Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Course Description and Objectives 438
Uploaded by
djvaughan01Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Course Description and Objectives 438
Uploaded by
djvaughan01Copyright:
Available Formats
Course title: Algebra II First Degree Equations Course description: Students will apply the properties of real numbers
to expressions, equalities, and inequalities including absolute value and compound inequalities and corresponding graphs according to the Common Core Standards. Course Overview: Students will study first degree equations and inequalities and apply what they learn to an individual project which will be presented via a powerpoint or video presentation. Students will also work on a comprehensive group project which models and analyzes real-world situations using linear equations and/or inequalities. Course Objectives: As stated in the new Common Core State Standards, at the end of this unit students will be able to: 1. Interpret parts of an expression such as terms, factors and coefficients.-- A.SSE.1a Interpret complicated expressions by viewing one or more parts as a single entity.-A.SSE.1b Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it.--A.SSE.2 2. Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems.-A.CED.1 Create equations in two or more variables to represent relationships between quantities. Graph equations on coordinate axes with labels and scales.--A.CED.2 Represent constraints by equations or inequalities, and by systems of equations and/or inequalities, and interpret solutions as viable or nonviable options in a modeling context.-A.CED.3 3. Explain why the x-coordinates of the points where the graphs of the equations of y = f(x) and y = g(x) intersect are the solutions of the equations f(x) = g(x); find the solutions approximately, e.g. using technology to graph the functions, make tables of values, or find successive approximations. Include cases for linear, polynomial, rational, absolute value, exponential and logarithmic functions.--A.REI.11 4. For a function that models a relationship between two quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in terms of quantities, and sketch graphs showing key features given a verbal description of the relationship.--F.IF.4 Relate the domain of a function to its graph and, where applicable, to the quantitative relationship it describes.--F.IF.5 Calculate and interpret the average rate of change of a function over a specified interval. Estimate rate of change from a graph.--F.IF.6 Graph functions expressed symbolically and show key features of the graph by hand in simple cases and with technology for more complicated cases. Graph square root, cube root, and piecewise-defined functions, including step functions and absolute value functions.--F.IF.7b Compare properties of two functions each represented in a different way (algebraically, graphically, numerically in tables, or by verbal descriptions).--F.IF.9
You might also like
- Project RubricDocument1 pageProject Rubricdjvaughan01No ratings yet
- DiscussionsDocument1 pageDiscussionsdjvaughan01No ratings yet
- Discussion RubricDocument1 pageDiscussion Rubricdjvaughan01No ratings yet
- Course Development Part 2Document1 pageCourse Development Part 2djvaughan01No ratings yet
- Grades and AssignmentsDocument1 pageGrades and Assignmentsdjvaughan01No ratings yet
- Course Description and ObjectivesDocument1 pageCourse Description and Objectivesdjvaughan01No ratings yet
- Algebra 2 CoverDocument1 pageAlgebra 2 Coverdjvaughan01No ratings yet
- Review For Test 1 LecturetteDocument8 pagesReview For Test 1 Lecturettedjvaughan01No ratings yet
- Unit 1 PageDocument1 pageUnit 1 Pagedjvaughan01No ratings yet
- Peer Evaluation 438Document1 pagePeer Evaluation 438djvaughan01No ratings yet
- Course Design Part 2 438Document1 pageCourse Design Part 2 438djvaughan01No ratings yet
- Webquest Project Unit 1Document1 pageWebquest Project Unit 1djvaughan01No ratings yet
- Course Description and ObjectivesDocument1 pageCourse Description and Objectivesdjvaughan01No ratings yet
- 438e LearningphilosophyDocument1 page438e Learningphilosophydjvaughan01No ratings yet
- HyperbolasDocument3 pagesHyperbolasdjvaughan01No ratings yet
- Example 1: Write The Following Equations in Standard Form. State WhetherDocument2 pagesExample 1: Write The Following Equations in Standard Form. State Whetherdjvaughan01No ratings yet
- 8 4Document3 pages8 4djvaughan01No ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic SystemsDocument2 pagesSolving Quadratic Systemsdjvaughan01No ratings yet
- 8 3Document3 pages8 3djvaughan01No ratings yet
- 8.1 & 8.2Document6 pages8.1 & 8.2djvaughan01No ratings yet
- Solving Rational Equations: Algebra 2 9-6 Name - 1Document3 pagesSolving Rational Equations: Algebra 2 9-6 Name - 1djvaughan01No ratings yet
- 6-4 Is Like 9-5Document4 pages6-4 Is Like 9-5djvaughan01No ratings yet
- Simplifying Rational ExpressionsDocument4 pagesSimplifying Rational Expressionsdjvaughan01No ratings yet
- Fractions, They Must First Be Written As Equivalent Fractions WithDocument3 pagesFractions, They Must First Be Written As Equivalent Fractions Withdjvaughan01No ratings yet
- Simplifying Rational Expressions: Algebra 2 9.1 NameDocument6 pagesSimplifying Rational Expressions: Algebra 2 9.1 Namedjvaughan01No ratings yet
- 10-4 07Document2 pages10-4 07djvaughan01No ratings yet
- Direct, Joint, and Inverse Variation Direct Variation: K Is The Constant of VariationDocument3 pagesDirect, Joint, and Inverse Variation Direct Variation: K Is The Constant of Variationdjvaughan01No ratings yet
- More 10-5 Content (Not in This Book)Document2 pagesMore 10-5 Content (Not in This Book)djvaughan01No ratings yet
- E Is An Irrational Number (Non-Terminating, Non-: Natural LogarithmDocument5 pagesE Is An Irrational Number (Non-Terminating, Non-: Natural Logarithmdjvaughan01No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Chapter Two (LPM)Document18 pagesChapter Two (LPM)Yohannes BelaynehNo ratings yet
- Lab 4-5 Applied Linear Algebra For It - 501032: 1 ExercisesDocument4 pagesLab 4-5 Applied Linear Algebra For It - 501032: 1 ExercisesAnh QuocNo ratings yet
- Guide to Coding with Mata in StataDocument16 pagesGuide to Coding with Mata in Statache_wang_7No ratings yet
- Sample Solutions For Exercise Sheet 2Document8 pagesSample Solutions For Exercise Sheet 2Jair CarneiroNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Business and Economics: 7 EditionDocument60 pagesStatistics For Business and Economics: 7 EditiondasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- CSS (Central Superior Service)Document14 pagesCSS (Central Superior Service)Asim ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Discrete Wavelet Transform Using Circular ConvolutionDocument6 pagesDiscrete Wavelet Transform Using Circular ConvolutionijsretNo ratings yet
- Measuring Change: Differentiation: Essential UnderstandingsDocument36 pagesMeasuring Change: Differentiation: Essential UnderstandingsReyansh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Method ExplainedDocument56 pagesLagrangian and Hamiltonian Method ExplainedayuNo ratings yet
- Sat Math Formulas PDFDocument2 pagesSat Math Formulas PDFkhalsa warriorNo ratings yet
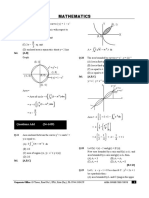
- (Single Correct Choice Type) (6 × 3 18) Class:XII Time: Min. M.M.: Dpp. No.Document4 pages(Single Correct Choice Type) (6 × 3 18) Class:XII Time: Min. M.M.: Dpp. No.Purushottam KumarNo ratings yet
- Bmte 144Document15 pagesBmte 144Njaan SnehamaakunnuNo ratings yet
- Area Under The Curve (Practice Question) PDFDocument8 pagesArea Under The Curve (Practice Question) PDFAditya SanjayBoob100% (1)
- Mathematics for ML: Linear Algebra Formula SheetDocument1 pageMathematics for ML: Linear Algebra Formula SheetBobNo ratings yet
- q1 Summative Assessment 4Document4 pagesq1 Summative Assessment 4Sean Patrick BenavidezNo ratings yet
- Banach Spaces Study GuideDocument8 pagesBanach Spaces Study GuidekarunakaranNo ratings yet
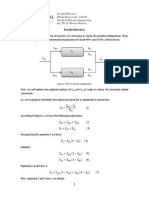
- Parallel Reactors Daniel Sierra Cód.: 244706 Chemical Reaction Engineering Ing. Ph. D. Herney RamírezDocument6 pagesParallel Reactors Daniel Sierra Cód.: 244706 Chemical Reaction Engineering Ing. Ph. D. Herney RamírezDaniel Sierra SantofimioNo ratings yet
- 1981-Dual-Rotation PropellersDocument49 pages1981-Dual-Rotation PropellersJianbo JiangNo ratings yet
- Standards in ItDocument16 pagesStandards in Itanwar kadiNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Methods and Structural OptimizationDocument8 pagesFinite Element Methods and Structural OptimizationAjith MosesNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Lab FitDocument5 pagesTutorial Lab FitOmer Altimimi OmerNo ratings yet
- 1.linear Equations in Two Variables ExplainedDocument10 pages1.linear Equations in Two Variables ExplainedmouneshskNo ratings yet
- HW1 SolutionDocument9 pagesHW1 SolutionJuan Carlos TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Mathematics area problemsDocument3 pagesMathematics area problemsSubrata KarmakarNo ratings yet
- 40 Questions To Test A Data Scientist On Time SeriesDocument26 pages40 Questions To Test A Data Scientist On Time SeriesRajeshree JadhavNo ratings yet
- Journal of Hydrology: Jamaludin Suhaila, Abdul Aziz Jemain, Muhammad Fauzee Hamdan, Wan Zawiah Wan ZinDocument10 pagesJournal of Hydrology: Jamaludin Suhaila, Abdul Aziz Jemain, Muhammad Fauzee Hamdan, Wan Zawiah Wan ZinBeatriz Cobo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- GenmathDocument2 pagesGenmathJosafatNo ratings yet
- MA6151 Part-A With Answer PDFDocument35 pagesMA6151 Part-A With Answer PDFEmmanuel ThomasNo ratings yet
- 40 Days Strategy IIT JAMDocument4 pages40 Days Strategy IIT JAMCassey WashingtonNo ratings yet