Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Simple Interest
Uploaded by
Aaron Joy Dominguez PutianOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Simple Interest
Uploaded by
Aaron Joy Dominguez PutianCopyright:
Available Formats
Simple Interest
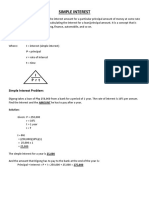
Debtor/Maker
an individual or institution that borrows money
for any purpose
Lender
an individual or institution who loans the money
Interest I
payment for the use of borrowed money or the
amount earned on an invested money
Definition of Terms (continued)
Principal P
the capital or sum of money borrowed or
invested
Rate of Interest r
fractional part of the principal that is paid on the
loan or investment (expressed as percent) and the
annual rate set by the lender
Time t
number of years for which the money is
borrowed or invested
Definition of Terms (continued)
Final Amount or Maturity Value F
combined amount of the principal and the
interest accumulated over a certain period of time
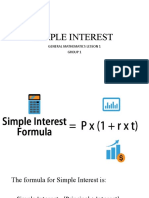
Simple Interest
interest computed based on the principal and is
paid at the end of the specified period of time
Formula:
I
= Prt
where
= principal invested P
= rate of interest in decimals r
= time in years t
r t
Find the Principal, Rate or Time Using the
Simple Interest Formula
P
r
t
I
P
r
t
I
P
r
t
I
P
r
t
I
I Pr t =
I
P
rt
=
I
r
Pt
=
I
t
Pr
=
Examples
1. Find the interest paid by Ms. April on Php25,000
that she borrowed for three years at 4% simple
interest.
2. Determine the simple interest to be paid by Lorna
if she borrowed Php1,200 at 6 % for 8 months.
3. At what rate of interest did Mary invest the
amount of Php27,500 for it to earn a simple interest
of Php3, 245 for three years?
Final Amount or Maturity Value F
SIMPLE INTEREST
F P I = +
F P Pr t P rt = + = + 1
Examples (continued)
4. How much was borrowed by Ms. Michelle if the
interest she paid after 3 months at 10.5% simple
interest is Php3,000?
5. How long should Dan invest the amount of
Php80,000 to earn an interest of Php4,500 at 6.5%
simple interest?
6. How much is the final amount would Ms. Nessy
receive if she invested Php75,000 for 4 years at 5
% simple interest?
Ordinary and Exact Interest
Ordinary Interest vs. Exact Interest
i
O
i
E
Default: Ordinary Interest
i
O
- a rate per day that assumes 360 days
per year
i
E
- a rate per day that assumes 365 days
per year
Examples
1. For 209 days, what would be the interest if Gretel
invested Php43,500 at
(a) 5 % ordinary simple interest?
(b) 5 % exact simple interest?
(c) How much is the difference between these two
investments?
2. Use ordinary interest to find the final amount due on
Php 75,150 for 420 days at 12.75%
3. Use exact interest to find the interest and final
amount due on Php25,345 for 636 days at 10.25%
Ordinary and Exact Interest
Why do you think banks prefer to use
ordinary interest in their business? Support
your answer.
Actual and Approximate Time
Default: Actual Time
Actual time based on counting the exact
number of days in a time period
Approximate time based on counting 30
days in each month
ACTUAL NUMBER OF DAYS PER MONTH
MONTH NUMBER OF DAYS
January 31 days
February
28 days, 29 in leap
years
March 31 days
April 30 days
May 31 days
June 30 days
July 31 days
August 31 days
September 30 days
October 31 days
November 30 days
December 31 days
Examples
The approximate time from July 12 to
September 12 is 60 days.
To find the actual time from July 12 to
September 12, add the following:
Days in July (31 - 12 ) 19
Days in August 31
Days in September +12
62 days
Interest Between Dates
( )
actual time
=
i act
O Pr
| |
|
\ .
360
( )
approximate time
=
i app
O Pr
| |
|
\ .
360
( )
actual time
=
i act
E Pr
| |
|
\ .
365
( )
approximate time
=
i app
E Pr
| |
|
\ .
365
Default
Examples
1. Using the four methods, find the interest on
Php23,250 at 5 2/3% simple interest from August 9,
2003 to May 18, 2004. (p. 20)
2. Determine the ordinary interest on Php53,000 at
11% from June 17, 2003 to October 9, 2003 using
actual and approximate time. (p. 19)
3. What amount should be paid on February 10, 2004
for a loan of Php16,020 made on October 7, 2003 with
4 3/5% simple interest? (p. 21)
Do it on your own
What final amount should
Carol pay for a loan of
Php8,200 at 14 % simple
interest she borrowed in
March 10, 2000 if she
promised to pay on
November 25, 2000?
Present Value
amount of loan or investment known as the
prevailing value of an amount scheduled at some
future time
also called principal and denoted by P
formula is given by
where
F
P
rt
=
+ 1
= accumulated amount F
= simple interest rate in decimals r
= term of loan or investment t
Examples
1. How much must Ivy invest today in order to have
Php32,500 available in 4 years if money is worth 12% simple
interest?
2. Find the present value of Php19,200 for 120 days at 4 5/8
% simple interest.
3. Determine the present value of a 7-month 12.3% simple
interest loan if its final amount is Php19, 345?
4. Find the present value of Dorys loan, which amounted to
Php45,650.75 from January 5, 2008 to April 25, 2008 if the
money is worth 8.5% simple interest.
PRESENT VALUE
You might also like
- Real Estate Investing Strategies: The Secret to Financial Independence with Real Estate: Real Estate Investing, #1From EverandReal Estate Investing Strategies: The Secret to Financial Independence with Real Estate: Real Estate Investing, #1No ratings yet
- Simple Interest DiscountDocument31 pagesSimple Interest DiscountElizabeth Solayao50% (2)
- Module 2 - Interest and Time Value of MoneyDocument19 pagesModule 2 - Interest and Time Value of MoneyNico Urieta De Ade0% (2)
- Lesson 1 Simple InterestDocument2 pagesLesson 1 Simple InterestSERALDYN SAMSONNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.simple InterestDocument29 pagesLesson 1.simple InterestMac Gabriel VillafrancaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4.2 Mathematics of Finance NotesDocument37 pagesLesson 4.2 Mathematics of Finance NotestemplaalexanderjhonNo ratings yet
- Cot 1Document46 pagesCot 1yeyadaguoiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Time Value of MoneyDocument122 pagesLesson 3 - Time Value of MoneyJannine Joyce Bergonio33% (3)
- Simple InterestsDocument14 pagesSimple Interestsprincessnylighte13No ratings yet
- Interest Earned CalculatorDocument41 pagesInterest Earned CalculatorClariza Mae BaisaNo ratings yet
- Interest and Annuities FinalDocument29 pagesInterest and Annuities FinalMaricon SorongonNo ratings yet
- Simple InterestDocument21 pagesSimple InterestJennifer LucindoNo ratings yet
- Simple InterestDocument28 pagesSimple InterestJunrie FerrerNo ratings yet
- simple and compound interestDocument44 pagessimple and compound interestcatherine saldeviaNo ratings yet
- Basic Business MathematicsDocument49 pagesBasic Business MathematicsJustine FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics of InvestmentsDocument14 pagesMathematics of InvestmentsYocib OtnicajNo ratings yet
- Module 2-Simple Interest and Simple DiscountDocument10 pagesModule 2-Simple Interest and Simple DiscountDhenver DimasacatNo ratings yet
- Simple Interest: I P R TDocument7 pagesSimple Interest: I P R TBloodmier Gabriel100% (1)
- BUSINESS MATHS 1 INTEREST-1Document24 pagesBUSINESS MATHS 1 INTEREST-1emmanuelifende1234No ratings yet
- Lesson notes on simple interest formulas and conceptsDocument9 pagesLesson notes on simple interest formulas and conceptsLouie Jay Remojo KilatonNo ratings yet
- Calculate Simple and Compound Interest EasilyDocument36 pagesCalculate Simple and Compound Interest EasilyJeweljoy PudaNo ratings yet
- INTERESTSDocument15 pagesINTERESTSAnastasia EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Module 6: The Mathematics of FinanceDocument16 pagesModule 6: The Mathematics of FinanceMabel LynNo ratings yet
- 8 Simple InterestDocument44 pages8 Simple InterestalamagelyzaNo ratings yet
- Simple Interest and Compound InterestDocument23 pagesSimple Interest and Compound InterestChristine Joy MaapoyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4finals in MMWDocument16 pagesLesson 4finals in MMWFire burnNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Q2 - Week1 - Simple and Compound InterestDocument27 pagesGen Math Q2 - Week1 - Simple and Compound InterestJohn Nicholas TabadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - The Time Value of Money (Part I)Document20 pagesChapter 3 - The Time Value of Money (Part I)Arin ParkNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Math1 Ge3Document10 pagesModule 3 Math1 Ge3orogrichchelynNo ratings yet
- Simple InterestDocument43 pagesSimple InterestPrimcess BanuaNo ratings yet
- Interest and Commission: Mr. Christian Rae D. Bernales, LPTDocument16 pagesInterest and Commission: Mr. Christian Rae D. Bernales, LPTAlissa MayNo ratings yet
- Simple InterestsDocument15 pagesSimple Interestssier waltersNo ratings yet
- Calculate Simple Interest and Final AmountDocument23 pagesCalculate Simple Interest and Final AmountLizbethHazelRiveraNo ratings yet
- Personal and Household Finance ExplainedDocument5 pagesPersonal and Household Finance ExplainedMuhammad SamhanNo ratings yet
- CALCULATE SIMPLE INTEREST AND MATURITY VALUEDocument12 pagesCALCULATE SIMPLE INTEREST AND MATURITY VALUEJORENCE PHILIPP ENCARNACION100% (1)
- General Mathematics Quarter 2-Module 1: Week 1 - Week 5: Department of Education - Republic of The PhilippinesDocument34 pagesGeneral Mathematics Quarter 2-Module 1: Week 1 - Week 5: Department of Education - Republic of The PhilippinesElaiza Gayta100% (1)
- LESSON 1 Simple InterestDocument10 pagesLESSON 1 Simple Interestjason a. un100% (1)
- Mathematics in The Modern World Lesson 1 2 FinalsDocument31 pagesMathematics in The Modern World Lesson 1 2 FinalsYumeko LeeNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 MathscapeDocument31 pagesChap 1 MathscapeHarry LiuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Simple Interest and Simple DiscountDocument38 pagesChapter 1 Simple Interest and Simple DiscountAbe Miguel BullecerNo ratings yet
- Engineering EconomyDocument159 pagesEngineering EconomyAlbert Aguilor88% (8)
- General Mathematics: LAS, Week 1 - Quarter 2Document16 pagesGeneral Mathematics: LAS, Week 1 - Quarter 2Prince Joshua SumagitNo ratings yet
- Simple InterestDocument58 pagesSimple InterestCleofeNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics (Interest Rates)Document36 pagesBusiness Mathematics (Interest Rates)Deryl GalveNo ratings yet
- Calculating Interest Rates and Loan PaymentsDocument13 pagesCalculating Interest Rates and Loan Paymentsdavid austriaNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Financial ManagementDocument18 pagesThe Nature of Financial ManagementJessa mae CabredoNo ratings yet
- quarter 2 Conversion periodDocument13 pagesquarter 2 Conversion periodcatherine saldeviaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 BASIC LT FINANCIAL CONCEPTDocument3 pagesChapter 5 BASIC LT FINANCIAL CONCEPTAiron Bendaña50% (2)
- Simple AND Compound InterestDocument17 pagesSimple AND Compound InterestBea Dacillo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Simulated Exam - Questions - General MathematicsDocument2 pagesSimulated Exam - Questions - General MathematicsWesly Paul Salazar CortezNo ratings yet
- EE40 Homework 1Document2 pagesEE40 Homework 1delacruzrae12No ratings yet
- MathDocument6 pagesMathLyndMargaretteVicencioNo ratings yet
- Compound InterestDocument16 pagesCompound Interestv.garganera.551005No ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument17 pagesTime Value of Moneyabdiel100% (3)
- Simple and Compound InterestDocument46 pagesSimple and Compound InterestPhill SamonteNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING ECONOMY: KEY CONCEPTSDocument13 pagesENGINEERING ECONOMY: KEY CONCEPTSbabadapbadapNo ratings yet
- Shs Genmath q2 w1 Studentsversion v1Document10 pagesShs Genmath q2 w1 Studentsversion v1Hanna Zaina AlveroNo ratings yet
- Lesson-2 EeDocument24 pagesLesson-2 EeChristian MagdangalNo ratings yet
- Mathemaics of Finance ExplainedDocument34 pagesMathemaics of Finance ExplainedWonde Biru75% (4)
- Taxation Corporate Tax Indirect Tax Personal Tax Tax Authority ThailandDocument2 pagesTaxation Corporate Tax Indirect Tax Personal Tax Tax Authority ThailandAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- Accounting StandardsDocument3 pagesAccounting StandardsAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- Thailand TaxationDocument14 pagesThailand Taxationde4zyNo ratings yet
- Thailand AsDocument3 pagesThailand AsAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- BOA TOS TaxDocument2 pagesBOA TOS TaxMr. CopernicusNo ratings yet
- China Accounting StandardsDocument3 pagesChina Accounting StandardsAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- Philippines AsDocument3 pagesPhilippines AsAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- South Korea Accounting StandardsDocument2 pagesSouth Korea Accounting StandardsAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- Philippnes TPDocument18 pagesPhilippnes TPAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- AustraliaDocument19 pagesAustraliaAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- Japan Tax Profile: Produced in Conjunction With The KPMG Asia Pacific Tax CentreDocument15 pagesJapan Tax Profile: Produced in Conjunction With The KPMG Asia Pacific Tax CentreKris MehtaNo ratings yet
- Boa Tos FarDocument1 pageBoa Tos FarAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- KoreaDocument21 pagesKoreaChimgeeChmgeNo ratings yet
- China TPDocument18 pagesChina TPAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standards Taxation ContdDocument41 pagesAccounting Standards Taxation ContdAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standards Taxation ContdDocument41 pagesAccounting Standards Taxation ContdAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- BOA Syllabus FARDocument3 pagesBOA Syllabus FARLouie de la TorreNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standards and Taxatio1Document7 pagesAccounting Standards and Taxatio1Aaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- Boa Pres (GTB)Document24 pagesBoa Pres (GTB)Aaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- BOA Revision in CPA Exam SubjectsDocument6 pagesBOA Revision in CPA Exam SubjectsAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- Boa Syllabus RFBTDocument4 pagesBoa Syllabus RFBTAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- Boa Tos MasDocument3 pagesBoa Tos MasAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- CPA licensure exam syllabus management accountingDocument3 pagesCPA licensure exam syllabus management accountingLouie de la TorreNo ratings yet
- BOA School Insp Pp1Document6 pagesBOA School Insp Pp1Aaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- Boa MraDocument14 pagesBoa MraAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- BOA School Insp PPDocument14 pagesBOA School Insp PPAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- BOA Intership ProgramDocument18 pagesBOA Intership ProgramAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- Advac 2Document5 pagesAdvac 2Aaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standards and Taxation: A. European Union I. Accounting Standards Adoption of IFRS by European UnionDocument12 pagesAccounting Standards and Taxation: A. European Union I. Accounting Standards Adoption of IFRS by European UnionAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- Non For Profit OrganizationDocument11 pagesNon For Profit OrganizationAaron Joy Dominguez PutianNo ratings yet
- My - Invoice - 12 Jan 2023, 18 - 01 - 08Document2 pagesMy - Invoice - 12 Jan 2023, 18 - 01 - 08Rohit Kumar DubeyNo ratings yet
- The Asian Financial Crisis of 1997 1998 Revisited Causes Recovery and The Path Going ForwardDocument10 pagesThe Asian Financial Crisis of 1997 1998 Revisited Causes Recovery and The Path Going Forwardgreenam 14No ratings yet
- Collection of HC and SC DecisionsDocument63 pagesCollection of HC and SC DecisionsDayavantiNo ratings yet
- ZF-02 Posting Credit Note SPPLDocument10 pagesZF-02 Posting Credit Note SPPLGhosh2No ratings yet
- 01 Basilan Estate V CIRDocument2 pages01 Basilan Estate V CIRBasil MaguigadNo ratings yet
- EF2A1 HDT Budget Upto Direct Taxes PCB4 1629376359978Document30 pagesEF2A1 HDT Budget Upto Direct Taxes PCB4 1629376359978Mamta Patel100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Recording of TransactiosDocument24 pagesChapter 4 Recording of TransactiosJohn Mark MaligaligNo ratings yet
- Virginia's Annual Holder Report Forms & Instructions: Unclaimed Property DivisionDocument27 pagesVirginia's Annual Holder Report Forms & Instructions: Unclaimed Property DivisionWilliamsNo ratings yet
- L5M4 New PaperDocument9 pagesL5M4 New PaperibraokelloNo ratings yet
- AF308 Tutorial 7Document2 pagesAF308 Tutorial 7Elisa SharmaNo ratings yet
- Measuring National IncomeDocument71 pagesMeasuring National IncomeMayurRawoolNo ratings yet
- TCCB Revision - ProblemsDocument4 pagesTCCB Revision - ProblemsDiễm Quỳnh 1292 Vũ ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Zimbabwe TogetherDocument23 pagesZimbabwe TogetherLionel MasawiNo ratings yet
- Nedbank Pricing 2020Document55 pagesNedbank Pricing 2020BusinessTech100% (1)
- Universalcoal Annual Report 2017Document128 pagesUniversalcoal Annual Report 2017satyr01No ratings yet
- Acc101 RevCh1 3 PDFDocument29 pagesAcc101 RevCh1 3 PDFWaqar AliNo ratings yet
- The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965Document15 pagesThe Payment of Bonus Act, 1965Raman GhaiNo ratings yet
- Total Compensation Framework Template (Annex A)Document2 pagesTotal Compensation Framework Template (Annex A)Noreen Boots Gocon-GragasinNo ratings yet
- Case Study Currency SwapsDocument2 pagesCase Study Currency SwapsSourav Maity100% (2)
- Chapter 6 - ProblemsDocument6 pagesChapter 6 - ProblemsDeanna GicaleNo ratings yet
- Citi Bank Kpi Summary 2021-2022Document5 pagesCiti Bank Kpi Summary 2021-2022tusharjaipur7No ratings yet
- Christopher P. Mittleman's LetterDocument5 pagesChristopher P. Mittleman's LetterDealBook100% (2)
- 09-MWSS2020 Part1-Notes To FSDocument44 pages09-MWSS2020 Part1-Notes To FSGabriel OrolfoNo ratings yet
- Consolidation of Wholly Owned Subsidiaries Acquired at More Than Book ValueDocument66 pagesConsolidation of Wholly Owned Subsidiaries Acquired at More Than Book ValueNadeem TahaNo ratings yet
- OBLICON - Chapter 1 ProblemDocument1 pageOBLICON - Chapter 1 ProblemArahNo ratings yet
- Equifax Credit Report - A New Credit Score in IndiaDocument4 pagesEquifax Credit Report - A New Credit Score in IndiaVyas Maharshi GarigipatiNo ratings yet
- IFC Promotes Private Sector Growth in Developing NationsDocument7 pagesIFC Promotes Private Sector Growth in Developing NationsJawad Ali RaiNo ratings yet
- Investment Decision MakingDocument16 pagesInvestment Decision MakingDhruvNo ratings yet
- Ifric 12Document12 pagesIfric 12Cryptic LollNo ratings yet