Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Property Information For Steel Alloys
Uploaded by
sarvaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Property Information For Steel Alloys
Uploaded by
sarvaCopyright:
Available Formats
Property Information for Steel Alloys
MatWeb has material property data sheets for over 5000 steel data sheets based on unique compositions, dimensions, producers, and/or heat treatments. The steels are primarily categorized by ASTM and AISI numbers, but users can also search MatWeb using designation systems from other countries - try entering these equivalent designations in our 'Quick Search'. Hundreds of steel data sheets from major mills (Allegheny Ludlum, Carpenter Steel, Allvac, Timken Latrobe, AK Steel, Uddeholm, etc.), including high performance stainless steel and other proprietary alloys, are also available in MatWeb's database listed under the manufacturer's name. MatWeb also has entries from producers of niche products such as welding filler metal and powders for sintering and metal injection molding. Some of the international alloy designation lists are incomplete, but new alloy designations are being added regularly. SAE UNS ISO (International) NBN (Belgium) VSM (Switzerland) NS (Norway) MSZ (Hungary) GOST (Russia) IS (India) FED DEF STAN (Canada) EURONORM (Europe) AFNOR (France) UNI (Italy) SIS & SS (Sweden) CSN (Czechoslovakia) BDS (Bulgaria) MIL-SPEC DGN (Mexico) BS (United Kingdom) DIN (Germany) UNE (Spain) SFS (Finland) AS (Australia) TS (Turkey) JIS (Japan) DoD COPANT (Pan America) NEN (Netherlands) ONORM (Austria) DS & FS (Denmark) PN (Poland) STAS (Romania) GB and YB (China)
For example, if you were to type the German alloy designation DIN 1.4828 (watch spacing and punctuation) in the Search box in the navigation bar, MatWeb's search would return AISI Type 309 Stainless Steels, which are similar in composition to DIN 1.4828 Steel. It is also possible to search for specific classes of steels such as low, medium, or high carbon steels, alloy steels, tool steels, stainless steel, etc. You can find typical values such as tensile strength, density, and thermal conductivity for steel alloys under the name Steels, General Properties. If you know the alloy number in which you are interested (i.e. 1020 Steel or DIN 1.0402), type it in the search box in the navigation bar at the top of each MatWeb page.
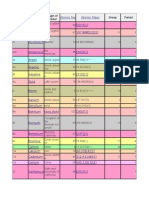
Electrode Reference Chart
This reference chart is a guide to the properties and usage of common arc welding electrodes. These are generic properties, there will be exceptions. Some manufacturers classify electrodes differently to other manufacturers and some electrodes do not fall perfectly into one category. For a guide to the codes used on electrodes see electrode classification, and for more information about which rods are suitable for which materials see welding different steels.
Electr ode
Curre nt type
OCV
Fille Positi Fini t/ on sh Butt
Penetra Spatt tion er
Arc Stren gth
Arc Gap
Tou ch arc
Comm on name/ Type
Notes
6010
DC+
High
All
Poo r
High
High
High
Varia ble
No
Mostly used in pipe Cellulos welding. High ic hydroge n weld content.
6011
AC DC+/ -
High
All
Poo r
High
High
High
Varia ble
No
Cellulos As ic above
6012
AC DC -
Any
D/ OH/ H/ V.up
F/B
Goo Med d
High
Med
Varia ble
Yes
Rutile
Once popular, superce ded by Low Hyd and 6013 electrod es.
6013
AC DC+/ -
Any
D/ OH/ H/V.u F/B p/ V.dn some
Bes t
Low
V.Lo w
V.Low
Varia ble
Yes
Rutile
General purpose electrod e.
7014
AC DC+/ -
Any/H igh
D/ H
Goo Low d
Low
Low
Varia ble
Yes
High efficienc Iron y Powder electrod e Good position al electrod e, high strength deposit. Good position al electrod e, high strength deposit.
7015
DC+
High
D/ OH/ H/ V.up
Goo High d
High
Med
Tight
No
Low Hydrog en/ Basic
7016
AC DC+/ -
Any/H igh
D/ OH/ H/ V. up
Goo High d
High
Med
Tight
No
Low Hydrog en/ Basic
7018
AC DC+/ -
Any/H igh
D/ OH/ H/ V.up
F/B
Goo High d
Low
Med
Tight
No
Low Hydrog en/ Basic
Good position al electrod e, high strength deposit, high efficienc y
7024
AC DC+/ -
Any/H igh
D /H
Goo Low d
V.Lo w
V.Low
Varia ble
Yes
High efficienc Iron y Powder electrod e
Notes
OCV - Rods referred to as Any/High vary with manufacturer. Some makes will need a high OCV. Position - D - Downhand/ Flat, OH - Overhead, H - Horizontal, V.up - Vertical Up, V.Down Vertical Down. If in bold, rod is particularly suited to this position. Arc Gap - Tight means the arc must be kept as tight as possible to ensure weld quality. Risk of pinholes/porosity and high hydrogen content in weld. Rod drying - Cellulosic rods normally need no drying. All other rods should be kept dry. Low Hydrogen rods should be dried/baked before use according to manufacturers instructions. 60xx, 70xx etc refers to strength of weld material. Higher values are available eg 80xx, 90xx, for specialist uses. Additional designations, eg 7018-1, may refer to low temperature impact values "High Efficiency" electrodes have a flux high in iron, which adds to the quantity of weld deposited.
The most commonly available electrodes in the UK are E6013 types, followed by E7018. In the US the E7014 is also popular. Other designations tend to be used for specific purposes in industry and may be difficult to obtain or uneconomic for the home user. E6013 are easy to use and store; E7018 are a good freeze/fill positional electrode but require careful storage and use. E7016 are normally identical to E7018 but with a thinner flux coating, hence are ideal for V.Up welds. E6010/6011 electrodes have a very thin coating, a strong harsh arc, can operate in any position and are a highly controllable rooting rod, but should be capped with other rods to avoid cracking. Other common types: Stainless steel rods are manufactured in many grades and types and will be specific to use/ position etc. Common grades include 308l, 309l, 312, 316l. Electrodes are available in many other materials for many uses. Manufacturers websites/ data sheets/ technical departments should be consulted for type, use and availability.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Chem 11 Exam Review With AnswersDocument100 pagesChem 11 Exam Review With Answerskatwal0963% (19)
- Table of Elements ChartDocument12 pagesTable of Elements ChartGRascia OnaNo ratings yet
- Registered Company Trade License NoDocument136 pagesRegistered Company Trade License NoJaveed Taji100% (1)
- Rutile Oct17Document2 pagesRutile Oct17api-308735650100% (3)
- Chemical Composition of Nickel AlloysDocument4 pagesChemical Composition of Nickel AlloysHeanjiaAlloysNo ratings yet
- Extractive MetallurgyDocument52 pagesExtractive MetallurgyMohamed TreXxNo ratings yet
- Isotopes and Atomic Mass LabDocument4 pagesIsotopes and Atomic Mass LabjustinNo ratings yet
- The Book of Alternative Photographic Processes 3rd EditionDocument61 pagesThe Book of Alternative Photographic Processes 3rd Editioncharles.chapman882100% (39)
- OSHA3348 Metal Scrap RecyclingDocument48 pagesOSHA3348 Metal Scrap RecyclingsarvaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Thermal Cutting PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 12 - Thermal Cutting PDFsarvaNo ratings yet
- Vidya Deep - Solar Reading Lamp - BrochureDocument2 pagesVidya Deep - Solar Reading Lamp - BrochuresarvaNo ratings yet
- Tech NovaDocument5 pagesTech NovasarvaNo ratings yet
- Feng Shui For OfficeDocument3 pagesFeng Shui For OfficesarvaNo ratings yet
- How To Build Trust To Empower RelationsDocument2 pagesHow To Build Trust To Empower RelationssarvaNo ratings yet
- Feng Shui For OfficeDocument3 pagesFeng Shui For OfficesarvaNo ratings yet
- Live A Better Life With RudrakshasDocument2 pagesLive A Better Life With Rudrakshassarva100% (1)
- The Infectious AcidityDocument3 pagesThe Infectious AciditysarvaNo ratings yet
- QMS FormDocument4 pagesQMS FormsarvaNo ratings yet
- Brain Teasers - With AnswersDocument4 pagesBrain Teasers - With AnswerssarvaNo ratings yet
- 11 Habits That Will Help You Live To LongerDocument4 pages11 Habits That Will Help You Live To LongersarvaNo ratings yet
- Sri Hanuman Chalisa in HindiDocument3 pagesSri Hanuman Chalisa in HindiSrivatsa97% (31)
- 11 Habits That Will Help You Live To LongerDocument4 pages11 Habits That Will Help You Live To LongersarvaNo ratings yet
- 100 Benefits of MeditationDocument4 pages100 Benefits of MeditationHero DevraniNo ratings yet
- Strengthening Weak TeethDocument2 pagesStrengthening Weak TeethsarvaNo ratings yet
- The Perfect Finish Special Desserts For Every OccasionDocument12 pagesThe Perfect Finish Special Desserts For Every OccasionsarvaNo ratings yet
- Good Health Comes FirstDocument2 pagesGood Health Comes FirstsarvaNo ratings yet
- Life Is A Football PitchDocument3 pagesLife Is A Football PitchsarvaNo ratings yet
- The BeginningDocument2 pagesThe BeginningsarvaNo ratings yet
- Know Your ComputerDocument20 pagesKnow Your ComputersarvaNo ratings yet
- FMTS-C PsDocument2 pagesFMTS-C PspostscriptNo ratings yet
- ExperimentDocument7 pagesExperimenttedfsx256No ratings yet
- Basic Water Quality Laboratory Procedures Manual PDFDocument160 pagesBasic Water Quality Laboratory Procedures Manual PDFFlorian Tiappi100% (1)
- Ch4 Watertreatment DisinfectionDocument30 pagesCh4 Watertreatment DisinfectionSUBHAM KumarNo ratings yet
- X1 Classic Brass and Alum.Document10 pagesX1 Classic Brass and Alum.Scott HoldmanNo ratings yet
- Chrome Yellow ExperimentDocument3 pagesChrome Yellow ExperimentAkhil KumarNo ratings yet
- PCA Chapter 7 - Mixing Water For ConcreteDocument29 pagesPCA Chapter 7 - Mixing Water For ConcreteMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- ATOMIC HYDROGEN WELDING PROCESSDocument56 pagesATOMIC HYDROGEN WELDING PROCESSsbs271187No ratings yet
- Radio PF6Document23 pagesRadio PF6FaustoCamachoNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Line ArrayDocument12 pagesCatalogo Line Arrayrafa8607No ratings yet
- Intensive Class Chemistry SPMDocument30 pagesIntensive Class Chemistry SPMnabahatumblr100% (2)
- Removal of Chromium From Tannery Solid WasteDocument7 pagesRemoval of Chromium From Tannery Solid WasteLuis Paz Soldán G100% (1)
- Gtaw 03Document40 pagesGtaw 03பத்மநாபன் ஶ்ரீநிவாஸன்No ratings yet
- Vitamins and Minerals Dietary Reference IntakesDocument3 pagesVitamins and Minerals Dietary Reference IntakesMashiachbendavid Covarrubias HurtadoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry WorksheetDocument1 pageCBSE Class 11 Chemistry WorksheetHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Hydrometallurgy: Hajime Miki, Michael NicolDocument5 pagesHydrometallurgy: Hajime Miki, Michael NicolOscar Salazar MorenoNo ratings yet
- Duplex Stainless Steel LDX 2101 - MEGA MEXDocument3 pagesDuplex Stainless Steel LDX 2101 - MEGA MEXNitinNo ratings yet
- Fe Fe3c Diagram PDFDocument2 pagesFe Fe3c Diagram PDFAmyNo ratings yet
- Anodizado PDFDocument5 pagesAnodizado PDFValentin GuzmanNo ratings yet
- K Factor For Several GasesDocument3 pagesK Factor For Several Gasesaldaadrina100% (1)
- Copper Alloy Cross ReferenceDocument3 pagesCopper Alloy Cross ReferencenotZm62FNo ratings yet
- Moles QPDocument10 pagesMoles QPishraqtazishraqNo ratings yet