Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Key Formulas
Uploaded by
Lily M MoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Key Formulas
Uploaded by
Lily M MoCopyright:
Available Formats
Key Formulas for physics
Dot Product
Cross Product
Magnitude
Direction
X-, Y-Components
Vector Addition Average Speed
average speed = Average Velocity
average velocity = Average Acceleration
average acceleration = One-Dimensional Motion with Uniform Acceleration (a.k.a. The Five Kinematic Equations)
Velocity of Two-Dimensional Projectiles
Newtons Second Law
Formula for Force of Kinetic Friction
Formula for Force of Maximum Static Friction
Work
Work Done by Gravity
Kinetic Energy
Work-Energy Theorem
Potential Energy
Gravitational Potential Energy
Mechanical Energy
Average Power
Instantaneous Power
Hookes Law
Period of Oscillation of a Spring
Frequency
Potential Energy of a Spring
Velocity of a Spring at the Equilibrium Position
Period of Oscillation of a Pendulum
Velocity of a Pendulum Bob at the Equilibrium Position
Linear Momentum Impulse of a Constant Force Conservation of Energy for an Elastic Collision of Two Particles Conservation of Momentum for a Collision of Two Particles Center of Mass for a System of n Particles
Acceleration of the Center of Mass Momentum of the Center of Mass Angular Position
Definition of a Radian
Average Angular Velocity
Average Angular Acceleration
Angular Frequency
Angular Period
Relations between Linear and Angular Variables
Equations for Rotational and Angular Kinematics with Constant Acceleration
Torque As Trigonometric Function
Component Form of the Torque Equation
Torque As Cross Product
Newtons Second Law in Terms of Rotational Motion
Moment of Inertia
Kinetic Energy of Rotation
Angular Momentum of a Particle
Component Form of the Angular Momentum of a Particle
Angular Momentum of a Rotating Rigid Body
Centripetal Acceleration
Centripetal Force
Newtons Law of Universal Gravitation
Acceleration Due to Gravity at the Surface of a Planet
Velocity of a Satellite in Orbit
Gravitational Potential Energy
Kinetic Energy of a Satellite in Orbit
Total Energy of a Satellite in Orbit
Keplers Third Law
Conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius
Conversion between Celsius and Kelvin
Relationship between Heat and Temperature
Coefficient of Linear Expansion
Coefficient of Volume Expansion
Ideal Gas Law
Boyles Law
Charless Law
First Law of Thermodynamics
Efficiency of a Heat Engine
Theoretical Limits on Heat Engine Efficiency
Coulombs Law
The Law of Superposition
Definition of the Electric Field
Electric Potential Energy
Work Done by an Electric Field
Electric Potential
Ohms Law
Resistance
Power Dissipated in a Resistor
Heat Dissipated in a Resistor Equivalent Resistance of Two Resistors in Series Equivalent Resistance of Two Resistors in Parallel
Stored Energy of a Capacitor
Equivalent Capacitance of Two Capacitors in Series Equivalent Capacitance of Two Capacitors in Parallel Magnetic Force on a Moving Charge
Magnitude of the Magnetic Force on a Moving Charge
Radius of the Circle Described by a Charged Particle Moving Perpendicular to a Magnetic Field
Magnetic Force on a Current
Magnetic Field Created by a Current
Motional Emf
Magnetic Flux
Faradays Law / Lenzs Law
Emf Induced in a Transformer
Frequency of Periodic Oscillation
Speed of Waves on a String
Wave Speed
Wavelength for the Harmonic Series
Frequency for the Harmonic Series
Beat Frequency
Doppler Shift
Frequency of an Electromagnetic Wave
Law of Reflection
Index of Refraction
Snells Law
Critical Angle
Focal Length for a Spherical Concave Mirror
Mirror and Lens Equation
Magnification
Maxima for Single Slit Diffraction
Minima for Single Slit Diffraction
Time Dilation
Length Contraction
Addition of Relativistic Velocities
Relativistic Mass
Relativistic Kinetic Energy
Mass-Energy Equivalence
Electron-Volts Related to Joules
Energy as a function of frequency
Kinetic Energy of Liberated Photoelectron
Radius of Electron Orbit
Electron Potential Energy in a Hydrogen Atom
De Broglie Wavelength
De Broglie Wavelength for Electron
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
Atomic Mass Units in Kilograms
Rate of Radioactive Decay
Half-Life of Radioactive Material
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Nus Iance Property Enhance MenDocument2 pagesNus Iance Property Enhance MenLily M MoNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Panis AngelicusDocument3 pagesPanis AngelicusLily M MoNo ratings yet
- Metodo de Escalas HrimalyScaleStudies PDFDocument36 pagesMetodo de Escalas HrimalyScaleStudies PDFosvaldoenrique12No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- You Are The New DayDocument2 pagesYou Are The New DayLily M MoNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Lecture 8 PDFDocument21 pagesLecture 8 PDFLily M MoNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- TrackMate - An Open and Extensible Platform For Single-Particle TrackingDocument11 pagesTrackMate - An Open and Extensible Platform For Single-Particle TrackingLily M MoNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- CHEM3407 Part 5 StuDocument20 pagesCHEM3407 Part 5 StuLily M MoNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Usefulness of Analytical Research Rethinking Analytical RDTDocument6 pagesUsefulness of Analytical Research Rethinking Analytical RDTLily M MoNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- 2 Light Scattering by Irregularly Shaped Particles With Sizes Comparable To The WavelengthDocument37 pages2 Light Scattering by Irregularly Shaped Particles With Sizes Comparable To The WavelengthLily M MoNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Medicinal Chemistry of AntibioticsDocument21 pagesThe Medicinal Chemistry of AntibioticsLily M MoNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Microbial Biosensors Engineered MicroorganismsDocument19 pagesMicrobial Biosensors Engineered MicroorganismsLily M MoNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Patrick TB Ch18aDocument50 pagesPatrick TB Ch18aLily M MoNo ratings yet
- ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE THREATS in The United States, 2013Document114 pagesANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE THREATS in The United States, 2013Virabase100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- DR Chris Walsh Tcm18 112374Document76 pagesDR Chris Walsh Tcm18 112374Lily M MoNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Topic 1 OverviewDocument65 pagesTopic 1 OverviewLily M MoNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- CHEM3407 Part 2 StuDocument48 pagesCHEM3407 Part 2 StuLily M MoNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- CHEM3407 Part 4 StuDocument44 pagesCHEM3407 Part 4 StuLily M MoNo ratings yet
- Topic 3Document29 pagesTopic 3Lily M MoNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial 2Document43 pagesAntibacterial 2Lily M MoNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial 3Document59 pagesAntibacterial 3Lily M MoNo ratings yet
- Functional Group Identification Homework Assignment: Due Thurs. Sept. 9Document3 pagesFunctional Group Identification Homework Assignment: Due Thurs. Sept. 9Lily M MoNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Practice Question AnswersDocument4 pagesPractice Question AnswersLily M MoNo ratings yet
- Patrick Problems 2 KeyDocument6 pagesPatrick Problems 2 KeyLily M MoNo ratings yet
- CHEM3407 Part 1 StuDocument34 pagesCHEM3407 Part 1 StuLily M MoNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Topic 2 Proteins As Drug Targets: Protein Structure-Chapter 3 Patrick and Part I CoreyDocument24 pagesTopic 2 Proteins As Drug Targets: Protein Structure-Chapter 3 Patrick and Part I CoreyLily M MoNo ratings yet
- P 1 MilestoneDocument77 pagesP 1 MilestoneLily M MoNo ratings yet
- Patrick TB Ch07Document20 pagesPatrick TB Ch07Lucia Ida Ayu KristianaNo ratings yet
- HW1 AnsDocument6 pagesHW1 AnsLily M MoNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- HW3 AnsDocument5 pagesHW3 AnsLily M MoNo ratings yet
- HW2 AnsDocument5 pagesHW2 AnsLily M MoNo ratings yet
- Signum-Technical-Guide LO SAMPLING GUIDEDocument30 pagesSignum-Technical-Guide LO SAMPLING GUIDEshirishkv100% (1)
- MY Pajero Sport VGT Service Plan & PriceDocument1 pageMY Pajero Sport VGT Service Plan & PriceNugroho FamNo ratings yet
- Safari - 21Document1 pageSafari - 21bernardNo ratings yet
- Alfa Laval Separartor s937 Alarms & Fault FindingsDocument19 pagesAlfa Laval Separartor s937 Alarms & Fault FindingsIgors VrublevskisNo ratings yet
- DepbDocument65 pagesDepbomkarniranjanNo ratings yet
- 1.6 66 77 2.0 105 110 135 KW TDI CR EngineDocument397 pages1.6 66 77 2.0 105 110 135 KW TDI CR EngineRSTNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document43 pagesModule 2Manchimsetty Sri NidhiNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test Lab Report MAE 361Document3 pagesTensile Test Lab Report MAE 361mrm3zaNo ratings yet
- Sugar Industrial ValvesDocument9 pagesSugar Industrial ValvesRajeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- AC018KN4DCH - WBMF Front Wind Baffle SubmittalDocument2 pagesAC018KN4DCH - WBMF Front Wind Baffle SubmittalChin Heng LimNo ratings yet
- Listino Velox 2011 Inglese (30-03-2011)Document39 pagesListino Velox 2011 Inglese (30-03-2011)panos320No ratings yet
- Dbatu Scheme - New & OldDocument9 pagesDbatu Scheme - New & OldDeepak BhopeNo ratings yet
- Pipe BranchDocument761 pagesPipe Branchjnmanivannanmech50% (2)
- Structures Module 3 Notes FullDocument273 pagesStructures Module 3 Notes Fulljohnmunjuga50No ratings yet
- UGC-01 sCHEDULEDocument6 pagesUGC-01 sCHEDULELingesh SivaNo ratings yet
- IVECO StralisDocument40 pagesIVECO StralismicakojicNo ratings yet
- 1 - Firewater Piping Spec - DIDocument2 pages1 - Firewater Piping Spec - DISuezie Iella100% (1)
- V-King CoreXY - Component Order ListDocument1 pageV-King CoreXY - Component Order Listfrankieb99No ratings yet
- Martillo Hyd Atlas Copco SB 150Document12 pagesMartillo Hyd Atlas Copco SB 150Nain murilloNo ratings yet
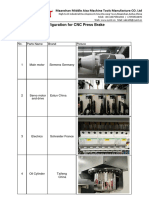
- ZYMT CNC Press Brake ConfigurationDocument8 pagesZYMT CNC Press Brake ConfigurationIonuţ RădescuNo ratings yet
- Ot SluiceDocument3 pagesOt Sluicegurumurthy38No ratings yet
- Mvjce Me 6 SemDocument101 pagesMvjce Me 6 SemAkash AkuNo ratings yet
- Demag DF 125 enDocument234 pagesDemag DF 125 enBaciu Nicolae50% (2)
- Chapter 3 - Part I - Slope StabilityDocument50 pagesChapter 3 - Part I - Slope Stabilitysam19961No ratings yet
- Manual de Peças Manipulador Telescopico 1200SJP 1350SJPDocument460 pagesManual de Peças Manipulador Telescopico 1200SJP 1350SJPAlessandro de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Dahilog Chemistry Activity On Gas LawsDocument7 pagesDahilog Chemistry Activity On Gas LawsYbur Clieve Olsen DahilogNo ratings yet
- A2 MECH Momentum QuestionsDocument8 pagesA2 MECH Momentum Questionsfootball_frenzy_2004No ratings yet
- TrainingManual PDFDocument234 pagesTrainingManual PDFJuan José Matos Ch100% (4)
- Fluid Flow MoldDocument41 pagesFluid Flow MoldSimoes JBNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of Cylinder Piston Impact Based On ANSYS/LS-DYNADocument4 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Cylinder Piston Impact Based On ANSYS/LS-DYNAvenalum90No ratings yet
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)