Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nanophotonics Class 2 - Surface Plasmon Polaritons
Uploaded by
Tyas ArifaniOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nanophotonics Class 2 - Surface Plasmon Polaritons
Uploaded by
Tyas ArifaniCopyright:
Available Formats
Nanophotonics
Class 2
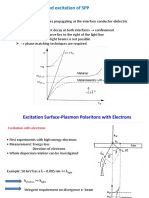
Surface plasmon polaritons
Surface plasmon polariton: EM wave at metal-dielectric
interface
EM wave is coupled to the plasma oscillations of the surface charges
( )
( ) t z k x k i
d d
z x
e E t z x E
e +
=
0 ,
, ,
( ) t z k x k i
m m
z x
e E t z x E
e
=
0 ,
) , , (
For propagating
bound waves:
- k
x
is real
- k
z
is imaginary
x
z
Derivation of surface plasmon dispersion relation: k(e)
Wave equation:
Substituting SP wave + boundary conditions leads to the
Dispersion relation:
2 / 1
" '
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
= + =
d m
d m
x x x
c
ik k k
c c
c c e
2
,
2
, 0 , 0 ,
2
t
E
E
m d
m d m d m d
c
c
= V
c c
x-direction:
( ) e c
|
.
|
\
|
= c
e
c
k
Note: in regular dielectric:
t 2
= k
Dispersion relation:
2 / 1
" '
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
= + =
d m
d m
x x x
c
ik k k
c c
c c e
x-direction:
( ) e c
Bound SP mode: k
z
imaginary: c
m
+ c
d
< 0, k
x
real: c
m
< 0
so: c
m
< -c
d
2 / 1
2
, , ,
" '
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
= + =
d m
m
m z m z m z
c
ik k k
c c
c e
z-direction:
|
.
|
\
|
= c
e
c
k
t 2
= k
( ) ( ) e e
e
e e c c c
c
i i m
Ne
E
Nex
E
P
p
= + = + =
2
2
2
0
2
0 0
1 1 1 1
0
2
c
e
m
Ne
p
=
Dielectric constant of metals
Drude model: conduction electrons with damping: equation of motion
with collision frequency and plasma frequency
If << e
p
, then:
e
e
c
e
e
c
3
2
2
2
" , 1 '
p p
= =
t i
eE
dt
dx
m
dt
x d
m
e
e
0
2
2
= +
no restoring force
Measured data and model for Ag:
e
e
c
e
e
c
3
2
2
2
" , 1 '
p p
= =
e
e
c
e
e
c c
3
2
2
2
" , '
p p
= =
Drude model:
Modified Drude model:
Contribution of
bound electrons
Ag: 45 . 5 =
c
200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800
-150
-100
-50
0
50
Measured data:
c'
c"
Drude model:
c'
c"
Modified Drude model:
c'
c"
c
Wavelength (nm)
c'
Bound SP modes: c
m
< -c
d
200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800
-150
-100
-50
0
50
Measured data:
c'
c"
Drude model:
c'
c"
Modified Drude model:
c'
c"
c
Wavelength (nm)
c'
bound SP mode: c
m
< -c
d
-c
d
e
e
p
d
p
c
e
+ 1
Re k
x
real k
x
real k
z
imaginary k
x
real k
z
real k
x
imaginary k
z
d
x
ck
c
Bound modes
Radiative modes
Quasi-bound modes
Surface plasmon dispersion relation:
Dielectric: c
d
Metal: c
m
= c
m
'
+ c
m
"
x
z
(c'
m
> 0)
(c
d
< c'
m
<
0)
(c'
m
< c
d
)
2 / 1
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
d m
d m
x
c
k
c c
c c e
e
Re k
x
d
x
ck
c
Surface plasmons dispersion:
large k
small wavelength
Ar laser:
vac
= 488 nm
diel
= 387 nm
SP
= 100 nm
Ag/SiO
2
3.4 eV
(360 nm)
X-ray wavelengths
at optical frequencies
2 / 1
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
d m
d m
x
c
k
c c
c c e
t 2
= k
Surface plasmon dispersion for thin films
Drude model
1
()=1-(
p
/)
2
Two modes appear
L
-
L
-
(symm)
Thinner film:
Shorter SP
wavelength
Example:
HeNe
= 633 nm
SP
= 60 nm
L
+
(asymm)
Propagation
lengths: cm !!!
(infrared)
Cylindrical metal waveguides
k
E
z
r
Fundamental
SPP mode
on cylinder:
E
Can this adiabatic coupling
scheme be realized in
practice?
taper theory first demonstrated by
Stockman, PRL 93, 137404 (2004)
Delivering light to the nanoscale
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
1.7
1.8
1.9
2.0
2.1
2.2
2.3
n
e
f
f
=
k
S
P
P
/
k
0
Waveguide width (m)
1 m
1 m
|E|
Field symmetry at tip
similar to SPP mode in
conical waveguide
E
+ +
+
+
+
+
+
Ewold Verhagen, Kobus Kuipers
k
E
x
z
nanoscale
confinement
Optics Express 16, 45 (2008)
Concentration of light in a plasmon taper: experiment
Ewold Verhagen, Kobus Kuipers
Au
Er
Al
2
O
3
= 1.5 m
exc
= 1490 nm
P
L
I
n
t
e
n
s
i
t
y
(
c
o
u
n
t
s
/
s
)
10 m
Ewold Verhagen, Kobus Kuipers
(
1
4
9
0
n
m
)
E
r
3
+
e
n
e
r
g
y
l
e
v
e
l
s
transmission
1 m
60 nm apex diam.
Nano Lett. 7, 334 (2007)
Concentration of light in a plasmon taper: experiment
550 nm
660 nm
Detecting upconversion luminescence from the air side of the film (excitation
of SPPs at substrate side)
Ewold Verhagen, Kobus Kuipers
Plasmonic hot-spot
Optics Express 16, 45 (2008)
k
E
x
z
Theory: Stockman, PRL 93, 137404 (2004)
Concentration of light in a plasmon taper: experiment
FDTD Simulation: nanofocussing to < 100 nm
z = -35 nm
Nanofocusing predicted: 100 x |E|
2
at 10 nm from tip
3D subwavelength confinement:
1.5 m light focused to 92 nm (/16)
limited by taper apex (r=30 nm)
n
1
= 1
n
2
= 1.74
1 m
1 m
|E|
2
start
tip
+
+
+
+
+ +
+
E
Ewold Verhagen, Kobus Kuipers
Optics Express 16, 45 (2008)
sym asym
E
t
, H
Coaxial MIM plasmon waveguides
FIB milling of coaxial waveguides
100 nm
100 nm
Silica substrates with 250-500 nm thick Ag
Ring width: 50-100 nm
Two-step milling process
~7 taper angle
<w>=100 nm, L=485 nm
<w>=50 nm, L=485 nm
Ren de Waele, Stanley Burgos
Nano Lett. 9, in press (2009)
Narrow channels show negative index
Excitation above
resonance, e>e
sp
25 nm-wide channel
in Ag filled with GaP
Simulation shows
negative phase
velocity with respect
to power flow
Negative refractive
index of -2
Ren de Waele, Stanley Burgos
Positive and negative index modes
Ren de Waele, Stanley Burgos
Plasmonic toolbox: e, c(e), d - Engineer (e)
0 200 400 600 800 1000
-1.0
-0.5
0.0
0.5
1.0
Y
A
x
i
s
T
i
t
l
e
Distance (nm)
thin section
Plasmonic concentrator
Plasmonic lens
Plasmonic multiplexer
And much more ..
Plasmonic integrated circuits
Conclusions: surface plasmon polariton
Surface plasmon: bound EM wave at metal-dielectric interface
Dispersion: e(k) diverges near the plasma resonance: large k, small
Control dispersion: control e(k), losses, concentration
Manipulate light at length scales
below the diffraction limit
You might also like
- S. V. Bulanov-Extreme Light - Matter Interactionthrough The Lensesof The Relativistic Flying Mirror ConceptDocument67 pagesS. V. Bulanov-Extreme Light - Matter Interactionthrough The Lensesof The Relativistic Flying Mirror ConceptELI BeamlinesNo ratings yet
- Interaction of Charged ParticlesDocument32 pagesInteraction of Charged ParticlesBenard MuliloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Carrier Transport PhenomenaDocument48 pagesChapter 2 - Carrier Transport PhenomenaYew Keong Ng100% (3)
- Drude Model For Dielectric Constant of MetalsDocument24 pagesDrude Model For Dielectric Constant of MetalsRupesh ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Carrier Transport PhenomenaDocument54 pagesChapter 2 - Carrier Transport PhenomenaDesmond Kuek100% (2)
- Course I.A. XPS BasicsDocument120 pagesCourse I.A. XPS BasicsSare GomezNo ratings yet
- Observations & Instrumentation II: SpectrosDocument155 pagesObservations & Instrumentation II: SpectrosEnrique Gamez CardenasNo ratings yet
- Bansal Classes Chemistry Study Material For IIT JEEDocument445 pagesBansal Classes Chemistry Study Material For IIT JEESankar Kumarasamy100% (5)
- Lecture 2Document55 pagesLecture 2Zahid SaleemNo ratings yet
- HighVoltageEngineering PDFDocument46 pagesHighVoltageEngineering PDFBruno LopesNo ratings yet
- 2002 CMD KordyukDocument29 pages2002 CMD KordyukXan TolusNo ratings yet
- Modal Analysis of Step-Index FibersDocument25 pagesModal Analysis of Step-Index Fibersd24testNo ratings yet
- Detectors and Energy Deposition in Media: (Thanks To J.Thomas (LBNL) )Document44 pagesDetectors and Energy Deposition in Media: (Thanks To J.Thomas (LBNL) )NenkIndahLestariNo ratings yet
- Ap2011 Solutions 04Document9 pagesAp2011 Solutions 04Zobeda MariumNo ratings yet
- Low-Voltage TheoryDocument10 pagesLow-Voltage Theorymichelle_lilNo ratings yet
- 2008 Test 1Document6 pages2008 Test 1Elias SigüenzaNo ratings yet
- Polarization Gating AutocorrelatorDocument6 pagesPolarization Gating AutocorrelatorParticle Beam Physics LabNo ratings yet
- Assignment For LecturesDocument16 pagesAssignment For LecturesDeepak JainNo ratings yet
- Introductory Lectures On Arpes-SantanderDocument35 pagesIntroductory Lectures On Arpes-Santanderpbm59No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Carrier Transport PhenomenaDocument56 pagesChapter 2 Carrier Transport PhenomenaMamapaiya HaariNo ratings yet
- Optics of Metals - PlasmonsDocument18 pagesOptics of Metals - PlasmonsyvvictorNo ratings yet
- CHP 2Document38 pagesCHP 2NK NKNo ratings yet
- BEF22903 Tutorial 1Document2 pagesBEF22903 Tutorial 1Patricia KC0% (1)
- Surface Spectroscopic Techniques XPSDocument67 pagesSurface Spectroscopic Techniques XPSsecate100% (1)
- 2012 Vcaa Physics Exam 2 SolutionsDocument2 pages2012 Vcaa Physics Exam 2 SolutionspappadutNo ratings yet
- Quantum-Mechanical Modeling and Simulation of A Novel Nano-Scale FET: Center-Channel (CC) Double-Gate (DG) MOSFETDocument6 pagesQuantum-Mechanical Modeling and Simulation of A Novel Nano-Scale FET: Center-Channel (CC) Double-Gate (DG) MOSFETanchit_virmaniNo ratings yet
- ENEL2PAH1 - Physical Electronics 1Document5 pagesENEL2PAH1 - Physical Electronics 1qanaqNo ratings yet
- PPM Surface Plasmon Presentation 2005Document27 pagesPPM Surface Plasmon Presentation 2005PHAM BAT THONGNo ratings yet
- Final FinalDocument8 pagesFinal FinalG Santosh BabuNo ratings yet
- Mihailova PresentationDocument37 pagesMihailova PresentationSonik AlexNo ratings yet
- CH 07Document36 pagesCH 07LAVTOLNo ratings yet
- RBS: A Lecture by Younes SinaDocument63 pagesRBS: A Lecture by Younes SinayounessinaNo ratings yet
- (Fawwaz T. Ulaby) Fundamentals of Applied Electrom Solution Chapter 7Document33 pages(Fawwaz T. Ulaby) Fundamentals of Applied Electrom Solution Chapter 7AchmadN.FauzieNo ratings yet
- Francqui 2 FHDocument70 pagesFrancqui 2 FHjnwkjwjkNo ratings yet
- PB Sheet 4 and Solutions LMODocument6 pagesPB Sheet 4 and Solutions LMOShootingStarPhotonsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document11 pagesChapter 6Dr-Dharmendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Radiowave Propagation: DR Costas ConstantinouDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Radiowave Propagation: DR Costas ConstantinouRenato MangilaNo ratings yet
- Surface Plasmon ExcitationDocument26 pagesSurface Plasmon ExcitationfilippoNo ratings yet
- Electrons KagDocument57 pagesElectrons KagsnabilatNo ratings yet
- Atomic Physics: Answers To Even-Numbered Conceptual QuestionsDocument21 pagesAtomic Physics: Answers To Even-Numbered Conceptual Questionsbast97No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Duct AcousticsDocument27 pagesFundamentals of Duct Acousticscarlosbrochinejr100% (1)
- Sky IsDocument31 pagesSky IsGopimarappanNo ratings yet
- CH 9-Acoustooptic EffectDocument42 pagesCH 9-Acoustooptic EffectJean Jacques Monga Kaboko100% (1)
- 4-Optical Properties of Materials-Dielectrics and MetalsDocument36 pages4-Optical Properties of Materials-Dielectrics and MetalsvenkateshsanthiNo ratings yet
- Micro Strip AntennasDocument26 pagesMicro Strip AntennasAshok RamavathNo ratings yet
- Advanced Microwave EngineeringDocument12 pagesAdvanced Microwave Engineeringkwizera evaNo ratings yet
- National University of SingaporeDocument11 pagesNational University of SingaporeJie RongNo ratings yet
- Laser Fundamentals: Basic Processes (A.Einstein, 1916)Document11 pagesLaser Fundamentals: Basic Processes (A.Einstein, 1916)sivamadhaviyamNo ratings yet
- PHYS1131 Solutions Tut 6 11Document14 pagesPHYS1131 Solutions Tut 6 11Jason Tan100% (2)
- 3-A Basic of Surface PlasmonsDocument57 pages3-A Basic of Surface PlasmonsHirak ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Search For Solar Axions Produced by Compton Process and Bremsstrahlung Using The Resonant Absorption and Axioelectric EffectDocument6 pagesSearch For Solar Axions Produced by Compton Process and Bremsstrahlung Using The Resonant Absorption and Axioelectric EffectAnonymous xF8SvqsrNo ratings yet
- Electron and Photon With SolutionDocument8 pagesElectron and Photon With SolutionChiruhaasNo ratings yet
- A Triple Wire Medium As An Isotropic Negative Permittivity MetamaterialDocument14 pagesA Triple Wire Medium As An Isotropic Negative Permittivity MetamaterialUlmoTolkienNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksFrom EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Electrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsFrom EverandElectrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsAndrzej LewenstamNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Baterías YuasaDocument122 pagesBaterías YuasaLuisNo ratings yet
- David-Huynh Indeed ResumeDocument3 pagesDavid-Huynh Indeed Resumeapi-546353822No ratings yet
- Discovering Computers 2016: Operating SystemsDocument34 pagesDiscovering Computers 2016: Operating SystemsAnonymous gNHrb0sVYNo ratings yet
- LEBV4830Document371 pagesLEBV4830anton100% (1)
- Details For Order #002 5434861 1225038: Not Yet ShippedDocument1 pageDetails For Order #002 5434861 1225038: Not Yet ShippedSarai NateraNo ratings yet
- Emergency Communication Procedures Communication Equipment Wake TurbulenceDocument38 pagesEmergency Communication Procedures Communication Equipment Wake TurbulenceRaluca StoicaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Case 2 - QuestionDocument7 pagesComprehensive Case 2 - QuestionPraveen RoshenNo ratings yet
- 2008 Reverse Logistics Strategies For End-Of-life ProductsDocument22 pages2008 Reverse Logistics Strategies For End-Of-life ProductsValen Ramirez HNo ratings yet
- Impact of Wrongful Termination On EmployeesDocument4 pagesImpact of Wrongful Termination On EmployeesAvil HarshNo ratings yet
- FinTech RegTech and SupTech - What They Mean For Financial Supervision FINALDocument19 pagesFinTech RegTech and SupTech - What They Mean For Financial Supervision FINALirvandi syahputraNo ratings yet
- CPA Taxation by Ampongan - Principles of TaxationDocument43 pagesCPA Taxation by Ampongan - Principles of TaxationVictor Tuco100% (1)
- Layer 3 Managed 8 10G Port Switch Controller: RTL9303-CGDocument55 pagesLayer 3 Managed 8 10G Port Switch Controller: RTL9303-CG박윤지100% (1)
- LIC Form - Intimation of Death Retirement Leaving ServiceDocument1 pageLIC Form - Intimation of Death Retirement Leaving ServicekaustubhNo ratings yet
- 036 ColumnComparisonGuideDocument16 pages036 ColumnComparisonGuidefarkad rawiNo ratings yet
- 20151201-Baltic Sea Regional SecurityDocument38 pages20151201-Baltic Sea Regional SecurityKebede MichaelNo ratings yet
- AngularJS Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesAngularJS Cheat SheetZulqarnain Hashmi100% (1)
- Final Exam - Comprehensive - 10.24.16Document5 pagesFinal Exam - Comprehensive - 10.24.16YamateNo ratings yet
- Sinamics gm150 sm150 Catalog d12 02 2020 enDocument238 pagesSinamics gm150 sm150 Catalog d12 02 2020 enGo andWatchNo ratings yet
- Heirs of Tancoco v. CADocument28 pagesHeirs of Tancoco v. CAChris YapNo ratings yet
- BSNL Project MBA NitishDocument92 pagesBSNL Project MBA NitishAnkitSingh0% (2)
- Qrqs"1 Xl/Ijj1L Joi?Llt'Lll: Transport Bhawan, 1, Parliament Street New Delhi-110001Document2 pagesQrqs"1 Xl/Ijj1L Joi?Llt'Lll: Transport Bhawan, 1, Parliament Street New Delhi-110001PrakashKommukuriNo ratings yet
- Energy Facts PDFDocument18 pagesEnergy Facts PDFvikas pandeyNo ratings yet
- IM0973567 Orlaco EMOS Photonview Configuration EN A01 MailDocument14 pagesIM0973567 Orlaco EMOS Photonview Configuration EN A01 Maildumass27No ratings yet
- Baling Press: Model: LB150S Article No: L17003 Power SupplyDocument2 pagesBaling Press: Model: LB150S Article No: L17003 Power SupplyNavaneeth PurushothamanNo ratings yet
- Beijing-Michael PageDocument71 pagesBeijing-Michael Pagejohndavsg8022No ratings yet
- Ein Extensive ListDocument60 pagesEin Extensive ListRoberto Monterrosa100% (2)
- Zambia MTEF 2015 - 2017 (Green Paper)Document27 pagesZambia MTEF 2015 - 2017 (Green Paper)Chola MukangaNo ratings yet
- Job Description: Extensive ReadingDocument12 pagesJob Description: Extensive ReadingNatalia VivonaNo ratings yet
- Pepsico IncDocument26 pagesPepsico IncYKJ VLOGSNo ratings yet
- Art 3 Sec 2Document157 pagesArt 3 Sec 2KELVINNo ratings yet