Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Passive Voice
Uploaded by
54769854Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Passive Voice
Uploaded by
54769854Copyright:
Available Formats
Passive Voice
Exercises on Passive Use of Passive
Passive voice is used when the focus is on the action. It is not important or not known, however, who or what is performing the action.
Example: My bike was stolen.
In the example above, the focus is on the fact that my bike was stolen. I do not know, however, who did it.
Sometimes a statement in passive is more polite than active voice, as the following example shows:
Example: A mistake was made.
In this case, I focus on the fact that a mistake was made, but I do not blame anyone (e.g. You have made a mistake.). Form of Passive
Subject + finite form of to be + Past Participle (3rd column of irregular verbs)
Example: A letter was written.
When rewriting active sentences in passive voice, note the following:
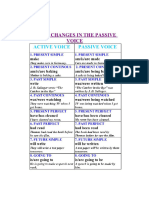
the object of the active sentence becomes the subject of the passive sentence the finite form of the verb is changed (to be + past participle) the subject of the active sentence becomes the object of the passive sentence (or is dropped) Examples of Passive Tense Simple Present Active: Rita Passive: A letter is written Simple Past Active: Rita Subject Verb writes a letter. by Rita. wrote a letter. by Rita. has written by Rita. a letter. a letter. Object
Passive: A letter was written Present Perfect Active: Rita
Passive: A letter has been written Future I Active: Rita will write
Passive: A letter will be written by Rita. Hilfsverben Active: Rita can write a letter.
Passive: A letter can be written by Rita.
Examples of Passive Tense Present Progressive
Subject Verb
Object a letter.
Active: Rita
is writing
Passive: A letter is being written by Rita. Past Progressive Active: Rita was writing by Rita. a letter. a letter.
Passive: A letter was being written Past Perfect Active: Rita
had written by Rita.
Passive: A letter had been written Future II Active: Rita
will have written
a letter.
Passive: A letter will have been written by Rita. Conditional I Active: Rita would write a letter.
Passive: A letter would be written Conditional II Active: Rita
by Rita. a letter.
would have written by Rita.
Passive: A letter would have been written
Passive Sentences with Two Objects
Rewriting an active sentence with two objects in passive voice means that one of the two objects becomes the subject, the other one remains an object. Which object to transform into a subject depends on what you want to put the focus on. Subject Verb Object 1 Object 2 Active: Rita wrote a letter to me. to me by Rita. a letter by Rita.
Passive: A letter was written Passive: I was written
As you can see in the examples, adding by Rita does not sound very elegant. Thats why it is usually dropped. Personal and Impersonal Passive
Personal Passive simply means that the object of the active sentence becomes the subject of the passive sentence. So every verb that needs an object (transitive verb) can form a personal passive.
Example: They build houses. Houses are built.
Verbs without an object (intransitive verb) normally cannot form a personal passive sentence (as there is no object that can become the subject of the passive sentence). If you want to use an intransitive verb in passive voice, you need an impersonal construction therefore this passive is called Impersonal Passive.
Example: he says it is said
Impersonal Passive is not as common in English as in some other languages (e.g. German, Latin). In English, Impersonal Passive is only possible with verbs of perception (e. g. say, think, know).
Example: They say that women live longer than men. It is said that women live longer than men.
Although Impersonal Passive is possible here, Personal Passive is more common.
Example: They say that women live longer than men. Women are said to live longer than men.
The subject of the subordinate clause (women) goes to the beginning of the sentence; the verb of perception is put into passive voice. The rest of the sentence is added using an infinitive construction with 'to' (certain auxiliary verbs and that are dropped).
Sometimes the term Personal Passive is used in English lessons if the indirect object of an active sentence is to become the subject of the passive sentence. Passiv mit 2 Objekten
Bilde Passivstze und Use das fett geschriebene Objekt als Subjekt des Passivsatzes. Rachel will give you some advice. I sent him a letter. The police officer showed us the way. Our neighbour gave me a lift.
We have asked him a favour. She told me a lie. They have written her a postcard. Kerrie will make you a cup of tea. The waiter has not brought us the coffee. They did not offer her a seat. Passiv mit 2 Objekten
Bilde Passivstze und Use das fett geschriebene Objekt als Subjekt des Passivsatzes. (Personal Passive) Rachel will give you some advice. I sent him a letter. The police officer showed us the way. Our neighbour gave me a lift. We have asked him a favour.
She told me a lie. They have written her a postcard. Kerrie will make you a cup of tea. The waiter has not brought us the coffee. They did not offer her a seat. Passive - various tenses - Exercise Explanation: PassivePut in the correct form of the verb in Passive into the gaps. Use the verb and the tense given in brackets.
Example: A letter __________ by Peter. (to write - Simple Present)
Answer: A letter is written by Peter.
1) The words ___________by the teacher today. (to explain - Simple Present) 2) We ________-a letter the day before yesterday. (to send - Simple Past) 3) This car__________ . It's too old. (not/to steal - will-future) 4) This street _________ because of snow. (already/to close - Present Perfect)
5) A new restaurant _________next week. (to open - will-future) 6) He t__________o the party yesterday. (to invite - Simple Past) 7) The blue box ____________. (can/not/to see - Simple Present) 8) I ___________ the book by my friend last Sunday. (to give - Simple Past) 9) The dishes _____________by my little brother. (not/to wash - Present Perfect) 10) I ______________by Robert. (not/to ask - will-future) Answers: 1) The words are explained by the teacher today. 2) We were sent a letter the day before yesterday. 3) This car will not be stolen. It's too old. 4) This street has already been closed because of snow. 5) A new restaurant will be opened next week. 6) He was invited to the party yesterday. 7) The blue box cannot be seen. 8) I was given the book by my friend last Sunday. 9) The dishes have not been washed by my little brother. 10) I will not be asked by Robert. Active to Passive Transformations
Put the following sentences into the passive voice or form. Once you have decided on your answer, click on the arrow to see if you have answered correctly. Remember that the agent should not be used unless important. For more information about how to use the passive voice, refer to this passive voice usage chart. They make shoes in that factory.
Shoes _____ in that factory. People must not leave bicycles in the driveway.
Bicycles _________ in the driveway. They built that skyscraper in 1934.
That skyscraper ________-- in 1934. The students will finish the course by July.
The course ___________S by July. They are repairing the streets this month.
The streets __________ this month. They make these tools of plastic.
These tools ______________of plastic. They have finished the new product design.
The new product _________design . They were cooking dinner when I arrived.
Dinner ___________when I arrived. Smithers painted 'Red Sunset' in 1986.
'Red Sunset' _________ in 1986 by Smithers. Did the plan interest you?
_________in the plan? They had finished the preparations by the time the guests arrived.
The preparations __________by the time the guests arrived. You should take care when working on electrical equipment.
Care ___________---when working on electrical equipment. They are going to perform Beethoven's Fifth Symphony next weekend.
Beethoven's Fifth Symphony ____________ next weekend. Someone will speak Japanese at the meeting.
Japanese __________ at the meeting. Karen is going to prepare the refreshments.
The refreshments __________by Karen.
Grammar rules with examples Form
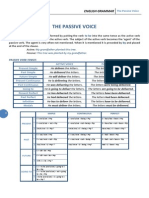
Present simple: The car is repaired. Present continuous: The car is being repaired. Past simple: The car was repaired. Past continuous: The car was being repaired. Present perfect: The car has just been repaired.
Past perfect: The car had been repaired. Future simple: The car will be repaired. Present conditional : The car would be repaired. Perfect conditional: The car would have been repaired.
The passive voice in English is formed with the verb to be and the past participle, which is different for regular verbs (translated, mended) and irregular verbs (taken, thrown). Statement: The letter is written. This shop has been opened. Question: Is the letter written? Has the shop been opened? Negative: The letter is not written. The shop has not been opened.
The continuous forms are as follows. (Other continuous tenses are normally used in the active voice, but not in the passive.) Present: A new house is being built in our street. Past: A new house was being built in our street.
In all the examples above the agent is not mentioned. We do not know it. Similarly: Flowers were planted in the garden. (We do not know who did it). If we want to say who planted the flowers we mention the agent at the end of the sentence and use the preposition by. The flowers were planted by my mother. But: The window was smashed with a stone. (The stone is not the agent. We do not know who smashed the window. We only know how he or she did it).
Direct and indirect objects
If there are both direct and indirect objects in the active voice, the indirect object becomes the subject in the passive voice. Active: My friend sent me a letter. Passive: I was sent a letter by my friend. (Not: A letter was sent to me by my friend. This sentence does not sound natural in English.) Similarly: They offer Trevor a place. - Trevor is offered a place.
The infinitive without to
In the active voice some verbs are followed by the infinitive without to. In the passive we use most such verbs with the infinitive with to. Active: We saw them come. She made him do it. Passive: They were seen to come. He was made to do it. But: They let us go. - We were let go. Use
The passive is used: 1. If the action is more important then the agent. A demonstration has been held. This theatre was built in 1868. The important thing is what happened, not who did it.
2. If the agent is not known. He was offered a job. (someone offered him the job) They are supposed to be good students. (some teachers suppose that)
The difference in meaning between the simple and continuous
A new house is built in our street. (The house is finished.) A new house is being built in our street. (They are building it these days, it is not finished.)
I was being introduced to Mrs. Jones when her husband arrived. (Her husband arrived in the middle of the introduction.) When her husband arrived I was introduced to Mrs. Jones. (Her husband arrived first and then she introduced me.)
Notes
This form is typical of an impersonal and formal style, that is why you can often find it in public notices, announcements, instructions or scientific articles. English is spoken in this shop. Visitors are not allowed to smoke. The seal must be removed.
In a less formal style the active voice is more usual. English is spoken in this shop. - We speak English in this shop. He was seen in Dover. - They saw him in Dover. The seal must be removed. - You must remove the seal.
In the English language this form is more frequent than in many other languages. Moreover, you can find some stuctures in English which are not possible in some languages. I am told that you are going to have a baby. It is thought that the crises will end soon.
You might also like
- GuíaBurros: Spanish Grammar Cheat Sheet: A quick and easy guide to Spanish GrammarFrom EverandGuíaBurros: Spanish Grammar Cheat Sheet: A quick and easy guide to Spanish GrammarRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Passive Voice ExercisesDocument7 pagesPassive Voice ExercisesMydays31No ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument8 pagesPassive VoicenguyenhoaianhthuNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument5 pagesPassive VoiceMonicaPuiNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument11 pagesPassive Voicealta_centaNo ratings yet
- INDIRECT QUESTIONS AND REPORTED SPEECHDocument7 pagesINDIRECT QUESTIONS AND REPORTED SPEECHOmar Chavez100% (1)
- PasivDocument7 pagesPasivAlexandra WeissNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice Formations and Uses in 40 CharactersDocument4 pagesPassive Voice Formations and Uses in 40 CharactersNenad YOvanovskyNo ratings yet
- Use of PassiveDocument29 pagesUse of PassiveAidafajriyaNot Zhacto-chazze Affaffoo-Horazz100% (1)
- Passive Voice For StudentsDocument23 pagesPassive Voice For Studentssdsakdjj jadslkka asNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice - TheoryDocument6 pagesPassive Voice - Theorynato.kharshiladze.1No ratings yet
- Use of PassiveDocument2 pagesUse of PassiveClaudia Crisanto H.No ratings yet
- Passive Voice 5Document5 pagesPassive Voice 5LalitheNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument7 pagesPassive VoiceAlejandro0% (1)
- Active Passive Voice For The BeginnresDocument18 pagesActive Passive Voice For The BeginnresWaqas AhmedNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument9 pagesPassive VoicePleine LuneNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice PRESENT & PASTDocument4 pagesPassive Voice PRESENT & PASTvane.ramz15No ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument20 pagesActive and Passive Voiceqweds westfdfNo ratings yet
- Understanding Active and Passive VoiceDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Active and Passive VoiceMarishka BivolNo ratings yet
- How to Identify and Form Passive Voice SentencesDocument4 pagesHow to Identify and Form Passive Voice SentencesAdnan BujakNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice Forms and UsesDocument2 pagesPassive Voice Forms and UsesElena MarianNo ratings yet
- Active Passive VoiceDocument10 pagesActive Passive VoiceSiddharth KalraNo ratings yet
- Use of Passive: Example: My Bike Was StolenDocument3 pagesUse of Passive: Example: My Bike Was StolennabornicolasNo ratings yet
- Example: A Letter Was Written.: Form of PassiveDocument16 pagesExample: A Letter Was Written.: Form of PassiveShana HayesNo ratings yet
- Passive Sentences With Two Objects LevelDocument1 pagePassive Sentences With Two Objects Leveljunot meeNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice ExerciseDocument6 pagesPassive Voice ExerciseIlyana HaniNo ratings yet
- 9 Passive Voice PDFDocument2 pages9 Passive Voice PDFIna SestacovschiNo ratings yet
- Modul Xiv English I 20Document8 pagesModul Xiv English I 20DarayaniNo ratings yet
- Use of the Passive Voice ExplainedDocument11 pagesUse of the Passive Voice ExplainedRachel GonzálezNo ratings yet
- M10 - Passive SentenceDocument4 pagesM10 - Passive SentencesriayuNo ratings yet
- BDNDJD Presentation 1Document19 pagesBDNDJD Presentation 154p6vpsjrmNo ratings yet
- Use of Passive: Example: My Bike Was StolenDocument3 pagesUse of Passive: Example: My Bike Was StolenMunirah YusoffNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument2 pagesActive and Passive VoiceNesrine AridNo ratings yet
- VOICE AND NARRATIONDocument15 pagesVOICE AND NARRATIONSukhwinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Use of Passive: Example: My Bike Was StolenDocument3 pagesUse of Passive: Example: My Bike Was StolenAneteisabelNo ratings yet
- Present Passive VoiceDocument3 pagesPresent Passive VoiceAde YantoNo ratings yet
- Use of Passive: Example: My Bike Was StolenDocument10 pagesUse of Passive: Example: My Bike Was StolenciciksherlyNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be in The PastDocument12 pagesVerb To Be in The PastAdalberto Jiménez100% (1)
- Tense and Aspect: Fallen in Love On His Eighteenth Birthday. The Auxiliary Has HereDocument10 pagesTense and Aspect: Fallen in Love On His Eighteenth Birthday. The Auxiliary Has HeredaljmerNo ratings yet
- Understanding Active and Passive VoiceDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Active and Passive VoicegotmyvampNo ratings yet
- notesDocument7 pagesnotesnur nashirahNo ratings yet
- Modals - PhrasalDocument9 pagesModals - PhrasalmilkoviciusNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice PDFDocument20 pagesPassive Voice PDFRoberth MoralesNo ratings yet
- The Passive Voice ExplainedDocument8 pagesThe Passive Voice ExplainedSandra Sánchez PérezNo ratings yet
- Subject + Be + V + by + O: Passive VoiceDocument5 pagesSubject + Be + V + by + O: Passive VoiceMuhammadNizarRafifNo ratings yet
- 11S2 ENG Ebook P1 Passive Voice & CausativeDocument12 pages11S2 ENG Ebook P1 Passive Voice & CausativeFathimah AqiylaNo ratings yet
- Examples of Passive: Tense Subject Verb Object Simple Present Simple Past Present Perfect Future I HilfsverbenDocument13 pagesExamples of Passive: Tense Subject Verb Object Simple Present Simple Past Present Perfect Future I HilfsverbenAnonymous 9AEuwccNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument5 pagesActive and Passive VoiceSaubhagya SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Passive Voice1Document10 pagesThe Passive Voice1AngelesNo ratings yet
- PASSIVE VOICEDocument4 pagesPASSIVE VOICEmélzio da assaNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice and Reported SpeechDocument11 pagesPassive Voice and Reported SpeechAlejandra B.100% (2)
- English GrammarDocument11 pagesEnglish Grammaralifiaar100% (1)
- Passive Voice 1Document3 pagesPassive Voice 1api-241242931100% (3)
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument49 pagesActive and Passive VoiceNoel Marcelo ManongsongNo ratings yet
- Tense Subject Verb Object: Simple PresentDocument4 pagesTense Subject Verb Object: Simple Presentfika cyNo ratings yet
- Morphology Pasive VoiceDocument11 pagesMorphology Pasive VoiceJulija JovanovskaNo ratings yet
- The PassiveDocument7 pagesThe Passivesolila67% (3)
- Passive Voice: Tense TranformationsDocument6 pagesPassive Voice: Tense TranformationsStephy PunctNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive English Learning: Your All-in-One Guide for ESL SuccessFrom EverandComprehensive English Learning: Your All-in-One Guide for ESL SuccessNo ratings yet
- Synonyms Question and AnswersDocument4 pagesSynonyms Question and AnswersSatyam VeerNo ratings yet
- PDF A1-USE-6 - English VersionDocument21 pagesPDF A1-USE-6 - English VersionEwing ChNo ratings yet
- Lista de Verbos Irregulares CBTIS CompletaDocument2 pagesLista de Verbos Irregulares CBTIS Completadarjaie67No ratings yet
- 3) VerbDocument5 pages3) VerbAnnas HanifNo ratings yet
- XX19Þ^Ò ...æ ÙçãμZZDocument22 pagesXX19Þ^Ò ...æ ÙçãμZZHarjinder Singh DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Los Grandes Cambios Siempre Vienen Acompañados de Una Fuerte Sacudida. No Es El Fin Del Mundo. Es El Inicio de Uno NuevoDocument2 pagesLos Grandes Cambios Siempre Vienen Acompañados de Una Fuerte Sacudida. No Es El Fin Del Mundo. Es El Inicio de Uno NuevoMAXIL MARQUEZ TELLEZNo ratings yet
- 7 Types of Meaning: A Guide to Semantic AnalysisDocument24 pages7 Types of Meaning: A Guide to Semantic AnalysisDann EpsonNo ratings yet
- June 2021 MS Paper 1 Edexcel B English Language IGCSEDocument20 pagesJune 2021 MS Paper 1 Edexcel B English Language IGCSEme.youshraNo ratings yet
- FUTURE SIMPLE TENSE PREDICTIONSDocument2 pagesFUTURE SIMPLE TENSE PREDICTIONSPuscariu Diana100% (1)
- Reading and Second Language Acquisition: HKBU Papers in Applied Language Studies Vol. 13, 2009Document22 pagesReading and Second Language Acquisition: HKBU Papers in Applied Language Studies Vol. 13, 2009SYAHRUL SHABRYNo ratings yet
- Pronombres Personales en InglésDocument23 pagesPronombres Personales en InglésJUAN MOSQUERANo ratings yet
- Procedure TextDocument2 pagesProcedure TextRamadanil FahriNo ratings yet
- Abreviaciones ChatDocument4 pagesAbreviaciones ChatrojarodNo ratings yet
- 0530_w23_ms_22Document11 pages0530_w23_ms_22Zenia GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Nef Upper Filetest 05 AnswerkeyDocument6 pagesNef Upper Filetest 05 AnswerkeyAino Minako100% (1)
- OLAF BEGINS HIS NEW CAREERDocument7 pagesOLAF BEGINS HIS NEW CAREERSoleluna LobaNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument3 pagesPassive VoicePeterNo ratings yet
- YEAR 4 LISTENING AND SPEAKING STANDARDS GUIDEDocument15 pagesYEAR 4 LISTENING AND SPEAKING STANDARDS GUIDEHaslina Abu HassanNo ratings yet
- Logan Encyclopedia Novel PDFDocument999 pagesLogan Encyclopedia Novel PDFIssam Jalal Eddine100% (2)
- Chapter 1 Language, Learning, and Teaching: @ming - EngtDocument37 pagesChapter 1 Language, Learning, and Teaching: @ming - Engt이주영No ratings yet
- Was or Were: Positive, Negative, QuestionsDocument4 pagesWas or Were: Positive, Negative, QuestionssamantaNo ratings yet
- Struktur Kurikulum Program Studi S-1 Pendidikan Bahasa Jepang No - Kode MK Nama Matakuliah Nama Matakuliah (In English) Kegiatan Status Semester Ke Prasyarat K PR W PDocument33 pagesStruktur Kurikulum Program Studi S-1 Pendidikan Bahasa Jepang No - Kode MK Nama Matakuliah Nama Matakuliah (In English) Kegiatan Status Semester Ke Prasyarat K PR W PNovelNo ratings yet
- Independent and Subordinate ClausesDocument3 pagesIndependent and Subordinate ClausesHectorNo ratings yet
- Language For SchoolDocument17 pagesLanguage For SchoolNiti BasaNo ratings yet
- Wilkinson Rosetta Spanish Language Advanced Training 3000 UsDocument274 pagesWilkinson Rosetta Spanish Language Advanced Training 3000 UsPatricia VargasNo ratings yet
- Majorel Panel Report on First Mass LocationDocument2 pagesMajorel Panel Report on First Mass LocationKristine Joie CastilloNo ratings yet
- Natural and Inverted Order of SentencesDocument31 pagesNatural and Inverted Order of SentencesFour FiveNo ratings yet
- Universidad Juárez Autónoma de Tabasco.: División Académica de Ciencias BásicasDocument4 pagesUniversidad Juárez Autónoma de Tabasco.: División Académica de Ciencias BásicasCRISTEL DEL CARMEN MAGAÑA RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Pengertian Narrative TextDocument11 pagesPengertian Narrative TextAz'End D'free LoveNo ratings yet
- Lexus Rc200t Rc350 2016 08 Workshop Service ManualDocument22 pagesLexus Rc200t Rc350 2016 08 Workshop Service Manualbradyyang220490iqz100% (40)