Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio 22 Lab - Post Lab 3 II
Uploaded by
Karl Jimenez SeparaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio 22 Lab - Post Lab 3 II
Uploaded by
Karl Jimenez SeparaCopyright:
Available Formats
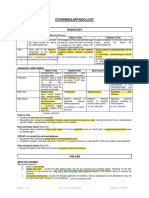
KIMBERLY S.
BELTRAN
Holds prey
Breathing
Equalize pressure in inner ear Tube leading to the lungs
Tube leading to stomach; Bolus passes
Aids in grabbing prey
Digestion
Secretes pancreatic juice, insulin & glucagon
Stores blood
Collects wastes, absorbs water
Nutrient absorption
Makes bile (aid in digestion)
hepatic artery
bring nutritional blood to the liver
Oxygen and nutrients to the liver
portal vein
bring functional blood to the liver
blood coming from the digestive tract, which the
hepatocytes function to detoxify.
bile ducts
bile flow is opposite blood flow bile (product of the hepatocytes) emulsify fat in the digestive system coalesce to form hepatic duct
9 BODY
4 pulmonary artery lungs
8 aorta
4 pulmonary artery
5 pulmonary veins
LUNGS (w/ O2)
4
7a aortic valve
5 pulmonary veins
6 left atrium
3a semilunar/ pulmonary valve
1 Superior Vena cava 2 right atrium
6a mitral valve
2a Tricuspid valve
7 left ventricle
1 Inferior Vena cava
3 right ventricle
Heart pumps blood to the different parts of the body Valves prevent backflow of blood Spiral valve (frog) prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood ARTERY carry oxygenated blood AWAY from the heart ; heart to tissues of the body
EXCEPT pulmonary artery
carries deoxygenated blood to lungs (for oxygenation & removal of excess CO2) VEIN carry deoxygenated blood TOWARDS the heart; All veins carry deoxygenated blood
EXCEPT pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from the the heart lungs to
The left ventricle is thicker and more muscular than the right ventricle because it pumps blood at a higher pressure. The left ventricle pumps blood to the entire body whereas the right ventricle pumps all of its blood directly to the lungs.
Vasa vasorum (blood vessels)
In comparison with artery, VEINS are thinner less elastic larger lumen located superficially same thickness of intima thinner media thicker adventitia fxn: carry blood toward the heart
In comparison with vein, arteries are thicker more elastic smaller lumen located deeper in the body same thickness of intima thicker media thinner adventitia Fxn: carry blood away from the heart
Nervi vasorum
1.
Tunica intima (innermost)
a.k.a. endothelium (simple squamous epithelium) only 1 layer
2.
Tunica media (middle)
Consists of smooth muscle cells
3.
Tunica adventitia (outermost)
Consists of connective tissues Nerve bundles (nervi vasorum) and vessels of the vessels (vasa vasorum) can be located
Basic structural and functional unit of the kidney Regulate water & soluble substances by filtering the blood PARTS A. renal corpuscle
Glomerulus (simple cuboidal epithelium) Bowmans capsule (simple squamous epithelium) Proximal convoluted tubule Loop of Henle Distal convoluted tubule
B. renal tubules
Bowmans capsule
Glomerulus Bowmans capsule Proximal convoluted tubule Loop of Henle Distal convoluted tubule Collecting duct Ureter Urinary Bladder Urethra MICTURITION
process of excretion of urine; urination
Sperm formation
Seminiferous tubules
spermatozoa Secondary spermatocyte
Interstitial cells/ Leydig cells - Secrete testosterone
Primary spermatocyte
1 Seminiferous tubules 1 Efferent duct 2 Epididymis 3 Ductus deferens Ejaculatory duct 4 Prostrate urethra 5 Penile urethra
Ovary egg cell formation
Eggs travel through these ducts
Oogenesis
Formation and maturation of oocytes from undifferentiated cells in the ovary Immediate covering of an oocyte Made up by follicle cells and oocytes Secreted by follicle cells Function: protects the oocyte Nourish the eggs Secrete estrogen
Vitelline membrane
Follicle cells
FROG STOMACH
FROG INTESTINE
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- 2011 Dec MCQDocument12 pages2011 Dec MCQKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- 2011 Dec MCQ AnswersDocument18 pages2011 Dec MCQ AnswersKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- 2011 April MCQ AnswersDocument22 pages2011 April MCQ AnswersKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Multiple-Choice Questions: I. Participants Have Up To 3 Years From TheDocument13 pagesMultiple-Choice Questions: I. Participants Have Up To 3 Years From TheKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- 2011 Dec MCQ AnswersDocument18 pages2011 Dec MCQ AnswersKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- 2018 CONTINUUM Neurologic Complications of Pediatric Intensive Care UnitDocument12 pages2018 CONTINUUM Neurologic Complications of Pediatric Intensive Care UnitKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- 2011 Aug MCQ PDFDocument14 pages2011 Aug MCQ PDFKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- 2011 Aug MCQ PDFDocument14 pages2011 Aug MCQ PDFKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- 2011 Dec MCQDocument12 pages2011 Dec MCQKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Multiple-Choice Questions: I. Participants Have Up To 3 Years From TheDocument13 pagesMultiple-Choice Questions: I. Participants Have Up To 3 Years From TheKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- 2010 Dec MCQDocument12 pages2010 Dec MCQKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- 2011 Aug MCQ AnswersDocument21 pages2011 Aug MCQ AnswersKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- 2014 CONTINUUM Neuromuscular Complications of DMDocument14 pages2014 CONTINUUM Neuromuscular Complications of DMKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- 2018 CONTINUUM Multimodality Monitoring in The Neurocritical Care UnitDocument13 pages2018 CONTINUUM Multimodality Monitoring in The Neurocritical Care UnitKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- 0-0013 PDFDocument24 pages0-0013 PDFisabellaprie3No ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- 2014 CONTINUUM Neurologic Complications of Rheumatic DiseaseDocument13 pages2014 CONTINUUM Neurologic Complications of Rheumatic DiseaseKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- Doença HepaticaDocument16 pagesDoença HepaticaInaraNo ratings yet
- 2014 CONTINUUM Neurologic Complications of Illicit Drug AbuseDocument15 pages2014 CONTINUUM Neurologic Complications of Illicit Drug AbuseKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Men CPGDocument42 pagesBacterial Men CPGKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- Rehab Scales and TablesDocument3 pagesRehab Scales and TablesKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- POGS Abnormal Labor and Delivery CPGDocument29 pagesPOGS Abnormal Labor and Delivery CPGKarl Jimenez Separa100% (2)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Use of Primary High Risk Human Papillomavirus.2Document6 pagesUse of Primary High Risk Human Papillomavirus.2Karl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- Drug Induced Limb DefectsDocument20 pagesDrug Induced Limb DefectsKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- ASCCP Guidelines PDFDocument29 pagesASCCP Guidelines PDFmisstina.19876007No ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Pathogenesis and Genetics of Split-Hand/Split-Foot MalformationDocument10 pagesPathogenesis and Genetics of Split-Hand/Split-Foot MalformationKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal and Pediatric VesselsDocument6 pagesNeonatal and Pediatric VesselsAhmed Gaber100% (1)
- FIGOCEDocument11 pagesFIGOCEAldwin TanuwijayaNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis and Genetics of Split-Hand/Split-Foot MalformationDocument10 pagesPathogenesis and Genetics of Split-Hand/Split-Foot MalformationKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- MED SCAPE 1 Ovarian Cancer - Practice Essentials, Background, PathophysiologyDocument15 pagesMED SCAPE 1 Ovarian Cancer - Practice Essentials, Background, PathophysiologyKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- INTERNS NOTES - OtorhinolaryngologyDocument15 pagesINTERNS NOTES - OtorhinolaryngologyKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal MRCPDocument18 pagesJurnal MRCPMaharani Eka SaputriNo ratings yet
- Gyan Niketan Girls School: Digha, PatnaDocument37 pagesGyan Niketan Girls School: Digha, PatnaMuskan ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Ascites Full TopicDocument15 pagesAscites Full TopicAashiNo ratings yet
- 1st Prof + Supl Questions Aio 2010-21Document87 pages1st Prof + Supl Questions Aio 2010-21Kashif GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Understand Fatty LiverDocument23 pagesUnderstand Fatty Liverbrijsing67% (3)
- Adventist Youth Class - ExplorerDocument52 pagesAdventist Youth Class - Explorerapi-270614046No ratings yet
- Pathology of LiverDocument15 pagesPathology of Liverערין גבאריןNo ratings yet
- Control of Liver FlukeDocument5 pagesControl of Liver FlukeAkinfeleye PeluolaNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Extraction & Biliary Metabolism OverviewDocument29 pagesHepatic Extraction & Biliary Metabolism Overviewdevi enjelikaNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam - Key AnswersDocument8 pagesMock Exam - Key Answerscrsdzx4c9gNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- A Review of Liver Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument41 pagesA Review of Liver Anatomy and PhysiologyVaseaPupchin0% (1)
- Choledocal CystDocument11 pagesCholedocal CystBilly JonatanNo ratings yet
- Ipi 262542Document6 pagesIpi 262542elsi mindahaNo ratings yet
- Digestion 1 MCQDocument11 pagesDigestion 1 MCQgopodNo ratings yet
- INTENSIVE CARE LIVER DISEASEDocument6 pagesINTENSIVE CARE LIVER DISEASEJulian HuningkorNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Managements of Gastrointestinal Diseases/DisordersDocument54 pagesNutritional Managements of Gastrointestinal Diseases/Disordersendang sry09No ratings yet
- Intergrated Science PDFDocument141 pagesIntergrated Science PDFAay Jay SequalsNo ratings yet
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument56 pagesAcute Gastroenteritisneil052298% (46)
- Presentation and Complications Associated With Cirrhosis of The LiverDocument14 pagesPresentation and Complications Associated With Cirrhosis of The LiverMoises OnofreNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis 2020Document27 pagesLiver Cirrhosis 2020Gabriela SalasNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Tokyoguidelines 2018 in The Management of Acute Cholangitis and Acute CholecystitisDocument13 pagesEffectiveness of Tokyoguidelines 2018 in The Management of Acute Cholangitis and Acute CholecystitisIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Sujok Cases 1Document282 pagesSujok Cases 1Trupti PurohitNo ratings yet
- Modified Cumulative Illness Rating Scale: Each System Is Rated As FollowsDocument1 pageModified Cumulative Illness Rating Scale: Each System Is Rated As FollowsFabi kNo ratings yet
- RETRACINGDocument54 pagesRETRACINGzer reNo ratings yet
- Liver Transplantation: What Is Liver Transplantation? Who Needs A Liver Transplant?Document12 pagesLiver Transplantation: What Is Liver Transplantation? Who Needs A Liver Transplant?RatihSeptianiNo ratings yet
- Abnormal liver function and mildly coarse liver: Diagnosing and managing NASH cirrhosis complicationsDocument38 pagesAbnormal liver function and mildly coarse liver: Diagnosing and managing NASH cirrhosis complicationsSandheepJanardhananNo ratings yet
- BraKay 5th January, Medical Nursing ClassDocument11 pagesBraKay 5th January, Medical Nursing ClassKwasikyie QuarshieNo ratings yet
- 120-Sam OCRDocument64 pages120-Sam OCRdionNo ratings yet
- Ati Teas 7 Exam Test Bank 300 Questions With AnswersDocument103 pagesAti Teas 7 Exam Test Bank 300 Questions With AnswersAbdelali AbarkanNo ratings yet
- Gallblad DER: ImagingDocument45 pagesGallblad DER: ImagingBohna FranciscoNo ratings yet