Professional Documents
Culture Documents
54
Uploaded by
Aditya SinhaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
54
Uploaded by
Aditya SinhaCopyright:
Available Formats
WATER POLLUTION CONTROL IN INTEGRATED WATER MANAGEMENT AND PROVIDING ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY
RECEP AHN VEYSEL ASLAN NERMN EK
Environment and Forestry Ministry , Environment Management General Directorate
ABSTRACT
Today besides the fact that water has an indispensable importance for human life and health and also for ecosystem survival, it is a fundamental necessity for the development of countries. Water scarity is becoming more&more significant&common issue&water quality has been fallen off rapidly almost any country. This problem causes a series of issues both from social&economic point of view. For instance, there exists children, men and women world wide who are unable to reach adequate and safe of water for their basic requirements. According to recent studies, in 20 years, water usage requirement shall increase by 40%; water for irrigation purposes shall increase by 17 %. Parallel to increase in civilization and industrialization, it is obvious that water requirement shall increase similarly. On the other hand, especially in 1990s, environmental pollution problem has emerged; this situation affected mostly water resources. Degradation of water quality caused limited sustainable water resources. In studies performed for water pollution control, it has been seen that identification of pollution loads discharged to rivers as point source and solution for this problems are not difficult. However even today either monitoring the accession to the river or locating the sources of the pollutants which reach to river as dispersed in field(non point source) is not being performed in the proper sense. For this reason, information is required beginning from water-soil relations in the basin to the examination of human life and activities in order to identify river pollution.
BASIN WATER MANAGEMENT
673
Water resources and ecosystems forming these resources and providing sustainability of them are under threat of contamination, unsustainable field usage changes, climate changes and lots of other effects. In this framework, evaluation of water resources within environmental integrity and management of them in a sustainable way are essential. At this study, integrated approaches about prevention of water pollution being an important branch of water management shall be examined and certain sample applications shall be presented. Key words: Water Pollution, Management of Water Resources, Sustainability.
1. INTRODUCTION
For a sustainable development, one of the most important urgent resources is water. Water, in other say, is a need material which can not be compensated with anything. Although, world population has increased three times from 19 to 20 century, water resources usage has increased six times (WSSD, 2002). Water crisis could be defined as more than one billion human could not reach healthy drinking water and half of the world population has no adequate water and waste water infrastructure. Sustainable development target has been set firstly in World Meeting in Rio in 1992. This has been a meeting in which environment and development concepts were handled together and in this framework sustainability concept was introduced. Today Rio Meeting exceeds more than 10 years and when environment and development is the matter sustainability concept appears. There is no exact definition of sustainability. In a general definition, sustainable development means that compensation of todays target and necessities and of future generations without threading their target and demands, development should be realized within this philosophy. 2. World Water Forum gathered in Haag, Holland, on March 2000, carried World water crisis to top of international agenda. Conference set out water safety for providing food safety and environmental safety. The key message of forum was the argument Water is Everyones business. Poorness and water safety relation becomes focus of international debates related to sustainable development. With this forum, Integrated water resource management has taken form of effective water management. In this point, it appears that management of water resource should be based on basin based management basis. At the beginning of 21 Century, earth faces an important water crisis. Some estimation shows that more than 3 billion persons shall face water scarcity by the year 2025 (WSSD 2002). All investigation indicates crisis has been reached serious levels
674
INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON RIVER BASIN MANAGEMENT
and shall continue rapidly if no action is taken. In the World Water Development Report published as a result of 3. World Water Forum arranged in Kyoto in 2003 states that water crisis affects life and health of poor societies mostly; besides natural environment is used carelessly without taking into consideration future results and generations. In the same report, all these problems are occurred due to deficiencies and failures in management of water resources. Therefore, together with scarcity world water crisis is management crisis. Needs for providing sustainability in management is stated. (UN, 2003). In Millennium Meeting on September 2000, 191 countries took the decision of reaching Millennium Development Goals aiming also decrease of poorness by half until year 2015. Thousand Year Targets are: 1. Decreasing number of person living under poorness and hunger limits by half. 2. Completion of primary school by everyone in world. 3. Giving priority to sex equivalence. 4. Decreasing deaths of child under age five by two third. 5. Decreasing mother deaths during pregnancy and birth by three forth. 6. Prevention of expansion of diseases like HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis etc. 7. Providing environmental sustainability. 8. Developing global partnership for a development containing targets related to decreasing help, trade and dept loads. In World Sustainable Development Meeting held on 26 August- 3 September 2002 in South Africa, Johannesburg, world water crisis was one of the most handled subjects. Parallel to Millennium Development Goals, by 2015, target of decreasing population who could not reach healthy water and water/waste water infrastructure by half has been adapted and in this direction below mentioned action are decided to be fulfilled: (WSSD, 2002). Developing and application healthy water infrastructure in houses Improving water/waste water services in public institutions and especially in schools Encouraging safe hygiene applications Encouraging training activities towards children Developing enterpriser finance and partnership mechanisms Integration of water resource management strategies and water/waste water infrastructure services
BASIN WATER MANAGEMENT
675
Preventing natural resource degradations and for this reason supplying financial source at national and international level, technology transfer, supporting capacity development for water infrastructure Development of integrated water resource management and of water efficiency plans, evaluation of recovery alternatives by preventing water losses and adaptation of basin based management until 2005. Sharing information related to management of water resources and application of projects on favor of women Giving support for the purpose of monitoring and evaluation of water resources of developing countries For the prevention of water contamination and ecosystems, development of house and industrial waste water treatment technologies.
2. WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN TURKEY
2.1 Water Resource of Turkey Mean precipitation: 643 mm/m2 Annual precipitation volume: 501 billion m3
SURFACE WATERS
Annual surface runoff: 186 billion m3 Annual surface runoff/ Annual precipitation volume: 0.37 Exploitable surface water: 98 billion m3
GROUNDWATERS
Annual groundwater safe yield extraction: 12 billion m3 Total Potantial: 110 billion m3 In our country, 16 % of the water is used as drinking water, 12% is used in industry, and 72 % is used in agricultural purposes. Water consumption per person (m3) > 10 000 3 000 - 10 000 1 000 - 3 000 < 1 000 Country Situation Water rich Sufficient water Insufficient-Water stress Water poor
676
INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON RIVER BASIN MANAGEMENT
In Middle East where Turkey is situated importance of water can be seen. The said region has a half dry climate feature and water rescource potential is low. On the other hand, the rapid growing population requires more water necessity. In technical and economic conditions, our countrys consumable surface and ground water potential is 110 billion m3. Water potential usage of our country reached 36% of economically consumable water potential. This means water amount per person in our country is 1700 m3, while this amount is over 10.000 m3 in rich countries like USA, Canada and East European countries. It is obvious that by the year 2030 Turkey shall face water scarcity. Therefore it is difficult to say our country is rich by means of water. 2.2 Water Management in Turkey In water management, lots of institutions are contained with changing liabilities. This is resulted from law and regulations on authority and liabilities of institutions for the same water resource. In 25 river basin studies defined towards water resource management and development, Ministry of Environment and Forestry is liable for quality of water, whereas General Directorate of State Hydraulics Works is liable for quantity of water. Ministry of Environment and Forestry (MOEF) is responsible for prevention of water resources from contamination, and for execution of related permits and audits. Since environment subject covers its own liability area, MOEF is responsible for establishment and application of environment policies, for adaptation of coordination of EU environment regulations. In addition, Water Pollution Control Regulation and EIA Regulation are also under liability of MOEF. General Directorate of State Hydraulics Works (DSI) has the liabilities of supplying drinking water, developing water resources by irrigation facilities and dams, besides monitoring surface and ground water, preventing and controlling floods. Ministry of Agricultural and Rural Affairs is liable for monitoring water resources and quality in water product areas, monitoring nitrate parameters in surface and ground water, field usage in rural areas, development of water resources (canalization system, irrigation), agricultural sourced water contamination, good agricultural applications and genetically modified organisms. Identification of drinking water standards, giving permits for management of current and new facilities, monitoring drinking water, mineral water and air quality are under responsibility Ministry of Health
BASIN WATER MANAGEMENT
677
(DS)
Efficient management of water resources is important for realization of a sustainable development. Turkey develops her water management policy parallel to growing population, rapid civilization, development at global and regional level, besides continuing EU participation stage. Water and energy are locomotives of sustainable development. In energy supply, it is important to assess other energy resources. To reach sustainable development, dams, reservoirs, hydro electrical water power centrals or irrigation systems have been constructed as a multi functioned water infrastructures. In new constructions, by taking into consideration ecosystems more, alternative technologies should be evaluated. Turkey considers the role of hydropower as a clean, affordable and renewable energy source for achieving sustainable development. The dams built over the last 50 years in Turkey have contributed significantly to the overall socio-economic development of the country. The Southeastern Anatolia Project in the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers Basin is recognized as an exemplary case for the transition from simple water development to efficient water management. It covers all sustainable development related sectors such as agriculture, hydropower, industry, transportation, infrastructure, health care and education. Turkey has already started to adapt EU regulations related to water as a candidate country and took major steps.
678
INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON RIVER BASIN MANAGEMENT
3. PREVENTION OF WATER CONTAMINATION IN SUSTAINABLE WATER MANAGEMENT
3.1 Polluter Sources Polluter sources are classified as point sources and expanded sources. If a pollution from a source to a media could be controlled and mix with measurable point discharge, this kind of sources are point sources. If pollution expands to a media, then polluter source is classified as expanded source. 3.2 Surface Water pollution It should not be forgotten that water is not only required for human life as a physical value but also is a media providing continuation of all living organisms. Providing continuation by protecting both sea and shore ecosystems and also surface inner water ecosystems contains important place in water protection and prevention of pollution. Arrangement of protection-usage balance according to our countrys socioeconomic conditions for a sustainable development and usage of natural resource by preserving them are very important. If management cover is taken into consideration, seeking answer to the question where and how much water were existed in past, today handling water quantity and quality are matters that emerged obligation to evaluate all factors affecting these two matters. To remove factors polluting water resources and changing natural balance, recently lots of studies have been performed. Especially, there shall be more need to drinking and usage water in future due to increasing agricultural networks, growing cities, developing industry together with growing population of developing and less developing countries. Especially, due to insufficient infrastructures and treatment facilities for disposal of home and industrial wastes resulted from industrial facilities growing each day and cities and insufficient payments and investments, important environmental problem arises basically at our surface water resources and seas. Natural resources and clean rural environment comprises important potential areas for the acceleration of rural development. Soil, water and forest sources, biological diversity (gene, spice and ecosystem diversity), natural resource are subjected negative impacts of rapid civilization, unplanned tourism activities, insufficient infrastructure of residents, natural disasters, unconscious and excessive source usage. Sustainable natural source management at basin basis gains importance in soil, forest and pasture sources usage. By means of evaluation of water product stocks and growing up potential, sustainable usage of stocks and control of water pollution prevention their importance.
BASIN WATER MANAGEMENT
679
3.3 Sea Contamination Our country is surrounded by three seas and has 833 km shore length. Contamination reasons of seas can be handled at two stages Sea contamination resulted from sea transportation Land sourced pollution due to industrial, house and agricultural usages coming by surface waters from inner regions. Regulation studies related to prevention of sea and surface water pollution resulted from sea transportation and petroleum pipe lines has been completed, emergency action plans are prepared and emergency action capacity are increased. For the purpose of researching reasons of sea pollution and prevention of contamination at source, countries have been established Barcelona and Bucharest Contracts with annex and protocols related to prevention of land based polluters. Towards this purpose in our country: National Action Plan Related to Pollution from Land Based Sources has been prepared. In this framework monitoring studies are seen as first step to be taken in identification of actions to control pollution. At regions in our country having coast at Aegean Sea, Mediterranean Sea, and Black Sea these studies are applied; Measurement and Monitoring at Coast and Reference Fields Measurement and Monitoring at Hot Fields Measurement and Monitoring at Land Based Point Pollution Sources Eutrofication Monitoring and Assessment.
For this purpose, eutrofication monitoring and determining studies has been included to MED POL phase III monitoring program in rural areas in Turkey, at Gulf of Mersin studies has already been started.
4. SUSTAINABILITY OF WATER SOURCES
Water resources and related ecosystems supplying continuation and forming these resources are under thread of field use changes, climate changes, and other effects. On the other hand, lakes, rivers, irrigated fields and seas are main sources economy based on fishing and similar water products. From drinking and usage water to water resources being one of important resource of economy, all these products and services depends on integration of aquatic ecosystems. Flood, dry air, contamination, and similar natural and/or anthropogenic effects are threading sustainability of these resources.
680
INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON RIVER BASIN MANAGEMENT
Development and management of water resource systems; general river, aquifer, and coast regions and surroundings and ecosystems of them have value as natural source, and these resource are needed to be protected and today societies has requirements to be compensated be water resources. During meeting these requirements showing diversity, differences between life quality region or inter-region societies should be minimized. Future societies have the right of economy, environment and life quality better than today. Therefore in water management, needs and targets of future societies should be taken into consideration. 4.1 Supplying Safe Drinking Water and Reuse of Water To supply healthy and adequate drinking water to all residences, protection and control of water resources should be cared. Priority should be given to drinking water and canalization investments that are acceptable in social way, healthy in environmental way, applicable economically, appropriate technologically, and meet sustainable development targets. Water demand increases, though water quantity on earth is stable. This requires rational allocation between certain usage aims of water resources. As world population increases, demand for water resource also increase, and thus pressure on world water resources increase each day. Between years 1900-1995, global water consumption has increased six times. In 1950, number of countries having water scarcity was 12 with total population of 20 million, whereas, In 1990, number of countries having water scarcity was 26 with total population of 300 million. However, increasing difference between usable natural water resources and water need has brought about agenda subject of treatment of waste water to reuse besides some other measures and studies related to this matter has reached important level in last twenty years. List of reuse importance of treated waste water is as follow: Irrigation water, Industrial water (cooling and process water), Artificial feeding of ground water, Reuse in resident region (double delivery systems), Formation of recreation areas, Other uses (Construction, preventing salty water, drinking water). Reuse of waste water is spread in countries where water resources are limited or alternative water sources are expensive. Progressing return technologies, increasing
BASIN WATER MANAGEMENT
681
water demand and decreasing water resources and therefore becoming more expensive make reuse of waste waters an important subject. 4.2 Supplying Water and Food Safety In supplying water safety in developing countries like our country; besides traditional food production methods for more qualified food production, supplying modern technology usage, supplying rational usage of water in agricultural sector for food production use, developing encouragements, regulations and policies are unavoidable when taking into consideration that water is used mostly at agriculture. Negative effects of polluted sediments could be also seen at human life through food chain besides increase in death in aquatic biota. Being healthy is basic need and right of a person. Food products are basic factors affecting our health easily. Food safety should be seen as a certain and unchanging quality parameters. Legal arrangement was done in Turkey for suppliying at food securitiy. This legislation was publicated at offical newespaper in 16 november 1997, also this legislation attentions to protection of water pollution. It inculudes According to Turkish Food Codecs Legislation, The system of HACCP was mandatory in food sector. Also, this standart of TS 13001 is based on the prensip of HACCP. 4.3 Protection of Biodiversity Turkey inhabits very different certain features due to its natural structure. Our country surrounded by three seas has different climates and a rich biodiversity due to its unique geography. Protection of unique biological riches our country possesses and sustainability of them are basic aim of our country. Within this context, our country has been party to lots of international contracts towards protection of biodiversity and lots of study has been realized. Our country possesses 36 National Parks, 17 Natural Parks, 34 Fields Protecting Nature, 102 Natural Monuments, 108 Wild Life Developing Areas, 12 Ramsar Areas, 14 Specially Protected Areas, lots of studies have been realized for protection of biodiversity, supplying integrity and sustainable development in these regions.
Main Ecosystems in Turkey
Forests Steps Irrigated Fields Sea Ecosystems (Coast Ecosystems, Sea Inns, Islands)
682
INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON RIVER BASIN MANAGEMENT
4.4 Economical Importance of Water As known, in access to fundamental water services, in 13th Sustainable Development Commission Meeting handling water, sanitation and human habiting subjects of Sustainable Development Commission tied to United Nations Economic Social Council, decision of targeting subventions towards poor persons including water connection fees, using all other policy means and amendments participating continuation of service supply, without intervening poor the purpose of cost and return for water access has been taken. On the other hand, using water resources is a right, but this right could not be given for free. .Process cost of water before becoming a drinking water should be reflected to the prices provided that right of poor persons has been guaranteed.. In our country, water services supplied by public and/or private sector (Municipalities, DS), are priced according to province and counties with different price tariff. Financing water management with itself is a key word. This means that pricing forms backbone of water management.
5. DEVELOPMENTS, TROUBLES, TARGETS WITHIN FRAMEWORK OF SUSTAINABLE WATER POLLUTION CONTROL IN TURKEY;
5.1 Developments Preparation to Thousand Years Target report in Turkey has been started in June 2003. In this report, all targets and objects have been evaluated for Turkey and connection of all these targets with objects has been stated. In report, definition of targets, their measurement methods, and data sources have been defined. Current situation has been explained. Developments expected to be occurred in near future have been planned according to information and data available. The fields with deficiencies have been searched and expectation related to future has been underlined. In addition, our studies related to prevention of water pollution and sustainable usage has been continuing at national and international level, EU stage has accelerated our studies. In the stage of participation to EU, adaptation studies of EU regulation to Turkish regulation have been started in 2000 and continuing. Within this context, Within EU concept, Environment heading comprises 8 sectors as Horizontal, Air Quality, Waste Management, Management of Natural Resources, Control of Industrial Pollution, Chemicals, Noise, and Water Management. Although there are lots of regulation related to water and water management, the requirements of EU Water Directives could not be met by these regulations. Un-
BASIN WATER MANAGEMENT
683
der Water Framework Directive, adaptation studies to 23 EU Directives on water have been continuing.
Regulations Set Within Framework of EU Adaptation Studies
Regulation of the protecting of waters against pollution by Nitrates from Agricultural sources, (18.02.2004 OJ.No 25337) Regulation of the quality required of surface water intended for the abstraction of drinking water. (20 .11.2005 OJ No 25999) Regulation on pollution caused by certain dangerous substances discharged into the aquatic environment.(26.11.2005-OJ No 26005) Regulation on the Urban Waste Water Treatment (08.01.2006-OJ No 26047) Regulation of the water quality on Human Consumption (17 .02. 2005 OJ No 25730 Studies on Regulation on Protection of Ground Water against Pollution by Hazardous Substances prepared for adaptation purpose of 17 December 1979 dated and 80/68/EEC numbered Council Directive on protection of ground water against pollution by hazardous substance are continued. 5.2 Effective enforcement system In Turkey, to avoid environmental pollution, penalties are applied within framework of related laws. In Turkey, 2872 numbered Environment Law puts sanctions, these sanctions are applied according to discharges monitored by governorships. The penalties given by governorships are informed to Ministry of Environment and Forestry periodically and these are archived. 2872 numbered Environmental Law (Official Gazette: 11 August 1983, number 18132) has been revised by 5491 numbered Law (Official Gazette: 13 May 2006), with this law sanctions have been increased and sanction power has been made more effective. According to 9.8.1983 dated and 2872 numbered Article 10 of Environment Law, institutions and managements, which can lead environmental problems due to their planned activities to be realized, prepares Environmental Impact Assessment Report. In this report, disposal method of wastes causing environmental pollution and measures to be taken about this matter are included. According to Article 37 of 31.12.2004 dated and 25687 numbered Water Control Regulation, for the purpose of preventing or changing quality of negative effects of intake water media current usage purposes by Environment and Forestry Ministry, it is stated that limitation could be done beyond the foreseen standards in regulation. It is explained that at this defined date, measures related to these limitations could be realized by management owner.
684
INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON RIVER BASIN MANAGEMENT
Within context of 167 numbered Law on Ground Water, there exist penalties for inappropriate usages and usages without permit. According to 1380 numbered Water Products Law and Water Products Regulation of this law, legal processes are applied to managements exceeding limit values referred in regulation during intake media and waste water discharge audits at water products points.
6. NATIONAL AND INTERNATIONAL PROJECTS
6.1 Anatolian Watershed Rehabilitation Project Project started in 2005 and supported by World Bank and GEF, shall be completed in 2012;
Project Purpose:
Providing a sound natural resources management, increasing the income of the people living in the Anatolia and Black Sea Regions and decreasing the pollution originated from agricultural activities and transported by means of Kzlrmak and Yeilrmak Rivers. The project is applied in Samsun, Amasya, Tokat, orum, Kayseri and Sivas cities located on Kzlrmak and Yeilrmak river basins.
Project objectives.
Identification of the effects of the agricultural pollutants on water and soil resources using N and P analysis, To control the nutrients transported to Black Sea through Kzlrmak and Yeilrmak Rivers Ensuring international quality standards in parameters and measurement methods, Making inventory studies to identify agricultural industries and pollutants, Making an action plan to prevent the pollutants coming from agricultural practices, Implementation of the Regulations of Protection of the Water Resources Against Nitrate Pollution Coming From Agricultural Activities (18.02.2004/The Official Gazette No:25377).
Related GEF sub project of this project, Village Services General Directorate and Environment and Forestry Ministry are responsible.
BASIN WATER MANAGEMENT
685
GEF Supported Project Compounds
1234567-
Animal Based Waste Management System Agricultural Industrial Based Pollution Monitoring Water and Soil Quality Public Awareness, Capacity Increase, and Repeating Strategy Designation of Legal Framework for Organic Agriculture Preparation of Good Agricultural Application Guide Improvement of Political and Institutional Structure Necessary for EU Adaptation Nitrate Directive
At the end of studies performed related to GEF compounds, agricultural activities and industries causing food product pollution shall be identified, food products monitoring studies for the control of water and soil qualities at macro and micro basins designated at four cities (Amasya, orum, Tokat, Samsun) determined on the Kzlrmak and Yeilrmak river basins basis shall be performed periodically for 7 years. By laying down kind of measures to be taken and rate of pollution caused by sources, province shall be identified in region and agricultural activities basis, the said pollution shall be controlled and prevented by establishing environment awareness, and participation of public is targeted by awareness campaigns about environmental subjects. ASHRP Finance Condition Organization World Bank Government Participant Total Credit ($) 20.000.000 7.300.000 7.700.000 35.000.000 Donation ($) 7.010.000 2.220.000 840.000 10.070.000 Total ($) 27.010.000 9.520.000 8.540.000 45.070.000
6.2 National Action Plan Preparation Project Related to Land Based Sources (LBS-NAP) According to Strategic Action Plan (SAP) accepted pursuant to Protection of Sea Media and Coast Region of Mediterranean Sea (Barcelona Contract) and its Annex Land Based Sources to which our country is party, preparation studies of National Action plan Related to Land Based Sources has been completed with coordination of Environment and Forestry Ministry and participation of related institutions and associations from the year 1997.
686 In Project;
INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON RIVER BASIN MANAGEMENT
At first stage; Studies have been performed in 11 basins situated near Mediterranean Sea in 2001 and near Aegean Sea in 2002. These basins are the basins among 26 basins divided by DS by means of drainage areas, and are as follow; West Mediterranean, Antalya, East Mediterranean, Seyhan, Ceyhan, Asi, North Aegean, Gediz, Small Menderes, Big Menderes, Meri-Ergene having coast to both Mediterranean and Aegean Seas. Later, by TBTAK MAM, by determining problem type and strength for Mediterranean and Aegean Coasts, polluters, natural media damages and physical changes, damage sources, preferential fields, and action for each basins; basing on National Detection Analysis (NDA) in 2003 and also in 2004 emission and discharge values of 2003, Base Line Budget studies defining pollution loads providing establishment of sector plans and national action plan from these values have been completed.. At second stage; by filling event/effect matrix, the stage of determining priorities has been completed by preparation of NDA. Matrix is updated in NAP. Third stage; according to updated matrix, preferential actions have been designated towards each basins for 2010 and 2025 in NAP. Forth stage; by taking into consideration priorities between regions, sector plans including subject like regional plans, general measures, environment quality criterions, emission limits, capacity development has been established. By determining priorities across Mediterranean- Aegean Sea Coasts, input has been supplied for the National Action Plan prepared for the purpose of control and prevention of said pollution. Sector plan have been performed towards 30 sectors by taking into consideration sector plans, pollution loads determined within context of BB and NDA and target years and discounts designated in SAP in Mediterranean and Aegean regions according to sector list referred in SAP. Within this context, to decrease pollution in sector basis, advance treatment technologies and clean production technologies have been proposed. In our country, within year 2004, sector programs have been started to be prepared. By the date 26 July 2005, these plans have been completed and introduced to Environment and Forestry Ministry. Fifth stage; Parallel to targets defined in SAP, national preferential action lists have been set for the years 2010 and 2025. At this stage, at house and industrial waste waters, priorities mentioned in below table have been determined. Sixth stage; Based on NDA, BB and Sector Plans published also at web site http://www.kkkuep.com, National Action Plan has been prepared and sent to UNEP/MAP Secretary.
BASIN WATER MANAGEMENT
687
6.2.1 Assessment As a result of project, by identification of current contamination in our seas, source of land based polluters, degree of pollution which polluters caused, and changes needed at legal and institutional structure for prevention by controlling said pollution with priorities at region and sector basis, investments plans have been prepared and economic means have been defined with investment priorities, a National Action Plan has been established to control and prevent said pollution. Obtained data shall light future plans, supply important benefits both for source usage and prevention of environment pollution by addressing investments at the most rational way. Especially, taxes, encouragements, etc. determined towards supply of sustainable usage of facilities using natural resources in environmental and financial manner in the plan are important economical instruments to provide support in application of said plan.
7. BOTTLENECK
Insufficient institutional capacity, Junctions in authority and liabilities, Needs for development of means towards start of polluter pays principle more actively within content of rationalist management of water Insufficient financing, polluter and user pay principle is not included in our regulation, Insufficient management in waste water facilities, Non-developed public-private sector cooperation towards operation, Difficulties encountered during application of penalties and sanctions, Non-developed engineering, consulting and manufacturer firms giving service at waste water sector, Regional planning deficiency.
8. RESULT AND ASSESSMENT
Although water on earth that is necessary for human life and health and also vital for ecosystems is stable, water demand increases rapidly. Estimation done for year 2050 indicates that number of countries to be suffered from water scarcity shall be 65 and number of affected persons shall be around 7 billion. Water resources are under threads of pollutions, usage not being sustainable, field use changes, climate changes and lots of other effects. For further qualified food production, water safety should be satisfied.
688
INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON RIVER BASIN MANAGEMENT
Turkeys national development priorities are included to countrys current reform stage and reflect commitments in Thousand Years Notification adapted by world leaders in UN Thousand Years Meeting in year 2000. Turkey is aware the fact that Thousand Years Report forms a strong framework towards development and creates real and important difference in peoples life. Report shall decrease poorness and non-equivalence by year 2015 and aim a development creating real and important difference in peoples life. Turkey adapting this global framework, while progressing in a path that shall create a sustainable and justified development for everyone, shall also complete participation stage of EU successfully. In this framework, for the rationalist public management of water; Determination of water pollution prevention with a good water management with a good planning principle, Powering legal and technical sub-structure towards realization of economical and social development targets appropriately in prevention of water pollution, Development of middle and long term strategies for protection of water and sustainable usage, For an effective management, powering institutional capacity, technical hardware and infrastructure, Selection and application of appropriate treatment technologies with low cost of investment and management necessary for house and industrial discharges, Establishment and usage of necessary financing sources, Especially, at industry, using clean production technologies and decreasing waste water at source, Reuse of treated waste water at appropriate sites due to differences between usable natural water resources and water demand, Developing public-private sector cooperation models at investment and operation, Effective audit, realization of monitoring and investment, Developing long term general principles for protection of water and sustainable usage and applying the principle Polluter pays. Pricing water in a manner that poor person could access it, socially acceptable, environmentally healthy and economically applicable drinking water and infra structure investments, Supplying rational usage of water especially in agricultural sector for food production.
BASIN WATER MANAGEMENT
689
As a result; Application of principle polluter pays constituting basis to establish database, monitor water, provide continuation by improving ecological structure of water, realize integrated water management and remove institutional debates and legal overlaps in our country and preparation of Water Law constituting basis for water pricing are important.
REFERENCES
Ministry of Environment and Forestry,(2006),Biodiversty of Turkey Ministry of Environment and Forestry and UNDP,(2004), World Summit on Sustainable Development, Implementation Report Millenium Devolopment Goals WSSD (2002). World Summit on Sustainable Development, Implementation Report, Johannesburg, 26 Austos 3 Eyll 2002. Gney Afrika, www.johannesburgsummit.org. Harmancolu N.(2004): Indcators For Sustanable Management Of Water Resources, stanbul Technical University Symposium on: IV. National Hydroloji Conference UN (2003). Water for People Water for Life The United Nations World Water Development Report. UNDP (2006) Human Devolopment Report Orhon D.,Szen S.,stn B.,Grgn E.,Karahan-Gl (2002) in Istanbul.Environmental and Sustainable Devolopment Panel Report on Water Management and Sustainable Devolopment.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 03.can-Bus and Sae-Bus j1939 - CatDocument29 pages03.can-Bus and Sae-Bus j1939 - CatEdison Pfoccori BarrionuevoNo ratings yet
- AAA Variable Spring Hangers CatalogDocument31 pagesAAA Variable Spring Hangers CatalogNopparut0% (1)
- Mill Test Certificate: Jindal Stainless (Hisar) LimitedDocument1 pageMill Test Certificate: Jindal Stainless (Hisar) Limitedhemantmech09920050% (2)
- (Teubner Studienbücher Chemie) Brian R. Eggins (Auth.) - Biosensors - An Introduction (1996, Vieweg+Teubner Verlag) PDFDocument221 pages(Teubner Studienbücher Chemie) Brian R. Eggins (Auth.) - Biosensors - An Introduction (1996, Vieweg+Teubner Verlag) PDFRicardo PatrickNo ratings yet
- SI44M 60H 80H-DeN1730-V12web DownloadedDocument4 pagesSI44M 60H 80H-DeN1730-V12web DownloadedtauraimukumbaNo ratings yet
- Medication - Safety - v4 Last Update 2015Document81 pagesMedication - Safety - v4 Last Update 2015Retno PalupiNo ratings yet
- TICSA - Diesel Uno Petroleos Guatemala (13.01.23)Document1 pageTICSA - Diesel Uno Petroleos Guatemala (13.01.23)Luis M LópezNo ratings yet
- South African Flora GlossaryDocument47 pagesSouth African Flora Glossarymr.bryceNo ratings yet
- Manoeuvrability Final EditedDocument12 pagesManoeuvrability Final EditedSaptarshi BasuNo ratings yet
- Borneo SporenburgDocument2 pagesBorneo SporenburgDorin TecuceanuNo ratings yet
- B.pharm Course Handbook 2017 18Document74 pagesB.pharm Course Handbook 2017 18Md RaquibNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Simplified Fatigue AnalysisDocument4 pagesFinite Element Simplified Fatigue AnalysisJin Hwan KimNo ratings yet
- Synopsis THESIS 2022: Aiswarya Vs Tqarebc005 S10Document5 pagesSynopsis THESIS 2022: Aiswarya Vs Tqarebc005 S10Asna DTNo ratings yet
- @MedicalBooksStore 2016 AntibioticDocument349 pages@MedicalBooksStore 2016 Antibioticant bee100% (1)
- Rapid Communication: Spontaneous Abortions and Policies On COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Use During PregnancyDocument14 pagesRapid Communication: Spontaneous Abortions and Policies On COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Use During PregnancyStéphane BoucherNo ratings yet
- HHG4M - Lifespan Development Textbook Lesson 4Document88 pagesHHG4M - Lifespan Development Textbook Lesson 4Lubomira SucheckiNo ratings yet
- Customer Part Exchange Program: Product InformationDocument8 pagesCustomer Part Exchange Program: Product InformationAdrian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Collab#2 (Edited)Document14 pagesCollab#2 (Edited)Yani BatoctoyNo ratings yet
- Ringing On A Transmission LineDocument33 pagesRinging On A Transmission LinePrem BhaskaraNo ratings yet
- Coley A4Document49 pagesColey A4mfiarkeeaNo ratings yet
- Modicon TM172PDG42R DatasheetDocument14 pagesModicon TM172PDG42R DatasheetRonnie SolomonNo ratings yet
- Ch1 PDFDocument54 pagesCh1 PDFChristian Jegues100% (2)
- Gas Turbine Performance Enhancement Update: GE Energy ServicesDocument45 pagesGas Turbine Performance Enhancement Update: GE Energy Servicesesteban100% (1)
- Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument6 pagesType 2 Diabetes MellitusJoy NisoladaNo ratings yet
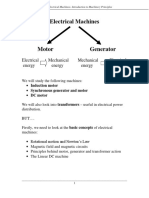
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Machinery PrinciplesDocument27 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Machinery PrinciplesYousab CreatorNo ratings yet
- GreyFox Intercom Install GuideDocument12 pagesGreyFox Intercom Install GuideAbdallah HashemNo ratings yet
- MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET FOR PREVENTOL-D6 PRESERVATIVEDocument3 pagesMATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET FOR PREVENTOL-D6 PRESERVATIVEAkshay PushpanNo ratings yet
- MR-JE - A SERVO AMPLIFIER INSTRUCTION MANUAL (Modbus RTU Protocol)Document114 pagesMR-JE - A SERVO AMPLIFIER INSTRUCTION MANUAL (Modbus RTU Protocol)Aung Naing OoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Power Steering System Design PDFDocument16 pagesHydraulic Power Steering System Design PDFAdrianBirsan100% (1)
- Australian 9 Grade Physics Lesson 1Document32 pagesAustralian 9 Grade Physics Lesson 1binoyrajcrNo ratings yet