Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SAP Basis Daily Operations
Uploaded by
ezabalaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SAP Basis Daily Operations
Uploaded by
ezabalaCopyright:
Available Formats
Contents 1. SAP Architecture 2. SAP Instances 3. SAP Active Servers (SM51) 4. Work process overview (SM50) 5.
Transaction Lock/Unlock (SM01) 6. Users overview/Active users (SM04, AL08) 7. System log (SM21) 8. ABAP Dump (ST22) 9. Database Size / Table space space check (DB02, BRTOOLS) 10. BRTOOLS 11. Client Administration 12. Logical System Creation (SALE) 13. User management (SU01, SUIM,EWZ5, PFCG, SU53,SU24,SU25,SU10) 14. System Profiles (RZ10, RZ11) 15. RFC Destinations setting (SM59) 16. Operation mode Configuration (RZ04, SM63, RZ03) 17. Logon Load balancing (SMLG) 18. Transport Management System (STMS) 19. Spool Administration (SPAD, SP01) 20. Kernel Upgrade 21. Applying Patches using (SPAM, SAINT) 22. Backup and Recovery (DB12) 23. SAP DBA Calendar (DB13) 24. Lock management (SM12) 25. Update Administration 26. CCMS Alert Monitoring (RZ20/RZ21) 27. Trouble Shooting 28. Start and Stop SAP 29. Daily System Check 30. WebAS 31. SAP Net weaver 32. BW Administration 33. Portal User Administration (SSO) 34. ECC fundamentals. 35. Q & A.
1. SAP Architecture
User/Client
Application Layer SD, MM, PP, FI/CO, HR, PS, PM etc. applications are configured here.
BASIS Layer/Middle Layer User Authorization, System Monitoring, Application Tuning, Backup/Recovery, Trouble Shooting etc.
OS Layer OS, CPU, Memory, Database, Hardware etc.
Explanation: When any user tries to access the application like SD, MM, PP, FI/CO, they first touch the application layer which contains the required data and configuration. In order to access the Application, the user has to be authorized, which is done at Middle layer. Similarly if there is an issue for server like at OS, at Database or at Hardware level, then Middle layer people have to identify and direct it to the corresponding responsible person to look at the issue. Because these Middle layer people sit in the middle and look to both sides and trouble shoot the problem at Application level and OS level as per the issue, these people are called BASIS Administrators.
2. SAP Instances SAP instance defines a group of resources such as memory, work processes and so on, usually in support of a single application server or database server within a client/server environment. Application servers share the same memory areas and are controlled by the same dispatcher process. There are 3 types of Instances available in SAP system as defined below. 1. Central Instance (Unique Instance or SID name for a SAP Server) 2. Database Instance (Which contains data with its own SID) 3. Dialog Instance (Used for Load balancing purpose when needed) SAP SID: 3 Alphanumeric Characters except some reserved ones. SID may look like ECP, SCP, BIP like this. System number: System number is the number which differentiates between multiple instances in a single host. System nr varies from 00 -99 (75 and 99 are reserved for TCP/IP use)
Work processes There are different types of work process on which SAP Instance depends to run as described below
Dialog Work process(D) :- Used by frontend users or frontend process every dispatcher requires at least two dialog work processes Backgorund Work process (B) : Used for long running Jobs .At least two for each R/3 system (more than one allowed for each dispatcher) Enqueue Work process (E) :Used for Locking /Unlocking purposes only one enqueue work process is needed for each system Update work process (V1) : Used for critical updates into Database at least one for each R/3 System (more than one allowed for each dispatcher) Update workprocess (V2): Used for normal updates after critical updates Gateway work process (G) : allows communication between R/3, R/2 and external application systems. Spool work process (S) : Used for Printing from SAP at least one process Message Service (M): Used for messaging purpose. The message server (MS or M) communicates between the distributed dispatchers within the R/3 System and is therefore the prerequisite for scalability using several parallelprocessing Application servers.
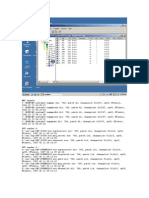
4. SAP Active Servers (SM51) Execute tcode SM51 at sap command line. It shows the active servers available for the Central Instance if there. See the fig below.
There are five Active Servers in above figure. 5. Work process overview (SM50)
The following are the points we observe from SM50 a. No of each work processes like (Dialog, Background, Enqueue, Update, spool ) b. What is the processes id for each work process c. Work process status, running or waiting d. IF any error is there , reported in Err field e. The field CPU show how much CPU time is consumed by the particular work process f. Time: It shows how long the work process is running g. Report: Which report is running currently by that work process h. Client: Specifies the client no for which this process is busy i. User: Specifies which user is running this report. j. Action: What exactly going on during this process k. Table: Which table is accessed during this process The point to concentrate from SM50 is Process Status, time, client and user. If Basis wants to cancel one running Work process then, select the work process by clicking on left check box as selected below Now Go to Process -> Cancel Without Core.
Click on Yes to terminate the process. Now you can see that process is in waiting status. Click on Refresh button to get the updated status.
6. Users overview/Active users (SM04, AL08) SM04: This tcode is used to check the status of users i.e how many users have been logged in, how many sessions a user is working. See the fig below.
From the above figure you can see, the users have logged in into client 300. Check the detail of each line. Take the example of user ALEXANDERA, this user has logged into client 300, from system achamma, executing tcode MIGO, time of login 11:40:28, 5 sessions. Two know more about session , select the user or line and double click on it.
Now if you want to delete one session, select /click on the specific line and click on End Session.
Click Click on
button to come out from the window. button to get most up to date data.
Active Users: Al08 Al08: To know how many users are active in all servers.
7. System log (SM21) To know /to investigate the problems in SAP system, Basis Admin checks the system logs to check the possible errors and the cause of the error. Any system related task are recorded into system logs and can be viewed and analyzed later to trouble shoot the problem. The figure below shows how to select the errors and warnings.
8. ABAP Dump (ST22) When users are working they face some kind of time out problem and any kind of problem for which their work gets terminated. That termination is reported in an area called ABAP dumps. Using ST22, Basis can analyze the errors. ST22 show the today and yesterday all the time. To get more dumps from previous days, you can select the date range.
Database Size / Table space space check (DB02)
Using the tcode DB02, Basis checks the database detail like database size, table space size, free space statistics, no of tables, table space growth, data files associated with tables and lot more. See the Fig shown below which shows over all database detail. To get more updated data, click on refresh button. Remember refreshing this take several mins.
Each time you refresh this screen, look for if any space critical objects are shown in space-critical objects field. Click on Current Sizes to check the tablespace size, utilization , free space available and associated datafiles as shown in Fig below.
To know the associated datafiles: select the tablespace and click on Goto Tablespaces DBA Datafiles button from the menu shortcut above. See the below Fig for datafile information.
To know about tablespace history like now much data load into which tablespace on daily, weekly, Monthly basis, click on tablespace history from the menu bar. Check below Fig for detail of history.
Now from tablespace utilization screen, If tablespace utilization is above 90% , then we have to add datafiles to the specific tablespace to bring it below 90% and will try to keep below 80%. One can only view the tablespace utilization and how many datafiles associated with the tablespace but cant add datafiles. 11. Client Administration
A client is, in organizational terms, an independent unit in the R/3 System. Each client has its own data environment and therefore its own master data and transaction data, assigned user master records and charts of accounts, and specific customizing parameters.
1. Client Overview 2. Client Creation 3. Local Client Copy 4. Remote Client copy 5. Client Deletion 6. Client Export 7. Client Import Client Overview (SCC4)
SCC4 SCC4 SCCL SCC9 SCC5 SCC8 SCC7
Creation of Client (SCC4) Execute SCC4 and see the screen above. Click on change button Click on New Entries Fill up the tabs as shown below.
Click Save
button.
Local Client Copy (SCCL)
Pre-Requisites 1. Make sure you have enough space in PSAPECP tablespace to complete the client copy. 2. Create a client in 3 digit number except 000, 001 and 066. 3. Check server has enough space to handle client copy before scheduling client copy. You can check this using tcode DB02. 4. Login to the new client using SAP* user and password PASS. 5. execute tcode SCCL in SAP command line 6. Select the profile you want to copy to new client, e.g. SAP_ALL 7. Select the source client e.g. 000 8. Select source client master data e.g. 000
9. Now click on schedule as background job
Click on continue 10. Select the back ground server you want to perform this action, default leave the field blank
11. Now click on schedule job 12. Click on Immediate. 13. Click check 14. click Save button.
15. A summary of client copy will be shown in the screen with test run 16. Make sure test mode is not selected at this moment. 17. Click on continue
18. now the client copy is scheduled in background
19. Client copy progress can be monitored using tcode SCC3
20. Job can be also seen in SM50 If client copy fails due to any reason, you can check the log in SCC3. Once the problem is solved, you can restart the client copy with same setting in restart mode. Remote Client Copy (SCC9) Remote client copy is performed in rare situation. When the client copy is done between two different SAP systems, the copy is called remote client copy.
Before remote client copy is performed, a RFC connection must be set between those systems using SM59.
1. Check RFC connection is working fine between two systems you want to perform remote client copy using SM59 2. create client in the target system you want to copy the client 3. login to target client using user SAP* and password PASS 4. execute tcode SCC9 and select the RFC for the source system 5. select the profile you want to copy like SAP_ALL 6. select source client number you want to copy 7. Select source client master data , mostly it is the same client number 8. Now click on schedule as background job. 9. Leave the background server field blank. 10. Click schedule. 11. Select Immediate from next screen. 12. Save the screen. 13. Client copy is scheduled now as a background job and client copy process started. 14. The progress can be monitored using tcode SCC3 Client Deletion (SCC5) Client deletion is performed when the client data is corrupted or client data is no longer needed to avoid confusion.
1. Dont delete the client using SCC4 the space occupied by the client cant be regained 2. login to the client you want to delete 3. run tcode SCC5 in sap command line 4. Tick mark on remove from table T000 to perform a complete removal. 5. Now click on schedule as background job 6. leave the background server blank 7. now click on schedule job 8. click on Immediate 9. click on save 10. Client deletion is started and log can be seen in SCC3
Administrative Database Operations (DB24) We use this transaction to display the backup logs to get first hand information whether the backup or archives have been completed successfully/ Failed or are in progress.
Oracle Lock monitor (DB01) This tcode is used to check the locks in Oracle.
You might also like
- Sap BasisDocument174 pagesSap Basisnaren2899100% (1)
- Sap Basis ActivitiesDocument129 pagesSap Basis ActivitiesShafeeq Mohammed100% (2)
- SAP Basis EBOOK PDFDocument362 pagesSAP Basis EBOOK PDFblackgoldboy50% (2)
- Sap BasisDocument35 pagesSap BasisNaveen Yarramsetty50% (2)
- Linux Commands For SAP BasisDocument3 pagesLinux Commands For SAP Basissai_balaji_8No ratings yet
- Sap Basis TipsDocument87 pagesSap Basis Tipsb_desarkarNo ratings yet
- Brief Description About SAP Basis ImplementationDocument76 pagesBrief Description About SAP Basis Implementationesram rajuNo ratings yet
- System Refresh With ScreenshotDocument18 pagesSystem Refresh With Screenshotmhku1No ratings yet
- SAP Basis Monitoring TcodeDocument13 pagesSAP Basis Monitoring Tcodemofibhai100% (2)
- Sap Hana - S4 Hana Administration Course ContentDocument7 pagesSap Hana - S4 Hana Administration Course ContentMohammad Zahid KhanNo ratings yet
- Sap BasisDocument41 pagesSap Basisapi-3766700100% (3)
- Basis FAQDocument106 pagesBasis FAQAvinash KallemNo ratings yet
- BASIS Latest Till Interview QuestionsDocument213 pagesBASIS Latest Till Interview Questionsdhanireddymadhu100% (1)
- Sap Basis PrepDocument73 pagesSap Basis PrepkryshhnaNo ratings yet
- Useful Troubleshooting TipsDocument81 pagesUseful Troubleshooting TipsPeter Naveen NaviNo ratings yet
- System RefreshDocument42 pagesSystem RefreshAtul As StreetwarriorNo ratings yet
- SAP BASIS Interview Questions and Answers.Document25 pagesSAP BASIS Interview Questions and Answers.aravindNo ratings yet
- Sap Basis Interview Questions and Answers For ExperiencedDocument64 pagesSap Basis Interview Questions and Answers For ExperiencedPILLINAGARAJUNo ratings yet
- Database Refresh ProcedureDocument55 pagesDatabase Refresh Proceduredebojoti100% (1)
- Sap Basis Interview QuestionsDocument31 pagesSap Basis Interview Questionssai_balaji_8No ratings yet
- Sap Basis Admin PDFDocument174 pagesSap Basis Admin PDFVamshi Krishna Daravath100% (1)
- SAP Basis How To DoDocument67 pagesSAP Basis How To Dochiruyours86% (7)
- Sap Meterial - 002Document88 pagesSap Meterial - 002Naveen YarramsettyNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandSAP HANA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- Monitoring - SAP SystemDocument151 pagesMonitoring - SAP Systemramanji ankam100% (1)
- SAP Made Easy - by ShannuDocument151 pagesSAP Made Easy - by ShannuSandeep Kumar T100% (1)
- SAP Made EasyDocument94 pagesSAP Made EasytushileceNo ratings yet
- Daily Check ListDocument40 pagesDaily Check ListVamshi Krishna DaravathNo ratings yet
- Daily Check List SummaryDocument40 pagesDaily Check List SummaryVamshi Krishna DaravathNo ratings yet
- Basis ActivitiesDocument68 pagesBasis ActivitiesreepakNo ratings yet
- SAP Basis Interview QuestionsDocument18 pagesSAP Basis Interview QuestionsPILLINAGARAJUNo ratings yet
- EP1 Daily Monitoring & Performance TunningDocument31 pagesEP1 Daily Monitoring & Performance TunningTushil KumarNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Types of Work Processes in Application ServerDocument11 pagesUnderstanding The Types of Work Processes in Application ServerKapil Satish PatilNo ratings yet
- Basis Impl TopicsDocument29 pagesBasis Impl TopicsgunturchilliNo ratings yet
- Ilide - Info Sap Basis Interview Questions PRDocument5 pagesIlide - Info Sap Basis Interview Questions PRArsalan TaufiqNo ratings yet
- Work Processes Overview and Troubleshooting (SM51Document54 pagesWork Processes Overview and Troubleshooting (SM51NagaNo ratings yet
- 01 FirstDocument11 pages01 FirstSurut ShahNo ratings yet
- Analyze SAP Memory Usage with ST02Document7 pagesAnalyze SAP Memory Usage with ST02Kishore KumarNo ratings yet
- SAP Systems ManagerDocument21 pagesSAP Systems Managermath_mallikarjun_sapNo ratings yet
- SAP BASIS Consultant's Role in System MonitoringDocument59 pagesSAP BASIS Consultant's Role in System Monitoringprachi wadraliNo ratings yet
- Category Archives: BDCDocument4 pagesCategory Archives: BDCAnand DuttaNo ratings yet
- Basis Daily Monitoring TDocument15 pagesBasis Daily Monitoring TMarcelo Del Canto RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions For SAP BasisDocument17 pagesInterview Questions For SAP BasisVideesh KakarlaNo ratings yet
- SAP Notes 1Document22 pagesSAP Notes 1sanu201982100% (14)
- How To Monitor SAP System and Do Performance ChecksDocument24 pagesHow To Monitor SAP System and Do Performance ChecksRupam DasNo ratings yet
- Timezone Changes Best PracticesDocument11 pagesTimezone Changes Best PracticesKrishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- ABAP Stack Checks: Key Transactions for Monitoring SAP SystemsDocument76 pagesABAP Stack Checks: Key Transactions for Monitoring SAP SystemsJulianGuillermoZipaquiraColinaNo ratings yet
- Thrinath Soma – SAP Basis Consultant ProceduresDocument179 pagesThrinath Soma – SAP Basis Consultant Proceduressoma3nathNo ratings yet
- SAP Java Troubleshooting MonitoringDocument24 pagesSAP Java Troubleshooting MonitoringTeegala BalreddyNo ratings yet
- SAS Programming Guidelines Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandSAS Programming Guidelines Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- SAP interface programming with RFC and VBA: Edit SAP data with MS AccessFrom EverandSAP interface programming with RFC and VBA: Edit SAP data with MS AccessNo ratings yet
- Top 100 Linux Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesTop 100 Linux Interview Questionsvinod.nalawadeNo ratings yet
- Splunk Enterprise Capacity Planning Manual 7.2.1: Estimate Your Storage RequirementsDocument3 pagesSplunk Enterprise Capacity Planning Manual 7.2.1: Estimate Your Storage RequirementsRaghavNo ratings yet
- CDJ-850 Update Guide ENDocument5 pagesCDJ-850 Update Guide ENC-Dryk ™No ratings yet
- ToscanDocument8 pagesToscanAhmed Abd ELHADYNo ratings yet
- Emulex Boot For NIC, iSCSI, and FCoE Protocols User GuideDocument280 pagesEmulex Boot For NIC, iSCSI, and FCoE Protocols User GuideAldozpNo ratings yet
- Oracle UPK Installation and AdministrationDocument78 pagesOracle UPK Installation and Administrationd.vasanthkumarNo ratings yet
- HP Color Laserjet Pro M452Dw: DatasheetDocument2 pagesHP Color Laserjet Pro M452Dw: DatasheetDaniel Concepcion RoigNo ratings yet
- Active Directory at the University of MichiganDocument61 pagesActive Directory at the University of MichiganPraveen RaiNo ratings yet
- Docu 69330Document584 pagesDocu 69330osama425No ratings yet
- Android Solution - Odin Guide On How To Flash and Install Stock ROM Firmware On Samsung Galaxy Y S5360Document11 pagesAndroid Solution - Odin Guide On How To Flash and Install Stock ROM Firmware On Samsung Galaxy Y S5360AdiKetoNo ratings yet
- Bitraser Cloud User Guide: Legal Notices About Stellar Contact UsDocument81 pagesBitraser Cloud User Guide: Legal Notices About Stellar Contact Usjitesh waghmareNo ratings yet
- PowerShell Transcript - montEMPPC.hcuzU4vi.20220413113738Document50 pagesPowerShell Transcript - montEMPPC.hcuzU4vi.20220413113738vb_pol@yahooNo ratings yet
- Splunk QueiriesDocument1 pageSplunk Queiriesjfrederickson7384No ratings yet
- Dell EMC-Red Hat-Cloud-Solutions PDFDocument54 pagesDell EMC-Red Hat-Cloud-Solutions PDFjagaenatorNo ratings yet
- DC-3 - Recovery Software Guide - V06 04 00 5465 - ECD117-1Document20 pagesDC-3 - Recovery Software Guide - V06 04 00 5465 - ECD117-1ДмитрийNo ratings yet
- Hummingbird Socks Client UsageDocument15 pagesHummingbird Socks Client UsageJayakumarNo ratings yet
- VVM Exam AppDocument11 pagesVVM Exam AppRUBIX PLANETNo ratings yet
- 7-Zip HistoryDocument23 pages7-Zip Historycarmstrong04No ratings yet
- BackdoorDocument15 pagesBackdoortechNo ratings yet
- Performing MySQL Backups Using LVM SnapshotsDocument14 pagesPerforming MySQL Backups Using LVM SnapshotsOleksiy Kovyrin100% (4)
- Setup Log 2022-11-25 #001Document55 pagesSetup Log 2022-11-25 #001Francesco RegestroNo ratings yet
- opsix Sound Librarian Owner's ManualDocument16 pagesopsix Sound Librarian Owner's ManualGraham KovalskyNo ratings yet
- Product Matrix of SAP GUI 7.50 PDFDocument7 pagesProduct Matrix of SAP GUI 7.50 PDFbianfa05No ratings yet
- MIET-IV Annexure Offers Computer Hardware, Office Admin CoursesDocument4 pagesMIET-IV Annexure Offers Computer Hardware, Office Admin CoursesHiral SavaliyaNo ratings yet
- Adms-15 FTM-200D Im Eng 2211-BDocument35 pagesAdms-15 FTM-200D Im Eng 2211-Bsoporte tecnico muleyNo ratings yet
- ResoluteDocument9 pagesResolutetechNo ratings yet
- Linux System Administration Certification CourseDocument16 pagesLinux System Administration Certification CourseAzhar StapaNo ratings yet
- Be2k Software User ManualDocument10 pagesBe2k Software User ManualSergio Ricardo IbañezNo ratings yet
- Virtualization Using Openvz and EasyvzDocument8 pagesVirtualization Using Openvz and EasyvzShuaib Zahda100% (1)