Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solar Energy
Uploaded by
Nick Stovall-KurtzOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solar Energy
Uploaded by
Nick Stovall-KurtzCopyright:
Available Formats
Nick Stovall-Kurtz Period 10 February 18, 2012 Solar Energy Solar energy has been used throughout history
and still used today. Many people had predicted that the 21st century would be getting a large percent of its electricity from solar energy but unfortunately, this has yet to happen. Only one-tenth of one percent of the nations electricity supply is obtained from solar power (John Tabak ,pg 1, solar power: sunlight and geometry). This is so unfortunate because solar energy is a relatively clean source of energy, is abundant and inexhaustible, and not only can be converted into electricity, but also into thermal energy. Its potential is limitless if scientists are able to harness huge amounts of sunlight around the clock. There are two types of solar power technologies that I will discuss. Photovoltaic technologies convert sunlight into electricity and thermal technologies convert sunlight into thermal energy. Thermal technologies, the older of the two ways of harnessing solar energy, has been used by ancient Indian and Greek civilizations. The civilizations built their homes so that the inside of the homes could harness as much sunlight as possible. The thick walls of the houses these civilizations built would absorb ample amounts of sunlight during the winter and be able to keep it warm. During the summer time, they would build overhangs that would shade the inside of the homes, thus letting the interior receive less sunlight. Today, the use of thermal technologies, also known as passive heating in buildings, has become scarce because of how expensive it is compared to burning fossil fuels for heat. However, some parts of Germany and the Netherlands have started to use passive heating and cooling in buildings commonly. Although it is more expensive than fossil fuels, it is a source of clean and ecofriendly energy. The reason why it is so expensive is because each passive heating design differs because of the location of the building and the local solar intensity, or in other words, how much sunlight the specific location receives. This can work to heat water by having a series of mirrors reflect a stream of sunlight on a central pipe, thus heating the water.
Photovoltaic technologies is a newer, more technologically advanced way to converting sunlight into energy. However, instead of converting the sunlight into heat, it converts it directly into electricity. Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel(1820-1891) was the first to generate an electrical current from sunlight but the observation was extremely weak. Then, in 1883, American inventor Charles Fritts was able to construct the first solar cell. Again, the observations of the energy output were weak. He understood the potential for the technology, but from a practical point of view his cells were useless because they converted less than 1 percent of the incident light into electricity (John Tabak, pg 6, brief history of solar power). It wasnt till the 1950s that efficient solar cells were invented by Albert Einstein. Hundreds of these cells are put into panels about three feet wide and six feet high. Each individual cell has a thin layer of metal that is covered by a thin layer of silicon. Then, behind these layers, is a semiconductor. When sunlight comes in contact with the silicon layer, electrons from the silicon atoms are jolted and moved through both the metal and semiconductor and then into an electric wire. This produces an electric current. This is the technology used by satellites, space stations, and robot landers that go to other planets (J.S Kidd, pg 1, clean energy and reducing air pollution). This came in handy when the United States and Soviet Union were competing for more sophisticated technology in space. The Soviet Union had originally used batteries for their first satellite. This posed a problem because they were much too heavy and the batteries were only good for so long. The United States then decided that it would be a much better idea to use solar cells as a source of energy on satellites. Today, the solar panels on the International Space Station produce about 33,000 watts of power each. Solar power is so much more eco-friendly than fossil fuels, which unfortunately is our most common source of energy today. Fossil fuels results in mass amounts of pollution daily and because of the CO2 given off when burned, it builds up over time in the atmosphere resulting in global warming. On the other hand, solar power gives off no CO2, no pollution, and is inexhaustible (unlike fossil fuels). Although fossil fuels is much cheaper than solar energy (which is why it isnt used more often), we need to start looking at what the effects of using them will be in the future. It would be better to shell out the extra money for solar panels than to have future generations never be able to see ice glaciers in Antarctica.
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- 44149389Document10 pages44149389Fabio PolimiNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- PM-9000 Service ManualDocument80 pagesPM-9000 Service Manualsebastian aleNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Solenoid Modification GL1200Document3 pagesSolenoid Modification GL1200Jose RojasNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- BOTONERASDocument61 pagesBOTONERASRonald LupaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Dielectric Constant, Tan Delta & Resistivity of Ester Oils As Insulating Oils in TransformerDocument7 pagesDielectric Constant, Tan Delta & Resistivity of Ester Oils As Insulating Oils in Transformertaufiqishak09No ratings yet
- Marechal DSN Plugs & Sockets Industrial Power Supply & Motor Connections (20 63A)Document8 pagesMarechal DSN Plugs & Sockets Industrial Power Supply & Motor Connections (20 63A)rocketvtNo ratings yet
- 100kva SpecDocument3 pages100kva SpecRicardoVásqezNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- SX1 enDocument12 pagesSX1 enwei leeNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityTanvi IsraniNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Inverter User ManualDocument40 pagesInverter User ManualArianna IsabelleNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
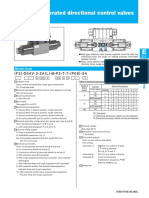
- Solenoid Operated Directional Control Valves DG4V-3: Model CodeDocument12 pagesSolenoid Operated Directional Control Valves DG4V-3: Model CodeBidawi ZubirNo ratings yet
- ADCDocument7 pagesADCsharadaNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Catalogo Switchgear BrochureDocument2 pagesCatalogo Switchgear BrochureSergio PediconiNo ratings yet
- ++++u30000 - Us Motor NameplateDocument2 pages++++u30000 - Us Motor NameplatevuongNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- c1255 Measurements and Instrumentation 3 0 0 100Document7 pagesc1255 Measurements and Instrumentation 3 0 0 100raghuramu23456No ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
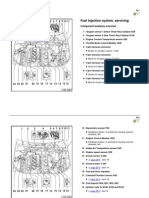
- VW Passat B5 24 Fuel Injection Sys, ServicingDocument126 pagesVW Passat B5 24 Fuel Injection Sys, ServicingJosé Luis Ormeño100% (5)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Standards ElectromagneticDocument3 pagesStandards ElectromagneticPramod KumbharNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Ad5724 5734 5754Document32 pagesAd5724 5734 5754Anam KhalidNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Tef 4732 Control Panel For Double Lantern Installation 230V (115V) SYSTEMDocument2 pagesTef 4732 Control Panel For Double Lantern Installation 230V (115V) SYSTEMAlan Barros SallesNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Test Report 1019349Document41 pagesTest Report 10193493DP HelloNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- LED Seminar PPT By, Er. Swapnil V. KawareDocument14 pagesLED Seminar PPT By, Er. Swapnil V. Kawareswapnil50% (2)
- F2639 PDFDocument100 pagesF2639 PDFAhmad Zubair RasulyNo ratings yet
- 4 (DC Ohmmeter)Document14 pages4 (DC Ohmmeter)Mohd Hafizat Ahmad ZikriNo ratings yet
- HIPASE-E 004-PS-500 Power Supply BoardDocument11 pagesHIPASE-E 004-PS-500 Power Supply BoardChi PhamNo ratings yet
- Immersion Heaters Water Heating Element Tubes in Copper, Iu, g2 Screw Plug in BrassDocument2 pagesImmersion Heaters Water Heating Element Tubes in Copper, Iu, g2 Screw Plug in BrassAndrei KrivdaNo ratings yet
- 60 GHZ Beamforming Transmitter Design For Pulse Doppler RadarDocument135 pages60 GHZ Beamforming Transmitter Design For Pulse Doppler Radarcowboy1980No ratings yet
- NLPWM v2.0 and v2.1 / Firmware 2.2 (Compatible With 2.0 and 2.1 Boards)Document1 pageNLPWM v2.0 and v2.1 / Firmware 2.2 (Compatible With 2.0 and 2.1 Boards)gaudeamus13No ratings yet
- Eaton-Ceag-El-Cps-Ba - Battery Rack - en - 40071860036 - CDocument40 pagesEaton-Ceag-El-Cps-Ba - Battery Rack - en - 40071860036 - COyewole EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Introductory Electricity and Magnetism Worksheets and SolutionsDocument34 pagesIntroductory Electricity and Magnetism Worksheets and SolutionsIbnu kusnoNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- ICEpower125ASX2 Datasheet 2.1Document29 pagesICEpower125ASX2 Datasheet 2.1betoarmaxNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)