Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dose The Right Amount of Chemicals
Uploaded by
rajachemOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dose The Right Amount of Chemicals
Uploaded by
rajachemCopyright:
Available Formats
DOSE THE RIGHT AMOUNT OF CHEMICALS By K.K.PARTHIBAN, Boiler Consultant Venus Energy Audit System Email ID:parthi2006@gmail.com / venus.energy@gmail.
com Recently I had come across a case of erratic chemical dosing and boiler water pH dipping below 7.5. It can happen on many occasions. 1. When we base blow down on silica in steam, we may not be able to make up the phosphate level suitably. 2. When we try intermittent blow down, there is a heavy drain of boiler water & phosphate. We will not be able to make up for the drained phosphate with regular dosage rates of chemicals. 3. During start up and during very high load variations, chemical make up may not be sufficient. 4. When there is a time lag between analysis and dosage setting, the chemical level would vary heavily. 5. When the deaerator water temperature is low, the boiler water pH may get upset. 6. When the condensate contamination is possible, then again we may not able to main boiler water chemistry. When there are several reasons for the boiler water chemistry upset, we need to know how much we need to dose to bring back normalcy. We need to know the fundamentals of chemical dosing calculations. The calculation sheet given in this paper briefs how to calculate the chemical requirement. Instead of looking at the water sample results and then correcting the dosage we can decide how much is to be dosed. If the chemical dosing pump is a limitation, then % dilution can be changed for some time to bring back to normalcy. This calculation is for the boilers where the basic chemicals are used. The calculations will however be similar for proprietary chemical as well. Knowing the water volume in boiler is necessary to decide the dump dosage of chemical during upsets. WATCH THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHEMICAL DOSING! Many boiler users leave the water chemistry management to chemical supplier. The dosage practices are decided by the chemical suppliers. But then how to ensure that the chemicals are protecting the boiler? The best way is to inspect the wetted surfaces of the boiler. In Shell type boiler it is rather easy to see the tubes for scale or pitting. But in water tube boiler, the steam drum only speaks. The best way is to open the steam drum and take a wipe of the drum internal surface with your palm. Generally the water tube boiler is fed with well treated water. Hence scale related problems are not experienced. However the corrosion of economizer / boiler could be a serious problem. The presence of loose reddish powder indicates the boiler is corroding. Presence of grey powder indicates the economizer / pre-boiler system corrosion.
ENWS-212-00
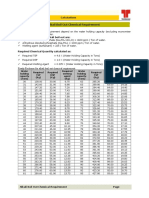
LP / HP CHEMICAL DOSING CALCULATIONS INPUTS Steam generation rate Nett = TDS in feed water = TDS permitted in boiler water = Oxygen in feed water = Oxygen permitted in feed water = Residual phosphate level in boiler water = Concentration of phosphate solution = Residual sulphite in feed water = Concentration of sulphite solution = Residual Hydrazine in Feed water = Concentration of hydrazine solution = HP CHEMICAL DOSING CALCULATION Chemical Dosed in HP Dosing System = Maximum steam generation capacity of boiler = TDS in feedwater = TDS permitted in Boiler water = Percentage blow down = = Actual blow down rate = = Recommended phosphate ppm in boiler water = Loss of phosphate in blow down water = = Loss of TSP in blow down water = = Tri sodium phosphate consumption per day = = LP CHEMICAL DOSING CALCULATION Chemical dosed = Maximum steam generation capacity of boiler = Oxygen in feedwater = Required oxygen level in feed water = Oxygen to be removed = = Oxygen to be removed in moles per hr = = Sulphite required in moles per hr = = Sulphite required in gms per hr = = = Concentration of sodium sulphite solution = Rate of dosing = = Sodium sulphite consumption per day = 10000 0.1 25 0.02 0.002 4 0.3 15 0.04 0.02 35 kg / hr ppm ppm ppm ppm ppm gm / 100 ml ppm gm / 100 ml ppm %
TRI SODIUM PHOSPHATE 10000 kg /hr 0.1ppm 25 ppm 100 x 0.1 / (25-0.1) 0.4 % 10000 x 0.4/100 kg/ hr 40 kg/hr 4 ppm 4 x 40 / 1000 g / hr 0.16 gm / hr 0.16 x 4 0.64 gm/h 0.64 x 24 / 1000 kg / day 0.01536 kg / day SODIUM SULPHITE 10000 kg / hr 0.02 ppm 0.002 ppm 0.02 - 0.002 x 10000 x 0.000001 kg / hr 0.00018 kg / hr 0.00018 / 32 0.000005625 kg / hr 2 x 0.000005625 1E-05 molecular wt (Na2SO3)x moles/h {1000x[(2X23)+ (32)+(3x16)]} x0.00001125gm/hr 1.4175 gm / hr 0.04 gm / 100 ml 100 x 1.4175 / 0.04 ml /hr 3543.75 ml / hr (1.4175 x (24 / 1000)) kg / day
Sh 1 of 2
ENWS-212-00
= LP CHEMICAL DOSING CALCULATION Chemical dosed = Maximum steam generation capacity of boiler = Oxygen in feedwater after deaeration @105 deg C = Required oxygen level in feed water = Oxygen to be removed = = Hydrazine reqd (30 times depending on reaction = kinetics) = Residual hydrazine to be kept = Total hydrazine required = = Total hydrazine required in kg/kg of evaporation = = Hydrazine required per hour = = Concentration of hydrazine solution = Hydrazine to be dosed @35% conc = = Hydrazine consumption per day = =
0.034 Kg / Day HYDRAZINE 10000 kg / hr 0.02 ppm 0.002 ppm 0.02 - 0.002 ppm 0.018 ppm 30 x 0.018 ppm 0.54 ppm 0.02ppm 0.54 + 0.02 ppm 0.56 ppm 0.56 x 0.000001 kg / kg 0.00000056 kg / kg 10000 x 0.00000056 kg / hr 0.0056 kg / hr 35% 0.0056x100 / 35 kg / hr 0.016kg / hr 0.01600x 24 kg / day 0.384 kg / day
Sh 2 of 2
You might also like
- Boiler Blow Down: Workshop On Efficient Operation & Maintenance of BoilersDocument3 pagesBoiler Blow Down: Workshop On Efficient Operation & Maintenance of Boilerskcp1986No ratings yet
- Cooling Water Treatment Introduction PDFDocument28 pagesCooling Water Treatment Introduction PDFHanik RufadaNo ratings yet
- Boiler Chemical Cleaning StepsDocument1 pageBoiler Chemical Cleaning StepsMike George MeyerNo ratings yet
- Welcome To: Cooling Water Treatment in Power Plants Recent Trends & Case StudyDocument17 pagesWelcome To: Cooling Water Treatment in Power Plants Recent Trends & Case StudyrpshvjuNo ratings yet
- Cooling Water Treatment Chlorination WorkoutDocument3 pagesCooling Water Treatment Chlorination WorkoutMohsin ModiNo ratings yet
- Boiler Water High PresureDocument43 pagesBoiler Water High PresureVinod SindhavNo ratings yet
- Boiler Cleaning ServicesDocument34 pagesBoiler Cleaning ServicesrakeshkjNo ratings yet
- Alkali Boil Out Chemical RequirementDocument1 pageAlkali Boil Out Chemical RequirementdinuNo ratings yet
- Boilers and Steam Lines Chemical CleaningDocument10 pagesBoilers and Steam Lines Chemical CleaningZaheer Ahmad RazaNo ratings yet
- LP HP Dosing CalculationDocument1 pageLP HP Dosing Calculationvikas_be1750% (4)
- OGN-OPS-CHEM-019 Rev.0 Guidelines On Cooling Water Treatment, Monitoring and Chemical Cleaning of Condenser TubesDocument38 pagesOGN-OPS-CHEM-019 Rev.0 Guidelines On Cooling Water Treatment, Monitoring and Chemical Cleaning of Condenser Tubesanil perala0% (1)
- Condensate Polishing UnitDocument35 pagesCondensate Polishing Unitrahult19No ratings yet
- Boiler Water Chemistry: Korba Simulator 339Document12 pagesBoiler Water Chemistry: Korba Simulator 339Rakesh Kiran100% (1)
- Chemical Boiling Out Procedure Boiler BDFB 350-1004. Rev.00Document7 pagesChemical Boiling Out Procedure Boiler BDFB 350-1004. Rev.00Ari Puji Hidayatullah0% (1)
- Cooling Water Chemistry: Specific Skills Training by Laeeq Ahmad RumiDocument31 pagesCooling Water Chemistry: Specific Skills Training by Laeeq Ahmad RumiIqbalAwais100% (1)
- Boiler Water Chemistry: 1. Formation of Scales & Deposits On The Boiler TubesDocument4 pagesBoiler Water Chemistry: 1. Formation of Scales & Deposits On The Boiler TubesKumaraswamyNo ratings yet
- Stator Water Chemistry R0Document6 pagesStator Water Chemistry R0vel muruganNo ratings yet
- Blowdown Economizer CalculationDocument2 pagesBlowdown Economizer CalculationSajjad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cathotic ProtectionDocument5 pagesCathotic Protectionkrishna_swaroop99No ratings yet
- Plant Efficiency & Heat Rate: 482.8 Mkcal/hr 420 Mkcal/hr 180.6 Mkcal/hr 172 Mkcal/hrDocument51 pagesPlant Efficiency & Heat Rate: 482.8 Mkcal/hr 420 Mkcal/hr 180.6 Mkcal/hr 172 Mkcal/hrkousikthiraviarajNo ratings yet
- 5 C Water Chemistry Training NotesDocument114 pages5 C Water Chemistry Training NotesFraser LamontNo ratings yet
- DM PlantDocument30 pagesDM Plantapi-19775783No ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2017.07.007Document23 pagesAccepted Manuscript: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2017.07.007Anand VarmaNo ratings yet
- Boiler Water ChemistryDocument63 pagesBoiler Water ChemistryDeepak JayNo ratings yet
- Pi Bond Collodial Silica in Power Plant Water ChemistryDocument4 pagesPi Bond Collodial Silica in Power Plant Water Chemistryak_thimiriNo ratings yet
- Condenser Failure MechanismDocument7 pagesCondenser Failure MechanismprakashNo ratings yet
- Preservation of Boiler 1Document21 pagesPreservation of Boiler 1DangolNo ratings yet
- EDI Water TreatmentDocument28 pagesEDI Water TreatmentAli FarooqNo ratings yet
- Condensate System ProtectionDocument8 pagesCondensate System ProtectionmnasiroleslamiNo ratings yet
- Specification For Chemical CleaningDocument41 pagesSpecification For Chemical CleaningSudhanshu DashNo ratings yet
- HRSG Lay-Up PracticesDocument4 pagesHRSG Lay-Up PracticesSundar MoorthyNo ratings yet
- Chlorination of Cooling Water Systems PDFDocument4 pagesChlorination of Cooling Water Systems PDFhappale2002No ratings yet
- Energy Saving Opportunities in IndustriesDocument70 pagesEnergy Saving Opportunities in IndustriesIrawan SutionoNo ratings yet
- Boiler Water Chemistry Analysis (PB QBook)Document8 pagesBoiler Water Chemistry Analysis (PB QBook)Ehsan Pappu100% (1)
- Cooling Water PDFDocument32 pagesCooling Water PDFnivasssvNo ratings yet
- Cooling Water TreatDocument10 pagesCooling Water TreatNavaganesh KannappenNo ratings yet
- Initial Treatment With Heat LoadDocument15 pagesInitial Treatment With Heat LoadSunny OoiNo ratings yet
- CWC TrainingDocument58 pagesCWC Trainingbalaji3110No ratings yet
- "Boiler Tube Failures": Project ReportDocument30 pages"Boiler Tube Failures": Project ReportmdjanNo ratings yet
- Bi-Drum Vs Single Drum - Research Paper 2Document6 pagesBi-Drum Vs Single Drum - Research Paper 2Parth Merchant100% (1)
- Characteristics of Boiler Feedwater - LenntechDocument1 pageCharacteristics of Boiler Feedwater - LenntechjagjitNo ratings yet
- Water Chemistry PDFDocument8 pagesWater Chemistry PDFalamNo ratings yet
- Title: Boiler No.:-PH0351 Page No. 1 of 22 Project: M/s Jacobs Netherlands BV A/c Schoonebeek Oil Field Redevelopment ProjectDocument24 pagesTitle: Boiler No.:-PH0351 Page No. 1 of 22 Project: M/s Jacobs Netherlands BV A/c Schoonebeek Oil Field Redevelopment ProjectRamalingam PrabhakaranNo ratings yet
- Handbook On Power Plant ChemistryDocument17 pagesHandbook On Power Plant ChemistrywertyyyNo ratings yet
- Boiler Water ConditioningDocument59 pagesBoiler Water ConditioningShikderNo ratings yet
- DM Water Supply System OverviewDocument20 pagesDM Water Supply System Overviewanon_33553517No ratings yet
- KURITA - Boiler Preservation Methods (Part1) PDFDocument7 pagesKURITA - Boiler Preservation Methods (Part1) PDFIyan MulyanaNo ratings yet
- Boiler Water ChemistryDocument60 pagesBoiler Water Chemistryنيرمين احمدNo ratings yet
- Real Time Boiler TreatmentDocument4 pagesReal Time Boiler TreatmentJustin GentryNo ratings yet
- pp57-65 MS06Document9 pagespp57-65 MS06vikaskatheriaNo ratings yet
- Nitrite Based Corrosion Inhibitor For Chilled WaterDocument2 pagesNitrite Based Corrosion Inhibitor For Chilled WaterChillerCNo ratings yet
- Report On Boiler Performance Audting in A Paper Plant by K.K.parthibanDocument129 pagesReport On Boiler Performance Audting in A Paper Plant by K.K.parthibanparthi20065768No ratings yet
- Bhatia Gummidipoondi WHRSG O&m Manual FinalDocument224 pagesBhatia Gummidipoondi WHRSG O&m Manual Finalt_syamprasadNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Throughput of Condensate Polishing UnitDocument5 pagesEnhancing Throughput of Condensate Polishing Unitprakash100% (2)
- The Use of Polymers To Improve Control of Calcium Phosphonate and Calcium Carbonate in High StressedDocument23 pagesThe Use of Polymers To Improve Control of Calcium Phosphonate and Calcium Carbonate in High Stressedwilmar100% (1)
- Water Steam ChemistryDocument4 pagesWater Steam ChemistryAshish ParasharNo ratings yet
- Cooling Water System: and Its ProblemsDocument25 pagesCooling Water System: and Its ProblemsHanif AbdillahNo ratings yet
- Sodium Sulfite Example:: Parts Per Million: Parts Per Million, PPM (Mass of Solute/mass of Solution) X 10Document6 pagesSodium Sulfite Example:: Parts Per Million: Parts Per Million, PPM (Mass of Solute/mass of Solution) X 10FAIDID AHASANNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions For Boiler Water TreatmentDocument5 pagesFrequently Asked Questions For Boiler Water TreatmentRaymundo Salazar JrNo ratings yet
- Feed Water System ComponentsDocument11 pagesFeed Water System ComponentsBlitz XyrusNo ratings yet
- Karthik Updated ResumeDocument2 pagesKarthik Updated ResumerajachemNo ratings yet
- TF-08 Therminol 66Document8 pagesTF-08 Therminol 66rajachemNo ratings yet
- Sample Chapter Steam TurbineDocument53 pagesSample Chapter Steam TurbineShawn WairisalNo ratings yet
- Field Experience With The Blasch VectorWall Reaction Furnace Checkerwall PTQ Q1 2014Document7 pagesField Experience With The Blasch VectorWall Reaction Furnace Checkerwall PTQ Q1 2014rajachemNo ratings yet
- Mole Fraction Volume FractionDocument9 pagesMole Fraction Volume FractionameyckulkarniNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Feasibility Study Co2 Carrier Ship Based Ccs Unmanned Offshore FacilityDocument112 pagesPreliminary Feasibility Study Co2 Carrier Ship Based Ccs Unmanned Offshore FacilityrajachemNo ratings yet
- Kast O Lite 97 L - DatasheetDocument1 pageKast O Lite 97 L - DatasheetrajachemNo ratings yet
- Dowtherm BookDocument30 pagesDowtherm BookMeghnad M GavitNo ratings yet
- PV Newslette June 2015Document20 pagesPV Newslette June 2015sklatakeNo ratings yet
- Hysys V8.0 Tutorial - Part 1 PDFDocument109 pagesHysys V8.0 Tutorial - Part 1 PDFrajachem100% (1)
- Hysys V8.0 Tutorial - Part 1 PDFDocument109 pagesHysys V8.0 Tutorial - Part 1 PDFrajachem100% (1)
- Greencast 94 PlusDocument1 pageGreencast 94 PlusAHMAD FAHRUR ROZAQNo ratings yet
- Boiling Heat TransferDocument16 pagesBoiling Heat Transferrr1819No ratings yet
- Boiling Heat TansferDocument33 pagesBoiling Heat TansferVineet K. MishraNo ratings yet
- PetroSync - TEMA HTRI - Heat Exchanger Design Cost Saving Management 2016Document5 pagesPetroSync - TEMA HTRI - Heat Exchanger Design Cost Saving Management 2016rajachemNo ratings yet
- Choosing API 650 and API 620 TanksDocument7 pagesChoosing API 650 and API 620 TanksrajachemNo ratings yet
- Choosing API 650 and API 620 TanksDocument7 pagesChoosing API 650 and API 620 TanksrajachemNo ratings yet
- C - 533 - 95 Calcium Silicate Block and Pipe Thermal InsulationDocument4 pagesC - 533 - 95 Calcium Silicate Block and Pipe Thermal Insulationhamid vahedil larijaniNo ratings yet
- Steam HXDocument1 pageSteam HXrajachemNo ratings yet
- CO2 Recovery Plant To Urea Production in Abu Dhabi: Back To Projects DatabaseDocument2 pagesCO2 Recovery Plant To Urea Production in Abu Dhabi: Back To Projects DatabaserajachemNo ratings yet
- Fuel Oil AdditivesDocument2 pagesFuel Oil AdditivesrajachemNo ratings yet
- BPHE Process Gas Waste Heat Recovery System EDocument20 pagesBPHE Process Gas Waste Heat Recovery System ErajachemNo ratings yet
- ASTM Grades For Insulating Fire BrickDocument2 pagesASTM Grades For Insulating Fire BrickrajachemNo ratings yet
- C - 533 - 95 Calcium Silicate Block and Pipe Thermal InsulationDocument4 pagesC - 533 - 95 Calcium Silicate Block and Pipe Thermal Insulationhamid vahedil larijaniNo ratings yet
- Hairpin Heat ExchangersDocument9 pagesHairpin Heat ExchangersrajachemNo ratings yet
- 110-Nb1 Anton Marco Fantolini SaipemDocument21 pages110-Nb1 Anton Marco Fantolini SaipemrajachemNo ratings yet
- 110-Nb1 Anton Marco Fantolini SaipemDocument21 pages110-Nb1 Anton Marco Fantolini SaipemrajachemNo ratings yet
- Hairpin Heat ExchangersDocument9 pagesHairpin Heat ExchangersrajachemNo ratings yet
- Project No. 16279S Project Name Bapco - JVTST: Calculation of Emissivity of Process GasDocument11 pagesProject No. 16279S Project Name Bapco - JVTST: Calculation of Emissivity of Process GasrajachemNo ratings yet
- PetroSync - TEMA HTRI - Heat Exchanger Design Cost Saving Management 2016Document5 pagesPetroSync - TEMA HTRI - Heat Exchanger Design Cost Saving Management 2016rajachemNo ratings yet
- KM170, KM171, KM172, F3A21, F3A22: 3 SPEED FWD (Lock Up & Non Lock Up)Document4 pagesKM170, KM171, KM172, F3A21, F3A22: 3 SPEED FWD (Lock Up & Non Lock Up)krzysiek1975No ratings yet
- CrimDocument29 pagesCrimkeziahmae.bagacinaNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Design PDFDocument1 pageReinforced Concrete Design PDFhallelNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly Examination, 2017-18: MathematicsDocument7 pagesHalf Yearly Examination, 2017-18: MathematicsSusanket DuttaNo ratings yet
- Banin Cawu 1: Panitia Ujian Perguruan Islam Mathali'Ul FalahDocument4 pagesBanin Cawu 1: Panitia Ujian Perguruan Islam Mathali'Ul FalahKajen PatiNo ratings yet
- Or HandoutDocument190 pagesOr Handoutyared haftu67% (6)
- Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana - CERTDocument35 pagesElasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana - CERTManuel VegaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document51 pagesLab 1aliNo ratings yet
- God Reproducing Himself in UsDocument6 pagesGod Reproducing Himself in UsLisa100% (1)
- Pull Cord Switch JayashreeDocument1 pagePull Cord Switch JayashreeNCNo ratings yet
- Richardson ResumeDocument3 pagesRichardson Resumeapi-549248694No ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment in Family Nursing PracticeDocument22 pagesNursing Assessment in Family Nursing PracticeHydra Olivar - PantilganNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Theories and Principles in The Use and Design of Technology Driven Learning LessonsDocument5 pagesUnit 3: Theories and Principles in The Use and Design of Technology Driven Learning Lessons서재배No ratings yet
- DatuinMA (Activity #5 - NSTP 10)Document2 pagesDatuinMA (Activity #5 - NSTP 10)Marc Alen Porlaje DatuinNo ratings yet
- Derivation Bragg's Snell Law PDFDocument4 pagesDerivation Bragg's Snell Law PDFVaswati BiswasNo ratings yet
- 03 IGT-Influence of Codes Guidelines and Other Regulations On The Tunnel Design in AustriaDocument48 pages03 IGT-Influence of Codes Guidelines and Other Regulations On The Tunnel Design in AustriaSudarshan GadalkarNo ratings yet
- Ass AsDocument23 pagesAss AsMukesh BishtNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression (Ex 5.1) Exercise 5.1Document8 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression (Ex 5.1) Exercise 5.1Akash DasNo ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance Manual Compressor Models: P105WJD, P130DWJD, P160DWJD, P175DWJDDocument70 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual Compressor Models: P105WJD, P130DWJD, P160DWJD, P175DWJDManuel ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Pizza Restaurant PowerPoint TemplatesDocument49 pagesPizza Restaurant PowerPoint TemplatesAindrila BeraNo ratings yet
- Icc Esr-2302 Kb3 ConcreteDocument11 pagesIcc Esr-2302 Kb3 ConcretexpertsteelNo ratings yet
- Science9 Q4 Week2Document16 pagesScience9 Q4 Week2Maria Josie Lopez TumlosNo ratings yet
- Te-Chemical Sem5 CPNM-CBCGS Dec19Document2 pagesTe-Chemical Sem5 CPNM-CBCGS Dec19Mayank ShelarNo ratings yet
- VERGARA - RPH Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesVERGARA - RPH Reflection PaperNezer Byl P. VergaraNo ratings yet
- Evan Lagueux - H Argument EssayDocument7 pagesEvan Lagueux - H Argument Essayapi-692561087No ratings yet
- DeadlocksDocument41 pagesDeadlocksSanjal DesaiNo ratings yet
- CBC DrivingDocument74 pagesCBC DrivingElonah Jean ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect and Present Perfect ProgressiveDocument5 pagesPresent Perfect and Present Perfect ProgressiveKiara Fajardo matusNo ratings yet
- WD Support Warranty Services Business Return Material Authorization RMA Pre Mailer For ResellerDocument3 pagesWD Support Warranty Services Business Return Material Authorization RMA Pre Mailer For ResellerZowl SaidinNo ratings yet
- Charter of The New UrbanismDocument4 pagesCharter of The New UrbanismBarabas SandraNo ratings yet