Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introductory Course For Trigonometry
Uploaded by
John AguilaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introductory Course For Trigonometry
Uploaded by
John AguilaCopyright:
Available Formats
Adamson University Chemical Engineering Society
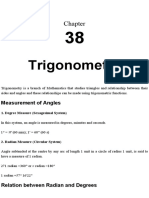
TRIGONOMETRY The branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and the angles of triangles and the calculations based on them, particularly the trigonometric functions. Angle of Depression CONVERSIONS a.) Degree to Radians b.) Radians to Degree
If the object is below the level of the observer, then the angle between the horizontal and the observer's line of sight
Rotational speed (N) - No. of Revolution per minute Angular speed () - 2 Linear speed (V) - 2 Coupled Wheels ] or Co-terminal Angles
Concentric Wheels
Coterminal angles are angles in standard position (angles with the initial side on the positive x-axis) that have a common terminal side. For example 30, 330 and 390 are all coterminal.
Quadrantal Angles
An angle in standard position with terminal side lying on x-axis or y-axis is called as Quadrantal Angle.
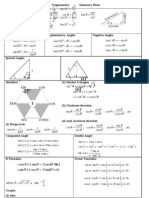
SIX TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS: TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES sin A = cos A = tan A = csc A = sec A = cot A = sin = cos = tan = 1 csc 1 sec 1 cot csc = sec = cot = 1 sin 1 cos 1 tan Reciprocal Identities
SOHCAHTOA SOH- Sine Opposite over Hypotenuse CAH- Cosine Adjacent over Hypotenuse TOA- Tangent Opposite over Adjacent Angle of Elevation
Pythagorean Identities a) b) c) sin + cos = 1 1 + tan = sec 1 + cot = csc RalphEdreanOmadto|2012
The angle of elevation of an object as seen by an observer is the angle between the horizontal and the line from the object to the observer's eye (the line of sight)
Adamson University Chemical Engineering Society
Quotient Identities
Product to Sum Identities
Angle-Sum and -Difference Identities sin( + ) = sin()cos() + cos()sin() sin( ) = sin()cos() cos()sin() cos( + ) = cos()cos() sin()sin() cos( ) = cos()cos() + sin()sin()
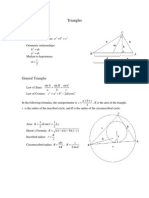
AREA OF TRIANGLE
Herons Formula:
AREA OF A SEGMENT Double-Angle Identities sin(2x) = 2sin(x)cos(x) cos(2x) = cos2(x) sin2(x) = 1 2sin2(x) = 2cos2(x) -1 AREA OF SECTOR
Half-Angle Identities
LAW OF SINES
The above identities can be re-stated as: sin2(x) = [1 cos(2x)] cos2(x) = [1 + cos(2x)]
If a < bsinA, no triangle. If a = bsinA, 1 triangle (right) If a > bsinA, 2 triangles LAW OF COSINES c2 = a2 + b2 2ab cos C a2 = b2 + c2 2bc cos A b2 = a2 + c2 2ac cos B
Sum to Product Identities
RalphEdreanOmadto|2012
Adamson University Chemical Engineering Society
importance for calculations in astronomy and earth-surface, orbital and space navigation. LOGARITHM - Inverse of Exponential Form
Properties of Logarithm 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Change of Base Formula
Natural Number ( - The number e is an important mathematical constant, approximately equal to 2.71828, that is the base of the natural logarithm Properties of Natural Number 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
SPHERICAL TRIGONOMETRY - Spherical trigonometry is a branch of spherical geometry which deals with polygons (especially triangles) on the sphere and the relationships between the sides and the angles. This is of great
RalphEdreanOmadto|2012
You might also like
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Trigonometry ReviewerDocument10 pagesTrigonometry ReviewerNiko Ramarama100% (1)
- TRIGONOMETRYDocument8 pagesTRIGONOMETRYurfriend_jjn05100% (1)
- TrigonometruyDocument3 pagesTrigonometruyRitu SharmaNo ratings yet
- TRIGONOMETRYDocument5 pagesTRIGONOMETRYMuhamamad ZamanNo ratings yet
- SAT II Math Level 2 Subject Test Notes: Trigonometric FunctionsDocument4 pagesSAT II Math Level 2 Subject Test Notes: Trigonometric Functionstomcantyyy100% (1)
- Essential Trigonometry ConceptsDocument23 pagesEssential Trigonometry ConceptsTitis PohanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field and Waves: EE 221 Spring 2004Document34 pagesElectromagnetic Field and Waves: EE 221 Spring 2004Ali Ahmad100% (1)
- EMT - 2A - Cylindrical CoordinatesDocument59 pagesEMT - 2A - Cylindrical Coordinates5610Umar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus TrigonometryDocument77 pagesPre Calculus TrigonometryTeacher JasonNo ratings yet
- ALGEBRA 1 LOGARITHM ALGEBRA 2 UNIFORM MOTION PROBLEMS REMAINDER AND FACTOR THEOREMSDocument33 pagesALGEBRA 1 LOGARITHM ALGEBRA 2 UNIFORM MOTION PROBLEMS REMAINDER AND FACTOR THEOREMSLala Hala100% (3)
- MATH Formulas PDFDocument33 pagesMATH Formulas PDFAnonymous 0Mduljho100% (3)
- Trigonometry Formulas GuideDocument8 pagesTrigonometry Formulas GuideVholts Villa VitugNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Measurement of AnglesDocument57 pagesTrigonometry: Measurement of AnglesLeo V. Baker100% (2)
- Trigonometry Formulas ListDocument6 pagesTrigonometry Formulas Listkarthik sivarajNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Angle MeasuresDocument36 pagesTrigonometry: Angle MeasuresKiran Kumar100% (1)
- Chapter 14: Stress Concentrations: - Locally High Stresses Can Arise Due ToDocument10 pagesChapter 14: Stress Concentrations: - Locally High Stresses Can Arise Due ToGuru75No ratings yet
- Iit Jee TRIGNOMETRY FORMULAS2.0Document16 pagesIit Jee TRIGNOMETRY FORMULAS2.0ARYAN SINGHNo ratings yet
- 1Document4 pages1jaga022017No ratings yet
- Illustrative Examples Physics Vectors RDocument20 pagesIllustrative Examples Physics Vectors RVishal KalraNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Formulas Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesTrigonometric Formulas Cheat SheetanjaliNo ratings yet
- S1Document37 pagesS1sbpathiNo ratings yet
- Opp Adj Opp Hyp Hyp Adj: Sin Sin Cos Cos Tan TanDocument3 pagesOpp Adj Opp Hyp Hyp Adj: Sin Sin Cos Cos Tan Tanchoosg100% (1)
- TrignometryDocument12 pagesTrignometryVardaan ThakurNo ratings yet
- Formula - by B B Susheel KumarDocument14 pagesFormula - by B B Susheel KumarB B Susheel KumarNo ratings yet
- Common P.G. Entrance Test 2020 Physics QuestionsDocument19 pagesCommon P.G. Entrance Test 2020 Physics Questionsamar nayakNo ratings yet
- ARML TheoremsDocument27 pagesARML Theoremsfreefall014No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions: 3.1 OverviewDocument27 pagesTrigonometric Functions: 3.1 OverviewkennedyNo ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Trigonometric FunctionsDocument27 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Trigonometric FunctionsPrasanth VarrierNo ratings yet
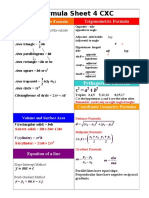
- CXC MATHS Formula SheetDocument7 pagesCXC MATHS Formula SheetEric D Medeci100% (1)
- MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONSDocument8 pagesMATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONSRhon Gleixner MandaweNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities (List of Trigonometric Identities - Proofs - PDFS)Document16 pagesTrigonometric Identities (List of Trigonometric Identities - Proofs - PDFS)Abdullahi ChuwachuwaNo ratings yet
- Ee Basics PDFDocument11 pagesEe Basics PDFravitejNo ratings yet
- HW1 A SolutionsDocument5 pagesHW1 A SolutionsAli Abbas SheriffNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Formulas: X X X X X XDocument3 pagesTrigonometry Formulas: X X X X X XMahendraKumarNo ratings yet
- Pure Bending of Curved BarsDocument15 pagesPure Bending of Curved BarsArifsalimNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Analysis 1: theory and solved exercisesFrom EverandMathematical Analysis 1: theory and solved exercisesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PGMA opens Port of San Juan and Laiya road in BatangasDocument4 pagesPGMA opens Port of San Juan and Laiya road in BatangasPanget AkoNo ratings yet
- Introductory Course For Physical Chemistry For Engineers 1Document3 pagesIntroductory Course For Physical Chemistry For Engineers 1John AguilaNo ratings yet
- PGMA opens Port of San Juan and Laiya road in BatangasDocument4 pagesPGMA opens Port of San Juan and Laiya road in BatangasPanget AkoNo ratings yet
- Introductory Course For Analytical ChemistryDocument3 pagesIntroductory Course For Analytical ChemistryJohn AguilaNo ratings yet
- Ra 7279Document34 pagesRa 7279Hendrix Gil100% (1)
- Introductory Course For Themodynamics 2Document3 pagesIntroductory Course For Themodynamics 2John AguilaNo ratings yet
- Introductory Course For College AlgebraDocument2 pagesIntroductory Course For College AlgebraJohn AguilaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Unit PlanDocument9 pagesTrigonometry Unit Planapi-535278422No ratings yet
- COT 4th QUARTER MATH 9Document2 pagesCOT 4th QUARTER MATH 9ariel velaNo ratings yet
- WSC1 ST Year NSQFFinalDocument187 pagesWSC1 ST Year NSQFFinalVadnala ArunNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Syllabus From JAMB - MyschoolDocument1 pageMathematics Syllabus From JAMB - Myschooljanebaldore48No ratings yet
- 10.3 The Six Circular Functions and Fundamental IdentitiesDocument26 pages10.3 The Six Circular Functions and Fundamental IdentitiesJerico VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Summative Test 2.Document2 pagesQ2 - Summative Test 2.REY PAMISNo ratings yet
- Maths SecondaryDocument42 pagesMaths Secondaryapi-290917857No ratings yet
- Assertion Based Question - Class XDocument2 pagesAssertion Based Question - Class XTHE ASSAM GAMER NILAV 01No ratings yet
- 1.5 AnglePairs Practice ADocument4 pages1.5 AnglePairs Practice ASaint TyagiNo ratings yet
- Akshara Coaching Classes: 2 Floor, Ss - Shetty Compex, Hosabettu 2 Pu Mathematics (Integrals)Document8 pagesAkshara Coaching Classes: 2 Floor, Ss - Shetty Compex, Hosabettu 2 Pu Mathematics (Integrals)akshara hosabettuNo ratings yet
- Demonstração Algébrica Das Fórmulas de Soma e Subtração de Arcos - Rodrigo R. GonçalezDocument6 pagesDemonstração Algébrica Das Fórmulas de Soma e Subtração de Arcos - Rodrigo R. GonçalezRodrigo GonçalezNo ratings yet
- Chap 20 Trigonometric Functions PDFDocument28 pagesChap 20 Trigonometric Functions PDFArahNo ratings yet
- Theory - ExerciseDocument63 pagesTheory - ExerciseRonan HenriquesNo ratings yet
- Revised Plan Ai TS 2022-2023 - XIDocument1 pageRevised Plan Ai TS 2022-2023 - XIAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Done Circular MeasureDocument12 pagesDone Circular MeasureSharvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Plane Trigonometry Todhunter KeyDocument340 pagesPlane Trigonometry Todhunter KeyOI HoNo ratings yet
- 252733geometry Sheet-14 - CrwillDocument20 pages252733geometry Sheet-14 - CrwillPradhumnNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Trigonometric FunctionsDocument1 pageGraphs of Trigonometric FunctionswolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- RPMS Lesson PlanDocument24 pagesRPMS Lesson PlanRoman John CabintoyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Surveying MeasurementDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Surveying MeasurementJoven LocsinNo ratings yet
- Torque Vs Angle of Twist: Cast IronDocument4 pagesTorque Vs Angle of Twist: Cast IronPrateek K srivastavaNo ratings yet
- 10 Maths FormulaeDocument7 pages10 Maths FormulaeRoyalmechNo ratings yet
- Pythogoras Practice Book AnswersDocument3 pagesPythogoras Practice Book AnswersPh DeNo ratings yet
- Trig and Circular Functions CalculatorDocument64 pagesTrig and Circular Functions CalculatorVrushti ShahNo ratings yet
- David Greenwood Et Al. - Essential Mathematics For The Australian Curriculum Gold-Cambridge University Press (2017)Document756 pagesDavid Greenwood Et Al. - Essential Mathematics For The Australian Curriculum Gold-Cambridge University Press (2017)ra100% (2)
- Trigo 2Document2 pagesTrigo 2Julie OcolNo ratings yet
- Circle - Circumference and AreaDocument38 pagesCircle - Circumference and AreaM JNo ratings yet
- Calculating The Truss Member ForcesDocument31 pagesCalculating The Truss Member Forcessurachs100% (2)
- 04 - Trig Ratios of Any Angle PDFDocument4 pages04 - Trig Ratios of Any Angle PDFMark Abion ValladolidNo ratings yet
- Basic Maths in PhyDocument56 pagesBasic Maths in PhyKaustav KaranNo ratings yet