Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Material Planning Process WWW - Sap Terp10.Com .Ar 1
Uploaded by
prashantitankarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Material Planning Process WWW - Sap Terp10.Com .Ar 1
Uploaded by
prashantitankarCopyright:
Available Formats
Use to derive a future demand program from the demand figures in the past
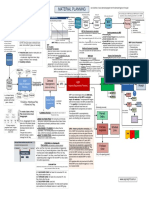
MATERIAL PLANNING
Plant Raw Not normally part of MRP because MRP doesn’t consider
Stock Final Good Activity Consum Stock Raw Assembly painting Areas of
Who does the work? capacities unless scheduling parameter is set in MRP.
Item Category: engineering responsibilities
3000 3000 3000 3000 Stock contain the list the sequence of steps
2 2 1 1
Non Stock BOM Activity Cost Work for producing a material:
Operations,
Variable size Routing
Documents Bill Of Material Types Center Center Operation Sequences
Usage
Text
Time elements
Material type: Class
Work Centers.
Raw materials Intra material MRP Net Requirements calculation Component allocations
Is executed in the planning run to determine if there is Control parameters for MRP
Operating supplies
Semi-finished products a shortage for a certain material. Processing key
SOP: planning and forecasting module with the
Finished products Create Purchase Requisit (mat. procured ext.)
logistic area. It provides a method for : Stock + fixed receipts that exists (PR, PO,Pln.O, PrO) Create Schedules lines (bis)
controls:
Sales plan: (data from the SIS, data from VS
Business process . Create MRP list (always, never, only except.
CO-PA, from past sales to forecast future MRP TYPES (how materials should be planned) Safety Stock + Requirements (Pln Ind. Req, Sales O) MRP Control Parameters
Views (Screens) = quantity available for planning. Planning mode (if existing data simply be
Department-specific data sales, from another P.group, or manually) MRP adjusted, whether BOM and routings should be (required for planning run)
Material # assignment NO PLANING re-exploded or whether the plann. Should be 1. Processing key
Procurement types CONSUMPTION BASED: Multilevel Backward Scheduling
The system calculates the start dates based on started from the beginning again. 2. Create Purchase Req.
GL- general ledger accounts _Based on historical rates of consumption (past cons) 3. Schedule lines
Production plan (based on sales plan) can _Appropriate for low value mat (b,c parts) a end date.
be created several ways: 4. Create MRP list
_No ref. to master plan (not triggered by ind. req) MRP RUN Scope of the Planning Run
= to sales plan, target stock level, days 5. Planning mode
_Net req. cons. is triggered when: Planning run can be done in 2 levels: Processing key field specify the type of planning:
Material supply, inventory to zero, manually) *stock levels fall below a reorder point (safety stock) or 1. Total planning (planning of all materials of NEUPL: Regenerative planning (plann of all MRP
Feasibility estimates *by forecast req. (from past cons. data). one or several plants.(online or in the background). relevant materials). (first time, errors)
_Appropriate for mat. with demand consistent 2. Single-item planning: NETCH: Net change for total horizon (plann all FI CO
_Ind-Dep. Req and sales order don’t affect them.
Variances
2.1. Multilevel. Planning of all BOM’s materials mat. we made changes).
NETPL: Net change for planning horizon settled
MD04: Stock/Req.list: info current status of stocks 2.2 Single-level. Planning of a specific material
Sales Info Controlling 2.2 Interactive. Interactive single-level planning
CO-PA Profitable
MRP list: info latest plann run
Syst E 2
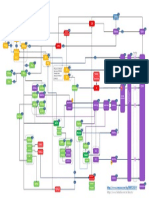
Analisys The purpose of MPS (Master Prod. Sched) and MRP (Material Req. Header Mvt 101
Planning) is to guarantee material availability on a 2 step planning process (inhouse production) + Items Release
SOP Demand
Product Disaggregation MRP Goods
Sales & Operation
and transfer to
Management MPS Planned Orders Production Order
Group Material Requirements Planning Receipt
Planning (Admin of Ind Req.)
Items 1
Product MRP is set of techniques that uses BOM data, OP
Is a Product family.
Group Manual Forecast Items
It groups together inventory data, and the MPS to calculate
requir. for materials. Time-phased MRP begins
Items
products with similar Sales Order = Customer
plann. charact. Forcasting = Warehouse Req. (Created in SD)
with the items listed on the MPS and determines
Ind. Req. 1. The quantity of all components and mat. OP C.O.T
= Planned Ind. Req. F
required to fabricate those items and (Externally procured)
2. the date that the components and material
Product Items
Disaggregation
are required. Costs debited
Group 1 To create a Sales or Prod. to Prod.Order
PLANNING STRATEGY controlls the diff. mode of action of
Prod. Prod.
Plan at one level we must Planned Ind. Req.
Time-phased MRP is accomplished by Planned
disaggregate. exploding the BOM, adjusting for inventory
Group A Group B
quant, and offsetting the net requirements
Orders Goods
MAKE TO STOCK PROD: Plan consump. are forecast,
Mat. Mat. Mat. Mat.
For ex. disaggregate the sales then procur. and prod. takes place without Sales Orders. Issue
A1 A2 B1 B2
plans of all the product groups Requirements covered by warehouse stock (=>shorter
P.Groups require a down to the materials, and delivery time).
proportion factor. A higher develop production plans at SUBASSEMBLY PLANNING: M.to.Stock Prod for Purchase Schedule
level is disaggregated to a (MPS) - Master production scheduling is a
lower level
that level. assemblies. The finished products are not produced to form of MRP that concentrates planning on the Requisition Lines
The plan that is sent to stock, rather the necessary assemblies are procured. parts or products that have the great influence
demand manag. is used to MM FI CO
MAKE TO ORDER PROD: products are procured and on company profits or which dominate the entire
manage the Ind. Req. produce once a Sales Order arrives. production process by taking critical resources.
These items are marked as ‘A’ parts (MPS
STRATEGY 40 – Planning with items) and are planned with extra attention.
Final Asembly =>fast reaction to customer demand These items are selected for a separate MPS
Purchase
Proc. and Prod. of all comp. and assemblies is triggered by run that takes place before the MRP run. The
MPS run is conducted without a BOM explosion Order
Plnnd. Ind. Req. in Demand Mgt before a Sales Order arrives.
Incoming Sales Orders consume these Plnnd. Ind. Req. so that the MRP controller can ensure that the
If Sales Ord. exceed Pl. Ind. Req, a new Plnnd Order for the Master schedule items (MSI) are correctly Only in the opening period
unplanned quantity is trigger for the next MRP run (thus Sales planned before the detailed MRP run takes
Ord. affect requirements). place.
MPS operates within only one level of the BOM,
CONSUMPTION While MRP can be utilized throughout all levels
Determines the direction on the time axis in which the arriving sales orders of a material’s BOM.
are to consume the Plnnd. Ind. Req.
M1. BACKWARD CONS: the Sales Ord. consumes Pln. Ind.
Req. that lie before this sale.
M3. FORWARD CONS: the Sales Ord. consumes Pln. Ind.
Req. that lie after this sale. www.sap-terp10.com.ar
M2. BACK/FORW CONS: uses both.
By default Backwards consumption. The mode and the periods
can be defined in the Material master or in each MRP group.
You might also like
- TerpDocument5 pagesTerpAnas DarifNo ratings yet
- Key Questions Topic For Sap Terp10 CourseDocument4 pagesKey Questions Topic For Sap Terp10 CoursepbtgNo ratings yet
- Part4 - Manufacturing ExecutionDocument63 pagesPart4 - Manufacturing ExecutionNithus Nate Apimonbutra100% (1)
- Implementing Integrated Business Planning: A Guide Exemplified With Process Context and SAP IBP Use CasesFrom EverandImplementing Integrated Business Planning: A Guide Exemplified With Process Context and SAP IBP Use CasesNo ratings yet
- TMI Blueprint 1-12-2004Document292 pagesTMI Blueprint 1-12-2004Dhanush Kumar100% (1)
- Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) Case Study - Lecturer NotesDocument15 pagesEnterprise Asset Management (EAM) Case Study - Lecturer NotesmeddebyounesNo ratings yet
- 1 MM-Master PDFDocument703 pages1 MM-Master PDFHitesh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Part10 - Enterprise Asset ManagementDocument70 pagesPart10 - Enterprise Asset ManagementNithus Nate ApimonbutraNo ratings yet
- IBP Part 00 Introduction v02 PDFDocument110 pagesIBP Part 00 Introduction v02 PDFGot Ham100% (1)
- ASAP Business BlueprintDocument670 pagesASAP Business BlueprintidevaldoNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire PPDocument112 pagesQuestionnaire PPRohan SinghNo ratings yet
- Material ManagementDocument88 pagesMaterial ManagementManojNo ratings yet
- Sap PP Interview QuestionDocument55 pagesSap PP Interview QuestionkumarNo ratings yet
- LSMW Step-By-Step GuideDocument22 pagesLSMW Step-By-Step GuideMargaret MationgNo ratings yet
- Apo10 PDFDocument227 pagesApo10 PDFashahmednNo ratings yet
- SAP Batch Management OverviewDocument70 pagesSAP Batch Management Overviewlibran_15No ratings yet
- Design Document Co Profitabilty Analysis Author/ApproverDocument19 pagesDesign Document Co Profitabilty Analysis Author/ApproverAncuţa CatrinoiuNo ratings yet
- Production Order Variance SAPDocument22 pagesProduction Order Variance SAPAni Nalitayui LifityaNo ratings yet
- MM Config DocumentDocument89 pagesMM Config DocumentRahul AmbalgiNo ratings yet
- IBP Part 10 Enterprise Asset Service v02Document121 pagesIBP Part 10 Enterprise Asset Service v02Rajesh Kumar Sugumaran100% (1)
- SAP Data Archiving: by Gayatri Narendra Patil, InfosysDocument31 pagesSAP Data Archiving: by Gayatri Narendra Patil, Infosysshyamvs2002No ratings yet
- SAP Note BookDocument8 pagesSAP Note Bookమనోహర్ రెడ్డిNo ratings yet
- Controlling - 02.11.2021Document189 pagesControlling - 02.11.2021Bhaskar ReddyNo ratings yet
- MRP Process Overview in 40 CharactersDocument28 pagesMRP Process Overview in 40 Charactersbalu4indiansNo ratings yet
- What Is A Planned IndependentDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Planned IndependentRizwan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- BPI - I - Student Book PDFDocument452 pagesBPI - I - Student Book PDFNaseer SapNo ratings yet
- Part8 - Financial AccountingDocument81 pagesPart8 - Financial AccountingNithus Nate Apimonbutra100% (2)
- SAP MM OverviewDocument26 pagesSAP MM Overviewsappp_vikasNo ratings yet
- Numbers and Symbols Definitions for FinanceDocument24 pagesNumbers and Symbols Definitions for FinancekmatomboNo ratings yet
- SAP Basic COPA OverviewDocument1 pageSAP Basic COPA OverviewYong BenedictNo ratings yet
- Interfacing SAP Systems GuideDocument17 pagesInterfacing SAP Systems GuideKarthik SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire PPDocument66 pagesQuestionnaire PPsambangiravi100% (1)
- SAP Connectivity With MS Excel SCNDocument21 pagesSAP Connectivity With MS Excel SCNGuillermo Vallejo SauraNo ratings yet
- Aa Alternative Items in BOMDocument14 pagesAa Alternative Items in BOMAhmed TalaatNo ratings yet
- 1 Batch Specific UoM and Active Ingredient ManagementDocument2 pages1 Batch Specific UoM and Active Ingredient ManagementpoojaNo ratings yet
- How To Guide For Transferring Data in SAPDocument66 pagesHow To Guide For Transferring Data in SAPSultanNo ratings yet
- Sappress Service With Sap CRMDocument97 pagesSappress Service With Sap CRMSrinivas ReddyNo ratings yet
- SAP FI ALL-SAP Document Split Configuration and Manual-V1.1-Trigger LauDocument20 pagesSAP FI ALL-SAP Document Split Configuration and Manual-V1.1-Trigger LauSubramanian ChandrasekarNo ratings yet
- Automated Batch Determination in SAP MMDocument107 pagesAutomated Batch Determination in SAP MMNitesh RawatNo ratings yet
- MM Version ItDocument252 pagesMM Version ItBalaji SNo ratings yet
- Con PPDocument61 pagesCon PPDhanush KumarNo ratings yet
- Subcontracting (BMY) - Process DiagramsDocument1 pageSubcontracting (BMY) - Process DiagramsAnonymous s1zWy06ZDNo ratings yet
- Year End Closing Activities PDFDocument60 pagesYear End Closing Activities PDFRaju Raj RajNo ratings yet
- TERP10 Unit4 Management Accounting CODocument34 pagesTERP10 Unit4 Management Accounting CONicole LadouceurNo ratings yet
- SAP Super Users PDFDocument105 pagesSAP Super Users PDFfarrukhbaig0% (1)
- Standard VMI: PrerequisitesDocument8 pagesStandard VMI: PrerequisitessaprajmmNo ratings yet
- SAP Cloud ALM Functional OverviewDocument40 pagesSAP Cloud ALM Functional Overviewdgsdgs7No ratings yet
- Sap-Plm140 PDFDocument270 pagesSap-Plm140 PDFEdu RonanNo ratings yet
- Inv Accountignwith MLDocument14 pagesInv Accountignwith MLSamik BiswasNo ratings yet
- Controlling Module: Operation MiteDocument56 pagesControlling Module: Operation MiteKRISHNA SASTRYNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For PRODUCTION PLANNING PDFDocument2 pagesSyllabus For PRODUCTION PLANNING PDFSabyasachi GhoshNo ratings yet
- SAPTERP10Document37 pagesSAPTERP10Raks ThuruthiyilNo ratings yet
- SAP Foreign Currency Revaluation: FAS 52 and GAAP RequirementsFrom EverandSAP Foreign Currency Revaluation: FAS 52 and GAAP RequirementsNo ratings yet
- Inventor 2011 ModelDocument1 pageInventor 2011 ModelJaime Omar EsparzaNo ratings yet
- Machine Harness Connector and Component Locations: Do Not PasteDocument4 pagesMachine Harness Connector and Component Locations: Do Not PasteYHONSATRIC100% (1)
- Attachment 10 Incident Invetigation and Reporting TechniquesDocument1 pageAttachment 10 Incident Invetigation and Reporting TechniqueslilizuryaniNo ratings yet
- Machine Harness Connector and Component Locations: Do Not PasteDocument4 pagesMachine Harness Connector and Component Locations: Do Not PasteNorman CoetzeeNo ratings yet
- Copernicus ProgrammeDocument1 pageCopernicus ProgrammeGemmaNo ratings yet
- Project Novus SIT Scenarios V1.3Document184 pagesProject Novus SIT Scenarios V1.3Vikram BhandeNo ratings yet
- Management Questions PDFDocument303 pagesManagement Questions PDFMohammed Arsalan khanNo ratings yet
- PGP (2016)- Sales Operations Planning (SOP) Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesPGP (2016)- Sales Operations Planning (SOP) Practice ProblemsSanjeev Ranjan25% (4)
- Chapter 7-The Conversion Cycle: True/FalseDocument8 pagesChapter 7-The Conversion Cycle: True/FalseKwini CBNo ratings yet
- Example MRP: L-4-L OrderingDocument26 pagesExample MRP: L-4-L Orderingajeng.saraswatiNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management Improvement TechniquesDocument62 pagesInventory Management Improvement TechniquesNadia Fernandes100% (1)
- Operation Management Workbook For StudentsDocument230 pagesOperation Management Workbook For StudentsVignesh Anguraj91% (11)
- Omfed CFP Sap PP End User ManualDocument118 pagesOmfed CFP Sap PP End User ManualDebasish GhoshNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Resource Planning Cia 1: A Group Project Proposal SubmittedDocument19 pagesEnterprise Resource Planning Cia 1: A Group Project Proposal SubmittedVimal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sap PP 01 Organizational Structure Overview PDFDocument52 pagesSap PP 01 Organizational Structure Overview PDFMahesh KamdeyNo ratings yet
- MCQ P Amp MMDocument15 pagesMCQ P Amp MMArjun Cardoza100% (1)
- SAP Procurement ConsultantDocument21 pagesSAP Procurement Consultant陳厚宇No ratings yet
- TSCM52 65Document48 pagesTSCM52 65Chirag SolankiNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument6 pagesQuestion BankLakhani PareshNo ratings yet
- D Sibe MCCBDocument8 pagesD Sibe MCCBdevadas1976100% (1)
- UB Beer Commercial DeptDocument42 pagesUB Beer Commercial DeptBommanahalli ChandrashekarNo ratings yet
- C TSCM42 65 Sample QuestionsDocument4 pagesC TSCM42 65 Sample QuestionsnpalemNo ratings yet
- Jan Aushadhi Scheme New BusinessplanDocument36 pagesJan Aushadhi Scheme New BusinessplaniddrxNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management at Makerere University Business School and Its Impact On The Revenue Performance of Small and Medium EnterprisesDocument16 pagesInventory Management at Makerere University Business School and Its Impact On The Revenue Performance of Small and Medium EnterprisesKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Production Order ECC 6Document18 pagesProduction Order ECC 6dokkNo ratings yet
- Figure and Graphics Download Pack (Chapters 1-8) : Presented byDocument134 pagesFigure and Graphics Download Pack (Chapters 1-8) : Presented byPopocatl FloresNo ratings yet
- DBR Winning ApproachDocument9 pagesDBR Winning ApproachDiego Andrés Triana RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Kanban Scheduling SystemsDocument8 pagesKanban Scheduling SystemsharsurajNo ratings yet
- Transactioncodes SAP PPDocument2 pagesTransactioncodes SAP PPDana BolocaNo ratings yet
- SHUBHAM BHARDWAJ Mini ProjectDocument48 pagesSHUBHAM BHARDWAJ Mini ProjectShubham TyagiNo ratings yet
- Optimize Material Requirements Planning ProcessesDocument6 pagesOptimize Material Requirements Planning ProcessesKalyan KumarNo ratings yet
- PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT SYLLABUSDocument15 pagesPRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT SYLLABUSK58 Đặng Thành VinhNo ratings yet
- Oracle Master Scheduling and Material Requirements Planning: Manufacturing Functional FoundationDocument28 pagesOracle Master Scheduling and Material Requirements Planning: Manufacturing Functional FoundationwellawellawellaNo ratings yet
- LP SemiconductorDocument7 pagesLP SemiconductorChennawit YulueNo ratings yet
- ERP - Enterprise Resource PlanningDocument57 pagesERP - Enterprise Resource PlanningdancoxxxNo ratings yet