Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hazardous Locations Classifications Descriptions
Uploaded by
vofaithOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hazardous Locations Classifications Descriptions
Uploaded by
vofaithCopyright:
Available Formats
Hazardous Locations Classifications Descriptions
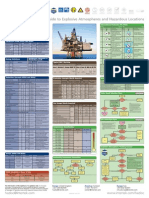
The essence of Hazardous area classifications is to protect installations from a potential explosion. It helps to ensure the correct selection and installation of equipment to prevent an explosion and to ensure safety of life in a potentially hazardous environment. The methods used to classify an installation are generally are two main types of classification namely: - The IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) philosophy referred to as Zoning - The North American installations classified by Classes, Divisions and Groups A summary of these classifications is provided in table 1 below
Another form of classification is the Auto-Ignition Rating summarized below in Table 2 below Auto Ignition Temperature (T) Rating European/IEC North Maximum Classification American Surface Classification Temperature T1 T1 450 T2 T2 300 T2A 280 T2B 260 T2C 230 T2D 215 T3 T3 200 T3A 180 T3B 165 T3C 160 T4 T4 135 T4A 120 T5 T5 100 T6 T6 85
Temperature
Table 2: Hazardous area classification based on Auto-ignition or T rating
CLASSIFICATION BY TYPE OF HAZARD Flammable material Gases, vapors, or liquids Benzene Butane Propane Combustible dusts Flour Starch Wood Plastic Fibers/materials producing combustible flyings Cotton Saw dust
Example(s) North American ANSI/NFPA/NEC Classification
Methane
Acetylene
Hydrogen
Ethylene
Metal -Dust
Carbon Charcoal
CLASS GROUP Divisions Div. 1
CLASS I
CLASS II
CLASS III
Div. 2 Group I Mining Zone 0-gases Zone 20-Dusts Zone 1-Gases Zone 21-Dusts Zone 2-Gases Zone 22- Dusts
GROUP European/IEC Grouping Zones
A B C D E F G Where ignitable concentration of gas, vapors or Where ignitable amount of dusts or flyings is present liquids is present within the atmosphere under within the atmosphere under normal conditions. normal conditions. Where ignitable amount of flammable material Where ignitable amount of dusts or flyings is present is present within the atmosphere under within the atmosphere under abnormal conditions. abnormal conditions. Group II Surface Industry C B A A hazardous atmosphere is highly likely to be present and may be present for long periods of time (>1000hrs/year) or even continuously A hazardous atmosphere is possible to be but unlikely to be present for long periods of time (>10<1000hrs/year). A hazardous atmosphere is not likely to be present in normal operation or infrequently and for short periods of time (<10 hrs/year)
Table 1: Summary of Hazardous area classification method
You might also like
- Intertek Poster A1 (HazLoc - Guide) - 0Document1 pageIntertek Poster A1 (HazLoc - Guide) - 0Antonio FilipeNo ratings yet
- Vickers General Hydraulic BookDocument29 pagesVickers General Hydraulic BookKarthik Sarang100% (15)
- Hazardous Area Classification FactsDocument1 pageHazardous Area Classification FactsLisbeth Roos RoosNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Standard: (R) Fittings, Straight Threaded Boss or Flanged, Fluid ConnectionDocument16 pagesAerospace Standard: (R) Fittings, Straight Threaded Boss or Flanged, Fluid ConnectionAlberto De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Hazardous Area ClassificationDocument8 pagesGuidelines On Hazardous Area ClassificationKalam NagappanNo ratings yet
- ASAT Class 7Document16 pagesASAT Class 7kamalsharma2014100% (1)
- Hazardous Area TerminologyDocument7 pagesHazardous Area TerminologyDayo IdowuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering - Hazardous Area ClassificationDocument1 pageChemical Engineering - Hazardous Area Classificationsl1828No ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Table IEC & NEC (NEMA) Cooper Crouse Hinds PDFDocument1 pageHazardous Area Table IEC & NEC (NEMA) Cooper Crouse Hinds PDFAgustinus Made Theo Dwijaya100% (4)
- Chemical Plant and Its Operation: Including Safety and Health AspectsFrom EverandChemical Plant and Its Operation: Including Safety and Health AspectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sample Pressure Vessel DatasheetDocument2 pagesSample Pressure Vessel Datasheetvofaith67% (3)
- Underground Pipe Stress Check CalculationsDocument6 pagesUnderground Pipe Stress Check Calculationsani_datNo ratings yet
- SAILMA Steel Grades & SheetsDocument2 pagesSAILMA Steel Grades & SheetsElumalai SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Basics of Explosion Protection - IecDocument4 pagesBasics of Explosion Protection - IecbenounaomarNo ratings yet
- FM-23-85 60mm Mortar M19 1967Document174 pagesFM-23-85 60mm Mortar M19 1967rigal849No ratings yet
- Rectangular Tank SizingDocument8 pagesRectangular Tank Sizingvofaith100% (16)
- Hazardous Area Classification & Intrinsic SafetyDocument35 pagesHazardous Area Classification & Intrinsic SafetyMukesh C ChavanNo ratings yet
- Ingress SafetyDocument1 pageIngress Safetyjohn_tigerNo ratings yet
- Hazardous AREA ClassificationDocument10 pagesHazardous AREA Classificationfarzam100% (1)
- Dubai Municipality G+12 Concrete & Shoring QuestionsDocument7 pagesDubai Municipality G+12 Concrete & Shoring QuestionsMohammed Nasih Vettathur100% (2)
- Use Electric Heaters HazardousDocument3 pagesUse Electric Heaters Hazardousn.hartonoNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Areas ClassificationsDocument6 pagesHazardous Areas ClassificationsAV ShrinivasNo ratings yet
- Cryogenics Safety Manual: A Guide to Good PracticeFrom EverandCryogenics Safety Manual: A Guide to Good PracticeNo ratings yet
- Ceng204P Separation Processes I Coursework 1: 1. Problem DescriptionDocument3 pagesCeng204P Separation Processes I Coursework 1: 1. Problem DescriptionKaren Chong Yap100% (1)
- 1 DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument96 pages1 DNA Structure and ReplicationmattMd100% (1)
- Design of Fatigue StrengthDocument21 pagesDesign of Fatigue StrengthRaviteja VgaNo ratings yet
- Class I Locations GuideDocument230 pagesClass I Locations GuideVea ValcorzaNo ratings yet
- EX Plakat GBDocument1 pageEX Plakat GBBohumil NáplavaNo ratings yet
- Safety. Everywhere.: Electrical Equipment Non-Electrical EquipmentDocument1 pageSafety. Everywhere.: Electrical Equipment Non-Electrical EquipmentNavin KeralaNo ratings yet
- Pump Sizing Calculation SheetDocument7 pagesPump Sizing Calculation Sheetvofaith100% (2)
- Hazardous Area Electrical Equipment: Area Classification, Zoning, Temperature LimitsDocument21 pagesHazardous Area Electrical Equipment: Area Classification, Zoning, Temperature Limitsakhilesh_kabra17100% (1)
- Critical Attributes of Folding Cartons 2Document8 pagesCritical Attributes of Folding Cartons 2Wanda Yee100% (1)
- Guide To Hazardous AreasDocument14 pagesGuide To Hazardous Areasayman jummaNo ratings yet
- At ExDocument2 pagesAt ExMoustafa Ibrahim YehyaNo ratings yet
- Norma AtexDocument4 pagesNorma AtexV_VicNo ratings yet
- 207-x Marking UkDocument4 pages207-x Marking UkgueridiNo ratings yet
- AMIE Project Synopsis ReportDocument10 pagesAMIE Project Synopsis ReportpavanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Hazardous Area Classification PDFDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Hazardous Area Classification PDFNaveed IrshadNo ratings yet
- WEG Guide To Explosive Atmospheres Wallchart 50042119 Quick Guide EnglishDocument1 pageWEG Guide To Explosive Atmospheres Wallchart 50042119 Quick Guide EnglishDave CNo ratings yet
- WEG Guide To Explosive Atmospheres Wallchart 50042119 Quick Guide EnglishDocument1 pageWEG Guide To Explosive Atmospheres Wallchart 50042119 Quick Guide EnglishJohnNo ratings yet
- Svacina Larson - Understanding Hazardous Area Sensing - Intrinsic Safety - Part2Document10 pagesSvacina Larson - Understanding Hazardous Area Sensing - Intrinsic Safety - Part2AbdelRahmanNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Classification General: Zone 0 Zone 1 Zone 2Document3 pagesHazardous Area Classification General: Zone 0 Zone 1 Zone 2Zulkernain Omer TariqNo ratings yet
- Explosion Protection BasicsDocument59 pagesExplosion Protection Basicspromod kalyaniNo ratings yet
- Eye C GasDocument3 pagesEye C GasLuis ReyesNo ratings yet
- Intertek MarkingsDocument15 pagesIntertek MarkingsAmir MobiniNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Locations: C.E.C. ClassificationsDocument4 pagesHazardous Locations: C.E.C. ClassificationsThananuwat SuksaroNo ratings yet
- Hazardous AreasDocument4 pagesHazardous AreasChoochart ThongnarkNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Classification & Explosion Prevention Techniques PDFDocument19 pagesHazardous Area Classification & Explosion Prevention Techniques PDFMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Signals Alarms CatalogDocument92 pagesSignals Alarms CatalogSrta IncognitaNo ratings yet
- MAXON PresentationDocument27 pagesMAXON PresentationJaroslav KurucNo ratings yet
- Install Harmony I/O in Class 1 Div 2 Hazardous LocationsDocument17 pagesInstall Harmony I/O in Class 1 Div 2 Hazardous LocationsYhony Gamarra VargasNo ratings yet
- Classification of Hazardous AreasDocument1 pageClassification of Hazardous Areasadhi2001No ratings yet
- Hazardous Area ClassificationDocument37 pagesHazardous Area ClassificationjovanivanNo ratings yet
- Eflare Hazard ChartDocument2 pagesEflare Hazard Chartastral05No ratings yet
- Electrical Equipment in Hazardous AreasDocument8 pagesElectrical Equipment in Hazardous AreasMehulkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Classification in AmericaDocument4 pagesHazardous Area Classification in AmericaIndrayana PratamaNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Areas Are Defined by Three Main CriteriaDocument10 pagesHazardous Areas Are Defined by Three Main CriteriaviddyadrianNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area ClassificationDocument27 pagesHazardous Area Classificationddkb.2255No ratings yet
- XP Rating ExplanationDocument5 pagesXP Rating ExplanationTom SwiatekNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area ZonesDocument8 pagesHazardous Area ZonessiddharthangandhiNo ratings yet
- Environments and Standards - The ATEX Standard - Petzl PDFDocument3 pagesEnvironments and Standards - The ATEX Standard - Petzl PDFtintucinbNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Classifications - A Comprehensive Safety GuideDocument26 pagesHazardous Area Classifications - A Comprehensive Safety Guidesatya krishna chagantiNo ratings yet
- Safety Master FileDocument9 pagesSafety Master FilePrathmesh GujaratiNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Classification Innoil & Gas IndustryDocument34 pagesHazardous Area Classification Innoil & Gas Industrygastro9956No ratings yet
- Data AtexDocument4 pagesData AtexdursosonoNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Electrical InstallationsDocument2 pagesMaintaining Electrical InstallationsRol2No ratings yet
- Hazardous Source ListDocument28 pagesHazardous Source ListmahradNo ratings yet
- LASL Explosive Property DataFrom EverandLASL Explosive Property DataTerry R. GibbsNo ratings yet
- Environment and Energy: Environmental Aspects of Energy Production and Use with Particular Reference to New Technologies a Report of the United Nations Economic Commission for EuropeFrom EverandEnvironment and Energy: Environmental Aspects of Energy Production and Use with Particular Reference to New Technologies a Report of the United Nations Economic Commission for EuropeNo ratings yet
- Eternal RewardsDocument1 pageEternal RewardsvofaithNo ratings yet
- The King ComesDocument1 pageThe King ComesvofaithNo ratings yet
- Transifiguration NovemberDocument2 pagesTransifiguration NovembervofaithNo ratings yet
- The King ComesDocument1 pageThe King ComesvofaithNo ratings yet
- PUMP SIZING FORMULAEDocument1 pagePUMP SIZING FORMULAEvofaithNo ratings yet
- Tutorials PumpDocument1 pageTutorials PumpvofaithNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Basic Principles & TechniquesDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Basic Principles & TechniquesHasan shaikhNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecules 9Document3 pagesBio Molecules 9SilVI MARDELNo ratings yet
- QSonic Brochure 209Document12 pagesQSonic Brochure 209Anish DonaldNo ratings yet
- Integrate Planck's Function Using Gamma FunctionDocument14 pagesIntegrate Planck's Function Using Gamma FunctionMaxtron Evelyn MoonNo ratings yet
- Polyaldo PolyglycerolEsters SLSDocument8 pagesPolyaldo PolyglycerolEsters SLSSantos GarciaNo ratings yet
- Rotary Heat ExchangerDocument32 pagesRotary Heat Exchangerntt_121987No ratings yet
- Antioxidant Enzyme EvaluationDocument14 pagesAntioxidant Enzyme EvaluationArpit JainNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 3Document6 pagesChemistry Paper 3NasaNo ratings yet
- Hardtop XP (Azad)Document5 pagesHardtop XP (Azad)Anonymous f1NlMPnNo ratings yet
- Device Code ListDocument383 pagesDevice Code ListBach BuiNo ratings yet
- Carbon Steel Flanges - Pressure and Temperature Ratings - Group 1.1 - Carbon SteelDocument7 pagesCarbon Steel Flanges - Pressure and Temperature Ratings - Group 1.1 - Carbon Steelnoha azamaliNo ratings yet
- Onqor: Product BulletinDocument2 pagesOnqor: Product BulletinAhmed ChahineNo ratings yet
- Tarlochan, 2013Document11 pagesTarlochan, 2013Farhan Fachrizal BahriNo ratings yet
- High Carbon Wire RodDocument9 pagesHigh Carbon Wire Rodninganray6316100% (1)
- Chemistry 9 Chap 1 Long QADocument17 pagesChemistry 9 Chap 1 Long QAAkbar Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- Drying Technology: An International JournalDocument53 pagesDrying Technology: An International JournalNishant Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- MHS-15 Prod NoteDocument2 pagesMHS-15 Prod Noteyenlitu50% (2)