Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unti 4-6 Study
Uploaded by
Jennifer Schulze AyscueOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unti 4-6 Study
Uploaded by
Jennifer Schulze AyscueCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 4-6 Study Ch 43:
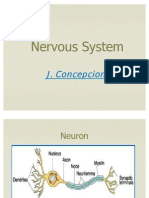
Assessment of the Nervous System CNS: Brain and spinal cord. PNS/ANS: Sympathetic (fight or flight), Parasympathetic (rest and digest). Cranial nerves: II Optic- central and peripheral vision, IV Trochlear- eye movement, VI Abducens- eye movement by lateral rectus muscles. Assess by the Six Cardinal field of vision. Sensory: Pain and light touch are most commonly assessed. Assess with any sharp or dull object (cotton tip or paperclip). Instruct pts with diminished touch sensation to look at feet for placement when walking, do not walk barefoot and avoid throw rugs. Motor Function: Observe for involuntary movements such as tremors, pill-rolling or intention tremors. Romberg sign, the problem is propriception (awareness of body position) this is done by having the pt. stand with arms out and eyes closed, check for swaying. Babinski sign- positive is the abnormal response with toe upgoing; this can occur with drug and alcohol intoxication, after a seizure, multiple sclerosis and liver disease. Posturing: Decerebrate is seen with dysfunction of the brain stem area, characterized by extension of arms and legs, pronation of the arms, feet are planter flexed and opisthotonos (body spasms in which the body is bowed forward). Decortication is seen with lesions that interrupt the corticospinal pathway, characterized by arms, wrist and fingers flexed with internal rotation and planter flexion of the feet. You will also see pinpoint or dilated, nonreactive pupils with these as well. Pupil constriction is a function of cranial nerve III. Accommodation: pt is asked to focus on a distant object and then immediately look at an object 4-5 inches from the nose. These eyes should cross and the pupil contract. Lab Test: PET scan- provides info about the function of the brain and cerebral blood flow. CT scan- assess for allergies, increase fluids after the procedure to flush the kidneys. EEG- records the electrical activity of the cerebral hemispheres, requires sleep deprivation and possible anticonvulsants withheld. Evoked Potentials: confirms neurological conditions such as MS, brain tumor, acoustic neuromas (tumors of the inner ear) and spinal cord injuries. Auditory evoked assess hearing loss, visual evoked assess loss of vision due to optic nerve damage, and somatosensory measures response to stimuli to detect nerve or spinal cord damage or nerve degeneration. Lumbar Puncture: insertion of spinal needle between the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebrae, done to obtain CSF for testing and can be used to inject drugs and anesthetics, and to reduce pressure. This test is contraindicated in pts with ICP and skin infection on or near site. Spinal headache is possible. Be sure the pt does not move, make sure proper placement by seeing CSF. Normal CSF pressure ranges from 50-180mm for children it is 10100mm. CSF can be tested for meningitis, bacterial, TB and fungal CSF will be yellow and viral meningitis will be clear. If a brain hemorrhage has occurred CSF may change from red to yellow to brown. Cloudy CSF may mean an infection such as meningitis or a brain abscess. CSF values: pressure <20cm H2O is normal, color clear is normal, cells- < 0.5, protein- 15-45 and up to 70 in older adults, glucose- 50*75 or 60-70% of glucose is normal.
You might also like
- Nurse Practitioner Board ReviewFrom EverandNurse Practitioner Board ReviewRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 835 (Health Care Claim PaymentAdvice) - HIPAA TR3 GuideDocument306 pages835 (Health Care Claim PaymentAdvice) - HIPAA TR3 Guideअरूण शर्माNo ratings yet
- PEDS Exam 2 - OutlineDocument67 pagesPEDS Exam 2 - OutlineBonquisha OrgamiNo ratings yet
- Neurology Short NotesDocument11 pagesNeurology Short NotesSachin Kumar Rastogi100% (1)
- NEURODocument201 pagesNEUROAilyn LoroNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve AssessmentDocument5 pagesCranial Nerve AssessmentBAdz TanNo ratings yet
- Seizure Disorder CaseStudyDocument29 pagesSeizure Disorder CaseStudyAnn50% (2)
- Cns ExaminationDocument17 pagesCns ExaminationJuana Maria Garcia Espinoza100% (1)
- Neuro 1 and 2 LabDocument3 pagesNeuro 1 and 2 LabHardikPatelNo ratings yet
- Neurological ExaminationDocument9 pagesNeurological Examinationmohitnet1327No ratings yet
- CN Nerves TestDocument6 pagesCN Nerves TestTosin FagbemiNo ratings yet
- Ati Med Surg Ati NotesDocument32 pagesAti Med Surg Ati NotesVin Lorenzo Campbell100% (6)
- Complete Physical Examination Eyes, Ears, Nose, ThroatDocument103 pagesComplete Physical Examination Eyes, Ears, Nose, Throatjennylyn guadalupe100% (3)
- Neuro PEDocument36 pagesNeuro PEkhaderbasha2020No ratings yet
- Assessment of The Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesAssessment of The Nervous Systemnovita100% (1)
- Neurological AssessmentDocument9 pagesNeurological AssessmentrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Operator's ManualDocument110 pagesOperator's ManualAdam0% (1)
- A Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesA Detailed Lesson PlanIsaac-elmar Agtarap74% (23)
- ASSESSMENT OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM (230 NursDocument72 pagesASSESSMENT OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM (230 Nursriya priyaNo ratings yet
- Neurological AssessmentDocument61 pagesNeurological AssessmentSamantha SunglaoNo ratings yet
- Neuro 101: Nursing Neuro Assessment: Kristen Ankrom, RN, SCRN, CCCC Stroke Coordinator Coliseum Medical CentersDocument29 pagesNeuro 101: Nursing Neuro Assessment: Kristen Ankrom, RN, SCRN, CCCC Stroke Coordinator Coliseum Medical CentersDarvin MathewNo ratings yet
- IoT Security Checklist Web 10 17 r1Document39 pagesIoT Security Checklist Web 10 17 r1SubinNo ratings yet
- Neurological ExamDocument6 pagesNeurological ExamTiti Daraban100% (2)
- How The Brain Works: Understanding Brain Function, Thought and PersonalityFrom EverandHow The Brain Works: Understanding Brain Function, Thought and PersonalityNo ratings yet
- The Neurological ExaminationDocument28 pagesThe Neurological ExaminationpremaNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular System: Med SurgDocument25 pagesNeuromuscular System: Med Surgp23bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Neurological ExaminationDocument13 pagesPaediatric Neurological ExaminationPrashant PalNo ratings yet
- By Abraham Belay: Approach To ComaDocument36 pagesBy Abraham Belay: Approach To ComaashuNo ratings yet
- Practical SkillsDocument15 pagesPractical SkillsAyni SindhiNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 - Neurological Study GuideDocument10 pagesExam 2 - Neurological Study GuideStephanieNo ratings yet
- Assess of Brain Involvement 15may2020Document4 pagesAssess of Brain Involvement 15may2020Harshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Neurological Examination: Dr. Salah Abdulkareem AlmezoriDocument50 pagesPaediatric Neurological Examination: Dr. Salah Abdulkareem AlmezoriAqid Hasan YBoyNo ratings yet
- Neurologic SystemDocument31 pagesNeurologic SystemMini VijayNo ratings yet
- NEUROLOGY BasicsDocument179 pagesNEUROLOGY BasicsmuntahaNo ratings yet
- Examination of Cranial NervesDocument7 pagesExamination of Cranial NervesrajtanniruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document182 pagesChapter 1muntahaNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Examination: Cranial NervesDocument68 pagesNeurologic Examination: Cranial Nerves2013SecBNo ratings yet
- ASESSMENT of Client With Diseases in Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesASESSMENT of Client With Diseases in Nervous SystemChristian San Jose TanNo ratings yet
- The Neurological ExamDocument88 pagesThe Neurological ExamsanNo ratings yet
- NeurologicalDocument89 pagesNeurologicalPaul DeliyosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document6 pagesChapter 8selva0315No ratings yet
- NEUROBEHAVIURrDocument21 pagesNEUROBEHAVIURrSandra DewiNo ratings yet
- Bulandos BSN3 NCM104 Skills Retdem EssayDocument6 pagesBulandos BSN3 NCM104 Skills Retdem EssayRolan BulandosNo ratings yet
- Neurologic ExaminationDocument116 pagesNeurologic ExaminationMikylla OrdanielNo ratings yet
- Blueprint For Final Exam - Doc Health AssessmentDocument13 pagesBlueprint For Final Exam - Doc Health AssessmentKim DepapeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of NeurologicDocument12 pagesNursing Care of NeurologicCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Brain DeathDocument43 pagesBrain Deathanimesh pandaNo ratings yet
- Neuro SGDocument29 pagesNeuro SGgew123No ratings yet
- Sensory ExamDocument24 pagesSensory Examsarguss14100% (2)
- Clinical Skills: Ms Focused ExaminationDocument2 pagesClinical Skills: Ms Focused ExaminationssNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Examination: Muhammad Iqbal BasriDocument79 pagesNeurologic Examination: Muhammad Iqbal Basribima sarewoNo ratings yet
- Unconsciousness: Law and MedicineDocument10 pagesUnconsciousness: Law and MedicineDhivya GaneshNo ratings yet
- Professional Skills Review Central Nervous System (CNS)Document25 pagesProfessional Skills Review Central Nervous System (CNS)Noora AlmuailiNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve Examination OSCE GuideDocument34 pagesCranial Nerve Examination OSCE Guideluq9fifNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Examination For PACESDocument3 pagesNervous System Examination For PACESتوفيق سعدNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0749073922000219 MainDocument15 pages1 s2.0 S0749073922000219 Mainbdjxk95cyhNo ratings yet
- Responses To Altered PerceptionDocument74 pagesResponses To Altered PerceptionANDREA JUSTINE CARDEÑONo ratings yet
- PE Cases Part 1Document15 pagesPE Cases Part 1Kylie YuNo ratings yet
- Biology 12 Section Assignment 4.1 Part A: Reflex Ares Laboratory Lab Report Willis Lee HypothesisDocument5 pagesBiology 12 Section Assignment 4.1 Part A: Reflex Ares Laboratory Lab Report Willis Lee HypothesisJames JungNo ratings yet
- UNCONSCIOUSNESSDocument61 pagesUNCONSCIOUSNESSVidhuma VidhumaNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Neurologic System PDFDocument10 pagesAssessing The Neurologic System PDFYudi TrigunaNo ratings yet
- LWW BATES 17 CranialMotorSystem Transcript FINALDocument8 pagesLWW BATES 17 CranialMotorSystem Transcript FINALRachel Lalaine Marie SialanaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Autonomic and Mitochondrial Disorders: Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment for Mind-Body WellnessFrom EverandClinical Autonomic and Mitochondrial Disorders: Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment for Mind-Body WellnessNo ratings yet
- Assessment SheetDocument1 pageAssessment SheetJennifer Schulze AyscueNo ratings yet
- Identify The NurseDocument1 pageIdentify The NurseJennifer Schulze AyscueNo ratings yet
- HypopituitarismDocument1 pageHypopituitarismJennifer Schulze AyscueNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Study Guide Exam 3Document4 pagesPharmacology Study Guide Exam 3Jennifer Schulze AyscueNo ratings yet
- MedicationDocument1 pageMedicationJennifer Schulze AyscueNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Take Home QuizDocument1 pageMicrobiology Take Home QuizJennifer Schulze AyscueNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1Document3 pagesLesson Plan 1api-311983208No ratings yet
- Gigabyte Ga b85m Ds3h A r10 PDFDocument30 pagesGigabyte Ga b85m Ds3h A r10 PDFMartha Lorena TijerinoNo ratings yet
- The Sandbox Approach and Its Potential For Use inDocument13 pagesThe Sandbox Approach and Its Potential For Use invalentina sekarNo ratings yet
- Aex-Kissan KeralaDocument25 pagesAex-Kissan Keralabsh08070No ratings yet
- KM170, KM171, KM172, F3A21, F3A22: 3 SPEED FWD (Lock Up & Non Lock Up)Document4 pagesKM170, KM171, KM172, F3A21, F3A22: 3 SPEED FWD (Lock Up & Non Lock Up)krzysiek1975No ratings yet
- Embedded Software Development ProcessDocument34 pagesEmbedded Software Development ProcessAmmar YounasNo ratings yet
- MC4 CoCU 6 - Welding Records and Report DocumentationDocument8 pagesMC4 CoCU 6 - Welding Records and Report Documentationnizam1372100% (1)
- 3E Hand Over NotesDocument3 pages3E Hand Over NotesAshutosh MaiidNo ratings yet
- Lahore Waste Management CompanyDocument45 pagesLahore Waste Management CompanyHadia NasirNo ratings yet
- CryptogrophyDocument37 pagesCryptogrophyFarah EssidNo ratings yet
- S4 Computer Sciences Exercises PDFDocument2 pagesS4 Computer Sciences Exercises PDFHenriette Desanges UwayoNo ratings yet
- All Nobel Prizes in LiteratureDocument16 pagesAll Nobel Prizes in LiteratureMohsin IftikharNo ratings yet
- GNSS COrs SystemDocument20 pagesGNSS COrs SystemKostPutriMalangNo ratings yet
- Cornish BoilerDocument3 pagesCornish BoilerDeepak KV ReddyNo ratings yet
- Immobilization of Rhodococcus Rhodochrous BX2 (An AcetonitriledegradingDocument7 pagesImmobilization of Rhodococcus Rhodochrous BX2 (An AcetonitriledegradingSahar IrankhahNo ratings yet
- Ishrana Studenata I Nastavnika Visoke Škole U Subotici Tokom Pandemije COVID-19Document4 pagesIshrana Studenata I Nastavnika Visoke Škole U Subotici Tokom Pandemije COVID-19DejanNo ratings yet
- God Reproducing Himself in UsDocument6 pagesGod Reproducing Himself in UsLisa100% (1)
- (Polish Journal of Sport and Tourism) The Estimation of The RAST Test Usefulness in Monitoring The Anaerobic Capacity of Sprinters in AthleticsDocument5 pages(Polish Journal of Sport and Tourism) The Estimation of The RAST Test Usefulness in Monitoring The Anaerobic Capacity of Sprinters in AthleticsAfizieNo ratings yet
- Lecture BouffonDocument1 pageLecture BouffonCarlos Enrique GuerraNo ratings yet
- Chain: SRB Series (With Insulation Grip)Document1 pageChain: SRB Series (With Insulation Grip)shankarNo ratings yet
- EDAG0007Document5 pagesEDAG0007krunalNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesISMAEL KRIS DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Midterm ReviewerDocument20 pagesMidterm ReviewerJonnafe IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication in ContextDocument19 pagesOral Communication in ContextAzory ZelleNo ratings yet
- Dummy 13 Printable Jointed Figure Beta FilesDocument9 pagesDummy 13 Printable Jointed Figure Beta FilesArturo GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste Management in The World's Cities, UN-HABITAT: January 2010Document17 pagesSolid Waste Management in The World's Cities, UN-HABITAT: January 2010Rajasri SNo ratings yet