Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ms Excel: By: SCLP
Uploaded by
Starsky Allence PuyocOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ms Excel: By: SCLP
Uploaded by
Starsky Allence PuyocCopyright:
Available Formats
MS EXCEL
By: SCLP
Understanding worksheet cells
Worksheet
Is a rectangular arrangement of rows and columns.
Row
Labeled w/ numbers
Column
Labeled w/ letters
Cell
Intersection of rows and columns.
Active cell
Selected cells
Three kinds of data
1.
Text
These entries are usually labels such as name, age, remarks, etc. that make a worksheet easier to read. Can be text/number combinations for items such as phone numbers and account code.
2.
Numbers
These entries can be dollar values, weights, interest rates or any other numerical quantity.
3.
Formulas
These are calculations involving two or more values such as 2*5 or A1+A2+A3 A formula always starts with equal sign ( = ).
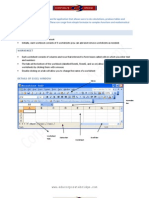
EXCELS SCREEN Active cell
Name box Formula bar
Excels worksheet navigation keys
PRESS Arrow keys Home Page down Page up Alt+Page down Alt+Page up Ctrl+End Ctrl+Home TO MOVE To left, right, up or down one cell The beginning of the row Down one screen Up one screen One screen to the right One screen to the left To the bottom right corner of the used portion of the worksheet To the beginning of the worksheet
Excels formatting keyboard shortcuts
PRESS
Ctrl+B Ctrl+I Ctrl+U Ctrl+5 Ctrl+Shift+! Ctrl+Shift+$ Bold Italic Underline Strikethrough Number(two decimal places, using thousand separator) Currency(two decimal places, using dollar sign and negative numbers surrounded by parenthesis).
To apply the following format
Ctrl+Shift+%
Ctrl+Shift+^ Ctrl+Shift+# Ctrl+Shift+@ Ctrl+Shift+~
Percentage (zero decimal places)
Scientific (two decimal places) Date (d-mm-yy) Time (h:mm AM/PM) General
Excels arithmetic operators
Operators
+ (addition) - (subtraction) negation) * (multiplication) / (division) % (percentage) =3+2 =3-2 =-3 =3*2 =3/2 =3%
Examples
5 1 -3 6 1.5 0.03
Result
^ (exponentiation)
=3^2
Excels comparison operators
Operators
= (equal to) > (greater than) < (less than) =3=2 =3>2 =3<2
Examples
Result
FALSE TRUE FALSE TRUE FALSE TRUE
>= (greater than or equal =3>=2 to) <= (less than or equal to) =3<=2 <> (not equal to) =3<>2
Excels order of calculation
Operator
(negation) % (percentage) ^ (exponentiation) * and / (multiplication and division) + and (addition and subtraction) = ,<, >, <=, >=, <> (comparison)
Order of calculation
First (1st) Second (2nd) Third (3rd) Fourth (4th) Fifth (5th) Sixth (6th)
Example of Excels Formula
Operation
SUM=A plus B DIFFERENCE = A minus B PRODUCT = A time B QUOTIENT = A divide by B EXPONENT=AB
Formula
=A+B =A B =A*B =A/B =A^B
You might also like
- The Convergent Parallel DesignDocument8 pagesThe Convergent Parallel Designghina88% (8)
- BIWS Excel ShortcutsDocument3 pagesBIWS Excel ShortcutsLeo Dahut100% (1)
- BM - GoPro Case - Group 6Document4 pagesBM - GoPro Case - Group 6Sandeep NayakNo ratings yet
- Excel Shortcuts (BIWS)Document3 pagesExcel Shortcuts (BIWS)Anthony Liang100% (1)
- Power Excel with MrExcel: Master Pivot Tables, Subtotals, Charts, VLOOKUP, IF, Data Analysis in Excel 2010–2013From EverandPower Excel with MrExcel: Master Pivot Tables, Subtotals, Charts, VLOOKUP, IF, Data Analysis in Excel 2010–2013Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Power Excel 2019 with MrExcel: Master Pivot Tables, Subtotals, VLOOKUP, Power Query, Dynamic Arrays & Data AnalysisFrom EverandPower Excel 2019 with MrExcel: Master Pivot Tables, Subtotals, VLOOKUP, Power Query, Dynamic Arrays & Data AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Microsoft Excel: Information and Communication TechnologyDocument49 pagesMicrosoft Excel: Information and Communication TechnologyEdrianne J.No ratings yet
- Finance&Excel CH 00 Excel WorkbookDocument58 pagesFinance&Excel CH 00 Excel WorkbookDavid Ioana100% (1)
- Introduction To Computing (COMP-01102) Telecom 1 Semester: Lab Experiment No.03Document5 pagesIntroduction To Computing (COMP-01102) Telecom 1 Semester: Lab Experiment No.03ASISNo ratings yet
- Excel HandoutDocument8 pagesExcel HandoutJemimah FV100% (1)
- Experiment # 04: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesExperiment # 04: ObjectiveAbuzarNo ratings yet
- Basics of A SpreadsheetDocument38 pagesBasics of A SpreadsheetLyca Den DewNo ratings yet
- MS Excel Shortcuts 20131124Document3 pagesMS Excel Shortcuts 20131124Abhiyan Anala ArvindNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1601367041808 6716620188926428611Document38 pagesOrca Share Media1601367041808 6716620188926428611John Edward PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Graphics. An Example Would Be Microsoft Word. Formulas Into The Spreadsheet For Easy Calculation. An Example Would Be Microsoft ExcelDocument6 pagesGraphics. An Example Would Be Microsoft Word. Formulas Into The Spreadsheet For Easy Calculation. An Example Would Be Microsoft ExcelLeopold LasetNo ratings yet
- BIWS Excel Shortcuts 2007 To 2013 PlusDocument4 pagesBIWS Excel Shortcuts 2007 To 2013 PlusvishnuvermaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Computer Chapter 2 (Calculations in Microsoft Excel)Document5 pagesClass 7 Computer Chapter 2 (Calculations in Microsoft Excel)gautamtotalaNo ratings yet
- Your Excel Formulas Cheat Sheet - 15 Tips For Calculations and Common TasksDocument5 pagesYour Excel Formulas Cheat Sheet - 15 Tips For Calculations and Common Tasksscama313No ratings yet
- Session 1 Excel Reading MaterialsDocument22 pagesSession 1 Excel Reading MaterialsfNo ratings yet
- 22 Excel BasicsDocument31 pages22 Excel Basicsapi-246119708No ratings yet
- Quick Reference Guide: The RibbonDocument4 pagesQuick Reference Guide: The RibbonMudassar AfzalNo ratings yet
- ExcelDocument28 pagesExcelHaydee LuyangNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 2Document10 pagesExperiment No 2Muhammad Tauseef ZafarNo ratings yet
- BIWS Excel Shortcuts MacDocument6 pagesBIWS Excel Shortcuts MacKim PatelNo ratings yet
- Excel Shortcut KeysDocument8 pagesExcel Shortcut KeysAmar RajureNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document29 pagesModule 4Reema SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Excel 2010 (NOTES)Document10 pagesMicrosoft Excel 2010 (NOTES)Shara Cañada CalvarioNo ratings yet
- Training WorksheetsDocument62 pagesTraining WorksheetsDurjoy ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Fourth Quarter NotesDocument8 pagesFourth Quarter NotesShara Cañada CalvarioNo ratings yet
- Excel Guide Handbook44Document62 pagesExcel Guide Handbook44Tata PovNo ratings yet
- Excel: Basic FeaturesDocument13 pagesExcel: Basic FeaturesBernadette P. FernandesNo ratings yet
- Js 02 Nizam FauziDocument15 pagesJs 02 Nizam FauziNizammudinMuhammadFauziNo ratings yet
- Excel (Third Quarter)Document10 pagesExcel (Third Quarter)Nefritiri BlanceNo ratings yet
- Excel Overview - NotesDocument11 pagesExcel Overview - Notessribalakarthik_21435No ratings yet
- Basic ExcelDocument13 pagesBasic ExcelRakesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Excel ShortcutsDocument6 pagesExcel ShortcutsNid KingNo ratings yet
- Electronic SpreadsheetsDocument62 pagesElectronic SpreadsheetsAyane Miyasawa Verona-Manila100% (1)
- Excel Guide Handbook11Document65 pagesExcel Guide Handbook11Tata PovNo ratings yet
- Excel Keyboard Shortcuts: Alt+Enter SHIFT+Arrow Keys SHIFT+CTRL+Arrow Keys Backspace Delete ESCDocument2 pagesExcel Keyboard Shortcuts: Alt+Enter SHIFT+Arrow Keys SHIFT+CTRL+Arrow Keys Backspace Delete ESCjohne877No ratings yet
- MS Excel For ConstructionDocument26 pagesMS Excel For ConstructionOPARA JOSIAH100% (1)
- Training WorksheetDocument259 pagesTraining Worksheetmaglalang_dexter_024No ratings yet
- Create A Workbook in ExcelDocument10 pagesCreate A Workbook in ExcelismaelmNo ratings yet
- Excel TipsDocument4 pagesExcel TipsJayson PintoNo ratings yet
- Excel Mac ShortcutsDocument2 pagesExcel Mac Shortcutsdrpsruk6165No ratings yet
- ExcelDocument113 pagesExcelZubair ShafeeqNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Introduction To Electronic SpreadsheetsDocument57 pagesUnit 3: Introduction To Electronic Spreadsheetsnjk19No ratings yet
- Computer Chapter-5 Introduction To Ms Excel 2010: Spreadsheet. Electronic Spreadsheet ProgramDocument16 pagesComputer Chapter-5 Introduction To Ms Excel 2010: Spreadsheet. Electronic Spreadsheet Programtezom techeNo ratings yet
- Excel 2007Document16 pagesExcel 2007Anurag GoelNo ratings yet
- Excel Tips For CHEM 105 Lab: Entering Numbers, Functions, Equations, and TextDocument4 pagesExcel Tips For CHEM 105 Lab: Entering Numbers, Functions, Equations, and TextkeenakinkinNo ratings yet
- Excel for Beginners: Learn Excel 2016, Including an Introduction to Formulas, Functions, Graphs, Charts, Macros, Modelling, Pivot Tables, Dashboards, Reports, Statistics, Excel Power Query, and MoreFrom EverandExcel for Beginners: Learn Excel 2016, Including an Introduction to Formulas, Functions, Graphs, Charts, Macros, Modelling, Pivot Tables, Dashboards, Reports, Statistics, Excel Power Query, and MoreNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Excel: Microsoft Excel User Interface, Excel Basics, Function, Database, Financial Analysis, Matrix, Statistical AnalysisFrom EverandMicrosoft Excel: Microsoft Excel User Interface, Excel Basics, Function, Database, Financial Analysis, Matrix, Statistical AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Keyboarding Skills: From the Typewriter to the ComputerFrom EverandFundamental Keyboarding Skills: From the Typewriter to the ComputerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Power Excel with MrExcel - 2017 Edition: Master Pivot Tables, Subtotals, Visualizations, VLOOKUP, Power BI and Data AnalysisFrom EverandPower Excel with MrExcel - 2017 Edition: Master Pivot Tables, Subtotals, Visualizations, VLOOKUP, Power BI and Data AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Excel for Scientists and EngineersFrom EverandExcel for Scientists and EngineersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Juggling Your Finances: Basic Excel Primer: Juggling Your FinancesFrom EverandJuggling Your Finances: Basic Excel Primer: Juggling Your FinancesNo ratings yet
- Different Varieties of English C1 WSDocument5 pagesDifferent Varieties of English C1 WSLaurie WNo ratings yet
- PI SQC 2015 R3 User GuideDocument50 pagesPI SQC 2015 R3 User Guideislam ahmedNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX - Sri Thiruppugal Vidhana Shodasa Upachara Puja PDFDocument73 pagesVdocuments - MX - Sri Thiruppugal Vidhana Shodasa Upachara Puja PDFDomnick WilkinsNo ratings yet
- CrossFit Wod Tracking JournalDocument142 pagesCrossFit Wod Tracking JournalJavier Estelles Muñoz0% (1)
- Rapid Prototyping and Rapid Tooling TheDocument24 pagesRapid Prototyping and Rapid Tooling TheGopinath GangadhariNo ratings yet
- Youth Policy Manual: How To Develop A National Youth StrategyDocument94 pagesYouth Policy Manual: How To Develop A National Youth StrategyCristinaDumitriuAxyNo ratings yet
- Sumit YadavDocument85 pagesSumit Yadavanuj3026No ratings yet
- Or SuperDocument2 pagesOr SuperJac BacNo ratings yet
- MacDonald, J.& MacDonald, L. (1974)Document17 pagesMacDonald, J.& MacDonald, L. (1974)Mariuca PopescuNo ratings yet
- Business Communication and Behavioural StudiesDocument10 pagesBusiness Communication and Behavioural StudiesBhujangam NaiduNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Wawa Elementary SchoolDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Wawa Elementary SchoolJONATHAN CALAGUINo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Paulene V. Silvestre Personal DevelopmentDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Paulene V. Silvestre Personal DevelopmentPau SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Derivative Pakistan PerspectiveDocument99 pagesDerivative Pakistan PerspectiveUrooj KhanNo ratings yet
- The Manuals Com Cost Accounting by Matz and Usry 9th Edition Manual Ht4Document2 pagesThe Manuals Com Cost Accounting by Matz and Usry 9th Edition Manual Ht4shoaib shakilNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing Unit-8Document4 pagesDigital Image Processing Unit-8Kpsteja TejaNo ratings yet
- Bhrighu Saral Paddhati - 1Document212 pagesBhrighu Saral Paddhati - 1ErrovioNo ratings yet
- Febryruthwahyuni Lds g1718 Bilphy MRDocument11 pagesFebryruthwahyuni Lds g1718 Bilphy MRfebry sihiteNo ratings yet
- Tle9cookery q1 m7 Presentingandstoringarangeofappetizer v2Document30 pagesTle9cookery q1 m7 Presentingandstoringarangeofappetizer v2Almaira SumpinganNo ratings yet
- 2406 Final ExamDocument10 pages2406 Final ExamChandan GargNo ratings yet
- Technical English For Mining (L3)Document21 pagesTechnical English For Mining (L3)Tō Rā YhNo ratings yet
- Intj MbtiDocument17 pagesIntj Mbti1985 productionNo ratings yet
- Region 2Document75 pagesRegion 2yoyiyyiiyiyNo ratings yet
- Certified List of Candidates For Congressional and Local Positions For The May 13, 2013 2013 National, Local and Armm ElectionsDocument2 pagesCertified List of Candidates For Congressional and Local Positions For The May 13, 2013 2013 National, Local and Armm ElectionsSunStar Philippine NewsNo ratings yet
- Rationale of Labour Welfare To Employers and EmployeesDocument20 pagesRationale of Labour Welfare To Employers and Employeesajit yadav100% (1)
- VB Knowledge Buying A Home Flashcards QuizletDocument1 pageVB Knowledge Buying A Home Flashcards QuizletSavaya CrattyNo ratings yet
- Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited: Prepared For: Prepared By: MavericksDocument18 pagesAl-Arafah Islami Bank Limited: Prepared For: Prepared By: MavericksToabur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Ring Spinning Machine LR 6/S Specification and Question AnswerDocument15 pagesRing Spinning Machine LR 6/S Specification and Question AnswerPramod Sonbarse100% (3)
- Sleeping GarmentsDocument1 pageSleeping GarmentsRosalie LazaroNo ratings yet