimNo ratings yet
- Calculus III Lecture NotesDocument287 pagesCalculus III Lecture NotesAhmad Jawdat75% (4)
- Splash Zone BrochureDocument5 pagesSplash Zone BrochureYoungtae KimNo ratings yet
- Thermal Expansion of Pipe-In-Pipe Systems, by Bokaian. Marine Structures, Vol 17, 2004Document27 pagesThermal Expansion of Pipe-In-Pipe Systems, by Bokaian. Marine Structures, Vol 17, 2004Youngtae KimNo ratings yet
- Calculus I CompleteDocument578 pagesCalculus I Completexenocid3r83% (6)
- On-Bottom Stability AnalysisDocument42 pagesOn-Bottom Stability AnalysisYoungtae Kim67% (3)
- RSPile - Laterally Loaded Pile Theory ManualDocument14 pagesRSPile - Laterally Loaded Pile Theory Manualjacs127100% (1)
- (Paper) Seawater Intake StructuresDocument8 pages(Paper) Seawater Intake StructuresYoungtae KimNo ratings yet
- Cathodic Protection DesignDocument23 pagesCathodic Protection DesignYoungtae Kim100% (6)
- Wave in Deck Loads On Exposed JettiesDocument23 pagesWave in Deck Loads On Exposed JettiesYoungtae KimNo ratings yet
- Fluid Accelerations Under Irregular WavesDocument12 pagesFluid Accelerations Under Irregular WavesYoungtae KimNo ratings yet
- Design of Offshore Pipelines - Shore ApproachDocument60 pagesDesign of Offshore Pipelines - Shore ApproachYoungtae KimNo ratings yet
- BP Energy Outlook 2035 BookletDocument96 pagesBP Energy Outlook 2035 BookletVizziniNo ratings yet
- CIVL4170Document46 pagesCIVL4170Hoài Phương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Linear and Nonlinear Shallow Wave Water Equations Applied To Tsunami Waves Over The China SeaDocument9 pagesComparison of Linear and Nonlinear Shallow Wave Water Equations Applied To Tsunami Waves Over The China SeaYoungtae KimNo ratings yet
- Regulations Pipelines & Subsea: 10. Mars 2009 Olav Fyrileiv - DNV Anders Husby - DNVDocument42 pagesRegulations Pipelines & Subsea: 10. Mars 2009 Olav Fyrileiv - DNV Anders Husby - DNVYoungtae KimNo ratings yet
- Design of Offshore Pipelines - MaterialsDocument39 pagesDesign of Offshore Pipelines - MaterialsYoungtae KimNo ratings yet
- Cathodic Protection Design in Offshore PipelineDocument3 pagesCathodic Protection Design in Offshore PipelineYoungtae KimNo ratings yet
- PTC 2015 GrahamDocument20 pagesPTC 2015 GrahamYoungtae KimNo ratings yet
- HDPE Pipeline Installation and DesignDocument13 pagesHDPE Pipeline Installation and DesignYoungtae Kim100% (4)
- STPM Chemistry Topic 16 Haloalkanes Short Notes PDFDocument2 pagesSTPM Chemistry Topic 16 Haloalkanes Short Notes PDFbendanNo ratings yet
- Chem Tech South 2013 - ConferenceDocument5 pagesChem Tech South 2013 - ConferenceAbirami PriyadharsiniNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument24 pagesElectrochemistryZainul AbedeenNo ratings yet
- 2nd Semester All Courses-100Document194 pages2nd Semester All Courses-100Ejiade PeterNo ratings yet
- Electronics Meet Animal BrainsDocument44 pagesElectronics Meet Animal BrainssherrysherryNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Final KshitijDocument108 pagesUnit-2 Final KshitijShubham JainNo ratings yet
- WIP CaseStudyDocument3 pagesWIP CaseStudypaul porrasNo ratings yet
- Alberta Highway and Flood Projects 2016-2019Document37 pagesAlberta Highway and Flood Projects 2016-2019Anonymous QRCBjQd5I7No ratings yet
- Welding Defects and AcceptanceDocument76 pagesWelding Defects and Acceptancearavindan100% (1)
- JKF8 Intelligent Reactive Power Compensation ControllerDocument4 pagesJKF8 Intelligent Reactive Power Compensation ControllerGuillermo Morales HerreraNo ratings yet
- ArtsDocument5 pagesArtsRhovi Christine AbandoNo ratings yet
- Development of The FaceDocument76 pagesDevelopment of The Facedr parveen bathla100% (1)
- ASSIGNMENTDocument10 pagesASSIGNMENTKoleen Lopez ÜNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Unit 1 - Part 1: Square RootsDocument20 pagesGrade 9 Unit 1 - Part 1: Square RootsWilson ZhangNo ratings yet
- Avh p6050dvd EngDocument119 pagesAvh p6050dvd EngcaimanaterNo ratings yet
- Calculator For SW Density Changes - Effect of List On Ships DraftDocument3 pagesCalculator For SW Density Changes - Effect of List On Ships DraftHein Thurein KyawNo ratings yet
- Anorexia NervosaDocument2 pagesAnorexia NervosaDhea Mae MadisNo ratings yet
- On The Problem of The External World in The Ch'Eng Wei Shih LunDocument64 pagesOn The Problem of The External World in The Ch'Eng Wei Shih LunGuhyaprajñāmitra3100% (1)
- Telemark PulloverDocument2 pagesTelemark Pulloverkidknits100% (1)
- 3-Ph Induction MotorDocument246 pages3-Ph Induction MotorAn00pgadzillaNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Tech Manual 2002Document28 pagesAmmonia Tech Manual 2002Talha Bin Zubair0% (1)
- RESISTANCEDocument9 pagesRESISTANCERohit SahuNo ratings yet
- Orpheus' Tragic Love and Quest to Save EurydiceDocument3 pagesOrpheus' Tragic Love and Quest to Save EurydiceShiedrose Allaina ArangorinNo ratings yet
- Volvo g900 Modelos PDFDocument952 pagesVolvo g900 Modelos PDFAdrianDumescu100% (3)
- Chinkon Kishin - Origens Shintoístas Do Okiyome e Do Espiritismo Na MahikariDocument2 pagesChinkon Kishin - Origens Shintoístas Do Okiyome e Do Espiritismo Na MahikariGauthier Alex Freitas de Abreu0% (1)
- Colistimethate Sodium 1 Million I.U. Powder For Solution For Injection - Colistin - (Emc)Document8 pagesColistimethate Sodium 1 Million I.U. Powder For Solution For Injection - Colistin - (Emc)hakim shaikhNo ratings yet
- Chocolate - Useful Physical ConstantsDocument2 pagesChocolate - Useful Physical ConstantsJuan CNo ratings yet
- FLIGHT CONTROLS: TROUBLESHOOTING AND COMPONENTSDocument3 pagesFLIGHT CONTROLS: TROUBLESHOOTING AND COMPONENTSBernardino Ferreira JúniorNo ratings yet
- What Is RTN/Microwave TechnologyDocument27 pagesWhat Is RTN/Microwave TechnologyRavan AllahverdiyevNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Soil-Structure Interaction as Finite Element Using SAP2000Document5 pagesModeling of Soil-Structure Interaction as Finite Element Using SAP2000Tariq MahmoodNo ratings yet