Professional Documents
Culture Documents
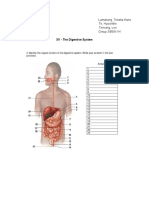
Know The Parts of Digestive System:: B. Type of Digestion That Occurs in Each Part?
Uploaded by
rswonickOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Know The Parts of Digestive System:: B. Type of Digestion That Occurs in Each Part?
Uploaded by
rswonickCopyright:
Available Formats
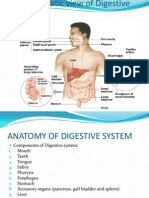
A & P II Review Digestion/Metabolism/Kidney Know The Parts of Digestive System: A. Mouth through Anus? 1. Mouth 2. Esophagus 3.
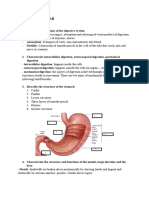
Esophagus Sphincter 4. Stomach 5. Pyloric Sphincter 6. Duodenum 7. Jejunum 8. Ileum 9. Ileum-Caecal Sphincter 10. Caecum 11. Ascending Colon 12. Transverse Colon 13. Descending Colon 14. Sigmoid Colon 15. Rectum 16. Anal Canal 17. Anus B. Type of digestion that occurs in each part? 1. Mouth- Salivary Glands which is a enzymes 2. Esophagus- Transport food to stomach 3. Stomach- Secrete enzymes 4. Small Intestine- Absorption of nutrients 5. Liver- Formation of bile / store glycogen / detoxifies blood 6. Gall Bladder- Store bile which emulsifies fates 7. Pancreas- Pancreatic Secretions 8. Large Intestine- Completes absorption mostly water Manufactures certain vitamins 9. Anus- bile exits C. Secretion/Enzymes of each part? 1. Mouth- Ptylan (salivary Amylase carbs and starches) 2. Stomach- Pepsinogen/ HCL/ Mucous/ Gastrin/ Rennin in infants 3. Small Intestine- Cholecystokinin (CCK) / Pancreatic Juices 4. Liver- Bilirubin 5. Pancreas- Pancreatic Amylase/ Maltase Sucrase Lactase Trypsinogen (inactive) / Trypsin (active) Chymotrypsin/ Carboxypolypeptidase/ Ribonucleas/ Deoxyribonuclease Pancreatic Lipase
D. pH of each secretion? 1. Mouth- pH 6.3 - 6.8 2. Stomach- pH 2 3. Small Intestine- pH 7.6 4. Liver- pH 7.6 - 8.6 5. Pancreas- collectively of pH 7 8 E. Layers of the GI Tract 1. Mucosa- thin lining of the lumen/Epithelia tissue with goblets 2. Submucosa- next layer thicker/ connective tissue/ blood vessel and nerves A. Plexus of Meissner (network of nerves) 3. Muscularis- near outer layer/ has 2 layers/ muscle tissue A. Inner Layer encircle the tract B. Outer Layer runs longitudinally C. One exception the stomach has 3 layers 4. Serosa- most outer layer/ Areolar tissue A. One exception esophagus dose not have a Serosa it has a Adventitia Know What These Words Mean: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Bolus mouth to the esophagus food and saliva mix together into a ball Mastication- Chewing Deglutition - Swallow Peristalsis wave like movement through GI Tract Chyme- Semifluid mass into which food is converted by gastric secretion which passes from the stomach into the small intestine 6. Rugae Fold or creases as in the lining of the stomach 7. Villi Wormlike processes on certain membranes. On the mucous membrane of the small intestine where they serve in absorbing nutriment 8. Emulsification Physical / To make into or form an emulsion (stool) Metabolism: Know the charts on the vitamins- minerals- hormones? ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS 1. Arginine (Arg) 2. Histidine (His 3. Isoleucine(Ile) 4. Leucine (Leu) 5. Lysine (Lys) 6. Methionine (Met) 7. Phenylalanine (Phe) 8. Threonine (Thr) 9. Tryptophan (Trp) 10. Valine (Val)
Tyrosine (Tyr) cannot be made unless Phenalalanine is present in the diet.
Define Metabolism: A. B. C. D. Anabolic Reactions- Build things up/ require energy Catabolic Reaction- Break things down/ gives off energy Oxidation Reaction- Remove electrons add oxygen Reduction Reaction- Add electrons or remove oxygen
Define Nutrient- The substance which the body needs to live What are they used for- To supply the body with the nutrients which it needs to Maintain homeostasis. What is an enzyme- They are a catalyst for chemical reaction How do they work- catalyst speeds up the chemical reaction by lowering the energy eact .
You might also like
- 6.1 Digestion and Absorption: Digestion of Food MoleculesDocument24 pages6.1 Digestion and Absorption: Digestion of Food MoleculesWILSON KosheyNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesDigestive SystemGabrielle Anne CarlosNo ratings yet
- 6 Human PhysiologyDocument29 pages6 Human PhysiologyRaynaahNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 8 Digestive SytemDocument15 pagesKelompok 8 Digestive SytemEzi RianaNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 NotesDocument36 pagesExam 2 NotesClara PianaltoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NotesDocument5 pagesDigestive System NotesRavenApigoNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 8 Digestive SytemDocument15 pagesKelompok 8 Digestive SytemRikeNindarsariNo ratings yet
- Part I: Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesPart I: Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemLleana TanNo ratings yet
- Module 14 AbdomenDocument22 pagesModule 14 Abdomenjohn maikeilNo ratings yet
- Nutrition NotesDocument8 pagesNutrition NotesDC MSME AttendanceNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: A. OverviewDocument7 pagesDigestive System: A. OverviewAlyesha MaloneyNo ratings yet
- The DIGESTIVE SYSTEMDocument22 pagesThe DIGESTIVE SYSTEMellaine.garciaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestina L Tract: (Digestive System)Document56 pagesGastrointestina L Tract: (Digestive System)Josephine AcioNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology - Lauras NotesDocument20 pagesHuman Physiology - Lauras NotesLaya ShrbagiNo ratings yet
- Sistim Pencernakan: Zaenal M. SOFRO Bagian Ilmu Faal FK - UGMDocument30 pagesSistim Pencernakan: Zaenal M. SOFRO Bagian Ilmu Faal FK - UGMDesi Dwi CahyantiNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE DIgestive SystemDocument7 pagesSCIENCE DIgestive SystemRichard MerkNo ratings yet
- Lea 417 510 2011Document121 pagesLea 417 510 2011Oliver TalipNo ratings yet
- Digestion Rev Horses ProteinDocument8 pagesDigestion Rev Horses ProteinKyle Gwyneth BobierNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal PDFDocument70 pagesGastrointestinal PDFCarol FuentesNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Gastro Intestinal SystemDocument13 pagesStructure and Functions of The Gastro Intestinal SystemhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- MLM10 Life Processes2Document18 pagesMLM10 Life Processes2anshuman2683No ratings yet
- Digestive System - MefloresDocument117 pagesDigestive System - MefloresJohnMichaelDominguezNo ratings yet
- Organs of Alimentary Tract and Accessory Organs. Digestion Begins in The Mouth or Oral Cavity. It Contains 32 Teeth ThatDocument4 pagesOrgans of Alimentary Tract and Accessory Organs. Digestion Begins in The Mouth or Oral Cavity. It Contains 32 Teeth ThatRhea Mae PerezNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Tugas Biology Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesJawaban Tugas Biology Digestive Systemaulia nurfadillahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2h - Digestive SystemDocument13 pagesChapter 2h - Digestive SystemMARC LOUIE F. BARNACHEANo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System Ppt.-NewDocument117 pagesGastrointestinal System Ppt.-NewFatima Syed100% (3)
- The Digestive System: S.Kep, NS., M.KepDocument10 pagesThe Digestive System: S.Kep, NS., M.KepAuliya AlfaNo ratings yet
- Digestive and Endocrine SystemDocument36 pagesDigestive and Endocrine SystemAldrei Vina Pauleah BorjaNo ratings yet
- #13 Digestive System - OllanasDocument9 pages#13 Digestive System - OllanasKirsten AletheaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument117 pagesDigestive SystemKBDNo ratings yet
- Wardlaws Perspectives in Nutrition A Functional Approach 1St Edition Byrd Bredbenner Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesWardlaws Perspectives in Nutrition A Functional Approach 1St Edition Byrd Bredbenner Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFcharles.osborne574100% (11)
- Class X Chapter 6 (Life Processes-Nutrition) - 1 PDFDocument11 pagesClass X Chapter 6 (Life Processes-Nutrition) - 1 PDFtiaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument43 pagesDigestive SystemDaniella100% (2)
- Digestive System NotesDocument10 pagesDigestive System NotesArchanna VyassNo ratings yet
- Genbio2-Lesson 2-Nutrient Procurement and Processing Part 2Document45 pagesGenbio2-Lesson 2-Nutrient Procurement and Processing Part 2yvetteNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: 1. Mouth 2. Pharynx (Throat)Document5 pagesDigestive System: 1. Mouth 2. Pharynx (Throat)Usita, Zackary, T.No ratings yet
- Digestive System in Non-RuminantsDocument5 pagesDigestive System in Non-RuminantsTumisang TlhabanoNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesDigestive Systemhimig the melodyNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY EXERCISE The Gastrointestinal System With Accessory GlandDocument5 pagesLABORATORY EXERCISE The Gastrointestinal System With Accessory GlandGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Chapter XV The Digestive System Arabis Bestudio Debalos Lasala Lumakang Te TimcangDocument14 pagesChapter XV The Digestive System Arabis Bestudio Debalos Lasala Lumakang Te TimcangRue Cheng MaNo ratings yet
- (GenBio2) Week 2 - Organ SystemsDocument111 pages(GenBio2) Week 2 - Organ SystemsmarielsolarteNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Parts and FunctionDocument15 pagesDigestive System: Parts and FunctionMica BernardoNo ratings yet
- HUMAN BODY Digestive SystemDocument41 pagesHUMAN BODY Digestive SystemFrancis MacasioNo ratings yet
- Science8 Lasq4 Week-1Document11 pagesScience8 Lasq4 Week-1Jinky AydallaNo ratings yet
- DU - Digestive System Ivana MajovskaDocument5 pagesDU - Digestive System Ivana MajovskaivkaamajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PresentationDocument82 pagesChapter 9 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PresentationMary Jane LubricoNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Q4 - Week 1 - Lesson 1Document19 pagesScience 8 - Q4 - Week 1 - Lesson 1Cris Tolentino100% (1)
- DU - Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesDU - Digestive SystemAlexandra MatysováNo ratings yet
- Organisma L BiologyDocument35 pagesOrganisma L BiologyJvc CawiliNo ratings yet
- Notes Ruth'sDocument31 pagesNotes Ruth'sSean PitmanNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesDigestive SystemFrancisco D. AndaquigNo ratings yet
- Biology 11 - June Final Exam NotesDocument15 pagesBiology 11 - June Final Exam NotesagbavaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System ReviewerDocument2 pagesDigestive System ReviewerDivino BauzonNo ratings yet
- Digestion Review SheetDocument7 pagesDigestion Review SheetPaola MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Answer Key1 PDFDocument4 pagesAnswer Key1 PDFsanthosh kumarNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Five Basic ActivitiesDocument5 pagesDigestive System: Five Basic ActivitiesCrystal MaidenNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Kaikiyi Sykay Pacheco BEED1Document3 pagesDigestive System Kaikiyi Sykay Pacheco BEED1Kaikiyi Sykay PachecoNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science NotesDocument20 pagesForm 2 Science NotesMeiiz YanShan100% (2)
- Bootstrap DatepickerDocument31 pagesBootstrap DatepickerdandczdczNo ratings yet
- " Thou Hast Made Me, and Shall Thy Work Decay?Document2 pages" Thou Hast Made Me, and Shall Thy Work Decay?Sbgacc SojitraNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior (Perception & Individual Decision Making)Document23 pagesOrganizational Behavior (Perception & Individual Decision Making)Irfan ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Grammar For TOEFLDocument23 pagesGrammar For TOEFLClaudia Alejandra B0% (1)
- Tangazo La Kazi October 29, 2013 PDFDocument32 pagesTangazo La Kazi October 29, 2013 PDFRashid BumarwaNo ratings yet
- Project TitleDocument15 pagesProject TitleadvikaNo ratings yet
- Hypnosis ScriptDocument3 pagesHypnosis ScriptLuca BaroniNo ratings yet
- Materials System SpecificationDocument14 pagesMaterials System Specificationnadeem shaikhNo ratings yet
- Physiology PharmacologyDocument126 pagesPhysiology PharmacologyuneedlesNo ratings yet
- Florida v. DunnDocument9 pagesFlorida v. DunnJustice2No ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Personal InformationDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Personal InformationMira ChenNo ratings yet
- RESO NO. 4 - LANYARD FinalDocument1 pageRESO NO. 4 - LANYARD FinalsharonleefulloNo ratings yet
- Pon Vidyashram Group of Cbse Schools STD 8 SCIENCE NOTES (2020-2021)Document3 pagesPon Vidyashram Group of Cbse Schools STD 8 SCIENCE NOTES (2020-2021)Bharath Kumar 041No ratings yet
- ISIS Wood Product Solutions Selects Cloud-Hosting Partner Real Cloud Solutions LLCDocument2 pagesISIS Wood Product Solutions Selects Cloud-Hosting Partner Real Cloud Solutions LLCdevaprNo ratings yet
- International Gustav-Bumcke-Competition Berlin / July 25th - August 1st 2021Document5 pagesInternational Gustav-Bumcke-Competition Berlin / July 25th - August 1st 2021Raul CuarteroNo ratings yet
- Motion Exhibit 4 - Declaration of Kelley Lynch - 03.16.15 FINALDocument157 pagesMotion Exhibit 4 - Declaration of Kelley Lynch - 03.16.15 FINALOdzer ChenmaNo ratings yet
- Gastric Emptying PresentationDocument8 pagesGastric Emptying Presentationrahul2kNo ratings yet
- Purposeful Activity in Psychiatric Rehabilitation: Is Neurogenesis A Key Player?Document6 pagesPurposeful Activity in Psychiatric Rehabilitation: Is Neurogenesis A Key Player?Utiru UtiruNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Sastra Semester Genap KLS Xi 2023Document3 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris Sastra Semester Genap KLS Xi 2023Ika Endah MadyasariNo ratings yet
- Psychology and Your Life With Power Learning 3Rd Edition Feldman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument56 pagesPsychology and Your Life With Power Learning 3Rd Edition Feldman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFdiemdac39kgkw100% (9)
- SQ1 Mogas95Document1 pageSQ1 Mogas95Basant Kumar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- 15.597 B CAT en AccessoriesDocument60 pages15.597 B CAT en AccessoriesMohamed Choukri Azzoula100% (1)
- Charles P. Jones, Investments: Analysis and Management, Eleventh Edition, John Wiley & SonsDocument20 pagesCharles P. Jones, Investments: Analysis and Management, Eleventh Edition, John Wiley & SonsRizki AuliaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Skills and Intention of Grade 12 Senior High School Students in Public Schools in Candelaria Quezon A Comprehensive Guide in Entrepreneurial ReadinessDocument140 pagesEntrepreneurial Skills and Intention of Grade 12 Senior High School Students in Public Schools in Candelaria Quezon A Comprehensive Guide in Entrepreneurial ReadinessAngelica Plata100% (1)
- Q3 Grade 8 Week 4Document15 pagesQ3 Grade 8 Week 4aniejeonNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To PPSTDocument52 pages1 Introduction To PPSTpanabo central elem sch.No ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Guide To HR Best Practices You Need To Know This Year (Infographic)Document42 pagesA Comprehensive Guide To HR Best Practices You Need To Know This Year (Infographic)MALATHI MNo ratings yet
- Marriage Families Separation Information PackDocument6 pagesMarriage Families Separation Information PackFatima JabeenNo ratings yet
- 60617-7 1996Document64 pages60617-7 1996SuperhypoNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds 1Document30 pagesCoordination Compounds 1elamathiNo ratings yet