Professional Documents
Culture Documents
By: Arunima Sharma Arpita Ghosh Bushra Zaheer Khan Md. Arif
Uploaded by
goluchetanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
By: Arunima Sharma Arpita Ghosh Bushra Zaheer Khan Md. Arif
Uploaded by
goluchetanCopyright:
Available Formats
By: Arunima Sharma Arpita Ghosh Bushra Zaheer Khan Md.
Arif
Object
Applicability
History Terminology Registration & Licensing Important sections Latest amendments Linkage with other acts Case studies Conclusion (Pros & cons)
Objective: An Act to regulate the employment of contract labour in certain establishments and to provide for its abolition in certain circumstances and for matters connected therewith. Applicability :
Employer Contractor
20 or more workmen employed on any day in the preceding 12months
1956- Service conditions of labourers, a topic of concern 1960- Vaccum Refining Co. case 1961- Indian labour conference 1962-Recommendation to the bill 1967- Bill moved to lok Sabha 1968- Reference to Joint committee 1970- Bill passed 1971- Enforcement of Act
Establishment Contractor Employer Intermittent Revocation Appropriate government
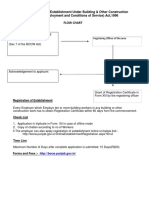
Registration (Sec 7) & Licensing (Sec 12)
Registration This is taken by the Principal Employer. License
This is taken by Contractor This is valid for only one year / should renewed before due date. License shall be displayed prominently at the premises where the contract work is being carried on.
This is not renewable on year to year basis Certificate of Reg.. Need not be displayed at the establishment by P.E.
Registration (Sec 7) & Licensing (Sec 12)
Registration Issued on Payment of fees. For only Bank Draft Required. No Conditions are attached as a part certt. License Issued on Payment of Fee & Security money Bank Draft + Certt. Of P.E. Is required (Form V) There is full Annx. Containing conditions for fulfillment by contractor.
To pay wages incase the contractor fails to do so To nominate a representative to be present at the time of disbursement of wages by the contractor To provide welfare and health facilities Right to recover the expenses involved from the Contractor through bills payable.
Maintain a register and records in form XII giving particulars like
No of Contractors and contract labour employed. Nature of work. Rate of wages.
Display Notice at a conspicuous place in English and Local Language containing information like
Rate of wages. Hour of work. Wage period. Date of payment of wages. Name and address of the Inspectors.
Submission of yearly return to Licensing Officer in Form XXV.
Maintain a register in form XIII containing information like
Muster Roll Wages Deductions. Over time Fines Advance Wage slips
Issue an employment card in form XIV to each worker and to issue a service certificate on termination of employment in form XV Submission of half yearly return to Licensing Officer in Form XXIV.
(Sec. 10) Prohibition of employment of contract labour. (Sec. 9) Effect of non-registration. (Sec. 14) Revocation, suspension and amendment of licences. (Sec. 16) Canteens. (Sec. 17) Rest-rooms. (Sec. 30) Effect of laws and agreements inconsistent with this Act. Sec 20 (Sec. 21) Responsibility for payment of wages. (Sec. 22) Obstructions. (Sec. 23) Contravention of provisions regarding employment of contract labour.
The Contract Labour (Regulation and Abolition) (Amendment) Act, 1986. The Delegated Legislation Provisions (Amendment) Act, 2004.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
Factories Act 1948. Employees Provident Funds & Miscellaneous Provision Act 1952. The Employees State Insurance Act 1948. The Payment of Wages Act 1936. The Minimum Wages Act 1948. The Industrial Disputes Act 1947. The Workmans Compensation Act 1923.
R.K. Panda v. Steel Authority of India Air India Statutory Corp. v. United Labour Union. Steel Authority of India Ltd. v. National Union Water Front Workers
Pros
Cons
Thank you
You might also like
- Introduction to Negotiable Instruments: As per Indian LawsFrom EverandIntroduction to Negotiable Instruments: As per Indian LawsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How to Do a 1031 Exchange of Real Estate: Using a 1031 Qualified Intermediary (Qi) 2Nd EditionFrom EverandHow to Do a 1031 Exchange of Real Estate: Using a 1031 Qualified Intermediary (Qi) 2Nd EditionNo ratings yet
- Transcript of Jail Cell Interview With Robert PicktonDocument175 pagesTranscript of Jail Cell Interview With Robert PicktonToronto Star100% (1)
- 2.-A-Journal & Ledger - QuestionsDocument3 pages2.-A-Journal & Ledger - QuestionsLibrarian 19750% (1)
- Forms - Factories Act & Contract Labour ActDocument6 pagesForms - Factories Act & Contract Labour ActRavikant Pandey0% (1)
- Labour Compliances COLPALDocument17 pagesLabour Compliances COLPALAshu TanejaNo ratings yet
- Louis Vuitton: by Kallika, Dipti, Anjali, Pranjal, Sachin, ShabnamDocument39 pagesLouis Vuitton: by Kallika, Dipti, Anjali, Pranjal, Sachin, ShabnamkallikaNo ratings yet
- Google Diversity Annual Report 2019Document48 pagesGoogle Diversity Annual Report 20199pollackyNo ratings yet
- Redundancy and the Law: A Short Guide to the Law on Dismissal with and Without Notice, and Rights Under the Redundancy Payments Act, 1965From EverandRedundancy and the Law: A Short Guide to the Law on Dismissal with and Without Notice, and Rights Under the Redundancy Payments Act, 1965Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Brief Notes Compliance Checklist Under Labour LawsDocument39 pagesBrief Notes Compliance Checklist Under Labour LawsJitendra Nagvekar100% (1)
- Vayu Issue Vayu Issue III May Jun 2018Document116 pagesVayu Issue Vayu Issue III May Jun 2018vs_3457000No ratings yet
- Portable IT Equipment PolicyDocument3 pagesPortable IT Equipment PolicyAiddie GhazlanNo ratings yet
- Investing in Indian Stock Markets - The 5 Minute WrapUp - EquitymasterDocument18 pagesInvesting in Indian Stock Markets - The 5 Minute WrapUp - EquitymasterAtanu PaulNo ratings yet
- Contract Labour (R&A) Act, 1970 and Ap Rules, 1971Document5 pagesContract Labour (R&A) Act, 1970 and Ap Rules, 1971MD IMRAN RAJMOHMADNo ratings yet
- Contract Labour Act.Document25 pagesContract Labour Act.mallika bajaj100% (1)
- Payment of Bonus Act, 1965Document31 pagesPayment of Bonus Act, 1965Milani NarulaNo ratings yet
- The Contract Labour Act 1970Document2 pagesThe Contract Labour Act 1970Shawn SriramNo ratings yet
- Contract Labour (R&A) Act, 1970 and Ap Rules, 1971Document5 pagesContract Labour (R&A) Act, 1970 and Ap Rules, 1971Palani KumarNo ratings yet
- The Harm Principle and The Tyranny of THDocument4 pagesThe Harm Principle and The Tyranny of THCally doc100% (1)
- Notes On Contract LabourDocument12 pagesNotes On Contract Labourflower87No ratings yet
- Family Relations - San Luis v. San Luis (CJ CARABBACAN)Document2 pagesFamily Relations - San Luis v. San Luis (CJ CARABBACAN)juna luz latigayNo ratings yet
- A Contractor's Guide to the FIDIC Conditions of ContractFrom EverandA Contractor's Guide to the FIDIC Conditions of ContractNo ratings yet
- Seventeenth Edition: Business Vision and MissionDocument28 pagesSeventeenth Edition: Business Vision and MissionMahmud TazinNo ratings yet
- HR Laws Check ListDocument18 pagesHR Laws Check Listdpak111No ratings yet
- Guidelines On Labour LawsDocument29 pagesGuidelines On Labour LawsSARANYAKRISHNAKUMARNo ratings yet
- EVIDENCE - Case 5 - Yap Vs LagtaponDocument3 pagesEVIDENCE - Case 5 - Yap Vs LagtaponJas ParasNo ratings yet
- People vs. Nadera, JR.: 490 Supreme Court Reports AnnotatedDocument11 pagesPeople vs. Nadera, JR.: 490 Supreme Court Reports AnnotatedFatzie MendozaNo ratings yet
- 4 Peter Newmarks Approach To TranslationDocument9 pages4 Peter Newmarks Approach To TranslationhendrysaragiNo ratings yet
- Fleeting Moments ZineDocument21 pagesFleeting Moments Zineangelo knappettNo ratings yet
- Rubberworld (Phils.), Inc. v. NLRCDocument2 pagesRubberworld (Phils.), Inc. v. NLRCAnjNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Compliance Applicable in GodrejDocument19 pagesComprehensive Compliance Applicable in GodrejPashinPatell100% (1)
- Statutory Compliances 162Document784 pagesStatutory Compliances 162Manni CoolNo ratings yet
- Compliances Under Labour LawDocument15 pagesCompliances Under Labour LawSudhakar GanjikuntaNo ratings yet
- Model Training For HRDocument42 pagesModel Training For HRhrdsprecisionNo ratings yet
- PF Esi Consultant - Gurgaon NCRDocument6 pagesPF Esi Consultant - Gurgaon NCRpeenay7No ratings yet
- Clra 1970Document5 pagesClra 1970L. BalajiNo ratings yet
- Contract Labour (Regulation & Abolition) ActDocument19 pagesContract Labour (Regulation & Abolition) Acthcm770fhNo ratings yet
- Audit of Contract LabourDocument18 pagesAudit of Contract LabourRavi Kiran NavuduriNo ratings yet
- A Brief Check List of Labour Laws: Composed by P.B.S. KumarDocument17 pagesA Brief Check List of Labour Laws: Composed by P.B.S. KumarShriya KhannaNo ratings yet
- A Brief Check List of Labour Laws: Composed by P.B.S. KumarDocument18 pagesA Brief Check List of Labour Laws: Composed by P.B.S. KumarSarvesh GhatnekarNo ratings yet
- Contractor License Under ContractLabour ActDocument5 pagesContractor License Under ContractLabour ActAnonymous 3ZvXNhY100% (1)
- A Brief Check List of Labour Laws: Composed by P.B.S. KumarDocument18 pagesA Brief Check List of Labour Laws: Composed by P.B.S. KumarvinodroyalraoNo ratings yet
- All FormsDocument27 pagesAll FormsSathyanarayana Reddy Antham100% (1)
- Faq Dish GomhDocument12 pagesFaq Dish Gomhmahesh battuNo ratings yet
- PF Consultant Gurgaon-Pee Nay Industrial ConsultantDocument5 pagesPF Consultant Gurgaon-Pee Nay Industrial Consultantpeenay7No ratings yet
- Contract Labour ActDocument13 pagesContract Labour ActAlok RoutNo ratings yet
- Applicablity of Labour Law in Service SectorDocument8 pagesApplicablity of Labour Law in Service SectorSameerNo ratings yet
- Registration of Establishment Under BOCW Act 1996Document7 pagesRegistration of Establishment Under BOCW Act 1996ramuNo ratings yet
- Discussion On Contract Labour Act 1970Document28 pagesDiscussion On Contract Labour Act 1970AniruddhShastreeNo ratings yet
- The Payment of Wages Act 1936Document7 pagesThe Payment of Wages Act 1936An MishraNo ratings yet
- Contractor Registration Information Booklet: Section I - General InformationDocument16 pagesContractor Registration Information Booklet: Section I - General InformationREDDYGAARI ABBAYINo ratings yet
- Ministry of Labour & Employment: Frequently Asked Questions On Labour LawsDocument22 pagesMinistry of Labour & Employment: Frequently Asked Questions On Labour Lawsyash12300% (1)
- A Brief Check List of Labour Laws: Composed by P.B.S. KumarDocument17 pagesA Brief Check List of Labour Laws: Composed by P.B.S. KumarkamalnetinNo ratings yet
- Contract Labour Act 494Document14 pagesContract Labour Act 494Sivaguru ArumugamNo ratings yet
- 1 Contract Labour Act, 1970Document29 pages1 Contract Labour Act, 1970Satish SinhaNo ratings yet
- A Brief Check List of Labour Laws: Satish KumarDocument17 pagesA Brief Check List of Labour Laws: Satish KumargirishtvktdNo ratings yet
- Contract Labour Rules Forms in Word FormatDocument38 pagesContract Labour Rules Forms in Word FormatAshwinSiddaramaiahNo ratings yet
- The Payment of Gratuity Act 1972Document51 pagesThe Payment of Gratuity Act 1972a.ravi100% (1)
- Labour Laws Compliance-HaryanaDocument7 pagesLabour Laws Compliance-HaryanaAshok Sharma100% (1)
- Labour LawsDocument18 pagesLabour LawssachinNo ratings yet
- Business Laws Related To HRDocument66 pagesBusiness Laws Related To HRmeetramesh111No ratings yet
- Establishment". Such Labour Can Be Distinguished From The Directly Employed Workers in Terms of EmployerDocument2 pagesEstablishment". Such Labour Can Be Distinguished From The Directly Employed Workers in Terms of EmployerRHEANo ratings yet
- A Brief Check List of Labour Laws: Composed by P.B.S. KumarDocument17 pagesA Brief Check List of Labour Laws: Composed by P.B.S. KumarJames MelwynNo ratings yet
- Statutory Compliances For HR - Full VersionDocument66 pagesStatutory Compliances For HR - Full VersionTashiGireesanNo ratings yet
- Painting - IrfanDocument8 pagesPainting - IrfanAnil KasliwalNo ratings yet
- Labour LawsDocument5 pagesLabour LawsDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Statutory Compliance HR Full Material PPT Download Business Laws Related HRDocument66 pagesStatutory Compliance HR Full Material PPT Download Business Laws Related HRarjun.ec633No ratings yet
- Contract Labour FORM IVDocument2 pagesContract Labour FORM IVhdpanchal86No ratings yet
- Procedure of Contract Labour Act 1970Document4 pagesProcedure of Contract Labour Act 1970Shravan KumarNo ratings yet
- A Brief Check List of Labour Laws: Composed by P.B.S. KumarDocument18 pagesA Brief Check List of Labour Laws: Composed by P.B.S. KumarAmaneet Singh BrarNo ratings yet
- Presented by Remyasree RDocument41 pagesPresented by Remyasree RphilsonmanamelNo ratings yet
- The Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020 - Part IVDocument40 pagesThe Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020 - Part IVNikita D'LimaNo ratings yet
- Business Laws Related To HRDocument66 pagesBusiness Laws Related To HRtanyagodwinNo ratings yet
- Labor Contract Law of the People's Republic of China (2007)From EverandLabor Contract Law of the People's Republic of China (2007)No ratings yet
- 6 Surprising Ways To Beat The Instagram AlgorithmDocument5 pages6 Surprising Ways To Beat The Instagram AlgorithmluminenttNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document2 pagesProblem Set 1edhuguetNo ratings yet
- Stross ComplaintDocument7 pagesStross ComplaintKenan FarrellNo ratings yet
- Historical Perspective of Financial Reporting Regulations in MalaysiaDocument2 pagesHistorical Perspective of Financial Reporting Regulations in Malaysiauglore100% (6)
- Sudan WikipediaDocument33 pagesSudan WikipediaUroš KrčadinacNo ratings yet
- Strategic Partnership Proposal For Daraz BangladeshDocument12 pagesStrategic Partnership Proposal For Daraz Bangladeshzamiar shamsNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 (2) - Theory of Cost - Lecture in ClassDocument44 pagesCHAPTER 6 (2) - Theory of Cost - Lecture in ClassMUHAMMAD ZAIM HAMZI MUHAMMAD ZINNo ratings yet
- Tutorial LawDocument5 pagesTutorial LawsyafiqahNo ratings yet
- Veneranda Dini Anggraeni 201071058 Grammer Mini TestDocument18 pagesVeneranda Dini Anggraeni 201071058 Grammer Mini TestAyu DaratistaNo ratings yet
- NPD and VMSDocument4 pagesNPD and VMSK V S MadaanNo ratings yet
- REM1Document48 pagesREM1Jem MadridNo ratings yet
- Alexandra Marotta Writing Sample 1Document3 pagesAlexandra Marotta Writing Sample 1api-315852783No ratings yet
- TOURISM AND HOSPITALITY ORGANIZATIONS Di Pa Tapooos 1 1Document101 pagesTOURISM AND HOSPITALITY ORGANIZATIONS Di Pa Tapooos 1 1Dianne EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Rebecca Sanchez Resume 2016Document2 pagesRebecca Sanchez Resume 2016api-311997473No ratings yet
- Senate Bill No. 982Document3 pagesSenate Bill No. 982Rappler100% (1)