Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presentation On Power Sector: 26 July 2010 by Arjun Srivastav
Uploaded by
Vamsi Krishna SivadiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Presentation On Power Sector: 26 July 2010 by Arjun Srivastav
Uploaded by
Vamsi Krishna SivadiCopyright:
Available Formats
PRESENTATION ON POWER SECTOR
26 July 2010 By Arjun Srivastav
POWER SECTOR
India has the fifth largest generation capacity in the world with an installed capacity of 152 GW as of September 2009, which is about 4 % of global power generation. The Indian government has set ambitious goals in the 11th plan for power sector owing to which the power sector is poised for significant expansion. The Government of India has an ambitious mission of POWER FOR ALL BY 2012. This mission would require that the installed generation capacity should be at least 200,000 MW by 2012 from the present level of 144,564.97 MW. Power requirement will double by 2020 to 400,000MW. The current installed transmission capacity is only 13 percent of the total installed generation capacity
FOCUS SECTOR - POWER
Contents
Overview of the sector Snapshot of Power Generation Industry Snapshot of Power Transmission Industry Snapshot of Power Distribution Industry Major Players
Overview of the Power Sector
The Challenge
it is to eradicate poverty and meet its human development goals.
India needs to sustain an 8% to 10% economic growth rate, over the next 25 years, if To deliver a sustained growth rate of 8% through 2031-32 and to meet the lifeline energy needs of all citizens, India needs, at the very least, to increase its primary energy supply by 3 to 4 times and, its electricity generation capacity/supply by 5 to 6 times of their 2003-04 levels.
How will India face this challenge ?
Meeting this vision requires that India pursues all available fuel options and forms of energy, both conventional and non-conventional. India must seek to expand its energy resource base and seek new and emerging energy sources. Finally, and most importantly, India must pursue technologies that maximize energy efficiency, demand side management and conservation. ( rational for having a power consultancy segment)
Composition of the Power Sector
The sector consists of 3 industries Power Generation , transmission and distribution
SNAPSHOT : Power Generation Industry
Overview
Indias power generation capacity as on March 2010 was 159,398 MW 64.28% - Thermal Sources 23.13% - Hydro Sources 9.74 - Renewable Sources 2.86 - Nuclear Sources
Favorable Trends
Rapid and progressive evolution Capacity Augmentation Conventional capacity 9585 MW during 2009-10 ( 2.5 times higher than the previous year) Productivity of power plants has been improving Increased Private Sector Participation Contribution has risen from 8.66 % 2003 to 18.2% in 2010 Pvt. projects aggregating over 100,000 MW are under various stages of development Forms of contribution Private power generation projects & Development of supercritical technology through Private Investment for Ultra Mega Projects Government policy to boost solar and wind power Emergence of new and alternate energy sources
Factors leading to growth
Projects and Opportunities
Ultra Mega Power Project (UMPP) Huge coal based projects with 4000 MW capacity each based on supercritical technology to be developed through private investment Govt. has planned 9 UMPPs 4 of the 9 planned UMPPs Mundra , Sasan , Krishnapatnam and Tilaiya have been allotted to private players 3 of the 9 planned UMPPs are in line - Sarguja ( Chattisgarh), Bhedabahal ( Orissa ), Cheyyur ( Tamil Nadu) Remaining 2 of the UMPPs are yet to be finalized Govt is keen to increase the no. of UMPPs from 9 to 14 Power Finance Corporation ( PFC) is the nodal agency for these projects Indigenization of supercritical equipment to meet future demand Central Electricity Authority ( CEA) issued a directive to central and state public sector utilities in Feb 2010 to procure supercritical equipment only from domestic manufacturers to encourage indigenous manufacturing Govt. Policy and Programmes to boost solar power generation Jawahar Lal Nehru National Solar mission launched in Nov 2009 Ambitious target of achieving 20,000 MW of solar capacity by 2022 in three stages
Govt. Policy and Programmes to boost solar power generation 12 MW of solar power is already connected to the grid More than 500 MW of solar photovoltaic plants and 350 MW of solar thermal are in the pipeline Plans to increase nuclear power generation Govt. is importing nuclear fuel ( uranium) to boost production Nuclear Power Corporation of India has commissioned two new reactors of 220 MW each and is set to commission another one It also plans to set up 8 reactors of 700 MW each and has begun work on 4 of these Plans are also on for setting up imported reactors in various sites in India Govt. plans to increase installed nuclear generation capacity from current 4560 MW to 20,000 MW by 2020 and 60,000 MW by 2030-31 Emphasis is also on enhancing gas and wind based power generation and Govt. is taking a series of steps in this direction
Challenges faced by the Power Generation Sector
Inadequate equipment capacity Fuel and manpower shortage
Delays in securing clearances and commitments from state utilities for power
purchase & resistance from environmentalists
SNAPSHOT : Power Transmission Industry
Overview
As of March 2010 , the State Transmission Units ( STU) and Central Transmission Unit ( CTU) , which are responsible for intra state and interstate transmission network respectively , together own and operate a complex transmission system comprising around 236,430 ct. km of lines and over 305,550 MVA and 14,000 MW of substation capacity of voltages above 220 KV
Favorable Trends
Significant Investments at Central and State Level
National Level Investment Powergrid corporation of India ( Powergrid) , the countrys CTU spent a total of Rs.147.1 billion ( Rs. 66.15 billion 2007-08) & (Rs. 80.95 billion in 2008-09) It has planned capital expenditure of Rs. 120 billion for 2009-10 Plans to make an investment of Rs. 550 billion during the current plan period State Level Investment STUs spent Rs. 185.84 billion during the 1st two years of the plan period ( 23% of the total utility spending during the period) Increased private sector participation
Projects and Opportunities
Development of the National Grid by the CTU High Voltage Transmission Corridors Powergrid is taking steps to develop 7 high voltage transmission corridors ( 800KV and 770 kv ) over the next 5 years investment of Rs. 489 billion to facilitate smooth transmission of about 55,000 MW of capacity that is proposed to be generated by private power plants in the states of Chattisgarh , Orissa and Jharkhand 2 more transmission corridors are expected to be developed by CTU to wheel power from coastal Tamil Nadu , where private projects based on imported coal are coming up . For this , Powergrid has signed long term transmission agreements with 37 private developers for a gross combined generation capacity of over 42,000 MW Development of Transmission Systems by Private Players Transmission systems associated with private generation projects are being developed by private players independently or in joint venture with the CTU and STU This includes Adani Powers Rs. 15 billion dedicated 1000km long bi-polar 500 KV high voltage direct current line from its Mundra Project in Gujrat to Mohindergarh in Haryana. The company is also developing a 765 KV line in joint venture with Mahatransco in Maharashtra to secure evacuation of power from its upcoming power plant in the state
100% Private Investment invited for Transmission Projects
14 transmission projects identified by the Power Ministry for 100% private investment The bidding process for the first 3 projects has been completed by the 2 nodal agencies Power Finance Corporation & Rural Electrification Corporation The 1st Project East North Interconnection was awarded to Sterlite Technologies Other 2 projects North Karanoura and TALCHER II were bagged by RPTL The bids for the remaining projects were invited by the nodal agencies in March 2010 Some states including Uttar Pradesh and Haryana have also invited tenders for state level projects
Challenges faced by the Power Transmission Sector
Delays in clearances Inadequate margins in the system Grid indiscipline Lack of basic infrastructure Unco-ordinated planning Inadequate equipment manufacturing capacity Fast changing technology leading to obsocelence Slow progress in strengthening and augmentation of networks
SNAPSHOT : Power Distribution Industry
Overview
Indias distribution infrastructure include more than Rs. 6.9 million ct. km of lines and over 284,365 MVA of distribution of transformer capacity as of march 2008 It is growing at a rate of 2.07% and 7.65% respectively over the period of 200203 and 2007-08
Favorable Trends
The level of metering has shown improvement Sales of power and state utility revenues are showing a steady increase every year Cash collections are improving A few utilities / State Electricity Boards have also registered an improvement in cash profits like West Bengal , Assam , Orissa , Andhra Pradesh , Punjab , Kerala and UP and Meghalaya More and more distribution companies are adopting sophisticated IT systems to improve operations and customer service spot billing , call centers , remote meter reading ,automated billing and energy accounting
Projects and Opportunities
Accelerated Power Development and Reform Programme ( 2002-03) Objective- reducing AT&C losses , improving the quality of power supply and consumer satisfaction Restructured Accelerated Power Development and Reform Programme Larger in scale than the original programme ( Rs. 500 Billion) It will be implemented in two parts Part A ( Rs. 400 billion) and Part B ( Rs. 100 billion) Part A establishment of baseline data and IT applications for enegery accounting /auditing and IT based consumer centre Part B Regular Distribution Strengthening Projects Nodal Agency Power Finance Corporation Rajiv Gandhi Gramin Vidyuti Karan Yojana Provides focus and funds to rural distribution systems as of April 2010 573 projects under the programme
Privatization of distribution Process has been slow to take off Orissa -1st state to privatize distribution followed by Delhi Benefits - Bringing down AT& C losses and improvement of customer services Franchise Model in privatization of distribution 1st Franchise operation launched in Maharashtra with the state transferring the rights to supply , maintain , recover electricity dues in certain sectors to Pvt. players UP Govt. introduced input based franchises in urban areas for power distribution Other states will also follow on the same model ( plans in place for Rajasthan , Karnataka and Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh)
Setting up of State Electrification Regulatory Commissions Established in 23 Indian States Has led to tariff rationalization
Challenges faced by the Power Distribution Industry
High aggregate technical and commercial losses Rampant power thefts
Technical issues
Policies of offering subsidized or free power Dilapidated networks Inadequate metering Poor recovery of dues Poor operational and financial management Lack of customer orientation
Major Players in the Power Sector
National Thermal Power Corporation - Single largest power producer in India
National Hydro Power Corporation -Largest hydro power generator in India
Power Grid Corporation of India - Largest Transmission Utility in India
Power Trading Company - 1st Power trading company of India ( 1999)
Power Finance Corporation - State run power sector financing corporation
Bharat Heavy Electricals Ltd - The largest engineering and manufacturing enteroprise in India
Tata Power Company - Biggest integrated power player in India
THANK YOU!
You might also like
- Montaje Cables Alta Tension DCDocument6 pagesMontaje Cables Alta Tension DCmauriciojj0% (1)
- 1.4 Power Sector MainDocument24 pages1.4 Power Sector MainAbhaSinghNo ratings yet
- Invoice: Thank You For Your Business!Document2 pagesInvoice: Thank You For Your Business!Mary Anne BantogNo ratings yet
- Comments: Inspection Points and Their ReasonsDocument2 pagesComments: Inspection Points and Their ReasonsBruno Samos100% (1)
- Indian Power SectorDocument38 pagesIndian Power SectorAbhay Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Pre Feasibility Study Mundargi Gas Based Power PlantDocument71 pagesPre Feasibility Study Mundargi Gas Based Power Plantrrs41100% (1)
- Rho 3 Application For Broken Conductor Detection On Overhead Line FeedersDocument1 pageRho 3 Application For Broken Conductor Detection On Overhead Line Feedersrtsr1990No ratings yet
- Small Hydro Power Schemes KeralaDocument105 pagesSmall Hydro Power Schemes KeralaAnish BabuNo ratings yet
- India's Power Sector: Ambitious Goals and Massive Investment NeedsDocument20 pagesIndia's Power Sector: Ambitious Goals and Massive Investment Needsyadavmihir63No ratings yet
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Document37 pagesInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768frankkenny ramirez gutierreNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy in IndiaDocument20 pagesRenewable Energy in IndiabenoypNo ratings yet
- Knowledge and Power: Lessons from ADB Energy ProjectsFrom EverandKnowledge and Power: Lessons from ADB Energy ProjectsNo ratings yet
- CAREC Energy Strategy 2030: Common Borders. Common Solutions. Common Energy Future.From EverandCAREC Energy Strategy 2030: Common Borders. Common Solutions. Common Energy Future.No ratings yet
- Presented by Bhakti Bhusan Parida Roll-16Document17 pagesPresented by Bhakti Bhusan Parida Roll-16bb2No ratings yet
- Power Sector in India ProjectDocument23 pagesPower Sector in India ProjectRajesh ParidaNo ratings yet
- Electricity Sector in India 1Document55 pagesElectricity Sector in India 1Gautham SidharthNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary: Industry ProfileDocument53 pagesExecutive Summary: Industry ProfileBhumi JaanviNo ratings yet
- Power Sector in India: All You Wanted To Know in 5 PointsDocument7 pagesPower Sector in India: All You Wanted To Know in 5 PointsJay ThakarNo ratings yet
- Tata Power Company Limited: - Mr. Prasad R. Menon, Managing Director, Tata PowerDocument22 pagesTata Power Company Limited: - Mr. Prasad R. Menon, Managing Director, Tata PowerncbaraiNo ratings yet
- India's Power Sector OverviewDocument5 pagesIndia's Power Sector OverviewRamaa KumarNo ratings yet
- Indian Power Sector Analysis PDFDocument9 pagesIndian Power Sector Analysis PDFvinay_814585077No ratings yet
- A Study On Diesel Generator Sets in IndiaDocument44 pagesA Study On Diesel Generator Sets in IndiaRoyal ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2013-14 EnglishDocument234 pagesAnnual Report 2013-14 EnglishMarkWeberNo ratings yet
- Energy Sector AssessmentDocument6 pagesEnergy Sector Assessmentmeendhami62No ratings yet
- Tata Welspun DealDocument17 pagesTata Welspun DealrkmouryaNo ratings yet
- Power Development: 6. EnergyDocument7 pagesPower Development: 6. EnergyAravindan MuthuNo ratings yet
- Hindustan Powerprojects To Lighten Up The Anuppur DistrictDocument3 pagesHindustan Powerprojects To Lighten Up The Anuppur DistrictRatul PuriNo ratings yet
- Policy For FutureDocument86 pagesPolicy For FutureoliviajasonNo ratings yet
- 22private Sect PowerDocument14 pages22private Sect PowerSanjana KoliNo ratings yet
- Approach Paper For Power ReformsDocument15 pagesApproach Paper For Power ReformsAnonymous loKgurNo ratings yet
- NPCL Power Procurement PlanDocument79 pagesNPCL Power Procurement PlanVikram Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- Industry Profile on India's Electrical Power SectorDocument21 pagesIndustry Profile on India's Electrical Power Sectorbb2No ratings yet
- Overview of Power SectorDocument26 pagesOverview of Power SectorRameswar DashNo ratings yet
- Status of Power Markets and Power Exchanges in Asia and AustraliaDocument72 pagesStatus of Power Markets and Power Exchanges in Asia and AustraliadanielraqueNo ratings yet
- "Power Sector": Project of Corporate Accounting Procedures-1 AND Special Transactions Accounting-1Document33 pages"Power Sector": Project of Corporate Accounting Procedures-1 AND Special Transactions Accounting-1maildarshitNo ratings yet
- India Will Miss Power Target of 62,000 MW: News, AnalysisDocument10 pagesIndia Will Miss Power Target of 62,000 MW: News, AnalysisdevavasanNo ratings yet
- Final Project 2Document79 pagesFinal Project 2Tmesibmcs MandviNo ratings yet
- Power: Public SectorDocument4 pagesPower: Public SectorHitesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Electricity Regulation in India OverviewDocument29 pagesElectricity Regulation in India OverviewPrashant DoundNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra Emerging as Wind Energy Hub with Over 4 GW Target by 2012Document14 pagesMaharashtra Emerging as Wind Energy Hub with Over 4 GW Target by 2012Devesh GhirnikarNo ratings yet
- PresentFutb - Saradhab.saradha ReEnergyScenarioinIndia - SPRINGERIndiaDocument9 pagesPresentFutb - Saradhab.saradha ReEnergyScenarioinIndia - SPRINGERIndiaharshaNo ratings yet
- Shankha Banerjee, 52, MBA - PMDocument10 pagesShankha Banerjee, 52, MBA - PMshankhab_1No ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Financial Performance of Power Sector CompaniesDocument103 pagesComparative Analysis of Financial Performance of Power Sector CompaniesAkhil Vigh100% (1)
- Indian Power System ScenarioDocument4 pagesIndian Power System ScenarioTanvi Ravindra MahatmeNo ratings yet
- Power Sector Analysis in IndiaDocument8 pagesPower Sector Analysis in IndiaSimranNo ratings yet
- India's Ultra Mega Power ProjectsDocument4 pagesIndia's Ultra Mega Power ProjectsVineet KumarNo ratings yet
- Market Size and Investment in India's Power SectorDocument13 pagesMarket Size and Investment in India's Power SectorajayNo ratings yet
- Ijmet: ©iaemeDocument9 pagesIjmet: ©iaemeIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- AP Power DetailsDocument4 pagesAP Power Detailsmadhvi2108No ratings yet
- SM Final ReportDocument23 pagesSM Final ReportSunil RathodNo ratings yet
- Introduction MDocument77 pagesIntroduction MAashi YadavNo ratings yet
- Finance Report SecBDocument26 pagesFinance Report SecBnickysweet21No ratings yet
- Annual Report 2013-14 English PDFDocument234 pagesAnnual Report 2013-14 English PDFAnirban BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Sapm Psda - Eic AnalysisDocument12 pagesSapm Psda - Eic AnalysisAkash SinghNo ratings yet
- Indian Power Sector Challenges and OpportunitiesDocument34 pagesIndian Power Sector Challenges and OpportunitiesparthppppNo ratings yet
- India EnergyDocument3 pagesIndia EnergySravan KatragaddaNo ratings yet
- The Sipat Super Thermal Power Project: "Coal Remains The Primary Fuel For Meeting Existing and Future Electricity Demand"Document8 pagesThe Sipat Super Thermal Power Project: "Coal Remains The Primary Fuel For Meeting Existing and Future Electricity Demand"Rishi PatelNo ratings yet
- Organization Summary: Thar Coal Power Project by Engro Powergen Thar Pvt. LTDDocument14 pagesOrganization Summary: Thar Coal Power Project by Engro Powergen Thar Pvt. LTDAshley WoodNo ratings yet
- Coal News From Ccai 24.04.2020 PDFDocument14 pagesCoal News From Ccai 24.04.2020 PDFSwarup Singh DeoNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Tech.Document47 pagesPower Plant Tech.firoj_khan967% (3)
- Nepal Energy Sector Assessment, Strategy, and Road MapFrom EverandNepal Energy Sector Assessment, Strategy, and Road MapNo ratings yet
- Guidebook for Utilities-Led Business Models: Way Forward for Rooftop Solar in IndiaFrom EverandGuidebook for Utilities-Led Business Models: Way Forward for Rooftop Solar in IndiaNo ratings yet
- EU China Energy Magazine 2023 September Issue: 2023, #8From EverandEU China Energy Magazine 2023 September Issue: 2023, #8No ratings yet
- One Goal, Two Paths: Achieving Universal Access to Modern Energy in East Asia and PacificFrom EverandOne Goal, Two Paths: Achieving Universal Access to Modern Energy in East Asia and PacificNo ratings yet
- Delhi'S Iconic Monuments Through Aarna'SDocument3 pagesDelhi'S Iconic Monuments Through Aarna'SArjun SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Printing Invoice for University of MaltaDocument1 pagePrinting Invoice for University of MaltaArjun SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Detailed Project Report: (For Implementation of Reservation For Obcs and Capacity Expansion)Document2 pagesDetailed Project Report: (For Implementation of Reservation For Obcs and Capacity Expansion)Arjun SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Learning Talent Development Survey ReportDocument38 pagesLearning Talent Development Survey ReportArjun Srivastav100% (1)
- SECTOR Roads & HighwaysDocument3 pagesSECTOR Roads & HighwaysArjun SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Statistical Review of World Energy 2010Document50 pagesStatistical Review of World Energy 2010Arjun SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Programa de Mantenimiento Preventivo ACS880Document2 pagesPrograma de Mantenimiento Preventivo ACS880JaimeNo ratings yet
- Complete System Ordering Information: Elspec LTDDocument8 pagesComplete System Ordering Information: Elspec LTDJose Garcia CossioNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Correction Mkk440-D-15-01Document3 pagesPower Factor Correction Mkk440-D-15-01Halil DemirNo ratings yet
- Major Project Report: Portable Air Charger "PAC"Document4 pagesMajor Project Report: Portable Air Charger "PAC"Tlm BhopalNo ratings yet
- Earthing and Bonding For 2 X25 KVDocument2 pagesEarthing and Bonding For 2 X25 KVNagi Reddy ChintakuntaNo ratings yet
- 1SDC200050L0201 - Leaflet - SACE Emax 2 MS-DCE at 1500VDC - 2021.04Document4 pages1SDC200050L0201 - Leaflet - SACE Emax 2 MS-DCE at 1500VDC - 2021.04Trijana SaltagaNo ratings yet
- Inverter: McmurrayDocument5 pagesInverter: McmurrayanshuNo ratings yet
- Switchgear DesignDocument32 pagesSwitchgear DesignAnonymous utxGVB5VyNo ratings yet
- 4.reliability in Electrical SystemsDocument31 pages4.reliability in Electrical SystemsCharles OndiekiNo ratings yet
- Lembar Data Produk: Tesys F Contactor - 3P (3 No) - Ac-3 - 440 V 185 A - Without CoilDocument3 pagesLembar Data Produk: Tesys F Contactor - 3P (3 No) - Ac-3 - 440 V 185 A - Without Coilincore1976No ratings yet
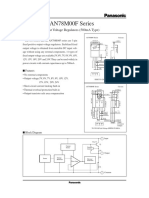
- AN78M20FDocument10 pagesAN78M20FFrantsiskoNo ratings yet
- Transform Ad or de Corrente IMB 60-300kVDocument16 pagesTransform Ad or de Corrente IMB 60-300kVmora tuaNo ratings yet
- Stepping Motor Driver: BA6845FSDocument7 pagesStepping Motor Driver: BA6845FSsmnguyenNo ratings yet
- Hf1016414 Hoffman VentiladorDocument4 pagesHf1016414 Hoffman VentiladorMoises AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Study of Advanced Current Control Strategies For Three-Phase Grid-Connected PWM Inverters For Distributed GenerationDocument6 pagesStudy of Advanced Current Control Strategies For Three-Phase Grid-Connected PWM Inverters For Distributed Generationapi-3826450100% (2)
- Capacitance and Esr Meter Using Pic16f873aDocument74 pagesCapacitance and Esr Meter Using Pic16f873aJ_renoNo ratings yet
- EasyLogic OEM EM1251 power & energy meter datasheetDocument2 pagesEasyLogic OEM EM1251 power & energy meter datasheetAnkur SharmaNo ratings yet
- LTspice Tutorial - The Complete CourseDocument2 pagesLTspice Tutorial - The Complete CoursersfdtdNo ratings yet
- TL-MC1400&TL-FC1420 IgDocument2 pagesTL-MC1400&TL-FC1420 IgKirito KidNo ratings yet
- A Micro-Grid Case Study: Lessons Learned From A Rural Electrification Project in IndiaDocument20 pagesA Micro-Grid Case Study: Lessons Learned From A Rural Electrification Project in IndiaNayyar HussainNo ratings yet
- TRAFODocument5 pagesTRAFOJayam KondanNo ratings yet
- 6SQ7GT, Tube 6SQ7GT Röhre 6SQ7GT ID2988, Double Diode-TriodDocument2 pages6SQ7GT, Tube 6SQ7GT Röhre 6SQ7GT ID2988, Double Diode-TriodRodrigo GarciaNo ratings yet
- MullerEnergy JBD BMS InstructionsDocument13 pagesMullerEnergy JBD BMS InstructionsgrillonNo ratings yet
- Simtec P450 Data SheetDocument2 pagesSimtec P450 Data Sheetacajevtic94No ratings yet
- Solenoid Valve SCE272ADocument2 pagesSolenoid Valve SCE272AVictor Ruiz FuentesNo ratings yet