Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diode
Uploaded by
prasanthiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diode
Uploaded by
prasanthiCopyright:
Available Formats
Q. 1: What is a PN junction? Explain the formation of depletion layer (potential barrier) in a PN junction. Q.
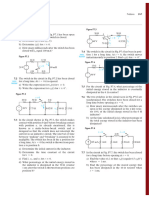
2: Discuss the behavior of a PN junction under forward and reverse biasing. Q.3: Draw and Explain the V-I Characteristics of a PN Junction. Q.4: Explain the following terms relating to PN junction (a) Knee Voltage (b) Break down voltage (c) Forward Current (d) Reverse Current (e) Maximum Forward Current (f) PIV (g) Maximum Power rating (f) Static and dynamic forward resistances (g) Reverse Resistances Q.5: Draw and explain the crystal diode equivalent circuits and models. (a) Approximate Model (b) Simplified model (c) ideal diode Q.6: Write the diode current equation and significance of used symbols. Explain the temperature effect on diode current. Q.7: Explain the limitations in the operating conditions of PN junction. Q.8: An a.c voltage of peak value of 20V is connected in series with a Si diode and a load resistance of 500 . If the forward resistance of diode is 10 find: (i) Peak current through diode (ii) Peak Output Voltage What will be these values if the diode is assumed to be ideal? Ans:(i) 37.8 mA, 18.9 V (ii) 40 mA, 20 V Q.9: Fig (1) Find the current through the diode .Assume diode to be ideal. Ans: 200 mA Q10: Fig (2) Calculate the current through 48 resistor. Assume Si diode and forward resistance of each diode is 1 . Ans: 172 mA
Fig (1)
Fig (2)
Q.11: Fig (3) Find the voltage VA using simplified model. Ans: 19.7 V Q.12: Fig (4) Determine the current I. Assume Si diodes and forward resistance of diodes to be zero. Ans: 9.65 mA
Fig (3)
Fig (4)
Q.13: Fig (5) Find VQ and ID. Use simplified model. Ans: ID = 1.55 mA, VQ = 6.2 V Q.14: Fig (6) Determine the current through each diode. Use simplified model. Assume diode to be similar. Ans: 14.3 mA
Fig (5)
Fig (6)
Q.15: Fig (7) Determine the currents I1, I2, I3. Use simplified model. Ans: I1=3.32 mA. I2= 0.212 mA, I3= 3.108 mA Q.16: Fig (8) Determine whether the diode is reversed biased or forward biased? Ans: Forward Q.17: Fig (9) Determine the state of diode and find ID and VD. Ans: OFF state, ID=0, VD=0.4V
Fig (7)
Fig (8)
Fig(9)
Q.18: Fig (10) what is the current in circuit. Assume the diode to be ideal. Ans: 10 mA Q.19: Fig (11) using equivalent, determine the current in the circuit. Assume the forward resistance of the diode to be 2 . Ans: 358 mA
Fig (10) Q.20: Fig (12) Find the voltage VA and Current I in the circuit. Q.21: Fig (13) Determine the magnitude of VA.
Fig (11) Ans: 14 V, 2 mA Ans: 9.5V
Fig (12)
Fig (13)
Q.22: Determine VO, I1, ID1 and ID2 for the parallel diode configuration of fig (14). Ans: VO = 0.7 V and ID1= ID2= 14.09 mA Q.23: Determine the dc resistance levels for the diode from its characteristics shown in fig (15). Ans: Forward resistances: 250 , 40 , reverse resistance: 10 M
Fig (14)
Fig (15)
Q.24: A Germanium diode carries a current of 1 mA at room temperature when a forward bias of 0.15 V is applied. Estimate the reverse saturation current at room temperature. Ans: 2.5 A
You might also like
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor diode and transistor tutorialDocument19 pagesSemiconductor diode and transistor tutorialmntykrNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Practice QuestionsDocument19 pagesAnalog Electronics Practice Questionssharma_rockstarNo ratings yet
- A51c146 29c4 11ed b197 02b17be2b734 - 20220910132547Document4 pagesA51c146 29c4 11ed b197 02b17be2b734 - 20220910132547narayanas1807No ratings yet
- 1 W7 Yavy 9 DN EDksrhrpukDocument7 pages1 W7 Yavy 9 DN EDksrhrpukmohinikushwaha736No ratings yet
- E-Note 12425 Content Document 20231105014816AMDocument6 pagesE-Note 12425 Content Document 20231105014816AMkartik.doye2005No ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet4 Unit2Document7 pagesTutorial Sheet4 Unit2premranjanv784No ratings yet
- ECE590 - Tutorial 3 (UiTM)Document5 pagesECE590 - Tutorial 3 (UiTM)NazhammerheartNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 1 Past Year Paper Set 2Document13 pagesElectrical and Electronic Principles 1 Past Year Paper Set 2DennyChiang60% (5)
- Basic Electronics Practive Assignment Diode1Document2 pagesBasic Electronics Practive Assignment Diode1YASHNo ratings yet
- = 6 V. (Ans. (a) 860 Ω; (b) 26.5 mW, 3.5 mW)Document2 pages= 6 V. (Ans. (a) 860 Ω; (b) 26.5 mW, 3.5 mW)Daudi Erasto MlangiNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Electronic DevicesDocument54 pagesPractice Questions For Electronic Devicesblessedgeraldie78No ratings yet
- HW 1Document9 pagesHW 1Kyto_oNo ratings yet
- Applied One Tutorial ExcerciseDocument18 pagesApplied One Tutorial ExcerciseABENEZER EPHREMNo ratings yet
- Tutorial #1Document3 pagesTutorial #1Greenhearthazel Varma PdgNo ratings yet
- Electronic 1st 7 8Document22 pagesElectronic 1st 7 8mohsindalvi87No ratings yet
- Experiment No 1 FinalDocument6 pagesExperiment No 1 Finaldipesh mandaviNo ratings yet
- BEC - ASSIGNMENT I and IIDocument6 pagesBEC - ASSIGNMENT I and IIMansi BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Tutorials Sheet No 1 Phys 2054 Nasey Fev 2022Document5 pagesTutorials Sheet No 1 Phys 2054 Nasey Fev 2022Arthur MoloNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet - PN Junction DiodeDocument2 pagesTutorial Sheet - PN Junction DiodeSubodh SinghalNo ratings yet
- University of Petroleum and Energy Studies Assignment - I: L L Z L L in S Z ZmaxDocument2 pagesUniversity of Petroleum and Energy Studies Assignment - I: L L Z L L in S Z ZmaxNikhil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems On Semiconductor DiodeDocument8 pagesSolved Problems On Semiconductor DiodeAravind KarthikNo ratings yet
- Homwork - 1Document15 pagesHomwork - 1TimoNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law Verification on Diodes Lab (EEE 3100Document9 pagesOhm's Law Verification on Diodes Lab (EEE 3100tengyanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document7 pagesTutorial 1mohammed.ksan8No ratings yet
- Electronic - 1st 7 8 PDFDocument22 pagesElectronic - 1st 7 8 PDFtazeb AbebeNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Question BankDocument1 pageModule 1 Question BankAbcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-QB-Semicond Diodes& ApplicsDocument3 pagesChapter 1-QB-Semicond Diodes& ApplicsRamyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Question BankDocument8 pagesBasic Electronics Question BankZaheer Ahmed TanoliNo ratings yet
- Assiginment QustionDocument1 pageAssiginment QustionShreyasNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 3-NOV23 - CH-1-2-3 - Feb22Document10 pagesQUIZ 3-NOV23 - CH-1-2-3 - Feb22MUHAMMAD NUR AMNI KHARIMANNo ratings yet
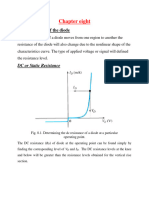
- Chapter Eight: Resistance Level of The DiodeDocument8 pagesChapter Eight: Resistance Level of The Diodedeepikat2005No ratings yet
- Voltage Regulators Tutorial: Designing Regulator Circuits for Variable Input VoltagesDocument9 pagesVoltage Regulators Tutorial: Designing Regulator Circuits for Variable Input Voltages马铃淑No ratings yet
- Important Questions For ExaminationDocument4 pagesImportant Questions For ExaminationSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Solution Sheet 2 Electronic CircuitsDocument15 pagesSolution Sheet 2 Electronic CircuitsWajdi BELLILNo ratings yet
- MCQs in Diode ApplicationsDocument16 pagesMCQs in Diode ApplicationsRJ BedañoNo ratings yet
- ECE 027 - Diode Resistance Levels and Equivalent CircuitsDocument80 pagesECE 027 - Diode Resistance Levels and Equivalent CircuitsMiyuki NakiriNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Diode - ExamplesDocument8 pagesPN Junction Diode - ExamplesNehemiah LemombianNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Principles of ElectronicsDocument13 pagesQuestion Bank - Principles of ElectronicsADDELYN CYNTHIA ANAK TONYNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 DiodesDocument52 pagesLecture 1 DiodesfaradeyisaheroNo ratings yet
- SDC- Important Questions for Semiconductor Diodes and CircuitsDocument5 pagesSDC- Important Questions for Semiconductor Diodes and CircuitsInstagramNo ratings yet
- EC101 BECE - Question BankDocument21 pagesEC101 BECE - Question Bankdarkhuntert9No ratings yet
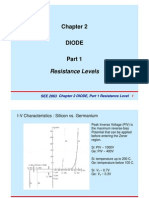
- SEE 2063 Chapter 2 DIODE Resistance Levels and Equivalent CircuitsDocument43 pagesSEE 2063 Chapter 2 DIODE Resistance Levels and Equivalent CircuitsVladMihaiVladMihaiNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 PDFDocument3 pagesSheet 2 PDFOmar Nashat100% (1)
- Sem 3 Module 1Document3 pagesSem 3 Module 1fczeroNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronic Circuits Assignment QuestionsDocument6 pagesAnalog Electronic Circuits Assignment QuestionschaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1 ElectronicsDocument4 pagesSheet 1 Electronicsbodyadel9999No ratings yet
- EE 211 Sample ExamDocument12 pagesEE 211 Sample Examlrg5092No ratings yet
- ELET1500 BJT Tutorial: E C E B C E B CDocument5 pagesELET1500 BJT Tutorial: E C E B C E B CCadane CodnerNo ratings yet
- ELET1500 BJT Tutorial: E C E B C E B CDocument5 pagesELET1500 BJT Tutorial: E C E B C E B CCadane CodnerNo ratings yet
- Tarea #1 3 2017Document4 pagesTarea #1 3 2017BayardoNo ratings yet
- DiodesDocument35 pagesDiodesTanya SoodNo ratings yet
- Ece 425. Labreport 2 LeynesDocument8 pagesEce 425. Labreport 2 LeynesRaymond LomerioNo ratings yet
- Diode Applications Tutorial Sheet Rectifier CircuitsDocument3 pagesDiode Applications Tutorial Sheet Rectifier CircuitsDaniel EkassiNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory 11Th Edition by Boylestad Nashelsky Isbn 0132622262 9780132622264 Full Chapter PDFDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory 11Th Edition by Boylestad Nashelsky Isbn 0132622262 9780132622264 Full Chapter PDFlouise.pushard527100% (17)
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory 11th Edition by Boylestad Nashelsky ISBN Test BankDocument10 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory 11th Edition by Boylestad Nashelsky ISBN Test Banklee100% (24)
- Semiconductor DiodeDocument74 pagesSemiconductor DiodeOnie EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Diode As A RectifierDocument4 pagesAssignment 3 Diode As A RectifierRajesh PathakNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Module-I: DC, DC, RMS, RMSDocument1 pageQuestion Bank For Module-I: DC, DC, RMS, RMSShubhang CharantimathNo ratings yet
- Induction Types VoltDocument7 pagesInduction Types VoltprasanthiNo ratings yet
- Measurement fundamentals, types, and instrument evolutionDocument9 pagesMeasurement fundamentals, types, and instrument evolutionprasanthiNo ratings yet
- QuesDocument7 pagesQuesprasanthiNo ratings yet
- Sequential CKTS IntroductionDocument7 pagesSequential CKTS IntroductionprasanthiNo ratings yet
- Flops Flips Char TablesDocument11 pagesFlops Flips Char TablesprasanthiNo ratings yet
- Sequential CKTS IntroductionDocument7 pagesSequential CKTS IntroductionprasanthiNo ratings yet
- Tu RCV 27MHz PCB Not AssembledDocument8 pagesTu RCV 27MHz PCB Not AssembledAndrei-Daniel BotezatuNo ratings yet
- CAT ESS Switch CalibrateDocument10 pagesCAT ESS Switch CalibrateGerichNo ratings yet
- 966F Wheel Loader Electrical SystemDocument2 pages966F Wheel Loader Electrical SystemAhmed Nahrawy82% (11)
- Push Buttons and SwitchesDocument130 pagesPush Buttons and SwitchesVijay BhureNo ratings yet
- HPGR Vega LsDocument24 pagesHPGR Vega LsLuis Kevin Talavera RojasNo ratings yet
- Peserta Dan Materi Kls ADocument3 pagesPeserta Dan Materi Kls ARuri nabillahNo ratings yet
- Sepcification of PSGSG149 CABLE TERMINATION PDFDocument10 pagesSepcification of PSGSG149 CABLE TERMINATION PDFzaheeruddin_mohdNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies: Weekly Test - 7/SEM-2Document3 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies: Weekly Test - 7/SEM-2rohitarya27No ratings yet
- ABB Electrical Wiring AccessoriesDocument2 pagesABB Electrical Wiring Accessoriesവർഗീസ് ജോസഫ്0% (1)
- Star Delta Starting Basics for AC MotorsDocument5 pagesStar Delta Starting Basics for AC Motorsjoe silverNo ratings yet
- Drdoreport Final PDFDocument43 pagesDrdoreport Final PDFRavinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Sample Material Checklist-DIANTHADocument2 pagesSample Material Checklist-DIANTHAMohd Jamal Mohd MoktarNo ratings yet
- Coordination of Reclosers With FusesDocument4 pagesCoordination of Reclosers With FusesKoifer Quispe ValdezNo ratings yet
- HVR Pentagon Heavy Duty Power Resistors SpecsDocument2 pagesHVR Pentagon Heavy Duty Power Resistors Specsrajeshgat2008No ratings yet
- HCI434FS/444FS - Technical Data SheetDocument8 pagesHCI434FS/444FS - Technical Data SheetHERS14No ratings yet
- 9D54203 Power Electronic Control of AC DrivesDocument1 page9D54203 Power Electronic Control of AC DrivesKiran Kumar100% (1)
- BMW WallboxDocument24 pagesBMW WallboxRicardo Feldhaus KrisanoskiNo ratings yet
- Mwakibete Substation-Final ReportDocument6 pagesMwakibete Substation-Final ReportNuru TwahaNo ratings yet
- DL PU酗尸: Products Ma■UalDocument24 pagesDL PU酗尸: Products Ma■UalMahmoudNo ratings yet
- BOSS Slow Gear SG-1 Attack DelayDocument1 pageBOSS Slow Gear SG-1 Attack Delay大石 真義No ratings yet
- ALTERNATOR EMF CALCULATIONSDocument7 pagesALTERNATOR EMF CALCULATIONSJay Mark BalaneNo ratings yet
- Power Distribution Systems and Its Characteristics IDocument16 pagesPower Distribution Systems and Its Characteristics IMohammedSaadaniHassani100% (1)
- P - Chapter 7Document17 pagesP - Chapter 7usa2017lapNo ratings yet
- EEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 3 - Diode ApplicationsDocument3 pagesEEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 3 - Diode Applicationsdonatello84No ratings yet
- Lme N7101Document27 pagesLme N7101alexjoelNo ratings yet
- DC - Machines and Batteries Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesDC - Machines and Batteries Lesson PlanBilalNo ratings yet
- Electrical Diagram Himoinsa PDFDocument10 pagesElectrical Diagram Himoinsa PDFTaras KutsykNo ratings yet
- How To Build A Simple But Powerful Flyback DriverDocument8 pagesHow To Build A Simple But Powerful Flyback DriverGabriel Droguett OleaNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance NotesDocument27 pagesInsulation Resistance NotessdvijayNo ratings yet
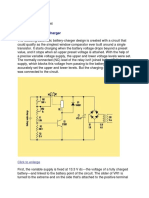
- Automatic Battery Charger: Schematics Beginners PowerDocument2 pagesAutomatic Battery Charger: Schematics Beginners PowerCris DucusinNo ratings yet