Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter-1: Business Communication
Uploaded by
Lina Ali AbdulOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter-1: Business Communication
Uploaded by
Lina Ali AbdulCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER-1
Business Communication What is Communication? Communication is the transfer of information (also opinion, idea, attitude etc.) from a sender to a receiver with a view to making it understandable to the latter. The conditions are: First, there must be at least two persons involved in communication. Second, there must be some information to be communicated. Third, some attempt must be made to transmit this information.
1
The Communication Process:
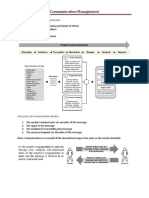
Communication process involves seven steps--thought, encoding, transmission, reception, decoding, and understanding and feed-back. In the case of feedback the receiver acts as the sender and the steps are repeated. This process is shown in the next diagram.
Elements of Communication: 1. Sender: One who sends a message is the writer or speaker, depending upon whether the communication is written or oral. Sender is the encoder of the message.
2. Message: The message consists of both verbal, written or spoken symbols and also nonverbal symbols to convey ideas from the sender to the receiver.
3. Channel: Channel is the medium through which the message is sent. 4. Receiver: The message receiver is the reader or listener and decoder of the message. 5. Feedback: Feedback is the receivers reaction indicating to the sender whether or not the message has been understood and correctly interpreted.
4
Communication Situation:
Communication situation is deemed to exit if:
1. There
is a person (sender) willing to pass on some information.
2. Another person (receiver) is there to whom the information is passed on. 3. The receiver understands the message (partly or wholly).
4. There is a feedback from the receiver.
Importance of Communication in Business:
1. Basis of effective leadership 2. Sharing ideas and information 3. Rational decision making 4. Interacting with environment 5. Developing companys public image 6. Helping delegation of authority and responsibility 7. Explaining policies and programs 8. Understanding the problem of subordinates 9. Fulfilling organizational objectives through coordination 10.Basis of information
6
Objectives of Communication
1. Receiving or Passing Information *External Information: They relate to: a) Demands for products in the market. b) Strategies of competitors. c) Supply of labor and raw materials. d) Government policies. e) Technological developments. f) Changes in tastes and fashions etc.
7
Internal Information
They relate to: a) Job performance of employees. b) Disciplinary conditions in the work palace. c) Job assignments. d) Demand for employees, raw materials, machinery and spare parts. e) Need for money, etc. In using information care should be taken about the following: a) Is the information coming from a reliable source? b) is it complete? c) Is it timely /recent?
2. Giving Advice to Colleagues /Subordinates:
Advice is given in order to influence the attitudes, opinions, behavior etc. of individuals concerned. It flows either horizontally or downwards. There are some tips to make advice effective a) It should be given in such a way that it suits the need of the recipient. b) The advisor should be courteous and polite. c) The advice should be given for the betterment of the staff concerned. d) The recipient of advice should be given freedom to react.
9
3. Counseling the Problem Employees:
4. Issuing Orders: Asking somebody to do something.
Types of Orders: a) Written and oral b) General and specific c) Mandatory and discretionary d) Procedural and operational Features of an effective order: a) Order must be precise, complete and clear. b) Execution of order must not be impossible. c) Order should be given in such a way that it is accepted cordially.
10
5. To Persuade: Making someone to comply.
The art of persuasion a) The art of persuasion requires conviction on the part of the person who wants to persuade. b) The persuader should not impose himself on the receiver of his communication.
c) A flexible mind of the receiver helps the persuader to persuade. d) The arguments, most acceptable to the receiver, should be used.
11
6. Raising Morale and Motivation:
Making employees to feel an inner urge to work to their full capability 7. Giving Warning Asking employees /customers to refrain from doing something. 8. Educating employees and prospective consumers (a) Giving instruction to employees about better methods of work. (b) Instructing consumers about the uses and abuses of products/services etc.
12
You might also like
- Chapter 1 Business Communication: Tip: SuccessDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Business Communication: Tip: SuccessAden Kheire MohamedNo ratings yet
- English 3 Modern Business CommunicationDocument3 pagesEnglish 3 Modern Business CommunicationAnna DerNo ratings yet
- Definition of CommunicationDocument5 pagesDefinition of CommunicationRedwan Afrid AvinNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Introduction To CommunicationDocument89 pagesChapter One: Introduction To CommunicationEng Abdulkadir MahamedNo ratings yet
- Communication Nature, Functions and ScopeDocument25 pagesCommunication Nature, Functions and ScopebasuNo ratings yet
- Ccs-Unit 1 Concepts of Effective CommuicationDocument16 pagesCcs-Unit 1 Concepts of Effective CommuicationPrajwal Muthanna100% (1)
- Source 1 - Communication Elements - Process - PrinciplesDocument5 pagesSource 1 - Communication Elements - Process - PrinciplesTrixie SannadNo ratings yet
- Purposes of CommunicationDocument3 pagesPurposes of CommunicationTamil Ka AmutharasanNo ratings yet
- Communication Notes Unit 1 To Unit 3Document35 pagesCommunication Notes Unit 1 To Unit 3Rohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument49 pagesCommunicationObaiah JamakalaNo ratings yet
- Discussion Question - 01 - BUS COMBUS COMDocument5 pagesDiscussion Question - 01 - BUS COMBUS COMRayhan BillahNo ratings yet
- BCSS Material FinalDocument123 pagesBCSS Material FinalMurthyNo ratings yet
- Jnu 1Document12 pagesJnu 1Red SunNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Communication: Md. Shahidullah KayserDocument35 pagesEssentials of Communication: Md. Shahidullah Kaysershk sunNo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument10 pagesBusiness CommunicationPrince VarmaNo ratings yet
- BC NotesDocument11 pagesBC NotesMeenakshi RajakumarNo ratings yet
- Business Communication Sem1 NotesDocument96 pagesBusiness Communication Sem1 NotesRitika ShindeNo ratings yet
- Presentation BCDocument44 pagesPresentation BCSubhash SoniNo ratings yet
- Communication Process - Definition, Importance, Components and How To ImproveDocument5 pagesCommunication Process - Definition, Importance, Components and How To ImproveVanshika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Soft Skils Unit 1 UpdatedDocument19 pagesSoft Skils Unit 1 UpdatedAdarsh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- How The Communication Process Works (Example Included) Indeed - Com IndiaDocument8 pagesHow The Communication Process Works (Example Included) Indeed - Com IndiaBhavyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 - Internal & External CommunicationDocument7 pagesUnit 9 - Internal & External CommunicationSi Eun LeeNo ratings yet
- Cs Notes Sem2Document21 pagesCs Notes Sem2paridhiNo ratings yet
- Communications Management ProcessesDocument6 pagesCommunications Management ProcessesBrian Jhones Chan Abundo100% (1)
- Electrical Engineering Revision NotesDocument107 pagesElectrical Engineering Revision Notesabuadano47No ratings yet
- Chap.1 SumadyDocument49 pagesChap.1 SumadyasdNo ratings yet
- CMS Chaptr 1 (1)Document5 pagesCMS Chaptr 1 (1)ShreyashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document11 pagesChapter 1lundubhai010No ratings yet
- Elements of CommunicationDocument6 pagesElements of CommunicationRoisa JoyNo ratings yet
- Notes Mba Sem-Ii BCDocument72 pagesNotes Mba Sem-Ii BCaryamakumari3No ratings yet
- Business EnglishDocument27 pagesBusiness EnglishMohsin KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - CommunicatingDocument36 pagesChapter 6 - CommunicatingCllyan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Meaning, Defination, Elements of CommunicationDocument14 pagesMeaning, Defination, Elements of CommunicationSudharani B BanappagoudarNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam. Business CommunicationDocument8 pagesMidterm Exam. Business CommunicationDuaa AsjadNo ratings yet
- Business Communication FileDocument6 pagesBusiness Communication FileYash PandeyNo ratings yet
- 4 Chapter2 Lesson 1 (The Communication Process)Document12 pages4 Chapter2 Lesson 1 (The Communication Process)rabby0611No ratings yet
- OHR Tutorial 7Document12 pagesOHR Tutorial 7fung223132No ratings yet
- Chapter One (Communication Foundation)Document8 pagesChapter One (Communication Foundation)Fatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- Ceb 203 78 105Document28 pagesCeb 203 78 105mvr1509No ratings yet
- Communication FoundationDocument22 pagesCommunication Foundationrotine3248No ratings yet
- Business EnglishDocument28 pagesBusiness EnglishajayNo ratings yet
- Garcia, Maharajah Kristking B. I2Ac: 7 Major Elements of Communication ProcessDocument2 pagesGarcia, Maharajah Kristking B. I2Ac: 7 Major Elements of Communication Processnotapernota101No ratings yet
- NOTES On COMMUNICATIONDocument10 pagesNOTES On COMMUNICATIONSharan PatilNo ratings yet
- Communication Process and Purpose - Unit 1Document17 pagesCommunication Process and Purpose - Unit 1ankit10869734No ratings yet
- Coms SkilsDocument9 pagesComs Skilsjocasam2000No ratings yet
- 15871781240COMGENE04 CommunicationDocument7 pages15871781240COMGENE04 CommunicationSaif AliNo ratings yet
- BC Priyanka JhaDocument8 pagesBC Priyanka JhaPriyanka JhaNo ratings yet
- Business Communication NotesDocument60 pagesBusiness Communication NotesYaswanth YashuNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 Communication & LeadershipDocument44 pagesChap 2 Communication & LeadershipbojaNo ratings yet
- Lecture One-Comm Process - 2018 To 2019Document22 pagesLecture One-Comm Process - 2018 To 2019daniloorestmarijaniNo ratings yet
- Module: 01 (Introduction) 1.1 Meaning of Business CommunicationDocument3 pagesModule: 01 (Introduction) 1.1 Meaning of Business CommunicationMd SaiduzzamanNo ratings yet
- Communication Management: Goals of Interpersonal CommunicationDocument8 pagesCommunication Management: Goals of Interpersonal CommunicationSameer SharmaNo ratings yet
- CCS - I Unit 1Document18 pagesCCS - I Unit 1Goutham VarmaNo ratings yet
- Communication and Its BarriersDocument35 pagesCommunication and Its Barriersdibyendu_mondal67% (6)
- Characteristics and Objectives of Successful CommunicationDocument7 pagesCharacteristics and Objectives of Successful CommunicationAbeer RizviNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 BM320Document31 pagesUnit 2 BM320osama samiNo ratings yet
- 100 Case Study In Project Management and Right Decision (Project Management Professional Exam)From Everand100 Case Study In Project Management and Right Decision (Project Management Professional Exam)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- E-BAnking 2Document1 pageE-BAnking 2Lina Ali AbdulNo ratings yet
- Strategic MarketingDocument39 pagesStrategic MarketingLina Ali AbdulNo ratings yet
- Coca ColaDocument6 pagesCoca ColaLina Ali AbdulNo ratings yet
- APUDocument5 pagesAPULina Ali AbdulNo ratings yet
- Gaps Model of Service QualityDocument9 pagesGaps Model of Service QualityLina Ali AbdulNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument31 pagesAccountingLina Ali AbdulNo ratings yet
- Airlines 101Document25 pagesAirlines 101Lina Ali AbdulNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Sample BeautyDocument13 pagesBusiness Plan Sample BeautyLina Ali Abdul100% (4)
- NestléDocument21 pagesNestléSolomon GeorgianaNo ratings yet
- Orientalism by Edward Said Is A Cononical Text of Cultural Studies in WhichDocument5 pagesOrientalism by Edward Said Is A Cononical Text of Cultural Studies in WhichLina Ali Abdul100% (1)
- Amicus PropertiesDocument5 pagesAmicus PropertiesLina Ali AbdulNo ratings yet
- Orientalism by Edward Said Is A Cononical Text of Cultural Studies in WhichDocument5 pagesOrientalism by Edward Said Is A Cononical Text of Cultural Studies in WhichLina Ali Abdul100% (1)
- Courses in Different Areas of BusinessDocument5 pagesCourses in Different Areas of BusinessLina Ali AbdulNo ratings yet
- Sample Marketing PlanDocument24 pagesSample Marketing Planphilp50100% (1)
- Standard Cost Versus Budgetary ControlDocument2 pagesStandard Cost Versus Budgetary ControlLina Ali AbdulNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument27 pagesSupply Chain ManagementskibcobsaivigneshNo ratings yet
- Ch06 Basic MotivationDocument36 pagesCh06 Basic MotivationLina Ali AbdulNo ratings yet
- Southend Sweater Company LimitedDocument120 pagesSouthend Sweater Company LimitedLina Ali Abdul100% (1)
- Chapter 5 - Adlerian TherapyDocument28 pagesChapter 5 - Adlerian TherapyRhalf100% (1)
- Attitude and ValuesDocument7 pagesAttitude and ValuesNeelam harchandaniNo ratings yet
- CoachingDocument5 pagesCoachingsnas2206No ratings yet
- Authoritative ParentingDocument3 pagesAuthoritative ParentingMohammed HussainNo ratings yet
- Enculturation and SocializationDocument19 pagesEnculturation and SocializationJaved MaralitNo ratings yet
- Julianna HCDocument3 pagesJulianna HCKim JulianNo ratings yet
- Inclusive LeadershipDocument13 pagesInclusive LeadershipAnkitNo ratings yet
- DuPaul, G. J., Weyandt, L. L., & Janusis, G. M. (2011) - ADHD in The Classroom Effective Intervention Strategies PDFDocument9 pagesDuPaul, G. J., Weyandt, L. L., & Janusis, G. M. (2011) - ADHD in The Classroom Effective Intervention Strategies PDFjuanNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Participant Guide Session 4Document18 pagesOxygen Participant Guide Session 4Gábor KárpátiNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument3 pagesPurposive CommunicationLeila Marie MartinezNo ratings yet
- Awareness CampaignsDraftWorkingPaperDocument38 pagesAwareness CampaignsDraftWorkingPaperKwadwo OwusuNo ratings yet
- School Counseling Lesson Plan TemplateDocument2 pagesSchool Counseling Lesson Plan Templateapi-253009486No ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence and Mindfulness: John DarwinDocument20 pagesEmotional Intelligence and Mindfulness: John Darwinemeka2012No ratings yet
- Humility Manuscript Hoekstra Bell PetersonDocument26 pagesHumility Manuscript Hoekstra Bell PetersonErik HoekstraNo ratings yet
- Sophie Rowan Happy at Work Ten Steps To Ultimate Job SatisfactionDocument225 pagesSophie Rowan Happy at Work Ten Steps To Ultimate Job SatisfactionchatelleyaNo ratings yet
- Kaplan Chapter 1Document27 pagesKaplan Chapter 1Elena UngureanuNo ratings yet
- 4 - SocializationDocument28 pages4 - SocializationJanel Castillo BalbiranNo ratings yet
- What Are Business CompetenciesDocument2 pagesWhat Are Business CompetenciesMac ShaikNo ratings yet
- Group DynamicsDocument29 pagesGroup Dynamicsmahfuzah100% (1)
- I Can C It All Over Your FaceDocument5 pagesI Can C It All Over Your FaceKLCNo ratings yet
- Rewards Giving and Its Effect On Students' Motivation in Learning MathematicsDocument16 pagesRewards Giving and Its Effect On Students' Motivation in Learning MathematicsSharmila ThangarajuNo ratings yet
- PMS RefresherDocument40 pagesPMS RefresherRohan Pai0% (1)
- Mental HealthDocument3 pagesMental HealthMary Jean Aguelo100% (1)
- Isaksen & HolthDocument22 pagesIsaksen & HolthMaithri SivaramanNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Unit 6Document2 pagesAnswer Key Unit 6Mohd Syazwan ArifNo ratings yet
- IB Psychology - Social Identity TheoryDocument2 pagesIB Psychology - Social Identity TheoryNoor Mohsin50% (2)
- Foundation of Individual BehaviorDocument19 pagesFoundation of Individual Behaviorfeya ayef100% (1)
- Effective Team LeadershipDocument16 pagesEffective Team Leadershipermiastenaw7401No ratings yet
- Introduction To Remedial ClassDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Remedial Classapipirashdan800750% (2)
- Herzberg Two Factor Motivation TheoryDocument4 pagesHerzberg Two Factor Motivation Theoryimdad ullahNo ratings yet