Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Managerial Accounting Examen
Uploaded by
abalasa54Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Managerial Accounting Examen
Uploaded by
abalasa54Copyright:
Available Formats
5.
Activity based costing(ABC) The basic premises of ABC: Activities consume resources and products consume activities Activities cause cost, not product
Organization is divided in small activities used to determine overheads. An activity is anevent, task or unit of work with a specified purpose, such as: designing products, setting up machines, operation machines, etc. ABC systems calculate the costs of individual activities and assign costs to cost objects by using cost drivers. Examples of cost drivers: Number of purchase orders Number of prod. set-ups Number of dispatches
Cost calculation
Product cost = Direct cost + A share of overheads related to the number of cost drivers units Overheads allocated to a product cost = Activity cost * number of cost driver units driver rates Activity cost driver rate=Activity cost/Total number of cost driver units
The Steps for developing an ABC system: Step 1: Analyse and define activities Step 2:Assign costs to activities Step 3: Determine the cost driver for each activity Step 4: Identify activities centre Step 5: Assign costs to products
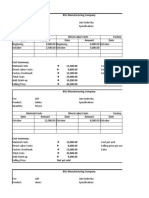
Example: Details regarding products are as follows:
Product
Output in units Costs per units(MU): Direct Materials Direct Labour Machine hours(per unit)
A
120 40 28 4
B
100 50 21 3
C
80 30 14 2
D
120 60 21 3
The four products are similar andare usually produced in production runs of 20 units and sold in batches of 10 units. The production overhead is currently absorbed by using a machine hour rate and the total of the production overhead for the period has been analysed as follows:
MU
Machine department cost(rent, business rates, depreciation and supervision) Set-up costs Stores receiving Inspection/quality control Materials handling and despatch 10430 5250 3600 2100 4620 26000
Cost drivers: Cost Set-up costs Stores receiving Inspection Material handling Cost driver Number of production runs Requisitions raised Number of production runs Orders executed
The number of requisitions raised on the stores was 20 for each product and the number of orders executed was 42 each order being for a batch of 10 of a product. Requirements: 1. To calculate the total costs for each productif all overhead costs are absorbed on a machine hour basis
2. To calculate the total costs for each product, using ABC 3. To calculate the unit product costs from your figures in items 1 and 2. Solution:
1. OAR= 26000/(120*4+100*3+80*2+120*3)= 20MU/machine hour
A
1.Prime cost 2.Overhead absorbed 3.Total cost per unit(1+2) 4.Total cost (3*number of units produced) 2. ABC 40+28(DM+DL) 20*4=80(OAV*No of hours) 148 17760
B
71 60 131 13100
C
44 40 84 670
D
81 60 141 16920
Activity
Total Cost
Driver
Number of drivers
13000 21(42/2) 80 21 42
Cost driver rate total cost(Cost per unit of driver)
8023 250 45 100 110
1.Machine department 2.Set-up act. 3.SR 4.Inspection 5.M
10430 5250 3600 2100 4620
Machine hour Production runs NR RR OE
Elements
1.Prime cost 2.Activities consumed 2.1.Machine Department 2.2.SR 2.3. SU 2.3. I 2.4. MH 3.Total cost(1+2) 4.Total cost/unit(3/number of units)
A
8160(68*120) 3851(8023*120*4) 1500(250*120/20) 900 600(100*120/10) 1320(110*120/10) 16331 13609
B
7100 1250 1250 900 500 1100 13257 13257
C
3520 1000 1000 900 400 880 7987 9980
D
9720 1500 1500 900 600 1320 16928 14107
Total
28500 10430 5250 3600 2100 4620
3.
A
Total cost/u(1) TC/u(2) Diff(2-1) 148 136.09 (11,91)
B
131 142.57 1,57
C
84 99.80 15,80
D
14130 14107 0,07
EXAM!!!
3 subjects: 1. Composed by 2 questions(theory) Eg: present 921 account Compare Financial accounting and managerial accounting 2. Eg: for cost calculation,profit calculation entries in interlocking accounting Apply a method to a specific company. DIDNT UNDERSTAND! DONT ASK! 3. Just some examples..: 1. Calculate breakeven point or sales for target Cost volume->profit analysis
2. Process costing a cost if 2 products are produced(eg. Physical units)
- divided segmentation costs(high point, algebrical,etc)
You might also like
- Prologue: Managerial Accounting and The Business EnvironmentDocument156 pagesPrologue: Managerial Accounting and The Business EnvironmentMarcus MonocayNo ratings yet
- A Company Produces Several Products Which Pass Through The TwoDocument1 pageA Company Produces Several Products Which Pass Through The TwoAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Before The Judge - Roger EDocument26 pagesBefore The Judge - Roger ELexLuther1776100% (4)
- Activity No 1Document2 pagesActivity No 1Makeyc Stis100% (1)
- Notes in Short Term FinancingDocument3 pagesNotes in Short Term FinancingLiana Monica LopezNo ratings yet
- MA Chap 23-3ADocument2 pagesMA Chap 23-3Aminh hiếu trịnhNo ratings yet
- Soal Tugas Problem Product CostingDocument2 pagesSoal Tugas Problem Product CostingMaria DiajengNo ratings yet
- Activity-Based Costing and Cost Management Systems: Answers To Review QuestionsDocument63 pagesActivity-Based Costing and Cost Management Systems: Answers To Review QuestionsVanessa HaliliNo ratings yet
- Garment CM Cost Estimation Using SAM or SMVDocument4 pagesGarment CM Cost Estimation Using SAM or SMVAbdul Rabban100% (3)
- CH 1 QuizDocument19 pagesCH 1 QuizLisa Marie SmeltzerNo ratings yet
- Backflush Accounting 1Document9 pagesBackflush Accounting 1Ai Lin ChenNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Cost AllocationDocument14 pagesChapter4 Cost AllocationNetsanet BelayNo ratings yet
- A-2 Final Review 15-16 KeyDocument10 pagesA-2 Final Review 15-16 KeydanNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument3 pagesCost Volume Profit Analysisshygirl7646617No ratings yet
- Management Accounting 1A - Lecture NotesDocument37 pagesManagement Accounting 1A - Lecture Notescathsangs0% (1)
- Cost Accounting Notes Fall 19-1Document11 pagesCost Accounting Notes Fall 19-1AnoshiaNo ratings yet
- 0568-Cost and Management AccountingDocument7 pages0568-Cost and Management AccountingWaqar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument21 pagesCost Accountingabdullah_0o0No ratings yet
- Job Order Cost SheetDocument4 pagesJob Order Cost SheetJasmine ActaNo ratings yet
- Costing Systems - A Focuc On Specific Order CostingDocument10 pagesCosting Systems - A Focuc On Specific Order CostingFred MutesasiraNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Paper: Cost Accounting McqsDocument8 pagesQuestion Bank Paper: Cost Accounting McqsNikhilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Product Costing SystemsDocument17 pagesChapter 4-Product Costing SystemsQuế Hoàng Hoài ThươngNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.2 206Document5 pagesAssignment No.2 206Halimah SheikhNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document12 pagesCH 11ShelviDyanPrastiwiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER FOUR Process CostingDocument10 pagesCHAPTER FOUR Process Costingzewdie100% (1)
- JOB, BATCH AND SERVICE COSTING-lesson 11Document22 pagesJOB, BATCH AND SERVICE COSTING-lesson 11Kj NayeeNo ratings yet
- Bell ComputersDocument3 pagesBell ComputersShameem Khaled0% (1)
- Cost I Chapter 4 EditedDocument10 pagesCost I Chapter 4 EditedWonde BiruNo ratings yet
- Hilton CH 14 Select SolutionsDocument10 pagesHilton CH 14 Select SolutionsHabib EjazNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document4 pagesCH 14Hoàng HuyNo ratings yet
- Standard CostDocument8 pagesStandard CostfasihxaydeeNo ratings yet
- Ch2.1 Cost Concepts and BehaviorsDocument42 pagesCh2.1 Cost Concepts and BehaviorsDouaa AbazeedNo ratings yet
- CIMA Process Costing Sum and AnswersDocument4 pagesCIMA Process Costing Sum and AnswersLasantha PradeepNo ratings yet
- Cma August 2013 SolutionDocument66 pagesCma August 2013 Solutionফকির তাজুল ইসলামNo ratings yet
- Financial and Managerial ExercisesDocument5 pagesFinancial and Managerial ExercisesBedri M Ahmedu50% (2)
- Mgt402 - 14midterm Solved PapersDocument125 pagesMgt402 - 14midterm Solved Papersfari kh100% (1)
- MGRL Corner 4e - PPT - CH 01 - IEDocument29 pagesMGRL Corner 4e - PPT - CH 01 - IEDitaNo ratings yet
- CA IPCC Cost Accounting Theory Notes On All Chapters by 4EG3XQ31Document50 pagesCA IPCC Cost Accounting Theory Notes On All Chapters by 4EG3XQ31Bala RanganathNo ratings yet
- Tarea 4Document2 pagesTarea 4Luisa Martinez Mateos100% (1)
- OLIGOPSONYDocument3 pagesOLIGOPSONYBernard Okpe100% (1)
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument9 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionCHAU Nguyen Ngoc BaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Securities Firms and Investment BanksDocument2 pagesChapter 16 - Securities Firms and Investment Banksmvlg26No ratings yet
- ACC103 Mid Term Revision Question 2019Document5 pagesACC103 Mid Term Revision Question 2019Reina TrầnNo ratings yet
- Kibrom Abrha Completed PaperDocument61 pagesKibrom Abrha Completed Papermubarek oumer100% (1)
- Question Bank - Practical QuestionsDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank - Practical QuestionsNeel KapoorNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1nurul izzatiNo ratings yet
- Service and Production Department Cost AllocationDocument58 pagesService and Production Department Cost AllocationLorena TudorascuNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting 2013Document3 pagesCost Accounting 2013GuruKPO0% (1)
- Underwriter AccountDocument9 pagesUnderwriter AccountQuin TimmyNo ratings yet
- Unit Four: Measuring Mix and Yield VariancesDocument6 pagesUnit Four: Measuring Mix and Yield VariancesTammy 27100% (1)
- Gusaba Umunsi Wo Kujya Gukoresha Kontorore 10022020182905Document1 pageGusaba Umunsi Wo Kujya Gukoresha Kontorore 10022020182905INGABIRE DROTHEE100% (1)
- Expenditure Cycle Part 1Document29 pagesExpenditure Cycle Part 1anon_879788236No ratings yet
- Shukrullah Assignment No 2Document4 pagesShukrullah Assignment No 2Shukrullah JanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Six Accounting For General, Special Revenue and Capital Project FundsDocument31 pagesChapter-Six Accounting For General, Special Revenue and Capital Project FundsMany Girma100% (1)
- A Company Sells and Services Photocopying Machines Its Sales DepartmentDocument2 pagesA Company Sells and Services Photocopying Machines Its Sales DepartmentAmit Pandey0% (1)
- HO3 - Cost Concepts and Estimation PDFDocument9 pagesHO3 - Cost Concepts and Estimation PDFPATRICIA PEREZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - AnswerDocument14 pagesChapter 11 - Answerlooter198100% (1)
- Activity Based CostingDocument20 pagesActivity Based CostingArpit SahaiNo ratings yet
- ABCDocument18 pagesABCRohit VarmaNo ratings yet
- Activity Based CostingDocument52 pagesActivity Based CostingraviktatiNo ratings yet
- Activity Based CostingDocument10 pagesActivity Based CostingEdi Kristanta PelawiNo ratings yet
- Activity Based CostingDocument70 pagesActivity Based CostingAnkur VermaNo ratings yet
- Teens Intermediate 5 (4 - 6)Document5 pagesTeens Intermediate 5 (4 - 6)UserMotMooNo ratings yet
- Tail Lamp Left PDFDocument1 pageTail Lamp Left PDFFrancis RodrigueNo ratings yet
- People v. Bandojo, JR., G.R. No. 234161, October 17, 2018Document21 pagesPeople v. Bandojo, JR., G.R. No. 234161, October 17, 2018Olga Pleños ManingoNo ratings yet
- ERRC Grid and Blue Ocean StrategyDocument2 pagesERRC Grid and Blue Ocean StrategyfereNo ratings yet
- Singles Inferno SpreekexamensDocument10 pagesSingles Inferno SpreekexamensIlhamNo ratings yet
- 6 Chase Nat'l Bank of New York V BattatDocument2 pages6 Chase Nat'l Bank of New York V BattatrNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 11 PDFDocument1 pageUnit Test 11 PDFYONo ratings yet
- The Diaries of Henry Chips' Channon - Snob's Progress - WSJ, January 20th 2023, Book Review by Joseph EPSTEINDocument6 pagesThe Diaries of Henry Chips' Channon - Snob's Progress - WSJ, January 20th 2023, Book Review by Joseph EPSTEINMariano DagattiNo ratings yet
- Department of Mba Ba5031 - International Trade Finance Part ADocument5 pagesDepartment of Mba Ba5031 - International Trade Finance Part AHarihara PuthiranNo ratings yet
- NPS Completed ProjectDocument53 pagesNPS Completed ProjectAkshitha KulalNo ratings yet
- Double Tax Avoidance Agreement ModelsDocument39 pagesDouble Tax Avoidance Agreement ModelsReubenPhilipNo ratings yet
- Brunon BradDocument2 pagesBrunon BradAdamNo ratings yet
- General Concepts and Principles of ObligationsDocument61 pagesGeneral Concepts and Principles of ObligationsJoAiza DiazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Re-Situating ConstructionismDocument2 pagesChapter 11: Re-Situating ConstructionismEmilio GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Gandhi An Exemplary LeaderDocument3 pagesGandhi An Exemplary LeaderpatcynNo ratings yet
- Who Is He? Where Is He? What Does He Do?Document3 pagesWho Is He? Where Is He? What Does He Do?David Alexander Pacheco Morales100% (1)
- rp200 Article Mbembe Society of Enmity PDFDocument14 pagesrp200 Article Mbembe Society of Enmity PDFIdrilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - AuditDocument26 pagesChapter 2 - AuditMisshtaCNo ratings yet
- Communication and Design Portafolio - Vanessa CerviniDocument34 pagesCommunication and Design Portafolio - Vanessa CerviniVanCerRNo ratings yet
- Nef Elem Quicktest 04Document2 pagesNef Elem Quicktest 04manri3keteNo ratings yet
- (BDMR) (DIY) (Building) (Green) (Eng) Munton - Straw Bale Family HomeDocument5 pages(BDMR) (DIY) (Building) (Green) (Eng) Munton - Straw Bale Family HomeMiklós GrécziNo ratings yet
- Juegos 360 RGHDocument20 pagesJuegos 360 RGHAndres ParedesNo ratings yet
- Dividend Discount ModelDocument54 pagesDividend Discount ModelVaidyanathan Ravichandran100% (1)
- 10th Grade SAT Vocabulary ListDocument20 pages10th Grade SAT Vocabulary ListMelissa HuiNo ratings yet
- WFP AF Project Proposal The Gambia REV 04sept20 CleanDocument184 pagesWFP AF Project Proposal The Gambia REV 04sept20 CleanMahima DixitNo ratings yet
- Glories of Srimad Bhagavatam - Bhaktivedanta VidyapithaDocument7 pagesGlories of Srimad Bhagavatam - Bhaktivedanta VidyapithaPrajot NairNo ratings yet
- .. Anadolu Teknik, Teknik Lise Ve Endüstri Meslek LisesiDocument3 pages.. Anadolu Teknik, Teknik Lise Ve Endüstri Meslek LisesiLisleNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument3 pagesEnglishYuyeen Farhanah100% (1)