Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Logistics Management
Uploaded by
Sana KhanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Logistics Management
Uploaded by
Sana KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
EIILM UNIVERSITY, SIKKIM
TERM END EXAMINATIONS, FEBRUARY, 2012 EXECUTIVE MBA- OPERATIONS MGMT., 2SEM/1YEAR LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT Time: 3 hours Note: - Attempt any 5 questions. All questions carry equal marks 1. What is logistics management? Logistics management is the governance of supply chain functions. Logistics management activities typically include inbound and outbound transportation management, fleet management, warehousing, materials handling, order fulfillment, logistics network design, inventory management, supply/demand planning, and management of third party logistics services providers. To varying degrees, the logistics function also includes customer service, sourcing and procurement, production planning and scheduling, packaging and assembly. Logistics management is part of all levels of planning and execution -- strategic, operational and tactical. It is an integrating function, which coordinates all logistics activities, as well as integrates logistics activities with other functions including marketing, sales manufacturing, finance, and information technology. 2. 3. 4. 5. Give the formulae that are used for calculating the total transportation cost. List the mission that a logistical system of an organization follows. What are the various transportation models. Give their advantage and disadvantages. What do you mean by physical distribution? M.Marks:60
Physical distribution is the set of activities concerned with efficient movement of finished goods from the end of the production operation to the consumer. Physical distribution takes place within numerous wholesaling and retailing distribution channels, and includes such important decision areas as customer service, inventory control, materials handling, protective packaging, order procession, transportation, warehouse site selection, and warehousing. Physical distribution is part of a larger process called "distribution," which includes wholesale and retail marketing, as well the physical movement of products.
Physical distribution activities have recently received increasing attention from business managers, including small business owners. This is due in large part to the fact that these functions often represent almost half of the total marketing costs of a product. In fact, research studies indicate that physical distribution costs nationally amount to approximately 20 percent of the country's total gross national product (GNP). These findings have led many small businesses to expand their cost-cutting efforts beyond their historical focus on production to encompass physical distribution activities. The importance of physical distribution is also based on its relevance to customer satisfaction. By storing goods in convenient locations for shipment to wholesalers and retailers, and by creating fast, reliable means of moving the goods, small business owners can help assure continued success in a rapidly changing, competitive global market.
A SYSTEM APPROACH
Physical distribution can be viewed as a system of components linked together for the efficient movement of products. Small business owners can ask the following questions in addressing these components:
Customer service hat level of customer service should be provided? Transportation will the products be shipped? Warehousing here will the goods be located? How many warehouses should be utilized? Order processing should the orders be handled? Inventory control much inventory should be maintained at each location? Protective packaging and materials handling can efficient methods be developed for handling goods in the factory, warehouse, and transport terminals?
These components are interrelated: decisions made in one area affect the relative efficiency of others. For example, a small business that provides customized personal computers may transport finished products by air rather than by truck, as faster delivery times may allow lower inventory costs, which would more than offset the higher cost of air transport. Viewing physical distribution from a systems perspective can be the key to providing a defined level of customer service at the lowest possible cost.
6. 7. 8. 9.
What is the role of Inventory in logistics management? Describe the concept of packaging. What are the logistical functions of packaging? Discuss and differentiate between marketing and logistics approaches. Write a note on the various forms of protective packaging.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- KX-NS Version 8.3 KX-NSX Version 5.3 Software Release Note: October 9, 2020Document70 pagesKX-NS Version 8.3 KX-NSX Version 5.3 Software Release Note: October 9, 2020Serge GolonNo ratings yet
- Additional Questionsv3Document222 pagesAdditional Questionsv3Konstantin TsolovNo ratings yet
- Estatement - 2022 09 19Document2 pagesEstatement - 2022 09 19Ishvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Tugas Pengantar Akuntansi-1Document23 pagesTugas Pengantar Akuntansi-1Wiedya fitrianaNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain DriversDocument11 pagesSupply Chain DriversamnaNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis of ICICI Bank Reveals Strengths and Growth OpportunitiesDocument6 pagesSWOT Analysis of ICICI Bank Reveals Strengths and Growth Opportunitiessouvikrock12No ratings yet
- Form Ngao Limited to acquire businessDocument6 pagesForm Ngao Limited to acquire businessJames WisleyNo ratings yet
- SLB Local Salary DeductionDocument1 pageSLB Local Salary DeductionRicardo HoustonNo ratings yet
- Hulo Integrated National High School Contact DetailsDocument36 pagesHulo Integrated National High School Contact DetailsHellen.DeaNo ratings yet
- StatementDocument3 pagesStatementDarshan70No ratings yet
- Radwin 2000 Portfolio: Carrier-Class Point-To-Point SolutionsDocument8 pagesRadwin 2000 Portfolio: Carrier-Class Point-To-Point Solutionsmarcelo arayaNo ratings yet
- Activity Working Capital ManagementDocument2 pagesActivity Working Capital ManagementJoshua BrazalNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management in Financial ServicesDocument24 pagesCustomer Relationship Management in Financial ServicesDharmikNo ratings yet
- Loop-AM3440-C Access DCS-MUXDocument44 pagesLoop-AM3440-C Access DCS-MUXDuncan GitauNo ratings yet
- KCCTech Services and Solutions TIP SIDocument7 pagesKCCTech Services and Solutions TIP SIKuda BetinaNo ratings yet
- Online Shoping With ShopeeDocument7 pagesOnline Shoping With ShopeeXII MM1Reiza Fauzan FirdausNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure Hosting and Deployment OptionsDocument31 pagesInfrastructure Hosting and Deployment OptionsNadia MaryamNo ratings yet
- Tally Spss PDFDocument42 pagesTally Spss PDFAkshay PoplyNo ratings yet
- Module - 2 Auditor'S Report: Objectives of The AuditorDocument20 pagesModule - 2 Auditor'S Report: Objectives of The AuditorVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Bar Graph Unit MonthDocument2 pagesBar Graph Unit MonthsushantinhbiNo ratings yet
- PEMI - Redemption Order Form (ROF)Document1 pagePEMI - Redemption Order Form (ROF)ippon_osotoNo ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument14 pagesTCP IprrrNo ratings yet
- International Commercial Terms (INCOTERMS)Document9 pagesInternational Commercial Terms (INCOTERMS)albertNo ratings yet
- Sustainability of MFI's in India After Y.H.Malegam CommitteeDocument18 pagesSustainability of MFI's in India After Y.H.Malegam CommitteeAnup BmNo ratings yet
- Gerontological Nursing: Principles of GeriatricsDocument20 pagesGerontological Nursing: Principles of GeriatricsMyrrha Velarde Filomeno TaganasNo ratings yet
- Server Side Web Application Attacks Cont...Document24 pagesServer Side Web Application Attacks Cont...Basharat AliNo ratings yet
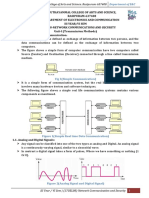
- NCS Unit 1 - Transmission MethodsDocument16 pagesNCS Unit 1 - Transmission Methodsnanobala15No ratings yet
- Fundamental of RetailingDocument1 pageFundamental of RetailingDeepak Singh NegiNo ratings yet
- Investment Fund Types and CostsDocument15 pagesInvestment Fund Types and Costsraqi148No ratings yet
- WRAP-hybrid satellite-terrestrial-communication-networks-maritime-Internet-of-Things-Chen-2021Document29 pagesWRAP-hybrid satellite-terrestrial-communication-networks-maritime-Internet-of-Things-Chen-2021Nenad VujovicNo ratings yet