Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Electrical Engineering
Uploaded by
Vishal BhoiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Electrical Engineering
Uploaded by
Vishal BhoiCopyright:
Available Formats
*4061104*
F.E. (Semester I) Examination, 2011 BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (2008 Pattern)
Time : 3 Hours Instructions :
[4061] 104
Max. Marks : 100 1) In Section I, attempt Q. 1 or Q. 2, Q. 3 or Q. 4, Q. 5 or Q. 6. In Section II, attempt Q. 7 or Q. 8, Q. 9 or Q. 10, Q. 11 or Q. 12. 2) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate answer books. 3) Figures to the right indicate full marks. 4) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary. 5) Use of non-programmable electronic calculator is allowed. 6) Assume suitable data, if necessary. SECTION I
1. a) With usual notations prove that
(1 2 ) = 1 2 (t 2 t1)
b) Two coils connected in series have resistances of 600 and 300 and temp. coefficient of resistance of 0.1% and 0.4% respectively at 20 C. Find the resistance of combination at a temperature of 50 C. What is the effective temperature coefficient of combination ? c) What are the indications which confirm that a lead acid cell is fully charged ? OR 2. a) Define insulation resistance and obtain an expression for insulation resistance of a single core cable. b) A diesel-electric generating set supplies an output of 50 kW. The calorific value of fuel used is 12,500 k cal/kg. If the overall efficiency of the unit is 35%. (i) Calculate the mass of oil required per hour and (ii) The electrical energy generated per tonne of the fuel. c) Compare lead acid cell and Nickel cadmium cell. 3. a) Explain the following terms with reference to dc resistive networks : 1) Unilateral and bilateral networks 2) Linear and non linear networks 3) Lumped and distributed networks 4) Active and passive networks. 6
6 6
6 6
8
P.T.O.
[4061] 104
-2-
*4061104*
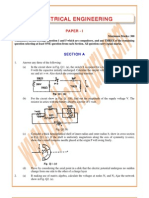
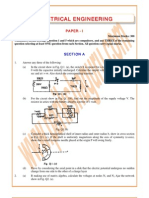
b) Formulate the Kirchhoffs voltage law equations for the ckt of Fig. 1 and find the values of I1, I2 and I3.
Fig. 1 OR 4. a) Derive an expression to convert Delta connected network into its equivalent star network. b) Find the current in 20 resistor connected across AB using Thevenins Theorem. 8 8
Fig. 2 5. a) Compare electric and magnetic circuits clearly stating similarities and dissimilarities between them. b) A coil of 2000 turns is wound uniformly over a nonmagnetic ring of mean circumference of 80 cm and cross sectional area of 0.6 cm2. If the current through the coil is 2 amperes, calculate (i) Magnetising force (ii) Reluctance (iii) Total flux (iv) Flux density. OR 8
*4061104*
-3-
[4061] 104
6. a) Derive the expression for the energy stored in the magnetic field in terms of energy stored per unit volume. b) Two coils X and Y, X of 12000 turns and Y of 15000 turns lie in parallel planes so that 45% of the flux produced by coil X links coil Y. A current of 5A in X produces 0.05 mwb, while the same current in Y produces 0.075 mwb. Calculate (i) the mutual inductance and (ii) the coefficient of coupling. SECTION II 7. a) Derive mathematical expression for voltage and current at any instant during charging of capacitor through resistance. Also sketch the graph of capacitor voltage and current with respect to time. b) Two flat parallel plates measuring 1m 2 m and separated 10 cm are charged by transferring 10 6 coulombs from one plate to other. The permittivity of the oil between the plates is 2. Calculate (i) capacitance of the parallel plates (ii) potential difference between the plates (iii) electric field intensity (iv) electric flux density between the plates. OR 8. a) Prove that an alternating quantity varying sinusoidally the maximum value is 2 times the effective value. Similarly maximum value is also equal to 1.569 times the average value. b) In a parallel ckt the three branches, the instantaneous branch currents are represented by i1 = 10 sin wt i2 = 20 sin (wt + 3 ) i3 = 12 sin (wt 6 ) Write down the expression for the total instantaneous current in the form
i = Im sin (wt + ) .
9. a) A sinusoidal voltage V = Vm sin wt is applied across a series R L ckt. Derive the expression for current and average power consumed by the ckt. b) A series R-L-C ckt with resistance of 50 , capacitance of 25 F and an inductance of 0.15 H is connected across 230 V, 50 Hz supply. Determine (i) impedance (ii) current (iii) power factor and (iv) power consumption of the ckt. OR
8 8
[4061] 104
-4-
*4061104*
10. a) What is impedance of ac ckt ? What are its components ? State the units these quantities. How is impedance expressed in rectangular and polar form ? b) A and B are two circuits connected in parallel across 200 V, 50 Hz supply. Ckt A consists of choke coil whose resistance is 5 and reactance 2 . Ckt B consists of non inductive resistor of 6 connected in series with a capacitor of capacitive
reactance 8 calculate (i) total current (ii) power factor of combined ckt and (iii) the resistance and reactance of a series ckt which will take the same current at the same power factor as the parallel combination. Solve by admittance method. 10 11. a) Write the advantages of 3 phase ac system over single phase ac system. b) Define the following terms related to 3 phase ckt. i) Symmetrical system ii) Phase sequence iii) Balanced load iv) Unbalanced load c) Three coils are connected in delta to a 3 phase, 3 wire, 415 V, 50 Hz supply and take a line current of 5A at a 0.8 power factor lagging. Calculate the resistance and inductance of the coils. If the coils are star connected to the same supply, calculate the line current and the total power. OR 12. a) Compare core type and shell type of transformers. b) From first principles derive the emf equation of a single phase transformer. 4 4 8 6 4
c) A transformer is rated at 100 kVA at full load its copper loss is 1200 W and its iron loss is 960 W. Calculate : i) The efficiency at full load, unity power factor ii) The efficiency at half load 0.8 power factor iii) The efficiency at 75% full load, 0.7 power factor iv) The load KVA at which maximum efficiency will occur v) The maximum efficiency at 0.85 power factor. 10
B/II/11/41,300
You might also like
- Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsFrom EverandImpedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsEvgenij BarsoukovNo ratings yet
- 9A02305 Electrical CircuitsDocument8 pages9A02305 Electrical CircuitssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- 9A02305 Electrical CircuitsDocument8 pages9A02305 Electrical CircuitssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A02305 Electrical CircuitsDocument8 pages9A02305 Electrical CircuitssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandElectricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Degree S1, S2 (S, FE) Examination May 2021 (2015 Scheme)Document3 pagesB.Tech Degree S1, S2 (S, FE) Examination May 2021 (2015 Scheme)Nigil ThomasNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code: 22115: B.E./B.Tech - Degree Examinations, April/May 2011 Regulations 2008Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Code: 22115: B.E./B.Tech - Degree Examinations, April/May 2011 Regulations 2008Vinodh GanesanNo ratings yet
- QbankDocument50 pagesQbankSourabhGuptaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering (6 Yrs FRM Jan 02)Document23 pagesBasic Electrical & Electronics Engineering (6 Yrs FRM Jan 02)Jay PandyaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsjayswamiiNo ratings yet
- 5 EE 2151 - Circuit TheoryDocument4 pages5 EE 2151 - Circuit TheoryBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engg-IDocument6 pagesElectrical Engg-IXYZNo ratings yet
- 120609-110005-Elements of Electrical EngineeringDocument2 pages120609-110005-Elements of Electrical EngineeringRajendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Elements of Electrical Engineering: 2013-14 (1 Sem) Question Bank From My PortionsDocument7 pagesElements of Electrical Engineering: 2013-14 (1 Sem) Question Bank From My PortionsWarren RiveraNo ratings yet
- 9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument8 pages9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- KEE101 Electrical Imp Ques SSDocument2 pagesKEE101 Electrical Imp Ques SStathagat maitrayNo ratings yet
- Elec2091st Semester Ex - 1705355554564Document6 pagesElec2091st Semester Ex - 1705355554564family7482pleaseNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument2 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringsanththaNo ratings yet
- May 2012Document8 pagesMay 2012satya_vanapalli3422No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsjayswamiiNo ratings yet
- Combined First and Second Semester B.Tech. Degree Examination, May 2009 Basic Electrical Engineering (Cmnphetarufb) (2003 Scheme)Document4 pagesCombined First and Second Semester B.Tech. Degree Examination, May 2009 Basic Electrical Engineering (Cmnphetarufb) (2003 Scheme)Emmanuel JosephNo ratings yet
- g485 5 1 3 Electromagnetism BDocument10 pagesg485 5 1 3 Electromagnetism Bapi-236179294No ratings yet
- B.Sc. (Aviation SC.) (I Sem.)Document3 pagesB.Sc. (Aviation SC.) (I Sem.)Vipan SharmaNo ratings yet
- U20EE201 - CT - Model QPDocument4 pagesU20EE201 - CT - Model QPvinothkumarNo ratings yet
- Questions BankDocument12 pagesQuestions BankshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields: 2006 Board QuestionsDocument50 pagesElectric Charges and Fields: 2006 Board Questionsgurveer sainiNo ratings yet
- BetDocument16 pagesBetShivendra SangwanNo ratings yet
- Ese 88Document8 pagesEse 88Prasanna KumarNo ratings yet
- Lagos City Polytechnic, IkejaDocument1 pageLagos City Polytechnic, IkejaOlatidoye EzekielNo ratings yet
- r7100206 Electrical Circuit AnalysisDocument4 pagesr7100206 Electrical Circuit AnalysissivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Bee Worksheet No-2 (2018-19)Document5 pagesBee Worksheet No-2 (2018-19)vikhli sallagargiNo ratings yet
- r05311801 Electrical EngineeringDocument9 pagesr05311801 Electrical EngineeringDumiso BaloyiNo ratings yet
- Shivaji University, KolhapurDocument9 pagesShivaji University, KolhapurNiranjan PatilNo ratings yet
- Assignment BEE CompleteDocument5 pagesAssignment BEE CompleteHarshit YadavNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS SyllabusDocument8 pagesELECTRICAL CIRCUITS SyllabusShareef KhanNo ratings yet
- WWW - Studyhaunters.blogspot - In: Question Paper Code: 22115Document5 pagesWWW - Studyhaunters.blogspot - In: Question Paper Code: 22115Sriram JNo ratings yet
- Civil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007Document147 pagesCivil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007venki3236No ratings yet
- Civil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007Document147 pagesCivil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007venki3236No ratings yet
- Civil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007Document147 pagesCivil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007venki3236No ratings yet
- r5100206 Electrical CircuitsDocument4 pagesr5100206 Electrical CircuitssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Bee 14 Question BankDocument10 pagesBee 14 Question BankprakashkerurNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - PTEE6201 - Circuit Theory QPDocument19 pagesAnswer Key - PTEE6201 - Circuit Theory QPSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Eoee 12 PDFDocument2 pagesEoee 12 PDFGirirajsinh ChudasamaNo ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 100 Marks: Seat NoDocument5 pages3 Hours / 100 Marks: Seat NoSiddhant ShindeNo ratings yet
- R07 Set No. 2Document8 pagesR07 Set No. 2dileepNo ratings yet
- Civil Services - Electrical Main Paper I & II - 1992-2012 - 7.6MBDocument253 pagesCivil Services - Electrical Main Paper I & II - 1992-2012 - 7.6MBAnika DixitNo ratings yet
- Fallsem2012-13 CP0696 ModqstDocument4 pagesFallsem2012-13 CP0696 ModqstThomas VargheseNo ratings yet
- 18 Ele 13Document2 pages18 Ele 13Avinash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Analysis 8Document16 pagesElectrical Circuits Analysis 829viswa12No ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: (10 2 20 Marks)Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10 2 20 Marks)Samraj JebasinghNo ratings yet
- Mid Bee Paper Set 3Document6 pagesMid Bee Paper Set 3raghusabale1No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsMayank BhattNo ratings yet
- ElectricalDocument4 pagesElectricalAkhilesh Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- R5100506-Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument1 pageR5100506-Basic Electrical EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Book 1 Complete Test 2024Document5 pagesBook 1 Complete Test 2024lukkuyadav050No ratings yet
- V Semester B.E. (E&E) Degree Examination, January 2013 (2K6 Scheme) Ee 504: Power ElectronicsDocument3 pagesV Semester B.E. (E&E) Degree Examination, January 2013 (2K6 Scheme) Ee 504: Power ElectronicsSumant ReddyNo ratings yet
- RR210303 Electrical EngineeringDocument2 pagesRR210303 Electrical EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Achievement Test Part - IiDocument3 pagesAchievement Test Part - Iiankit1754qNo ratings yet
- SIZE 250: 1. Transformer ApplicationDocument2 pagesSIZE 250: 1. Transformer ApplicationAferNo ratings yet
- Protection of Synchronous Machines: Application GuideDocument44 pagesProtection of Synchronous Machines: Application GuideDerouich2019No ratings yet
- TRF Diff-Ref CalculationDocument5 pagesTRF Diff-Ref CalculationNagasowjanyaJonnalagaddaNo ratings yet
- Medida de Descargas Parciais OmicronDocument10 pagesMedida de Descargas Parciais Omicronjjcanoolivares100% (1)
- B2 Series Characterized Control Valve, Spring Return ActuatorDocument6 pagesB2 Series Characterized Control Valve, Spring Return ActuatorIvan SilvaNo ratings yet
- 400+ TOP ELECTRICAL Engineering Interview Questions & Answers PDFDocument1 page400+ TOP ELECTRICAL Engineering Interview Questions & Answers PDFZedo ZedoNo ratings yet
- AP DU STANDARDS - GUIDELINES For LINES - POLES VER 1.0.4Document44 pagesAP DU STANDARDS - GUIDELINES For LINES - POLES VER 1.0.4Evander Sasarita MonteroNo ratings yet
- Es710 D00109 01 D XxenDocument8 pagesEs710 D00109 01 D XxenAlaa M El-adlNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Electrical Substation Components and Their WorkingsDocument22 pagesAssignment 1 Electrical Substation Components and Their WorkingsAP13 AP13No ratings yet
- ABB - Outdoor Instrument Transformers Buyers GuideDocument64 pagesABB - Outdoor Instrument Transformers Buyers GuideLuis Miguel ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Power Quality AnalysisDocument71 pagesPower Quality AnalysisFikre HailuNo ratings yet
- Polarity Test of 1 Phase TransformerDocument3 pagesPolarity Test of 1 Phase TransformersivaiahjettiNo ratings yet
- Cooper - Automatic Sectionalizing LinkDocument8 pagesCooper - Automatic Sectionalizing LinkAerwin BautistaNo ratings yet
- % Z of TransformerDocument2 pages% Z of TransformerNevil ModiNo ratings yet
- Euserc DrawingsDocument115 pagesEuserc Drawingsirsyad.wicaksonoNo ratings yet
- WIC1 - CT Powered Time Overcurrent And: Earth Current RelayDocument38 pagesWIC1 - CT Powered Time Overcurrent And: Earth Current RelaysadeghzendehboodiNo ratings yet
- Main CatalogueDocument12 pagesMain Catalogueferpa_ferNo ratings yet
- Testing Power TransformersDocument65 pagesTesting Power TransformersAbdul Kadhir83% (6)
- Electrical SafetyDocument68 pagesElectrical SafetyRafaelAndresOspinoNo ratings yet
- DTTN-DT2-PC-MET-EL-0004 A Method Statement For Inverter and Transformer Installation and CommissioningDocument13 pagesDTTN-DT2-PC-MET-EL-0004 A Method Statement For Inverter and Transformer Installation and CommissioningTariq Ali SialNo ratings yet
- IS 2026 Part 2Document20 pagesIS 2026 Part 2jm.mankavil623050% (2)
- Standard Specification For Transformers For Solar Park Pooling StationDocument260 pagesStandard Specification For Transformers For Solar Park Pooling Station400KVNo ratings yet
- Technical Background On Linear Induction Motors in Transportation Jun 1970Document99 pagesTechnical Background On Linear Induction Motors in Transportation Jun 1970Shantanu GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Maple Leaf Cement Power Flow Internship ReportDocument13 pagesMaple Leaf Cement Power Flow Internship ReportSaeed Anwar Khan100% (1)
- ApplicationDocument8 pagesApplicationGilberto MejiaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Services Our Knowledge. Your Experts.: SticsDocument24 pagesTransformer Services Our Knowledge. Your Experts.: SticsknsbNo ratings yet
- Application of Low Frequency Dielectric Spectroscopy To EstimateDocument4 pagesApplication of Low Frequency Dielectric Spectroscopy To EstimateAnggiNo ratings yet
- PS LAB Manual - B.tech - FinalDocument44 pagesPS LAB Manual - B.tech - Finalstriker_hemantNo ratings yet
- Transformatoare de CurentDocument54 pagesTransformatoare de CurentMoise RazvanNo ratings yet
- EE3741 - L2 - Transformer and Per UnitDocument105 pagesEE3741 - L2 - Transformer and Per UnitYoga Aditya RachmanuNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tFrom EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosFrom EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (543)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersFrom Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonFrom EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Power System Control and ProtectionFrom EverandPower System Control and ProtectionB. Don RussellRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeFrom EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Multiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...From EverandMultiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...No ratings yet
- Retro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsFrom EverandRetro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsFrom EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialFrom EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Guide to the IET Wiring Regulations: IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2008 incorporating Amendment No 1:2011)From EverandGuide to the IET Wiring Regulations: IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2008 incorporating Amendment No 1:2011)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (331)
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionFrom EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (15)
- Analog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceFrom EverandAnalog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceNo ratings yet
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesFrom EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Empires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldFrom EverandEmpires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (87)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)