Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pain Med Charts
Uploaded by
NursingSchoolNotesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pain Med Charts
Uploaded by
NursingSchoolNotesCopyright:
Available Formats
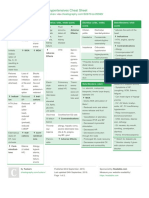
Pain and Inflammation Med Charts
Name Mechanism of Action Therapeutic Uses Side Effects/ Precautions Interactions Nursing/Pati ent teaching Common Drugs Name Mechanism of Action Therapeutic Uses Side Effects/ Precautions Interactions Nursing/Pati ent teaching Common Drugs Name Mechanism of Action Therapeutic Uses Side Effects/ Precautions Nonsteroidal Antinflammatory Drugs inhibition of cyclooxygenase, results in decrease in platelet aggregation, inflammation, fever, pain inflammation, mild analgesia, fever, dysmenorrhea, inhibition of platelet aggregation (protection against stroke, MI) GI upset, damage to gastric mucosa, renal dysfunction, increased risk of MI and stroke(for non ASA NSAIDS), Salicylism risk for ASA(tinnitus, sweating, HA, respiratory aklaosis) increased risk of bleeding with other anticoagulants, glucocorticoids, alcohol. Ibuprofen decreases antiplatelet effects of ASA take NSAIDS with food to decrease gastric discomfort, notify provider if symptoms of salicylism occurs, concurrent use with opioids allow for lower dosages of opioids ASA, Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Indomethacin (Indocin), Ketorolac (Toradol), Meloxicam (Mobic), Colecoxib (Celebrex) Acetaminophen slows production of protaglandins in CNS analgesic, antipyretic acute toxicity results in liver damage (early symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, sweating, abdominal discomfort) alcohol increases risk of liver damage, slows metabolism of warfarin do not exceed 4 mg/ day, acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) is antidote for overdose tylenol
Opioid Agonist act on mu and kappa receptors, produces analgesia, respiratory depression, euphoria, sedation, decreased GI motility moderate to severe pain respiratory depression, constipation, orthostatic hypotension, urinary retention, cough suppression, sedation, emesis
Interactions
CNS depressants have additive depression action. Anticholinergics, antihistamines, tricyclic antidepressants have additive anticholinergic effects. MAOIs may cause hyperpyrexic coma. overdose triad: coma, repiratory depression, pinpoint pupils. Administer very slowly, over 4 to 5 minutes. Narcan is antidote. Do not administer more than 600 mg/24 hour period for meperidine (Demerol). morphine, Fentanyl (Sublimaze, Duragesic), Meperidine (Demoerol), Methadone (Dolophine), Codeine/oxycodone (OxyContin) Agonist - antagonist opioids antagonists act on mu and kappa receptors, lower potential for abuse, less respiratory depression, and less analgesic effect compared to pure opioid agonists moderate to sever pain, treament of opioid dependence, adjunct to balanced anesthesia,, sedation, respiratory depression, dizziness, increased intracranial pressure, HA, increased cardiac workload. abstinence syndrome (for those who are dependant on opioids) additive CNS depression with other CNS depressants, opioid agonists may antagonize and reduce analgesic effects (do not use concurrently) caution when undisclosed opioid use is suspected. Again, opioid agonist and opioid agonist antagonist should not be used together. Naloxone (narcan) is antidote butorphanol (Stadol), hydrochloride (Nubain), Buprenorphine hydrochloride (Buprenex) Adjuvant Medications for Pain: used with a primary pain medication, usually an opioid agonist in order to reduce opioid dosage to reduce side effects.
Nursing/Pati ent teaching Common Drugs Name Mechanism of Action Therapeutic Uses Side Effects/ Precautions Interactions Nursing/Pati ent teaching Common Drugs
NSAIDS Tricyclic antidepress ants Anticonvulsa nts CNS stimulants Antihistamin es
treats inflammation. side effects: bone marrow suppresion, GI distress treats depression, neuropathic pain such as cramping/aching/burning. (amitriptyline (Elavil)) side effects: orthostatic hypotension, sedation, anticholinergic effects neuropathic pain (carbamazepine (Tegretol), gabapentin (Neurontin)) side effects: bone marrow suprresion, GI distress analgesia, decrease sedation. (methylphenidate (Ritalin)) side effects: weight loss, insomnia decrease anxiety, prevent insomnia and relieve nausea (hydroxyzine (Vistaril))
Bisphosphon ates glucocorticoi ds
manage hypercalcemia and bone pain (etidronate (Didronel)) side effects: flu like symptoms, venous irritation, renal failure decrease pain from intracranial pressure and spinal cord compression. (dexamethason (Didronel)) side effects: adrenal insufficiency, osteoporosis, hypokalemia, glucose intolerance, peptic ulcer disease
Name Mechanism of Action Therapeutic Uses Side Effects/ Precautions Interactions Nursing/Pati ent teaching Common Drugs
Migraine Meds prevent inflammation and dilation of the intracranial blood vessels, relieving migraine pain stopping acute migraine attacks, prevention of chronic migrains depends on type (pg 473) depends on type avoid trigger factors that cause stress (alcohol, fatigue, tyramine containing foods (aged cheese)) Ergot alkaloids: ergotamine (Ergostat) Serotonin receptor agonist: sumatriptan (Imitrex) Beta Blockers: propranolol (Inderal) Anticonvulsants: divalproex (Depakote) Tricyclic antidepressants: anitriptyline (Elavil) Calcium channel blockers: verapamil (Calan) Estrogens: Estraderm Ergot alkaloids: Cafergot
Name Mechanism of Action Therapeutic Uses Side Effects/ Precautions Interactions Nursing/ Patient
Local Anesthetics decrease pain by blocking conduction of pain impulses in a specific area dental procedures, minor surgical procedures, labor and delivery, regional anesthesia, skin and mucous membrane disorders, minor procedures (IV insertion, injection, wart removal) CNS excitation (seizures, followed by respiratory depression, leading to unconsciousness), hypotension, can prolong labor additive hypotensive effects with parenteral administration vasoconstrictors (epinephrine) often used in combination with local anesthetic to stop the spread. topical cream applied one hour before
teaching Common Drugs
procedure. lidocaine (Xylocaine), tetracain (Pontocaine), procain (Novocain)
You might also like
- Pain and Inflammation Med ChartsDocument4 pagesPain and Inflammation Med Chartssurviving nursing school100% (1)
- Pulmonary Med Charts Part 2Document2 pagesPulmonary Med Charts Part 2NursingSchoolNotes100% (3)
- Of Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart FailureDocument31 pagesOf Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart Failurenaikram420No ratings yet
- Pharmacology ChartDocument6 pagesPharmacology ChartPaula67% (3)
- Emergency DrugsDocument9 pagesEmergency DrugsaldwinngNo ratings yet
- OB Drug ChartsDocument2 pagesOB Drug ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Hmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, InteractionsDocument6 pagesHmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, Interactionswaste78No ratings yet
- Drugs WorksheetDocument16 pagesDrugs Worksheetninja-2001No ratings yet
- Studying Patho For Nursing School - EasyDocument1 pageStudying Patho For Nursing School - EasyMarie J100% (1)
- Student Clinical Report SheetDocument2 pagesStudent Clinical Report SheetMike100% (4)
- Drugs MnemonicsDocument6 pagesDrugs MnemonicsDarrylJavier100% (1)
- Template Drug Card1Document1 pageTemplate Drug Card1Kay TaylorNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System and Nutrition Drug ChartsDocument3 pagesGastrointestinal System and Nutrition Drug ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: System DisorderDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was: System DisorderDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- 12 Points To Answering Pharmacology Questions PDFDocument2 pages12 Points To Answering Pharmacology Questions PDFbsebi763271No ratings yet
- Head To Toe AssessmentDocument3 pagesHead To Toe Assessmentsandaman2225No ratings yet
- Common Psych DrugsDocument3 pagesCommon Psych Drugsrexinne noahNo ratings yet
- Antidepressant Cheat Sheet: TCA Ssri SnriDocument1 pageAntidepressant Cheat Sheet: TCA Ssri SnriLillianNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology OutlineDocument11 pagesCardiovascular Pharmacology OutlineLhay de OcampoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology Inflammation Study GuideDocument11 pagesNursing Pharmacology Inflammation Study GuideChelsea Smith100% (1)
- Sudden Onset (Within 2 Weeks) of at Least One of TheDocument2 pagesSudden Onset (Within 2 Weeks) of at Least One of TheNeicole BandalaNo ratings yet
- Drug ChartDocument8 pagesDrug Chartstudentalwaysstudy100% (1)
- Pharmacology HandoutDocument5 pagesPharmacology HandoutMark Elben Teodoro100% (1)
- Pneumonia Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesPneumonia Cheat Sheet: by ViaGayle MarieNo ratings yet
- Differentiating Abbreviations From Acronyms: MuscleDocument10 pagesDifferentiating Abbreviations From Acronyms: MusclePrince Rener Velasco PeraNo ratings yet
- Medication Classes Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesMedication Classes Cheat SheetJoax Wayne SanchezNo ratings yet
- Nursing and PharmacologyDocument9 pagesNursing and PharmacologyJennifer ViciosoNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics For NursesDocument29 pagesMnemonics For Nursesashdmb217100% (2)
- Drug Outline: Autonomic Nervous System Drug Class Drug OtherDocument4 pagesDrug Outline: Autonomic Nervous System Drug Class Drug OtherCess Lagera YbanezNo ratings yet
- Final Coaching DrugsDocument8 pagesFinal Coaching DrugsSherlyn BesasNo ratings yet
- Top 200 Drug Study Reference RLPDocument31 pagesTop 200 Drug Study Reference RLPYathrika YathrikaNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAntihypertensive Cheat SheetRigley GarmanNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Review: Pharmacology Charlene Natale, BSN, RNDocument43 pagesNCLEX Review: Pharmacology Charlene Natale, BSN, RNMenly Susada100% (1)
- 3639 - Basic Patient DataDocument1 page3639 - Basic Patient DataRaven247No ratings yet
- Med CardsDocument4 pagesMed CardsSonia FernandesNo ratings yet
- Antidepressant DrugsDocument21 pagesAntidepressant DrugsKashis SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Chart 3Document2 pagesPharmacology Chart 3Omar ClorNo ratings yet
- Newborn Hal ManualDocument74 pagesNewborn Hal ManualPedz RomanoNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisDocument1 pageCheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisAkasha FrostmourneNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Study Guide For NursesDocument3 pagesAntibiotics Study Guide For NursesLauren Trotman100% (7)
- Clinical Med CardsDocument26 pagesClinical Med CardsLila DanielsNo ratings yet
- Care PlanDocument11 pagesCare PlanAlyssa Cardinal100% (1)
- Labs 1.19 ABG AnalysisDocument1 pageLabs 1.19 ABG AnalysisMonica GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapeutic Drugs: Pam Pam LamDocument7 pagesPsychotherapeutic Drugs: Pam Pam Lamchubbygunny_29776413No ratings yet
- EBP & ResearchDocument6 pagesEBP & ResearchangieswensonNo ratings yet
- Psycho PharmaDocument8 pagesPsycho PharmaMark JosephNo ratings yet
- Condition Drug Class: Cardiovascular MedicationsDocument5 pagesCondition Drug Class: Cardiovascular MedicationsCasey Fioravante100% (1)
- Anti Infective Drug ChartDocument1 pageAnti Infective Drug ChartJessica100% (1)
- Drug Cards 1Document20 pagesDrug Cards 1Keying Chen100% (1)
- Pharm 1.31 SOCK Method For Learning Pharm 1Document1 pagePharm 1.31 SOCK Method For Learning Pharm 1Angie Mandeoya100% (1)
- Pharmacology MnemonicsDocument17 pagesPharmacology MnemonicsJuvenis SampangNo ratings yet
- Nursing AssessmentDocument16 pagesNursing AssessmentJihan Novita100% (1)
- Individual Performance Profile PN Mental Health 2011 Form BDocument4 pagesIndividual Performance Profile PN Mental Health 2011 Form BStan TanNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Chart 1Document7 pagesAntibiotics Chart 1Vee MendNo ratings yet
- Beta Blockers Cheat Sheet: Happy Nursing!Document1 pageBeta Blockers Cheat Sheet: Happy Nursing!GloryJaneNo ratings yet
- AnalgesicsDocument1 pageAnalgesicsPaul AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- NociceptionDocument8 pagesNociceptionfootballjeinNo ratings yet
- Neuro Study GuideDocument7 pagesNeuro Study GuideNursingSchoolNotes100% (2)
- GI Study GuideDocument11 pagesGI Study GuideNursingSchoolNotes75% (4)
- Resp Lecture NotesDocument17 pagesResp Lecture NotesNursingSchoolNotes100% (3)
- Endocrine Study GuideDocument4 pagesEndocrine Study GuideNursingSchoolNotes100% (1)
- Adult III Cardiac Study GuideDocument15 pagesAdult III Cardiac Study GuideNursingSchoolNotes100% (6)
- ECG StripsDocument5 pagesECG StripsNursingSchoolNotes100% (1)
- Psych Med ChartsDocument5 pagesPsych Med ChartsNursingSchoolNotes100% (5)
- Chart of Neuro DisordersDocument1 pageChart of Neuro DisordersNursingSchoolNotes100% (2)
- OB Drug ChartsDocument2 pagesOB Drug ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Study Guide Part 2Document7 pagesUnit 4 Study Guide Part 2NursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System and Nutrition Drug ChartsDocument3 pagesGastrointestinal System and Nutrition Drug ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Stuff That You Have To MemorizeDocument1 pageCardiac Stuff That You Have To MemorizeNursingSchoolNotes100% (1)
- Cardiac Med ChartsDocument6 pagesCardiac Med ChartsNursingSchoolNotes100% (15)
- Rhetoric Essay Super High MeDocument8 pagesRhetoric Essay Super High MeNeana LueckNo ratings yet
- DPA Fact Sheet - Approaches To Decriminalization - (Feb. 2016) PDFDocument4 pagesDPA Fact Sheet - Approaches To Decriminalization - (Feb. 2016) PDFwebmaster@drugpolicy.org100% (2)
- Serotonin (5-HT)Document35 pagesSerotonin (5-HT)adeesasaadNo ratings yet
- Drugs:: Side Effects of Psychotropic MedicationsDocument32 pagesDrugs:: Side Effects of Psychotropic MedicationsMARIE ROSE L. FUNTANARNo ratings yet
- Part XVIDocument17 pagesPart XVIphp_czarina04421No ratings yet
- Difference Between Codeine Linctus and PholcodineDocument6 pagesDifference Between Codeine Linctus and PholcodineClipping ValleyNo ratings yet
- AnorecticDocument10 pagesAnorectickarstenMNo ratings yet
- Temazepam (Restoril)Document1 pageTemazepam (Restoril)E100% (2)
- Barbiturates and TranquilizerDocument4 pagesBarbiturates and TranquilizerSherryl ZamonteNo ratings yet
- Ketamine, PCP, LSD, N20 & Another DrugsDocument18 pagesKetamine, PCP, LSD, N20 & Another Drugsapi-3699610100% (1)
- Classifications of Drugs and AbuseDocument5 pagesClassifications of Drugs and AbuseRoma Diane AvigueteroNo ratings yet
- DB01 Drug ClassificationDocument20 pagesDB01 Drug ClassificationMayank TewatiaNo ratings yet
- Foundation Course-I Project (SEM-1) 2017-18: and Remedial MeasuresDocument21 pagesFoundation Course-I Project (SEM-1) 2017-18: and Remedial MeasuresYasin Shaikh75% (4)
- BenadrylDocument2 pagesBenadrylE100% (1)
- Module BPEd 118 Drug Education Consumer Health and Healthy EatingDocument117 pagesModule BPEd 118 Drug Education Consumer Health and Healthy EatingPhilip Mangaoang100% (5)
- Sedative HypnoticsDocument39 pagesSedative HypnoticsFatima ShaukatNo ratings yet
- Morphine Milligram Equivalent (MME) CalculatorDocument4 pagesMorphine Milligram Equivalent (MME) Calculatorjleehongkong1No ratings yet
- Etonitazene - An Opioid Selective For The Mu Receptor Types - Moolten MS, Fishman JB, Chen JC, Carlson KR - Life Sci 52 (1993) PL199-PL203Document5 pagesEtonitazene - An Opioid Selective For The Mu Receptor Types - Moolten MS, Fishman JB, Chen JC, Carlson KR - Life Sci 52 (1993) PL199-PL203muopioidreceptorNo ratings yet
- PhenobarbitalDocument3 pagesPhenobarbitalChristine Joy Pepito50% (2)
- Opioid-BenzosTapering FlowchartDocument1 pageOpioid-BenzosTapering FlowchartjuanchibarberoismNo ratings yet
- Olney Police Report On Bill Milner 2015Document9 pagesOlney Police Report On Bill Milner 2015Anonymous AxMUxbZNo ratings yet
- TEST I. Modified TRUE or FALSE. Write TRUE If The Statement Is Correct and FALSE If It Is Not and Underline TheDocument1 pageTEST I. Modified TRUE or FALSE. Write TRUE If The Statement Is Correct and FALSE If It Is Not and Underline TheJefray OmongosNo ratings yet
- CDI4002Document11 pagesCDI4002Justine MacapobreNo ratings yet
- Handout Physical and Psychological Effects of Substance Use: Alcohol Abuse Is A Pattern of ProblemDocument3 pagesHandout Physical and Psychological Effects of Substance Use: Alcohol Abuse Is A Pattern of ProblemDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- NSTP Narrative Essay DrugsDocument3 pagesNSTP Narrative Essay DrugsNikki Arinsol100% (1)
- MDMA PowerpointDocument16 pagesMDMA Powerpointapi-26938624No ratings yet
- Registros-Cannabis Octubre 2019Document38 pagesRegistros-Cannabis Octubre 2019Laura María Trujillo RendónNo ratings yet
- Arc QuestionnaireDocument1 pageArc QuestionnaireJanet FernandezNo ratings yet
- Recommended Methods For The Identification and Analysis of Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists in Seized Materials (2013)Document66 pagesRecommended Methods For The Identification and Analysis of Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists in Seized Materials (2013)Luděk SpurnýNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Neurobiology of Psychedelic Drugs: Adam L. Halberstadt Franz X. Vollenweider David E. Nichols EditorsDocument434 pagesBehavioral Neurobiology of Psychedelic Drugs: Adam L. Halberstadt Franz X. Vollenweider David E. Nichols EditorsJosé Carlos Solís SuárezNo ratings yet