Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prelab 12
Uploaded by
Trixy CarreonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prelab 12
Uploaded by
Trixy CarreonCopyright:
Available Formats
Lourdes Patricia L.
Carreon Zaborah Eunice Bobadilla, Nerissa Unielle Quenga, Bernadette Toledo
February 7, 2012
Carboxylic Acids And Acid Derivatives
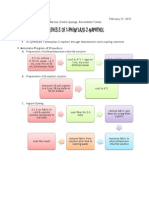
I. Objectives To examine the reactivities of carboxylic acids and acid derivatives via qualitative analysis II. Schematic diagram of procedure A. Solubility of Carboxylic Acids in 5% NaHCO3 1 drop glacial acetic acid + small pinch benzoic acid in two sep. micro test tubes +1 drop 0.5M NaHCO3 to each test tube record any visible change
B. Test for Acetic Acid 2 drops 2% NaOH + glacial acetic acid dropwise C. Test for Benzoic Acid 3 drops water in micro test tube + small pinch benzoic acid + 3.0 M NH4OH dropwise until solution is slightly basic to litmus +1 drop 0.1 FeCl3 soln and record any change soln slightly acid to litmus +2-3 drops 0.1 M FeCl3 solution record any observable change
heat until solid dissolves then cool
boil off excess ammonia
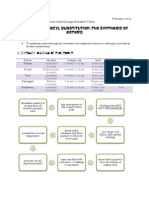
D. Formation of Esters From a carboxylic acid
+5 drops of ethanol + 2 drops glacial acetic acid in mictro test tube
+ 1 drop conc. H2SO4 and warm solution
note smell of product formed
From acyl halides
micro test tube with 10 drops ethanol + 2 dops of benzoyl chloride
stopper with cork and shake
note smell of product formed
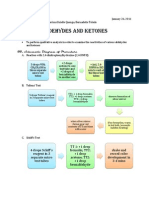
E. Hydroxamic Acid Test for the ester group +1 drop ethyl acetate +1 drop ether in micro test tube +1 drop alcoholic NH2OH HCl +1 drop alcoholic KOH heat over small flame to almost boiling and then cool a little acidify with alcoholic HCl +1 drop 0.1 M FeCl3 soln
F. Hydrolysis of Acid Derivatives Acetic Anhydride +5 drops water in micro test tube +3 drops acetic anhydride moisten blue litmus paper with soln
note change in color
Esters 2 mL ethyl acetate in 10 mL round bottom flask +5 mL 25% NaOH reflux reaction mixture for 30 mins observe disappearance of pleasant sell
neutralize mixture with 6.0 M HCl
observe sour smell of carboxylic acid formed
Amides small pinch of benzamide in micro test tube
+5 drops 2% NaOH
heat solution and note odor of gas evolved
III. TABLE OF REAGENTS/PRODUCTS
Reagent/Product Glacial CH3COOH
Structure
Physical Properties
Benzoic acid
Hazards Causes severe irritation and burns. May Be harmful if swallowed. Avoid breathing vapor or dust. Use with adequate ventilation. Avoid contact with eyes, skin, and clothes. Wash thoroughly after handling. Keep container closed. May be fatal if inhaled, swallowed or absorbed thru the skin Avoid all contact. Use with adequate ventilation. Wash thoroughly after use. Keep container closed.
Eye: Causes eye irritation. Causes redness and pain. Skin: May cause skin irritation. Repeated or prolonged exposure may cause drying and cracking of the skin. Ingestion: May cause irritation of the digestive tract. Inhalation: May cause respiratory tract irritation. Chronic: Prolonged or repeated skin contact may cause irritation.
5% NaHCO3
95% CH3CH2OH
Can be fatal or cause blindness if swallowed in quantity. Causes headache, dizziness, nausea, narcosis. Chronic overexposure can cause damage to gastrointestinal
Conc. H2SO4
25% NaOH
tract, liver, kidneys and cardiovascular system. Prolonged contact causes irritation to skin and eyes. Causes severe irritation and burns. May be harmful if swallowed. Avoid breathing vapor or dust. Use with adequate ventilation. Avoid contact with eyes, skin, and clothes. Wash thoroughly after handling. Keep container closed. Ingestion: Corrosive! Swallowing may cause severe burns of mouth, throat, and stomach. Skin Contact: Corrosive! Contact with skin can cause irritation or severe burns and scarring with greater exposures. Eye Contact: Corrosive! Causes irritation of eyes, and with greater exposures it can cause burns that may result in permanent impairment of vision, even blindness. Chronic Exposure: Prolonged contact with dilute solutions or dust has a destructive effect upon tissue.
0.1 M HCl
Ethyl acetate
Ingestion: Corrosive! Swallowing hydrochloric acid can cause immediate pain and burns of the mouth, throat, esophagus and gastrointestinal tract. Skin Contact: Corrosive! Can cause redness, pain, and severe skin burns. Eye Contact: Corrosive! Vapors are irritating and may cause damage to the eyes. Chronic Exposure: Long-term exposure to concentrated vapors may cause erosion of teeth. Ingestion: Causes irritation to the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms may include nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Skin Contact: Causes irritation to skin. Symptoms include redness, itching, and pain. Repeated or prolonged contact with the skin has a defatting effect and may cause dryness, cracking, and possibly dermatitis. Eye Contact: Causes irritation, redness, and pain.
Acetic anhydride
Ether
Causes severe irritation and burns. Harmful if swallowed. Avoid breathing vapor or dust. Use with adequate ventilation. Avoid contact with eyes, skin, and clothes. Wash thoroughly after handling. Keep container closed. Eye: Causes eye irritation. Skin: Causes skin irritation. May be absorbed through the skin in harmful amounts. Ingestion: May cause irritation of the digestive tract. Symptoms may include: headache, excitement, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, stupor, and coma. Inhalation: May cause respiratory tract irritation. May be harmful if inhaled. Exposure to high concentrations may produce narcosis, nausea and loss of consciousness. Chronic: Prolonged or repeated skin contact may cause defatting and dermatitis. Chronic exposure may cause liver damage.
10% NaOH
10% NH4OH
Ingestion: Corrosive! Swallowing may cause severe burns of mouth, throat, and stomach. Skin Contact: Corrosive! Contact with skin can cause irritation or severe burns and scarring with greater exposures. Eye Contact: Corrosive! Causes irritation of eyes, and with greater exposures it can cause burns that may result in permanent impairment of vision, even blindness. Chronic Exposure: Prolonged contact with dilute solutions or dust has a destructive effect upon tissue. Eye: Contact with liquid or vapor causes severe burns and possible irreversible eye damage. Skin: Causes severe skin irritation. Causes skin burns. May cause deep, penetrating ulcers of the skin. Ingestion: Causes gastrointestinal tract burns. Causes throat constriction, vomiting, convulsions, and shock. Inhalation: Causes severe irritation of upper respiratory tract with coughing, burns, breathing
Acetylsalicylic acid
difficulty, and possible coma. Chronic: Prolonged or repeated exposure may cause corneal damage and the development of cataracts and glaucoma. Eye: Causes eye irritation. Skin: Causes skin irritation. May be harmful if absorbed through the skin. Ingestion: Ingestion may cause high blood pressure, labored breathing, unsteady gait, lung edema, and coma. Human systemic effects include acute renal failure, acute tubular necrosis, cough, diarrhea, dyspnea (labored breathing), headache, hypermitility, nausea, vomiting, ulceration or bleeding from stomach. Toxic if swallowed. Inhalation: Causes respiratory tract irritation. Aspiration may lead to pulmonary edema. Chronic: Prolonged or repeated skin contact may cause dermatitis.
Benzoyl chloride
Ingestion: May cause irritation of the digestive tract. May cause cardiac disturbances. Inhalation: May cause respiratory tract irritation. May cause cardiac abnormalities. Inhalation at high concentrations may cause CNS depression and asphixiation. Skin: May cause skin irritation. Eyes: May cause eye irritation.
Benzamide
Ingestion: Harmful if swallowed. May cause gastrointestinal irritation with nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Inhalation: May cause respiratory tract irritation. Skin: May cause skin irritation. Eyes: May cause eye irritation.
IV. Diagram of set-up
Figure 1. Reflux Setup v. waste disposal All aqueous solutions dilute with water and pour down the sink Organic solutions organic waste jars
You might also like
- Prelab 16Document5 pagesPrelab 16Trixy CarreonNo ratings yet
- Prelab 9Document3 pagesPrelab 9Trixy CarreonNo ratings yet
- Hello EarthDocument1 pageHello EarthTrixy CarreonNo ratings yet
- Hinsberg's Method For Characterizing Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary AminesDocument4 pagesHinsberg's Method For Characterizing Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary AminesTrixy CarreonNo ratings yet
- Prelab 7Document6 pagesPrelab 7Trixy CarreonNo ratings yet
- Prelab 11Document5 pagesPrelab 11Trixy CarreonNo ratings yet
- Prelab 13Document5 pagesPrelab 13Trixy CarreonNo ratings yet
- Prelab 14Document2 pagesPrelab 14Trixy CarreonNo ratings yet
- Prelab 10Document4 pagesPrelab 10Trixy CarreonNo ratings yet
- Prelab 6Document3 pagesPrelab 6Trixy CarreonNo ratings yet
- Prelab 8Document3 pagesPrelab 8Trixy CarreonNo ratings yet
- Prelab 1Document7 pagesPrelab 1Trixy CarreonNo ratings yet
- Prelab 4Document4 pagesPrelab 4Trixy CarreonNo ratings yet
- Prelab 3Document2 pagesPrelab 3Trixy CarreonNo ratings yet
- Prelab 2Document3 pagesPrelab 2Trixy CarreonNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- PRACTICE TEST CHEMISTRY PRACTICE TEST CHEMISTRY PRACTICE TEST CHEMISTRY PRACTICE TEST CHEMISTRYDocument11 pagesPRACTICE TEST CHEMISTRY PRACTICE TEST CHEMISTRY PRACTICE TEST CHEMISTRY PRACTICE TEST CHEMISTRYsabhari_ram100% (1)
- The Language of Organic Chemistry: Answers To Worked ExamplesDocument22 pagesThe Language of Organic Chemistry: Answers To Worked ExamplesDana Capbun100% (1)
- FOSFA Acceptable List 1 July 2017Document4 pagesFOSFA Acceptable List 1 July 2017Saurabh MittalNo ratings yet
- Pod66 Tang PDFDocument9 pagesPod66 Tang PDFM Jodi AlfayedNo ratings yet
- Facile Synthesis of 4-HydroxycoumarinDocument3 pagesFacile Synthesis of 4-HydroxycoumarinSolomon EricksonNo ratings yet
- Spirit Soluble Rosin Modified Maleic ResinDocument1 pageSpirit Soluble Rosin Modified Maleic ResinMOHAMEDNo ratings yet
- Preformulation Studies: Key Characterization TechniquesDocument73 pagesPreformulation Studies: Key Characterization TechniquesVijay Babu0% (1)
- Facile Oxidation of Aldehydes To Acids and Esters With OxoneDocument4 pagesFacile Oxidation of Aldehydes To Acids and Esters With Oxonejonster2No ratings yet
- Chemical Weekly Aug29Document238 pagesChemical Weekly Aug29Chaitanya AyyagariNo ratings yet
- List of Ester Odorants: Ester Name Formula Odor or OccurrenceDocument5 pagesList of Ester Odorants: Ester Name Formula Odor or OccurrenceJasonTenebrosoNo ratings yet
- 21-22 - Prelim - S4E - Chemistry - QP - FBP - 2946Document15 pages21-22 - Prelim - S4E - Chemistry - QP - FBP - 2946Wisnuhandan SutrisNo ratings yet
- Bergmann Stern Azlactone Synthesis PDFDocument4 pagesBergmann Stern Azlactone Synthesis PDFOmar TomasNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Part 2 Guess Paper 2023Document14 pagesCHEMISTRY Part 2 Guess Paper 2023hassan932No ratings yet
- PLC Chemistry Year 13Document4 pagesPLC Chemistry Year 13Hoyam ANo ratings yet
- Reduced 12 TH Organic Salt EMDocument10 pagesReduced 12 TH Organic Salt EM19 Vasanth PurushothamanNo ratings yet
- Full Download Ebook Ebook PDF Organic and Biological Chemistry 7th Edition by H Stephen Stoker PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook Ebook PDF Organic and Biological Chemistry 7th Edition by H Stephen Stoker PDFjanet.martino412100% (35)
- Lampiran Tabel PP74Document13 pagesLampiran Tabel PP74Rutmauita Fanny Purba SKMNo ratings yet
- A2 Chemistry Revision Notes in 40 CharactersDocument13 pagesA2 Chemistry Revision Notes in 40 CharactersJobe Bryer50% (4)
- Alcohol & EthersDocument45 pagesAlcohol & Ethersrusnah chungNo ratings yet
- PyrazolopyrimidinesDocument50 pagesPyrazolopyrimidinesglreddy09No ratings yet
- XXXVI. Paper and Board For Food Contact: As of 01.04.2022Document17 pagesXXXVI. Paper and Board For Food Contact: As of 01.04.2022刘佳奇No ratings yet
- Chemical Composition of Saudi Arabian Sukkari Variety of Date Seed Oil and Extracts Obtained by Slow PyrolysisDocument12 pagesChemical Composition of Saudi Arabian Sukkari Variety of Date Seed Oil and Extracts Obtained by Slow Pyrolysisfarkad rawiNo ratings yet
- What Is Cracking?: Chemistry Skor A Chemistry IGCSE 2021Document12 pagesWhat Is Cracking?: Chemistry Skor A Chemistry IGCSE 2021AlyANo ratings yet
- Biochemistry I (SGS 236)Document25 pagesBiochemistry I (SGS 236)Mustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- Us 2618651Document3 pagesUs 2618651Maulic ShahNo ratings yet
- Cirujano2015 PDFDocument8 pagesCirujano2015 PDFHenry ArceoNo ratings yet
- Name: Srisudharshan Manikandan Register Number: 21BEC2104Document6 pagesName: Srisudharshan Manikandan Register Number: 21BEC2104Srisudharshan Manikandan 21BEC2104No ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Textile Finishing PDFDocument2,777 pagesEncyclopedia of Textile Finishing PDFFERNANDO JOSE NOVAES100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Lipids Study GuideDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Lipids Study GuideJanNo ratings yet
- GCE Chemistry Data Booklet Issue 2Document35 pagesGCE Chemistry Data Booklet Issue 2purityplus89% (9)