Professional Documents
Culture Documents
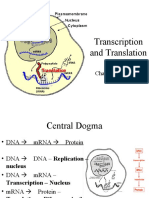
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Uploaded by
abisantiago6131Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Uploaded by
abisantiago6131Copyright:
Available Formats
Polymerase Chain Reaction - PCR
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique to amplify a piece of DNA very rapidly outside of a cell.
Some applications of PCR.
Forensic medicine.
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis
(PGD). Archeology. Paternity testing.
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
A cycle of PCR consists of three steps.
DNA denaturation at 95 degrees C.
Primer annealing at 50-60 degrees C. DNA polymerization by a thermostable
DNA polymerase at 72 degrees C.
Starting with a single molecule of DNA, 25 rounds or cycles of PCR will produce about 10 million identical DNA molecules!!
Forensic uses of PCR
PCR can be used to amplify DNA from a
small amount of cells (about 1000 cells). The amplified DNA from cells can be used in DNA fingerprinting analysis to determine who was at the crime scene.
DNA fingerprinting using PCR in forensic investigations.
DNA is isolated from blood at a crime
scene and amplified by PCR. The amplified DNA is digested with restriction enzymes and resolved on an agarose gel. Southern blot analysis is performed to give a DNA fingerprint.
Restriction fragment analysis by Southern blotting.
DNA fingerprints from a murder case.
Individuals have unique DNA fingerprints because of restriction length polymorphisms (RFLPs).
How reliable is DNA fingerprinting?
DNA regions chosen are ones known to be
highly variable from one person to another. In most forensic cases, the probability of two people having identical DNA fingerprints is between one chance in 100,000 and one in a billion. The exact number depends on the number of probes used to different regions of human chromosomal DNA.
Many argue that DNA evidence is more reliable than eyewitnesses in placing a suspect at the scene of a crime.
Satellite DNA can be used as markers for DNA fingerprinting.
Satellite DNA consists of tandemly repeated
base sequences within the human genome. The most useful satellite DNA for forensic purposes are microsatellites having repeating units of only a few base pairs, and the number of repeats are highly variable from one person to another. Microsatellite DNA is also called a simple tandem repeats (STRs).
An example of simple tandem repeat (STR) alleles.
STRs in DNA fingerprinting.
The greater the number of STRs
analyzed in a DNA sample, the more likely the DNA fingerprint is unique to an individual. PCR is used to selectively amplify particular STRs before electrophoresis. PCR is especially valuable when DNA is in poor condition or available in minute quantities.
PCR use in Pre-implantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD).
PGD is a way to determine if human embryos
from in vitro fertilization have genetic defects (for example, cystic fibrosis). A cell is removed from an eight cell embryo and the DNA is analyzed by PCR for genetic defects. Only healthy embryos are implanted into a mothers uterus. Should this technology be used for things like gender selection?
You might also like
- LamarckVsDarwin RegentsDocument6 pagesLamarckVsDarwin Regentsabisantiago6131100% (1)
- Biology WorkbookDocument193 pagesBiology Workbookabisantiago6131100% (4)
- Ecosystem Energy FlowDocument30 pagesEcosystem Energy Flowabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Multimedia Presentation RubricDocument4 pagesMultimedia Presentation Rubricabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- EcosystemsDocument13 pagesEcosystemsabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Strawberry DNA ExtractionDocument17 pagesStrawberry DNA Extractionabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Macro Evolution and SpeciationDocument41 pagesMacro Evolution and Speciationabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Symbiotic RelationsDocument13 pagesSymbiotic Relationsabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Lamarck Vs Darwin IntroDocument16 pagesLamarck Vs Darwin Introabisantiago613180% (5)
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesHuman Reproductive Systemabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Heredity Regents QuestionDocument5 pagesHeredity Regents Questionabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Regents Protein SynthesisDocument5 pagesRegents Protein Synthesisabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument18 pagesProtein Synthesisabisantiago6131100% (1)
- Mutations PowerpointDocument31 pagesMutations Powerpointabisantiago6131100% (1)
- Gentic MutationsDocument3 pagesGentic Mutationsabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Human Genetic DisorderDocument4 pagesHuman Genetic Disorderabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument8 pagesMitosis and Meiosisabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Human Body System Regents QuestionsDocument11 pagesHuman Body System Regents Questionsabisantiago613125% (4)
- Which Diagram Represents Binary Fission?: Asexual Reproduction Feb. 5, 2013 Mrs. MenteDocument5 pagesWhich Diagram Represents Binary Fission?: Asexual Reproduction Feb. 5, 2013 Mrs. Menteabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Nervous System PowerpointDocument45 pagesNervous System Powerpointabisantiago6131100% (3)
- Lymphatic System RegentsDocument2 pagesLymphatic System Regentsabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Nervous System RegentsDocument2 pagesNervous System Regentsabisantiago6131100% (1)
- Endocrine System RegentsDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Regentsabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Lymphatic System PowerpointDocument20 pagesLymphatic System Powerpointabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Respiratory & Circulatory System Regents QuestionsDocument10 pagesRespiratory & Circulatory System Regents Questionsabisantiago613140% (5)
- Immune System PowerpointDocument16 pagesImmune System Powerpointabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Respiratory & Circulatory SystemDocument32 pagesRespiratory & Circulatory Systemabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Urinary & Excretory System RegentsDocument3 pagesUrinary & Excretory System Regentsabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Digestion Regents QuestionsDocument3 pagesDigestion Regents Questionsabisantiago613175% (4)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The lac Operon RegulationDocument8 pagesThe lac Operon RegulationAlina RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Allosteric EnzymeDocument22 pagesAllosteric EnzymeAhmed ImranNo ratings yet
- Ganong's Physiology Chapter 1-2 ReviewDocument2 pagesGanong's Physiology Chapter 1-2 ReviewMaine AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Practical Hand Outs-Molecular Biology (BIO302)Document33 pagesPractical Hand Outs-Molecular Biology (BIO302)Anaya MalikNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Ch-14 BIOMOLECULESDocument4 pagesAssignment On Ch-14 BIOMOLECULESReet ShindeNo ratings yet
- Answers Proteins EnzymesDocument9 pagesAnswers Proteins EnzymesMaria AngelinNo ratings yet
- Tinjauan Pustaka: Respon Imunologi Pada Dermatitis Kontak IritanDocument7 pagesTinjauan Pustaka: Respon Imunologi Pada Dermatitis Kontak IritanSatriadwykiyprasetya ThiodwkiyNo ratings yet
- Principles of innate immunity (Abbas Chapter 4Document31 pagesPrinciples of innate immunity (Abbas Chapter 4foreveraldyNo ratings yet
- MBB Quizzes on Biotechnology Products and DNA StructureDocument3 pagesMBB Quizzes on Biotechnology Products and DNA StructureRichlie Magtulis IINo ratings yet
- Difference Between Dna & Rna: Students NameDocument5 pagesDifference Between Dna & Rna: Students NameHisham MustafaNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: The Cell Cycle and DNA Replication ProcessDocument57 pagesDNA Replication: The Cell Cycle and DNA Replication ProcessJeevikaGoyalNo ratings yet
- Https Learn - Cellsignal.com Hubfs Pdfs 19-Cel-11131-Pwh-DigitalDocument2 pagesHttps Learn - Cellsignal.com Hubfs Pdfs 19-Cel-11131-Pwh-DigitaltamaraNo ratings yet
- Intro To DNA Profiling - Greg.hampianDocument24 pagesIntro To DNA Profiling - Greg.hampianszachtarNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 8th Edition Berg Test BankDocument12 pagesBiochemistry 8th Edition Berg Test Bankscarletwilliamnfz100% (28)
- Introduction to Molecular BiologyDocument58 pagesIntroduction to Molecular BiologyNanda SapitriNo ratings yet
- Types of ElectrophoresisDocument3 pagesTypes of ElectrophoresisSridharan VNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY - Assignment: Chapter: BiomoleculesDocument9 pagesBIOLOGY - Assignment: Chapter: Biomoleculesyogesh ahireNo ratings yet
- DNA RNA WorksheetDocument5 pagesDNA RNA WorksheetKathleen FrancoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Genome OrganizationDocument53 pagesProkaryotic Genome OrganizationAqsa YaminNo ratings yet
- Jacqueline Levana Huliselan (X511)Document11 pagesJacqueline Levana Huliselan (X511)Jacqueline Levana HuliselanNo ratings yet
- Edvotek S-51 ManualDocument33 pagesEdvotek S-51 Manualjellyfish27100% (1)
- AP Bio CH 14 Gene ExpressionDocument24 pagesAP Bio CH 14 Gene ExpressionLuisa RamosNo ratings yet
- Genomics & ProteomicsDocument1 pageGenomics & ProteomicsVanshika SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationDocument46 pages2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationAcyl HoteitNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Replikasi, Repair DNA Dan Rekombinan DNADocument50 pagesMekanisme Replikasi, Repair DNA Dan Rekombinan DNAnolaNo ratings yet
- Protein First AttemptDocument3 pagesProtein First AttemptAica ContempratoNo ratings yet
- PCR Application Manual 3rd EdDocument340 pagesPCR Application Manual 3rd EdSurendar Kesavan100% (1)
- Tr1rol15sziolw51zzmxxg0cDocument3 pagesTr1rol15sziolw51zzmxxg0csaurabhNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 (Saloni Rose)Document10 pagesAssignment 2 (Saloni Rose)saloniNo ratings yet
- 4) PPT On Mechanism of Action of Alcohol DehydrogenaseDocument7 pages4) PPT On Mechanism of Action of Alcohol DehydrogenaseSubha MaheswariNo ratings yet