Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ITIL 2011 Mind Maps
Uploaded by
Nguyen HungOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ITIL 2011 Mind Maps
Uploaded by
Nguyen HungCopyright:
Available Formats
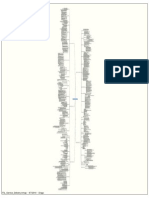
Service Management as a Practice ITIL Service Strategy ITIL Service Strategy Processes ITIL Service Design ITIL Service
vice Design Processes ITIL Service Transition ITIL Service Transition (SACM) ITIL Service Transition (Change and Evaluation) ITIL Service Operation ITIL Service Operation Functions ITIL Service Operation Processes ITIL Continual Service Improvement ITIL CSI Improvement Processes
13 ITIL Mind Maps:
ITIL 2011 Mind Maps
ITIL is a registered trademark of the Cabinet Office. The Swirl Logo is a registered trademark of the Cabinet Office.
ITIL is a registered trademark of the Cabinet Office. This document can be shared internally.
ITIL - Service Management as a Practice
Facilitates outcomes without costs & risks Uncertainty of outcome Functionality Fitness for purpose What the customer gets Fitness for use Performance How service is delivered Economic value Reputation Customer Perception Core Enabling Enhancing Maintenance Prime customer contact Ensures delivery meets requirements Identify areas for input into CSI register / raise RFC's Communication with Process Owners Reporting & monitoring Accountable for delivery of service Classification Coordinated activities Performance driven Creates value for customers Process Defines roles, activities, guidelines Measurable Characteristics Specific Results Customers Responds to triggers Shown by Warranty Value to customers Utility Risk Sources Standards - ISO20000 Training and education Internal and external experience Research Industry practice - Sarbanes Oxley (SOX), Financial Services Authority (FSA) Employees Customers Enablers Suppliers Advisors Technology Knowledge to achieve business objectives
Service
Best Practice
Service Owner
Service Management as a Practice
Definitions
Function Role
Specialised units Perform certain types of work
Responsibility within process or function Responsible Accountable One person
Defines Strategy, policy, standards Assists with design Documentation Audits Communication Input to CSI register Process manager Process practitioner Control RACI Model
Consulted Informed Clarifies roles and responsibilities
Process Owner
Owner Documentation Objectives Feedback
Set of specialised capabilities Provides value for customers via services IT service management
Service Management
Process Model
Activities Procedures Process Metrics Improvement Roles Enablers Capabilities Resources
For Online ITIL Training and Details of Special Offers - Visit:
www.itiltrainingzone.com
ITIL is a registered trademark of the Cabinet Office. This document can be shared internally.
ITIL Service Strategy
Current state assessment target state definition Gap analysis Project estimation Project consolidation Roadmap Definition of roles Service portfolio, customer portfolio, customer agreement portfolio Demand management procedures, techniques and tools Interfaces between all service strategy processes and other processes Rules, policies, processes by which businesses are operated, regulated, controlled Designing the strategy Automation can affect performance Simplify processes
Technology Implementation
Understand flow of activities Minimise interactions Define the market and identify customers Understand the customer Quantify the outcomes Classify and visualise the service Understand the opportunities Define services based on outcomes Service models Core Services - deliver basic outcomes
Establish and maintain business relationships Ensure service provider can meet needs of the business Assists business in articulating value of service
Evaluates, direc ts, monitors the strategy, policies and plans Evaluate Direct Monitor Establish responsibilities Strategy to set and meet objectives Acquire for valid reasons Ensure performance when required Ensure conformance with rules Ensure respect for human factors Service through collaboration Service through coordination Services through delegation Services through direction Services through network What is our business? Who is our customer? What does the customer value? Who depends on our services? How do they use our ser vices? Why are they valuable to them? Internal (Type I) Shared Service Unit (SSU) (Type II) External (Type III) Supplies service to one or more customers Outsourcing Insourcing Disaggregation Aggregation Defined by customers Affordable mix of features Achievement of objectives Changes over time and circumstance Business outcome achieved Customer's preferences Customer's perception of what was delivered Basic Factors Excitement Factors Performance Factors Creating value Stages Framework Activities
Strategy principles
Define service units and packages
Enabling services are needed in order for a core service to be delivered Enhancing services are excitement factors Deliver the basic outcomes desired by the customer Represent the value the customer wants Supporting Services Either enable or enhance the value proposition
Governance
Packaging core and supporting services is an essential aspect of market strategy Packaging will also have an impact on the design and operation of a service Service Management Finances Infrastructure Resources Applications People Information Service Assets Management Organisation Capabilities Processes Knowledge People Future vs Present
Strategic Asset
Marketing mind set
Service Strategy
Assets
Service provider
Opposing dynamics
Operational effectiveness vs improvements in functionality Value capture Vision Business Portrayal How to achieve vision Ongoing Actions
Perspective Positions
4 P's Value
Plans Patterns
Cost effectiveness Value for customer Standardised processes Services create value Respond quickly to changes in business environment
Benefits Kano model
For Online ITIL Training and Details of Special Offers - Visit:
www.itiltrainingzone.com
ITIL is a registered trademark of the Cabinet Office. This document can be shared internally.
ITIL Service Strategy Processes
Service Design Development Operational Services Service Pipeline Service Catalogue Retired Services To ensure service provider has the right mix of services to balance the investment in IT with ability to meet business outcomes Tracks investment through lifecycle and ensures appropriate returns are achieved Ensures services clearly defined and linked to business outcomes Why should a customer buy these services? Why should they buy these services from us? What are our pricing and chargeback models? What are our strengths, weaknesses, priorities and risks? How should our resources and capabilities be allocated? Strategy management Business relationship management CSI Other service management processes Process initiation Clarify the answers to key strategic questions Purpose Contents
How a service provider will enable an organization to achieve its business outcomes Analyse internal and external factors Assessment Define market spaces Identify strategic industry factors Establish objectives Determine perspective Generation Form a position Craft a plan Adopt patterns of action Align assets with outcomes Execution Optimise CSFs Prioritise investments Measurement and evaluation Annual planning cycles New business opportunity Triggers Changes to internal and external environments Mergers or acquisitions CSI Expansion and growth
Strategy Management for IT Services
Process
Enhanced decision making Strategy Request from business Service improvement opportunities Service suggestion Existing services Service, customer and business outcomes Service models Impact on service portfolio and service model Service portfolio review Analyse investments, value and priorities Articulate value proposition Funding models Retain Replace Rationalise Refactor Renew Retire Change proposal Change management authorisation Change proposal authorised Communicate with stakeholders Service design and transition processes Track progress and update portfolio Analysis of previous budget Opportunity Value proposition Business outcomes supported Business cases Priorities Risks Offerings & packages Investments required Cost & pricing To identify and analyse the patterns of business activity that initiate demand for services User Profiles Analyse patterns of business activity Work with capacity management Achieve balance between cost and value of outcomes Refines understanding of interactions Enable executives to evaluate real investment Value to business Objective Accounting Scope Portfolio Contents Budgeting Assessment of plans Specification of changes to funding and spending Cost and income estimation Budget(s) Cost model Cost centres and cost units Cost types and elements Cost classification Chart of accounts Analysis and reporting Action plans Cost recovery or break even Charter Business Impact Assessment (BIA) Outputs Approve Analyse Process Define Value to the business Speed of change SPM Finance compliance and control Operational control Value capture and creation
Portfolio Management
Policy decisions
Cost centre Profit centre Funding External Internal Rolling plan Zero based Trigger based Service valuation Service Investment Analysis Compliance Cost optimisation Seeks to translate outage severity into a financial value Aid to decision making and prioritisation Helps to identify Planning confidence Cost of service outage Relative value of services Assesses the value or return of a service over the total lifecycle Based on the value received and the costs incurred
Service Strategy Processes
Financial management
Demand Management
Policies Charging Pricing Billing Service provider
Recovery with margin Cross subsidisation Notional charging
Decide on chargeable items
Establish and maintain business relationships Ensure service provider can meet needs of the business Assists business in articulating value of service Objective
Contract
Business Relationship Management
Risks
Design Operational Market
For Online ITIL Training and Details of Special Offers - Visit:
www.itiltrainingzone.com
ITIL is a registered trademark of the Cabinet Office. This document can be shared internally.
Statement of requirements (SOR) Invitation to tender (ITT) Business case Award contract Negotiate Select supplier
ITIL Service Design
Identify business need People
Evaluation and procurement of new contracts and suppliers Supplier and contract categorisation Maintains supplier and contract management information system (SCMIS)
Value for money
Supplier Management Design IT services, together with the governing IT practices, processes and policies, to realize the service providers strategy and to facilitate the introduction of these services into supported environments ensuring quality service delivery, customer satisfaction and cost-effective service provision.
4 P's
Products Partners Processes Service solutions Why should a customer buy these services? Why should they buy these services from us? What are the pricing or chargeback models? What are our strengths and weaknesses, priorities and risks? How should our resources and capabilities be allocated? Opportunity Service portfolio Value proposition Business outcomes supported Business cases Systems and tools Contents Priorities Risks Offerings and packages Investments required Ongoing costs and pricing
Manage supplier and contract performance
Ensure contracts are aligned to business Define and maintain policies and methods Plan design resources and capabilities Coordinate design activities Manage design risks and issues Improve service design Plan, coordinate and monitor individual designs Review designs and ensure handover of SDPs Corporate visions, strategies, etc Service management visions, strategies, policies, objectives and plans Constraints and requirements for compliance with standards and regulations IT strategies, policies and plans Business requirements Service portfolio ITSM processes, risks and issues registers Revisions to IT strategies, policies, designs, plans, architectures, processes Service level package Reduced total cost of ownership (TCO) Improved quality of service Consistency of service Easier implementation of new services Better service alignment Improve service performance Improve IT governance Improved service alignment More effective service management Better IT processes Improved information and decision making
Design coordination
Inputs
Key Principles
5 major aspects
Services Supported levels of performance Policies Minimum requirements Service catalogue Ordering and request Support terms and conditions Dependencies Points of contact
Service Design
Technology and management architectures
Pricing and charging Business / organisation Enterprise Service Application Data / Information Environment IT Infrastructure Design top down, build bottom up Processes required Progress Measurement methods and metrics Compliance Effectiveness Efficiency Functionality
Benefits
Coordinate all design activities
Plan and coordinate the resources and capabilities required to design new or changed services Produce associated service design packages Ensure service designs and/or SDPs are produced and handed over to service transition Manage the quality criteria, requirements and handover between design, strategy and transition Ensure all service models and service solution designs conform to strategic, architectural, governance and other corporate requirements Improve the effectiveness and efficiency of service design activities and processes Ensure that all parties adopt a common framework of standard, reusable design practices Monitor and improve the performance of the service design lifecycle stage
Balanced design
Resources Schedule
Objectives Other Service Design Processes
See "Service Design Processes" Map
ITSC Availability Capacity Service Level Service Catalogue
For Online ITIL Training and Details of Special Offers - Visit: www.itiltrainingzone.com
ITIL is a reg istered trademark of the Cabinet Office. This document can be shared internally.
ITIL Service Design Processes
Align IT security with business security Effectively manage information security Management of risks Training & awareness Security strategy and plan Management of suppliers and contracts regarding access to systems and services Management of all security breaches and incidents associated with all systems and services Proactive improvement of security controls, and security risk management and the reduction of security risks Integration of security aspects within all other IT service management processes Manage information security management system Control Plan Implement Evaluate Maintain Preventive Reductive Detective Repressive Corrective Agreed level of IT Service Achievable targets Proactive measures Improvements to service Produce and agree service level requirements (SLRs) Negotiate between internal service providers Service Multi Level Customer External contractors Contracts Agree Measure Monitor Regular Ad-Hoc Red, amber, green (RAG) / Service level agreement monitor (SLAM) charts Review Cost justifiable capacity available in time Capacity matched to evolving agreed needs of customer Supply vs demand Cost vs resource Capacity plan Proactive activities Assistance with Capacity incident resolution Modelling and trending Application sizing Monitoring Tuning Analysis Demand management Threshold management and control Future business needs Requires financial plans and business strategy Live service capacity Incident / problems Performance, capacity, utilisation Business capacity management Service capacity management Component capacity management Ongoing operations Implementation Iterative Techniques Activities Initiation Report Required services resumed within required and agreed timescales Support business continuity management (BCM) Agreed and required timescales Policy setting Terms of reference and scope Resource allocation Project organisational and control structure Agree project and quality plans Business impact analysis (BIA) Risk analysis Manual Requirements & strategy Process ITSC strategy Reciprocal Gradual Intermediate Fast Immediate Develop plans / procedures Testing Education, awareness, training Review & audit Testing Change management Invocation Negotiate between IT and customer Service level agreement (SLA) Document Operational level agreement (OLA) Define Proactive Activities Measures Reliability Availability Security Framework Manage information contained in service catalogue Ensure service catalogue is available and accurate Ensure service catalogue supports evolving needs of service management processes Live services Business service catalogue Technical service catalogue
Service Catalogue Management Information Security Management
Delivered service matches or exceeds needs of customer Perform as agreed Service availability Component availability Design for availability and recovery Perform as its agreed function Speed to restore to normal working Ability of 3rd party to meet terms of contract Identifying vital business functions (VBFs)
Maintainability Serviceability
Availability Management
Designing in availability Component failure impact analysis (CFIA) Single point of failure (SPOF) Fault tree analysis (FTA) Modelling Risk assessment Planned maintenance
Service Level Management
Process
Service Design processes
Projected service outage document (PSO) document Monitor, measure, analyse, report Expanded incident lifecycle Reactive Activities Unavailability analysis Service failure analysis (SFA) Component failure impact analysis (CFIA)
IT Service Continuity Management (ITSC) Capacity Management
For Online ITIL Training and Details of Special Offers - Visit:
www.itiltrainingzone.com
ITIL is a registered trademark of the Cabinet Office. This document can be shared internally.
ITIL Service Transition
Speed vs accuracy Safety critical services Restricted resources Working with difficult customers Stakeholder change Communications Stakeholder map Stakeholder commitment analysis Emotional cycle of change Leadership Organisational adoption Governance process Organisational capabilities Business and service performance measures Strong communication process Kotter's 8 steps Organisational change
Plan and manage service changes efficiently and effectively Manage risks relating to new, changed or retired services Successfully deploy service releases into supported environments
Difficulties
Objectives
Set correct expectations on the performance and use of new or changed services Ensure that service changes create the expected business value Provide good-quality knowledge and information about services and service assets. Confidence that a new or changed service will deliver the value and outcomes required of it Benefits Understanding of risk Provides a measured degree of confidence. Define customer requirements Design Define service requirements Design service solution Design service release V Model Validate service packages Service acceptance Test Service operational readiness Service release package Component and assembly Library of tests Plan and design tests Test environment Levels of testing Verify test plan and designs Process Prepare test environment Perform tests Evaluate exit criteria Report Test and clean up
Managing People
Release policy Provide clear comprehensive plans Assure quality Produce transition strategy Prepare for transition Plan and coordinate transition Provide transition process support Activities
Transition Planning and Support
Service Validation and Testing
Service Transition
See "Change and Change evaluation Map" See "Change and Change evaluation Map" See "Knowledge, Service Asset and Configuration Map"
Change Evaluation
Service Asset and Configuration Knowledge Big bang / phased Push / pull Automated / manual Full Delta Package Planning Preparation Build and test Service testing and pilot Planning and preparing for deployment Performing transfer, deployment and retirement Early life support
See "Knowledge, Service Asset and Configuration Map"
Other Service Transition Processes
Should be separate to release and deployment manager Enable projects to estimate the cost, timing, resource requirement and risks associated with the service transition stage more accurately Result in higher volumes of successful change Be easier for people to adopt and follow Enable service transition assets to be shared and re-used across projects and services Reduce delays from unexpected clashes and dependencies
Release options
Benefits
Enable projects to estimate the cost, timing, resource requirement and risks associated with the service transition stage more accurately Result in higher volumes of successful change Be easier for people to adopt and follow Enable service transition assets to be shared and re-used across projects and services Reduce delays from unexpected clashes and dependencies
Release unit
Release and Deployment Management
Activities
To assist organisations seeking to plan and manage service changes and deploy service releases into the production environment successfully
Review and closure of deployment and Service Transition Role should be separate to test manager
For Online ITIL Training and Details of Special Offers - Visit: www.itiltrainingzone.com
ITIL is a registered trademark of the Cabinet Office. This document can be shared internally.
ITIL Service Transition - SACM
IT staff to understand the configuration and relationships of services and the configuration items Better forecasting and planning of changes Successful assessment, planning and delivery of changes and releases Resolution of incidents and problems within the service level targets Delivery of service levels and warranties Better adherence to standards, legal and regulatory obligations More business opportunities as the service provider is able to demonstrate control of assets and services Traceability of changes from requirements Ability to identify the costs of a service Reduced cost and time to discover configuration information when it is needed Proper stewardship of fixed assets that are under the control of the service provider Configuration manager Configuration item (CI) identification External / internal Categories Define Planning & management Policies Objectives, scope, resources CSFs Involve change/release Start small Regulatory compliance An asset, service component or other item which is or will be, under the control of configuration management Types Naming convention Attributes Relationships Business case Service lifecycle Service management plans Hardware People Accommodation Software Documentation Organisation Internal policies Business strategy
SACM Benefits
Design, manage & maintain configuration management system (CMS) Control receipt, identification, storage of CI's Create process & procedures & training Regular housekeeping Amend database to suit business requirements Design & maintain asset management systems Asset management system processes & procedures Agrees naming convention
Configuration librarian Configuration analyst CMS tools administrator
SACM Roles
SACM Activities
Service asset manager
Service Transition:
Service Configuration control Status accounting Authorised CIs CIs under change control Define each status Before /after major change Verification and audit After IT service continuity invoked Planned, regularly, random Automate
Service capability assets Service resource assets
Configuration management databases (CMDB's) Definitive media libraries (DML's) information Known error databases (KEDB) Availability management information system (AMIS) Capacity management information system (CMIS) Data mining Modelling Information integration layer Knowledge processing layer Reports Presentation layer Data, Information, Knowledge, Wisdom (DIKW) Improve the quality of management Enable the service provider to be more efficient and improve quality of service, increase satisfaction and reduce the cost of service by reducing the need to rediscover knowledge Ensure that staff have a clear and common understanding of the value of their services Maintain a service knowledge management system (SKMS) that provides controlled access to knowledge, information and data that is appropriate for each audience Gather, analyse, store, share, use and maintain knowledge, information and data throughout the service provider organization. Service knowledge management system (SKMS) Data, information & tools layer
- Knowledge Management - Service Asset and Configuration Management
Knowledge Management SACM CMS
Configuration management databases (CMDB's) Definitive media libraries (DML's) Data, information & tools layer Known error databases (KEDB) Availability management information system (AMIS) Capacity management information system (CMIS) Physical storage information Definitive spares Definitive media library
For Online ITIL Training and Details of Special Offers - Visit:
www.itiltrainingzone.com
ITIL is a registered trademark of the Cabinet Office. This document can be shared internally.
Raised by Reason Return Risks Resource Responsible Relationship Cost Regular Assess, plan, schedule changes Review previous changes Flexible membership Change schedule (CS) Projected service outage (PSO) 7 R's Impact
Change and Evaluation
(ChM) Change assessment (ChM) Change process
Recorded Assessed/evaluated Authorised Prioritised Planned Tested Implemented Reviewed Strategic
(ChM) Change advisory board (CAB)
Tactical
Service Transiti on
Password reset Operational activity User access request Reboot Project change proposal Preauthorised, accepted procedure Standard change Emergency change Normal change Interface with request fulfilment
- C hange M anagement ( ChM) - Change Evaluation (ChE)
Control using change model Consider remediation / back out plans Test as much as possible Retrospective RFC
(ChM) Request for Change
(ChM) Emergency change advisory board (ECAB)
Set stakeholder expectations correctly Provide effective and accurate information to change management Evaluate the intended and unintended effects of a service change Provide good-quality outputs so that change management can expedite an effective decision about whether or not a service change is to be authorized. Evaluation required before each of authorization by the suitable authority to provide advice and guidance Change evaluation is concerned with value. Establish the use made of resources in terms of delivered benefit
Lack of commitment to the process by the business, management or IT staff
(ChE) Change evaluation
(ChM) Change risks
Bypassing the process Change assessment being reduced to box ticking Overly-bureaucratic process Insufficient time
For Online ITIL Training and Details of Special Offers - Visit:
www.itiltrainingzone.com
ITIL is a registered trademark of the Cabinet Office. This document can be shared internally.
ITIL Service Operation
Reduced labour / costs Reduced duration / frequency of service outages Meet goals of ISM policy Increased effectiveness and efficiency Services Service management processes Technology People Maintain business satisfaction Minimise impact of service outages Ensure access to service for authorised users
Value to business
Undertake activities & processes that manage and deliver services at agreed levels to business users and customers. To manage the technology used to deliver the services and to collect information on performance & Service metrics
Manage operational costs Maintain live services to defined service standards
Scope
Benefits
Identify incidents & problems Protect live services Proactive activities
Objectives
Service Operation
Objectives
Deliver services at agreed levels to the business Manage day to day activities and processes Monitor ongoing performance Manage the service technology Harvest data & report against agreed metrics Technical management
Internal (technology) vs external (services) Stability vs responsiveness Cost vs quality Reactive vs proactive Incident management Event management Problem management Access management Request fulfilment See "Service Operation Processes" map
Balance
See "Service Operation Functions" map
IT Operations management Common service operation activities Service desk Application management
Functions Processes
For Online ITIL Training and Details of Special Offers - Visit:
www.itiltrainingzone.com
ITIL is a registered trademark of the Cabinet Office. This document may be shared internally.
ITIL Service Operation Functions
Manage knowledge and expertise Single point of contact Manage service requests Incident management Request fulfilment Record changes Supplier liaison Provide information Complaints Improve customer service Improve communication Virtual and follow the sun Central Local Specialised Business Technical Interpersonal Outsourcing Super users Retention Skill set Staffing depends on organisational requirements Types Ensure applications appropriately designed Assist in resolution of failures
Application Management
Design and deployment of applications Provide resource throughout lifecycle Research and development Training programmes Application portfolio Manage and maintain IT infrastructure
Service Desk
Provide stable environment Diagnose & resolve IT failures Console management Job scheduling Operations Control Back ups Restores Print & output management Ongoing maintenance Physical environment
IT Operations Management
Directory service IT Operations Middleware Internet/Intranet Network Server Mainframe Database Storage / Archive Desktop and mobile support Facilities / Datacentre management Improvement of operations activities Active / Passive Reactive / Proactive Continuous / Exception Open Closed Control loops Monitoring
Service Operation Functions
Facilities Management
Recovery sites Datacentres
Standard operating procedures (SOP) Documentation Operations logs Shift schedules and reports Manage technical knowledge Help in planning, implementation and maintenance of infrastructure Guidance to Service Operations for live environment
Technical management Common Service Operation Activities
Technical specialisation Activity
Guidance to Service Design in development Training programmes Definition of standards Research and development Problem management Provide resource throughout lifecycle
Internal / External Reporting
Organisational Structures
Process Geography Hybrid Combined
For Online ITIL Training and Details of Special Offers - Visit:
www.itiltrainingzone.com
ITIL is a registered trademark of the Cabinet Office. This document may be shared internally.
ITIL Service Operation Processes
Objective Restore normal service operation as quickly as possible Identify training requirements Align business with IT activity Identify potential improvements Increased availability and customer satisfaction Restore service asap Incident is an unplanned interruption to an IT Service Reduction in the quality of an IT Service Failure of a CI that has not yet impacted an IT service Event Management Web interface Telephone eMail Identification Logging Categorisation Urgency Business Impact Technical Hierarchical Prioritisation Process Input Incident Benefits Workaround Purpose Problem
Eliminate recurring incidents Minimise impact of incidents that cannot be prevented Prevent problems and resulting incidents from happening Underlying cause of one or more incidents Reactive Proactive Temporary way of overcoming difficulties Predefined Problem diagnosis complete and workaround identified
Known Error (KE) Detection Logging
Categorisation Prioritisation Investigation and diagnosis Create KE Raise RFC Resolution Closure Possible major problem review
Incident Management
Process
Investigation and Diagnosis Escalation
Problem Management
Event management Incident management Input Service desk Proactive problem management Supplier or contractor Updated records Resolved problems RFCs Workarounds Known errors Problem management reports
Resolution and Recovery Closure Specific incidents Standardised method Pre defined steps Major Incident Follow policies from Information security management Verify identity of users User's rights / privileges Restricting non users access Logging and tracking access RFC Service request Request from HR or manager Detect, analyse, take appropriate control action Early detection of events Automated operations Assign support before outage occurs Detectable or discernable occurrence Informational Warning Exception Constant state CIs Software licence Security Normal activity Any change of state that has significance for the management of a CI Active Passive Reactive Proactive Monitoring Event Scope Types of event Triggers Incident Model Output
Kepner & Tregoe Ishikawa Brainstorming
Access Management
Chronological Pain value
Service Operation Processes
Techniques
Pareto Affinity mapping 5 Whys Hypothesis testing Lotus blossom Technical observation
Request model
Predefined method to handle repeat requests Day to day demands from users Small changes
Service Request
Low risk and cost Frequently performed Pre approved by change authority
Event Management
Request Fulfilment
Self service and self select tools Standard change Managed as service request Pre-approved change
Standard service request Channel for: Information on availability of services General information Comments and complaints
For Online ITIL Training and Details of Special Offers - Visit:
www.itiltrainingzone.com
ITIL is a registered trademark of the Cabinet Office. This document may be shared internally.
ITIL Continual Service Improvement
To align IT services to the changing business needs by identifying and implementing improvements to IT services that support business processes.
Lead to a gradual and continual improvement in service quality Ensure that IT services remain continuously aligned to business requirements Gradual improvements in cost effectiveness through a reduction in costs and or the capability to handle more work at the same cost Identify opportunities for improvement in all lifecycle stages and processes through monitoring and reporting Identify opportunities for improvements in organizational structures, resourcing capabilities, partners, technology, staff skills, training and communications Provides an environment within which CSI can operate and thrive Business governance Responsibility of board of directors and executive management. IT governance Ensures IT sustains and extends the organisation's strategies and objectives Leadership Processes Organisational structure
Define success Build framework Choose measures Define procedures & policies Assessment Gap analysis Benchmarking Comparison with industry norms Process maturity comparison Total cost of ow nership (TCO) Return on investment (ROI) Availability reporting Predict and report service performance against targets Performance Availability CSF KPI End to end service Resources Functionality Schedule Financial Customer Innovation Internal Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats Used to establish an initial data point to determine if a service or process needs to be improved Must be documented, recognized and accepted throughout the organization Strategic goals and objectives Tactical process maturity Operational metrics and KPIs To validate To direct To justify To intervene Contains important information for the overall service provider Introduces a structure and visibility to CSI ensuring all initiatives are captured and recorded, and benefits realized Improvement opportunities should be categorized into initiatives that can be achieved quickly, or in the medium or longer term Each improvement initiative should show the benefits that will be achieved by its implementation Should be held and regarded as part of the service knowledge management system (SKMS) Provides a coordinated, consistent view of the potentially many improvement activities CSI register Measure value Must be established at each level: Baselines SWOT Balanced Scorecard Balancing elements Tension Service measurement Technology Steps
Value
Enterprise Governance
Process Service Metrics
Ensure applicable quality management methods are used to support continual improvement activities Ensure that processes have clearly defined objectives and measurements that lead to actionable improvements Understand what to measure, why it is being measured and what the successful outcome should be Ownership is fundamental to any improvement strategy
Continual Service Improvement
Methods and Techniques
Objectives
Accountable for ensuring best practice is adopted and sustained throughout the organization Chief advocate and owns all CSI issues CSI manager Accountable for the success of CSI in the organization Ensures adequate resources to support and enable CSI Not accountable for improvements to specific services which are the responsibility of the appropriate service owner working within the CSI framework
Critical Roles
Service Owner
Accountable and responsible for the production and maintenance of the CSI register Accountable for the delivery of a specific IT service Responsible to the customer for the initiation, transition and ongoing maintenance and support of a particular service Accountable to the IT director or service management director for the delivery of the service Reviews and analyses data from components, systems and sub systems in order to obtain a true and end-to-end service achievement
Reporting analyst Service level manager
CSI processes and Inte gration with other processes
CSI approach see "CSI Integration" Map 7 Step improvement Deming cycle
For Online ITIL Training and Details of Special Offers - Visit:
www.itiltrainingzone.com
ITIL is a registered trademark of the Cabinet Office. This document may be shared internally.
ITIL CSI Processes and Interaction
What is the vision? Where are we now? Where do we want to be? How will we get there? How do we know we have arrived? How do we keep the momentum going? Plan Do Check Act To align business needs with IT service delivery Involving the business to determine its service level requirements (SLRs) Identifying internal relationships in IT organizations, negotiating terms and responsibilities and codifying them with operational level agreements (OLAs) Working with the supplier manager to Identify existing contractual relationships with external vendors and verifying that the underpinning contracts (UCs) meet the revised business requirements Using the service catalogue as the baseline to negotiate service level agreements (SLAs) with the business Reviewing service achievement and identifying where improvements are required, feeding them into CSI Component failure impact analysis Fault tree analysis Service fault analysis Technical observation Extended incident lifecycle SIPs and reports Business Service Component Iterative activities Application sizing Demand management Modelling SIPs and reports Manage RFCs from SIPs Implementing improvement Post Implementation review CAB Kotter's 8 steps SKMS CMS CMDB Documenting and reviewing incident trends on incidents, service requests and telephony statistics over a period of time to identify any consistent patterns
CSI Approach CSI 7 Step Process
Identify strategy for improvement Define what will you measure Gather the data Process the data Analyse the information and data Present and use the information Implement improvement
CSI Deming Cycle
Defining security monitoring and data collection requirements Monitoring, verifying and tracking the levels of security according to the organizational security policies and guidelines Assisting in determining effects of security measures on the data monitoring and collection from the confidentiality, integrity and availability perspectives Processing response and resolution data on security incidents Creating trend analyses on security breaches Validating success of risk mitigation strategies Utilizing the agreed upon reporting format Analysing processed data for accuracy Monitoring and collecting data associated with the actual expenditures versus budget Provides input on questions such as whether costing or revenue targets are on track
Security Service level
Availability
Continual Service Improvement processes and interaction with other processes
Financial
Monitors the ongoing cost per service etc Provides the necessary templates to assist CSI to create the budget and expenditure reports for the various improvement initiatives Provides the means to compute the ROI of the improvements SIP Root cause Analysis
Problem Capacity
Identify improvements / trends Preventative action Reporting
Change & Release
Service Desk and Incident Management
Comparing results with prior months, quarters or annual reports Comparing results with agreed-to levels of service Identifying improvement opportunities Analysing processed data for accuracy Input into SIPs
Identify risk Identify changes that affect ITSC Regulatory impact
ITSC
Data, information, knowledge, wisdom
Knowledge
Shared knowledge Inclusion in CSI register Building SIPs
For Online ITIL Training and Details of Special Offers - Visit:
www.itiltrainingzone.com
You might also like
- Board Meeting Agenda TemplateDocument1 pageBoard Meeting Agenda TemplatemmatearNo ratings yet
- ITSM Best PracticesDocument1 pageITSM Best PracticesАлексей Лукацкий0% (1)
- Risk-Management-Guide-Cso-2010 - SampleDocument17 pagesRisk-Management-Guide-Cso-2010 - SampleJohnson Joshiraj Paul JeyarajNo ratings yet
- IIBA Global BusinessAnalysis CoreStandardDocument50 pagesIIBA Global BusinessAnalysis CoreStandardkorrait100% (1)
- ITIL Service Management FundamentalsDocument32 pagesITIL Service Management FundamentalsXtine Ramos100% (1)
- Measurement and Evaluation in Human Performance (James R Morrow JR., Dale P. Mood Etc.)Document759 pagesMeasurement and Evaluation in Human Performance (James R Morrow JR., Dale P. Mood Etc.)Matias Lopes VieiraNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment for Earthmoving OperationsDocument42 pagesRisk Assessment for Earthmoving OperationsHolly SmithNo ratings yet
- 2006-07 Sports Medicine HandbookDocument121 pages2006-07 Sports Medicine Handbookilona ilincaNo ratings yet
- ITSM Assessment ReportDocument175 pagesITSM Assessment Reportmarcelo_linero100% (1)
- ITSM Best PracticesDocument62 pagesITSM Best PracticesJames McCracken100% (3)
- ITIL Handbook WhitepaperDocument42 pagesITIL Handbook WhitepaperRodrigo Silva100% (11)
- IT Service ManagementDocument21 pagesIT Service ManagementSreedhar Dachepalli100% (1)
- Stages of a Marriage from Dating to DeathDocument18 pagesStages of a Marriage from Dating to DeathIvan100% (1)
- Ola TemplateDocument8 pagesOla Templatetoto_falaNo ratings yet
- Risks and controls for working with electricityDocument9 pagesRisks and controls for working with electricityLogesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Urdg 758Document33 pagesUrdg 758rupeshsingh1986No ratings yet
- Itsm Academy Project Charter 04-25-07v3Document12 pagesItsm Academy Project Charter 04-25-07v3kkuppachiNo ratings yet
- Achieving Business Availability Objectives through IT Service Continuity ManagementDocument1 pageAchieving Business Availability Objectives through IT Service Continuity ManagementgringoricanNo ratings yet
- The Surefire LTT Ebook PDFDocument16 pagesThe Surefire LTT Ebook PDFLoixs Knard TanNo ratings yet
- ISO 20000 Master List of DocumentsDocument1 pageISO 20000 Master List of DocumentsAditya YerunkarNo ratings yet
- Rose's Strategy of Preventive Medicine - Geoffrey RoseDocument39 pagesRose's Strategy of Preventive Medicine - Geoffrey RoseJesus Esteban HernándezNo ratings yet
- Itil v3 Service Design GuidelinesDocument72 pagesItil v3 Service Design GuidelineslatifahmadpoorNo ratings yet
- ITIL+Service Operation 1203Document49 pagesITIL+Service Operation 1203Андрей ИвановNo ratings yet
- Checklist of Recommended ITIL Documents For Processes and Functions enDocument18 pagesChecklist of Recommended ITIL Documents For Processes and Functions enFeleke AfeworkNo ratings yet
- ITIL Service Design PosterDocument1 pageITIL Service Design PosterDominic Benedito100% (6)
- Materna ITIL Poster v4.0.0Document2 pagesMaterna ITIL Poster v4.0.0desertedtweek93% (15)
- ITIL Self-Assessment Approach For Small and MediumDocument7 pagesITIL Self-Assessment Approach For Small and MediumaminaNo ratings yet
- ISO 20000 Implementation Diagram - ENDocument1 pageISO 20000 Implementation Diagram - ENAyahnyaAzkaAzmiNo ratings yet
- Tle9agricropproduction - q1 - m9 - Observingworkplacepracticesandreportingproblemsincompletingworkforhorticulturalproduction - v3Document24 pagesTle9agricropproduction - q1 - m9 - Observingworkplacepracticesandreportingproblemsincompletingworkforhorticulturalproduction - v3Maricris Pamulaklakin AlmendrasNo ratings yet
- ITIL4FEN Practices v1.1Document42 pagesITIL4FEN Practices v1.1Wilfried Foalem100% (1)
- ITIL Process Maturity FrameworkDocument2 pagesITIL Process Maturity FrameworkpdsramaraoNo ratings yet
- SITXWHS007 Student Assessment Task 2Document14 pagesSITXWHS007 Student Assessment Task 2Sushma karki100% (1)
- ITIL+4 HandsOnDocument45 pagesITIL+4 HandsOnKathia Lissbeth Rodriguez100% (1)
- ITIL Service Operation ProcessesDocument1 pageITIL Service Operation ProcessesDominic Benedito100% (7)
- Organizing Itsm: Transitioning the It Organization from Silos to Services with Practical Organizational ChangeFrom EverandOrganizing Itsm: Transitioning the It Organization from Silos to Services with Practical Organizational ChangeNo ratings yet
- Implementing ITILDocument27 pagesImplementing ITILvimpat100% (3)
- BMC - Service Portfolio Management WhitepaperDocument10 pagesBMC - Service Portfolio Management WhitepaperRoss ManningNo ratings yet
- ITIL and Software DevelopmentDocument31 pagesITIL and Software DevelopmentnirmalrameshNo ratings yet
- Interfacing and Adopting ITIL and COBIT PreviewDocument13 pagesInterfacing and Adopting ITIL and COBIT PreviewwilmertorresdNo ratings yet
- Problem Management - ItilDocument27 pagesProblem Management - ItilivofabiorodriguesNo ratings yet
- 03 Derek Gillard - Service Catalogue JourneyDocument28 pages03 Derek Gillard - Service Catalogue Journeyarsman1100% (1)
- Service Catalogue TemplateDocument3 pagesService Catalogue TemplateJerod King100% (1)
- ITIL Awareness and Service Management MaturityDocument15 pagesITIL Awareness and Service Management MaturityManoj KulkarniNo ratings yet
- ITIL V3 Service Design MindmapDocument1 pageITIL V3 Service Design MindmapIgor100% (3)
- Sample Metrics For ITIL ProcessesDocument3 pagesSample Metrics For ITIL ProcessessantuchetuNo ratings yet
- ITIL® Guide to Software and IT Asset Management - Second EditionFrom EverandITIL® Guide to Software and IT Asset Management - Second EditionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- ITIL V3 Service Operation MindmapDocument1 pageITIL V3 Service Operation MindmapAllanNo ratings yet
- Screenshots Itil Process Map VisioDocument16 pagesScreenshots Itil Process Map Visionico0j100% (1)
- Itsm and Itil Capability Assessment ChecklistDocument1 pageItsm and Itil Capability Assessment ChecklistFarina James0% (1)
- Planning To Implement Service Management Green Book)Document195 pagesPlanning To Implement Service Management Green Book)api-3744926100% (3)
- Measures and Metrics (Study Guide)Document29 pagesMeasures and Metrics (Study Guide)Eduardo MucajiNo ratings yet
- Pragmatic Application of Service Management: The Five Anchor ApproachFrom EverandPragmatic Application of Service Management: The Five Anchor ApproachNo ratings yet
- Itil 2011 Process ModelDocument1 pageItil 2011 Process ModelAlexandru Dan GheorghiuNo ratings yet
- IT4IT Reference Card4Document1 pageIT4IT Reference Card4GuillermoVillalonNo ratings yet
- ITIL 4 - IT Process WikiDocument1 pageITIL 4 - IT Process WikiLea DevNo ratings yet
- Itil at A GlanceDocument1 pageItil at A Glancefernandomp100% (1)
- Service Integration and Management (SIAM™) Professional Body of Knowledge (BoK), Second editionFrom EverandService Integration and Management (SIAM™) Professional Body of Knowledge (BoK), Second editionNo ratings yet
- ITIL Lifecycle Essentials: Your essential guide for the ITIL Foundation exam and beyondFrom EverandITIL Lifecycle Essentials: Your essential guide for the ITIL Foundation exam and beyondNo ratings yet
- ITIL 2011 Edition Quick Reference GuideDocument2 pagesITIL 2011 Edition Quick Reference GuideMadhur Sawant100% (2)
- Itil® 4 Specialist: High-Velocity It Elearning Course: AudienceDocument3 pagesItil® 4 Specialist: High-Velocity It Elearning Course: AudienceEugene ArkadievNo ratings yet
- ITIL Service Support and Service DeliveryDocument2 pagesITIL Service Support and Service DeliveryhyrtksnNo ratings yet
- FNAL OLA TemplateDocument23 pagesFNAL OLA Templatehallarmemon0% (1)
- ITIL V3 roles definitions guideDocument9 pagesITIL V3 roles definitions guidePratul SharmaNo ratings yet
- CAP Mindmap v4Document1 pageCAP Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNo ratings yet
- Release Management Process Documentation Standard RequirementsFrom EverandRelease Management Process Documentation Standard RequirementsNo ratings yet
- 5.1 HIRA For Installation of DUCTDocument3 pages5.1 HIRA For Installation of DUCTRAM KUMAR K RNo ratings yet
- Dean Lebaron (Batterymarch), Hbs 1960, Was With An Investment Services Firm When HeDocument20 pagesDean Lebaron (Batterymarch), Hbs 1960, Was With An Investment Services Firm When HemilkenNo ratings yet
- Arif Habib Bank LimitedDocument80 pagesArif Habib Bank LimitedAnam TahirNo ratings yet
- Learning Material 4 PROVISION: Contingent Liability A. Discussion of Accounting PrinciplesDocument11 pagesLearning Material 4 PROVISION: Contingent Liability A. Discussion of Accounting PrinciplesJay GoNo ratings yet
- 15 18 106 0C - Notice - 12M26.2 - GEB - ENDocument132 pages15 18 106 0C - Notice - 12M26.2 - GEB - ENsxturboNo ratings yet
- Model of Decision MakingDocument34 pagesModel of Decision MakingPalalikesjujubesNo ratings yet
- SOX Matrixes in Tenaris: StartDocument388 pagesSOX Matrixes in Tenaris: StartDiego Martin MatillaNo ratings yet
- Reporte Anual 2019 - IkeaDocument54 pagesReporte Anual 2019 - IkeaLeodan ZapataNo ratings yet
- HSBC Bank Malta PLC ProspectusDocument54 pagesHSBC Bank Malta PLC ProspectusBilly LeeNo ratings yet
- Prev Injuries 052407Document124 pagesPrev Injuries 052407Anonymous 1sd8foGfGNo ratings yet
- ARR 190514 Book1Document187 pagesARR 190514 Book1Jun Rey LincunaNo ratings yet
- Nur Halili Binti Muhammad Rozani - 2019702089 - Ap2256aDocument23 pagesNur Halili Binti Muhammad Rozani - 2019702089 - Ap2256ahalili rozaniNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Hazard and Risk?Document3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Hazard and Risk?Donniever AbianNo ratings yet
- Finance Chapter RSM330Document11 pagesFinance Chapter RSM330JhonGodtoNo ratings yet
- MSC Dissertation Finance TopicsDocument6 pagesMSC Dissertation Finance TopicsWhereCanIBuyResumePaperAkron100% (1)
- Grantee Final Activity Report - APSI TemplateDocument3 pagesGrantee Final Activity Report - APSI Templatesong neeNo ratings yet
- Factors influencing adaptive building reuseDocument18 pagesFactors influencing adaptive building reuseWoo JungNo ratings yet