Professional Documents
Culture Documents
41-K.todorova Implementation of Advanced Technologies
Uploaded by
Awode TolulopeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
41-K.todorova Implementation of Advanced Technologies
Uploaded by
Awode TolulopeCopyright:
Available Formats
Implementation of Advanced Technologies in Ontology-based E-learning Model
Korneliya Todorova
125 Tzarigradsko Shausse Blvd., bl.2, fl.3 Sofia 1113, Bulgaria cornelia@fmi.uni-sofia.bg Abstract. Paper discusses how advanced technologies like educational software and Web 2.0 tools could be successfully integrated in e-learning in order to create and deliver high quality e-learning content using ontology-based model. We propose here a possible solution for implementation of advanced technologies in this model and how different social tools and educational software could be used in ontology as RLOs. We describe advantages of the solution and how set requirements for effective e-learning are satisfied by the suggested model for integration of new technologies. Keywords: ontology, educational software, game-based learning, Web2.0
1 Introduction
Basic problem of advanced learning is to guarantee that students will be able to apply acquired skills and knowledge in practice. For this reason modern e-learning should integrate new technologies in different learning activities and this way to achieve highly interactive and social-oriented education. In the same time learning should be flexible, attractive and adaptive to the specific needs of learners. Ontology-based e-learning model seems to be the most flexible and adaptive to the preferred learning style and previous educational background of students [11]. Main task of this research is to explore and offer how new technologies like gamebased learning and social tools could be successfully integrated in ontology-based elearning model in order to provide high level of interactivity and quality of learning.
2 Models for effective and interactive online learning and trends in advanced forms of e-learning
In this paper we use a model of online learning [1] describing 2 basic types of interaction in e-learning: interaction among participations in education and interaction with learning content e.g. independent study or structured learning resources. This model illustrates required elements of knowledge/content interface that should be provided and supported like search and retrieval of information, simulations, games and virtual labs and capabilities for communication
260
K. Todorova
and collaboration. The second model we apply in order to define requirements for high quality learning is the model for effective learning proposed by Anderson in [4]. It described basic phases of design and implementation of effective education. The paper focuses on research of existing learning theories that will support flexible, attractive and adaptable forms of education. We analyzed several theories (Behaviourism, Cognitive, Constructivist, Activity-based, Socially situated learning) [2]. We use provided comparative analysis of these theories based on their basic characteristics, advantages, disadvantages and potential for their application in elearning. We selected the most appropriate one for our flexible, adaptable and effective education. Selected theory should satisfy the requirements for effective and interactive e-learning process set by the models. Based on these criteria we choose Constructivist learning theory and Socially situated learning as the most appropriated ones. Constructivist provides opportunities for gaining experience during the learning which is one of the basic criteria for effective learning[4]. Socially situated learning allows and supports high level of interactivity both among the participant in education and with learning content. Another advantage of Social tools is that they are common used and well accepted by the users. For this reason we combined both theories and we selected to use Social-constructivist learning theory described by Vygotsky [3]. The selected Social-constructivism learning theory combines advantages of both learning theories and allows users to gain experience using capabilities of social tools. Social-constructivist learning theory allows students to gain experience during the education by social interactions. Our next task is to choose the most appropriate model for this learning theory and to implement it in the design and development of the learning. For this purpose we used methodological approach offered in [2]: to review learning theories, to identify their common characteristics, to build a model using these characteristics and to map learning theories to the model. Using this methodology we select the most appropriate model for this type of education. It is used for Conversational framework developed by Laurillard [10] and is described in details in [2]. It is represented by 3 pairs of elements: Individual Social, Reflection Non-reflection, and Information Experience. Selected model allows users to receive individualized learning which is very important factor for a successful education. It should be based on the specific educational needs of the learner and it should be appropriate for preferred learning style and previous educational experience of the student. In the same time learning is organized in social learning environment where users could communicate and collaborate using Web 2.0 tools. Another advantage of this type of education is capability of social tools for reflection of students experience and impressions during the education in blogs, wikis, forums, etc. In this social learning environment information could be shared and exchanged by users and learners could find out the most appropriate learning content based on the rates and comments of other students. This way they have access to the most interesting and related to their interests resources as well as they can share information. The selected model satisfies the requirement for effective learning represented in [4]. It emphasis on the importance of interaction with the learning content and collaboration and communication between participants in education which is critical for effective learning through support of information exchange and
Implementation of Advanced Technologies in Ontology-based E-learning Model
261
options for reflection. Necessary variety of learning activities supports social and individual learning as well as option for gaining experience. Combination of all available components of the model allows acquired knowledge and skills to gain personal meaning for the student and at the end of education learners should be able to apply them in real life which is one of the most important impacts of education [4]. Ontology-based model of e-learning illustrated on Fig.1 represents basic elements of successful e-learning described in details in [11]. Learning environment should provide different components that support effective learning process. Next levels of content complexity and flexibility in the model are structuring and organization of learning content. In this model learning content is organized as ontology in a given domain and main concepts are linked with relations among them as well as reasoning rules and axioms. Integration of Learning 2.0 technologies [9] in learning process allows students to use and create socially constructed learning content. In the same time applying the model we can use flexibility, adaptability and reusability of learning resources that this model supports. At implementation level we will create learning environment using capabilities of Learning 2.0 and edutainment as basic components of the learning system. Edutainment represented by simulators, educational software and serious games provides and supports capabilities of gaining experience[12]. This way the concept of Constructivist theory for gaining experience with authentic real life problem and situations will be achieved [13]. This way tasks set by selected conversational framework model and chosen learning theory will be executed. For ontology representation we can use Multimedia Web Ontology Language (MOWL) using the advantaged of Web Ontology Language (OWL) and multimedia used in the last level of complexity of the model.- content asset In the same time the selected language supports some option for reasoning. On the next level of content complexity we have to create RLOs using definition of LAllier [5] for LO. Smaller part of learning content used both in e-learning and knowledge management is information object. Here we have to define different concepts related to the topic as well as principles and procedure for the selected domain of science. For this purpose we can apply learning sequenced defined by Gagne [6] in order to use different concepts, principles and procedure of the target domain. Last element of flexible and adaptive e-learning is content asset where we use multimedia for learning content representation [7, 8]. Learning environment uses ontology for content organization. Concepts of ontology are represented by LO with related information for each concept. Information objects are used by RLO for procedures description and each information object contains content assets with multimedia elements. In design of learning environment we use the concept of its representation as combination of Web 2.0 tools and edutainment. For ontology development we can use MOWL. Information for each ontology concept is represented by RLOs containing social tools and educational software. In each LO use can use IO for principles and procedures description for gaining high order experience [12]. This information is represented by multimedia content assets.
262
K. Todorova
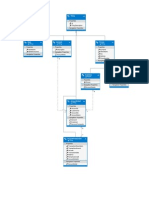
Abstract level
E-learning Knowledge management Learning environment
Components DB Communication
Ontology
Concepts Relations Axioms Reasoning rules
Learning object
Objective Practice Assess
Information object
Concept Principle Procedure
Content asset
Text Audio Animation Graphic Video
Content & Complexity Reusability Flexibility & Adaptability
Elements of Learning 2.0 and edutainment
Components:
Ontology Language:
MOWL
Elements of Web 2.0 tools Gagnes learning Multimedia and games entities sequence
RLOs:
IO:
CA:
Implementation level
Fig. 1. Ontology-based e-learning model.
3 Application of advanced technologies in ontology-based e-learning model
Based on different models and learning theories discussed in previous sections we suggest an ontology-based e-learning model integrating advanced technologies like Web 2.0 tools and educational software. Concepts of ontology are linked by relations and each concept has a LO that contains information about it. Usually standard type of resources like pdf, doc and ppt files, is enhanced by different social tools like blogs, wikis, etc. in order to provide high quality education. They are integrated in ontology as RLOs and allow learners to share their own experience, comments and ideas about the concept. We can add different types of educational software, serious games and simulations as RLOs in the ontological structure. Thus designed and developed e-learning allows students to gain experience in social learning environment, to share and exchange information using Web 2.0 tools, to choose individualized learning resources according to their specific educational needs and to use advantages of educational software for experience gaining and sharing with other participants in education. This knowledge and learning content becomes social constructed. Students not only share and exchange information about learning content, but they create learning resources using Web 2.0 technologies. They comment, rate, recommend and develop learning content. This way they become active participants in learning process not only passive consumers of e-learning resources. Advantages of proposed solution is that flexibility and adaptability of ontology-based models are used.
Implementation of Advanced Technologies in Ontology-based E-learning Model
263
In the same time development of learning content as small part of information e.g. RLOs, information objects, and content assets allows high level of reusability. On the other hand we use enhanced capabilities of advanced technologies like Web 2.0 tools and educational software like simulations and serious games. Integration of described tools as RLOs allows advantages of ontology to be applied and to develop highly interactive multimedia e-learning content in order to create high effective and high quality e-learning using learning sequence defined by Gagne. The requirements for effective learning defined by model described in [4] as well as the model of online learning represented in [1] are satisfied by the solution offered. Some assumptions of Social-constructivist learning theory for gaining experience in social environment by users interactions are applied.
4 Conclusion and future research plans
In this paper we set requirement for successful high interactive and effective education represented by the models of Ally and Anderson. We analyzed existing resources describing different e-learning theories and selected the most appropriate one according to set of criteria for effective and interactive learning represented by the models. We choose appropriate for the selected theory model and we described how the new technologies could be integrated in ontologybased e-learning model. At the end we outlined the advantages of proposed solution. Our future research plans will be focus on investigation on methods and tools for shared development and editing of ontologies, capabilities for mobile delivery of learning content organized as ontology structure and application of wireless technologies in social software and game-based learning. Acknowledgements. The work on this paper has been partly sponsored by the SISTER Project funded by the EC 7th FP.
References
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Anderson, T., TOWARD A THEORY OF ONLINE LEARNING, InTheory and Practice of Online Learning, Anderson, T. and Elloumi, F. (eds.), Athabasca University, (2004) Conole, G., et al. Mapping pedagogy and tools for effective learning design, Computers & Education 43, 1733 (2004) Vygotsky, L. (1978). Mind in Society. London: Harvard University Press Ally, M., FOUNDATIONS OF EDUCATIONAL THEORY FOR ONLINE LEARNING, In Theory and Practice of Online Learning, Anderson, T. and Elloumi, F. (eds.), Athabasca LAllier, James J. (1997) Frame of Reference: NETgs Map to the Products, Their Structure and Core Beliefs. NetG., http://www.netg.com/research/whitepapers/ frameref.asp Gagne, R. M., The conditions of learning (2nd ed.). New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston Newby, T., Stepich, D., Lehman, J., & Russell, J., Instructional technology for teaching and learning (2nd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merrill (2000)
264
K. Todorova
8.
9. 10. 11. 12. 13.
Yordanova, K., Interactive multimedia course for teachers education in e-learning concept and its possible application in vocation training and educational process, In International Review on Computers and Software, July, ISSN1828-6003,Vol. 2N. 4, pp. 415-420 (2007) Yordanova, K, Application of CSCL capabilities in virtual communities, Open PhD Workshop on Technology-Enhanced Learning and Semantics, Software and Services, 03 September, Varna, Bulgaria, (2008) Laurillard, D., Rethinking University Teaching: A Framework for the Effective Use of Educational Technology. Routledge, London, (1993) Yordanova, K., Learning Systems as Ontology-based Learning Object Repository, International Conference CompSysTech10, 17-18, June, (2010) Antonova, A., Todorova, K., Serious games and Virtual Worlds for high level learning experience, S3T, September 11-12, 2010, Varna, Bulgaria (2010) (accepted) Jonassen, D. Designing constructivist learning environments. In C. M. Reigeluth (Ed.), Instructional theories and models (2nd ed.) (pp. 1-21). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum. (1998)
You might also like
- Elearning Theories & Designs: Between Theory & Practice. a Guide for Novice Instructional DesignersFrom EverandElearning Theories & Designs: Between Theory & Practice. a Guide for Novice Instructional DesignersNo ratings yet
- E-Blended Learning Using Web TechnologyDocument4 pagesE-Blended Learning Using Web TechnologyIJARTETNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence in E-Leaning-Pedagogical and Cognitive Aspects - WCE2011 - pp997-1002Document6 pagesArtificial Intelligence in E-Leaning-Pedagogical and Cognitive Aspects - WCE2011 - pp997-1002Jabar H. YousifNo ratings yet
- E LearningDocument9 pagesE LearningSalma JanNo ratings yet
- Mutia Dwi Ayu Tirsasani - Latihan 2Document8 pagesMutia Dwi Ayu Tirsasani - Latihan 2Mutia TirsasaniNo ratings yet
- Virtual Teaching-Learning Environments for Network-Based EducationDocument16 pagesVirtual Teaching-Learning Environments for Network-Based EducationMiguel CiprianNo ratings yet
- The Use of Social Networking Platforms As New, Efficient Technology Tools For E-LearningDocument7 pagesThe Use of Social Networking Platforms As New, Efficient Technology Tools For E-LearningIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNo ratings yet
- LEARNING ENGLISH THROUGH AN LMS AND LECTURESDocument9 pagesLEARNING ENGLISH THROUGH AN LMS AND LECTURESHạt ĐậuNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Usability in Learning Management System MoodleDocument6 pagesEvaluating Usability in Learning Management System MoodleAgung SupraptoNo ratings yet
- Assistive Tools for PLEDocument4 pagesAssistive Tools for PLEShravan VanjariNo ratings yet
- Moodle: Using Learning Communities To Create An Open Source Course Management SystemDocument16 pagesMoodle: Using Learning Communities To Create An Open Source Course Management SystemMuseu Alfonso X MarianaNo ratings yet
- JJG 01Document14 pagesJJG 01Naba kamal DuttaNo ratings yet
- Make It Easier For Other People To Find Your Content by Providing More Information About It.Document6 pagesMake It Easier For Other People To Find Your Content by Providing More Information About It.mohmedtanta2No ratings yet
- Reflections Omde610Document5 pagesReflections Omde610api-255596495No ratings yet
- Systems: Adaptation in E-Learning Content Specifications With Dynamic Sharable ObjectsDocument11 pagesSystems: Adaptation in E-Learning Content Specifications With Dynamic Sharable ObjectsIvetNo ratings yet
- Mobile Applications Within Education PDFDocument13 pagesMobile Applications Within Education PDFpantelios21No ratings yet
- Mobile Learning MatrixDocument6 pagesMobile Learning Matrixapi-322322376No ratings yet
- Integration of Web 2.0 Tools in Learning A Programming CourseDocument7 pagesIntegration of Web 2.0 Tools in Learning A Programming CoursemonangfransiskusNo ratings yet
- ZL 2103121Document4 pagesZL 2103121Shrilaja KNo ratings yet
- Objectives: at The End of The Unit, I Am Able ToDocument11 pagesObjectives: at The End of The Unit, I Am Able ToSuga MinNo ratings yet
- Mobile Learning MatrixDocument8 pagesMobile Learning Matrixapi-278852361No ratings yet
- Jurnalinter 3Document5 pagesJurnalinter 3Mutia FatmawatiNo ratings yet
- Web 2.0 and ElrnDocument5 pagesWeb 2.0 and Elrnrjoshi_45No ratings yet
- Report On The Eskwela Instructional Model ComponentDocument43 pagesReport On The Eskwela Instructional Model Componentmameltan0% (1)
- DTISA09Document8 pagesDTISA09Kazzy SourNo ratings yet
- Best e-Learning Practices ComparisonDocument7 pagesBest e-Learning Practices Comparisonile_may91No ratings yet
- Ontology-Based Modeling of The Learner in A Web Educational System: Towards Learning Analytics and Adaptive LearningDocument10 pagesOntology-Based Modeling of The Learner in A Web Educational System: Towards Learning Analytics and Adaptive LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Agregacion de Contenido e Intercambio de Conocimiento en Los PLEDocument8 pagesAgregacion de Contenido e Intercambio de Conocimiento en Los PLEEderson ElcorelNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document2 pagesModule 5prof_kt0% (1)
- Supporting Collaborative Learning Activities With ScormDocument10 pagesSupporting Collaborative Learning Activities With ScormPhilstar JillNo ratings yet
- E-Learn 2009 ProceedingsDocument5 pagesE-Learn 2009 Proceedingsmakahaz1No ratings yet
- A Case Study For Measuring Informal Learning in PlesDocument9 pagesA Case Study For Measuring Informal Learning in PlesEderson ElcorelNo ratings yet
- Learning Activities EditorDocument3 pagesLearning Activities EditorPedro Emanuel Dos ReisNo ratings yet
- Educational TechnologyDocument3 pagesEducational Technologyapi-430689866No ratings yet
- SMART E-LEARNING PROJECT REPORTDocument6 pagesSMART E-LEARNING PROJECT REPORTMICROWAY SKILLNo ratings yet
- Interaction: Principles and Practice: ELI Summer Session 2005Document9 pagesInteraction: Principles and Practice: ELI Summer Session 2005donadthNo ratings yet
- E Learning and Learning Management Systems Advantages, Disadvantages and SuggestionsDocument4 pagesE Learning and Learning Management Systems Advantages, Disadvantages and SuggestionsEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Trainable Generator of Educational ContentDocument10 pagesTrainable Generator of Educational ContentInternational Journal of Advances in Applied Sciences (IJAAS)No ratings yet
- Social MediaDocument26 pagesSocial MediaAbhishek BiyaniNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Tutoring Systems: Effective Tool For Open and Distance LearningDocument6 pagesIntelligent Tutoring Systems: Effective Tool For Open and Distance LearningVivian.O. Nwaocha100% (4)
- Pedagogical Approaches and Technical Subject Teaching Through Internet MediaDocument1 pagePedagogical Approaches and Technical Subject Teaching Through Internet MediapraveennagarajanNo ratings yet
- Digital Learning Ecosystem by Nancy Slawski & Nancy ZomerDocument10 pagesDigital Learning Ecosystem by Nancy Slawski & Nancy ZomerNancy SlawskiNo ratings yet
- Tech Integration Matrix - Mobile LearningDocument5 pagesTech Integration Matrix - Mobile Learningapi-309006467No ratings yet
- Emerging Technologies for the Classroom: A Learning Sciences PerspectiveFrom EverandEmerging Technologies for the Classroom: A Learning Sciences PerspectiveNo ratings yet
- Paper 18-Using Semantic Web To Support Advanced Web-Based EnvironmentDocument10 pagesPaper 18-Using Semantic Web To Support Advanced Web-Based EnvironmentEditor IJACSANo ratings yet
- Developing Instructional Materials for Website CreationDocument11 pagesDeveloping Instructional Materials for Website CreationApril PornillosNo ratings yet
- Et 247 Matrix 1Document11 pagesEt 247 Matrix 1api-316948987No ratings yet
- Is micro-learning the future of learningDocument5 pagesIs micro-learning the future of learningHemanth KittuNo ratings yet
- Schoology-Learning Management SystemDocument42 pagesSchoology-Learning Management SystemRechelleRuthM.Deiparine100% (2)
- Et 347 Eportfolio Matrix Miranda SiemensDocument9 pagesEt 347 Eportfolio Matrix Miranda Siemensapi-302040335No ratings yet
- Ijet 28273Document6 pagesIjet 28273Hassaan AliNo ratings yet
- Et347 Eportfolio MatrixDocument6 pagesEt347 Eportfolio Matrixapi-316927427No ratings yet
- M Learning Adaption ModelDocument4 pagesM Learning Adaption ModelWiroot Mountain FoxNo ratings yet
- INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY-BASED LEARNING STRATEGIES APPLICATIONSFrom EverandINSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY-BASED LEARNING STRATEGIES APPLICATIONSNo ratings yet
- Pedagogical Approaches and Technical Subject Teach PDFDocument15 pagesPedagogical Approaches and Technical Subject Teach PDFMaheshwor PokhrelNo ratings yet
- p80 Ardito PDFDocument5 pagesp80 Ardito PDFEvelin SoaresNo ratings yet
- Contextualised Media for Learning: A Technical FrameworkDocument11 pagesContextualised Media for Learning: A Technical FrameworkBilel El MotriNo ratings yet
- Discrete Structures Set Theory: Duy BuiDocument8 pagesDiscrete Structures Set Theory: Duy BuiAwode TolulopeNo ratings yet
- Sets in Mathematics ExplainedDocument8 pagesSets in Mathematics ExplainedAwode TolulopeNo ratings yet
- Core Banking SolutionDocument11 pagesCore Banking SolutionAwode TolulopeNo ratings yet
- Test PDFDocument3 pagesTest PDFHung ManhNo ratings yet
- Set TheoryDocument8 pagesSet TheoryHernán Noguera HeviaNo ratings yet
- Planning For Library Automation: Academic LibrariesDocument10 pagesPlanning For Library Automation: Academic LibrariesAwode TolulopeNo ratings yet
- Werkstuk Bruyn Tcm235 862258Document5 pagesWerkstuk Bruyn Tcm235 862258Awode TolulopeNo ratings yet
- Set TheoryDocument8 pagesSet TheoryHernán Noguera HeviaNo ratings yet
- FinnacleDocument8 pagesFinnaclesamjoechandyNo ratings yet
- FinnacleDocument8 pagesFinnaclesamjoechandyNo ratings yet
- FFDocument8 pagesFFAwode TolulopeNo ratings yet
- DetailsDocument76 pagesDetailsAwode TolulopeNo ratings yet
- ModelCryptoBiometrics PDFDocument1 pageModelCryptoBiometrics PDFAwode TolulopeNo ratings yet
- FFDocument8 pagesFFAwode TolulopeNo ratings yet
- 06 Cross ImpactDocument19 pages06 Cross ImpactjaherrerarNo ratings yet
- RFIDDocument1 pageRFIDAwode TolulopeNo ratings yet
- ParallelDocument11 pagesParallelAwode TolulopeNo ratings yet
- LiuuiDocument1 pageLiuuiAwode TolulopeNo ratings yet
- Base 1Document4 pagesBase 1kamalahasanmNo ratings yet
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Application RequirementsDocument1 pageApplication RequirementsAwode TolulopeNo ratings yet
- Compressive Strength of Concrete of Green GlassDocument7 pagesCompressive Strength of Concrete of Green GlassAwode TolulopeNo ratings yet
- Main Differences - Enculturation vs AcculturationDocument6 pagesMain Differences - Enculturation vs AcculturationChristopher CelisNo ratings yet
- Pornography DefinitionDocument9 pagesPornography DefinitionJessa Marie Tan MikaniNo ratings yet
- الامتحان الوطني في اللغة الإنجليزية 2020 مسلك اداب الدورة العاديةDocument7 pagesالامتحان الوطني في اللغة الإنجليزية 2020 مسلك اداب الدورة العاديةirik minotaurNo ratings yet
- Kisi-Kisi Asas Kelas XDocument3 pagesKisi-Kisi Asas Kelas Xafanet.fcNo ratings yet
- The Ethical Dilemmas of Robotics (Reflection)Document2 pagesThe Ethical Dilemmas of Robotics (Reflection)Jamie Medalla100% (1)
- Service PersonalDocument14 pagesService PersonalquadranteRDNo ratings yet
- Self ConceptDocument10 pagesSelf ConceptFèdòrá MischkáNo ratings yet
- The New Story of The Hare and The TortoiseDocument4 pagesThe New Story of The Hare and The Tortoisefurqanhaider31100% (2)
- Stormweaver Ii - Chapter 5Document18 pagesStormweaver Ii - Chapter 5Bishwa SilwalNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 DLL Health 1Document7 pagesGrade 8 DLL Health 1Cath E RineNo ratings yet
- Jim Rohn The Five Major Pieces To The Life PuzzleDocument1 pageJim Rohn The Five Major Pieces To The Life Puzzlezoranle236367% (3)
- Super Simple Ironman 70.3 Training PlanDocument6 pagesSuper Simple Ironman 70.3 Training Planpriest1988No ratings yet
- Department of Education: 12 Confucius Humanities and Social SciencesDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: 12 Confucius Humanities and Social SciencesJesh Manansala-DesavilleNo ratings yet
- Bbi2424 SCL Worksheet 2 (Week 3-4) - Citation & Referencing ConventionsDocument6 pagesBbi2424 SCL Worksheet 2 (Week 3-4) - Citation & Referencing ConventionsLuqman Hakim0% (1)
- CAPE Biology U1 P1 Answers PDFDocument1 pageCAPE Biology U1 P1 Answers PDFKaylia WilsonNo ratings yet
- Project CharterDocument14 pagesProject Charterwaveinocean100% (1)
- Visual Impairment ScriptDocument3 pagesVisual Impairment Scriptapi-285548719No ratings yet
- Assess Your Entrepreneurial CompetenciesDocument1 pageAssess Your Entrepreneurial CompetenciesJeph PedrigalNo ratings yet
- IT Project Management Solutions ManualDocument7 pagesIT Project Management Solutions ManualMinato ArisatoNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument12 pagesScriptWaleed Nadeem50% (2)
- Future Forms Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesFuture Forms Lesson PlanOANA SAMSONNo ratings yet
- Ok Teaching by Principles H Douglas Brown PDFDocument491 pagesOk Teaching by Principles H Douglas Brown PDFUser PlayNo ratings yet
- Active Listening Techniques HandoutDocument2 pagesActive Listening Techniques HandoutJane Limsan Paglinawan100% (6)
- USAID/Ethiopia Organizational Capacity AssessmentDocument98 pagesUSAID/Ethiopia Organizational Capacity AssessmentAlemneh Tadele100% (1)
- Forbidden Images of Homosexual and Lesbian Sex in Shunga.20121223.032422Document2 pagesForbidden Images of Homosexual and Lesbian Sex in Shunga.20121223.032422anon_37107986No ratings yet
- English 10 - Module 6Document91 pagesEnglish 10 - Module 6Hannah YsabelleNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Classroom Management On Students Academic Performance in Selected Junior Secondary Schools in Municipal Area CouncilAbuja PDFDocument14 pagesThe Impact of Classroom Management On Students Academic Performance in Selected Junior Secondary Schools in Municipal Area CouncilAbuja PDFGari Vi LaoNo ratings yet
- 04 - 01 - Sample Onsite AgendaDocument1 page04 - 01 - Sample Onsite AgendaJohn WickNo ratings yet
- Assignment Educ 211Document3 pagesAssignment Educ 211Gerald Jem BernandinoNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Interview Professor Safeya Effat: I History Taking 1. Personal DataDocument4 pagesPsychiatric Interview Professor Safeya Effat: I History Taking 1. Personal DataAcha Angel BebexzNo ratings yet