Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drugs
Uploaded by
Ah Sej MaeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drugs
Uploaded by
Ah Sej MaeCopyright:
Available Formats
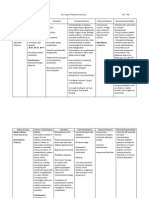
NAME OF DRUG Cefazolin
DATE ORDERED
01-24-12
CLASSIFICATION DOSE FREQUENCY ROUTE Anti-infectives 2gm Q8 IVTT
MECHANISM OF ACTION Bind to bacterial cell wall membrane; active against many gram - + cocci including GABS and S.pneumoniae; penicillinsproducing staphylococci
SPECIFIC INDICATION Skin and Skin structure infections
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING IMPLICATIONS BEFORE: Assess pt for infection, history of allergic reaction to cephalosporins, check results of C &S DURING: Have the pt state his name, explain the importance of giving the medication and administer cautiously AFTER: Observe pt for S & Sx of anaphylaxis. Discontinue if those occurs and notify physician; keep epinephrine, antihistamine and resuscitation equipment
Diarrhea Nausea Vomiting Cramps Rashes Urticaria Phlebitis at IV site
close in case of anaphylactic reaction; instruct pt to report if fever and diarrhea develop.
NAME OF DRUG Gentamycin
DATE ORDERED
CLASSIFICATION
01-24-12
DOSE FREQUENCY ROUTE Aminoglycosides 80mg Q8 IVTT
MECHANISM OF ACTION Bactericidal: inhibits protein synthesis in susceptible strain of gramnegative bacteria; appears to disrupt functional integrity of bacterial all membrane, causing cell death.
SPECIFIC INDICATION Infections of soft tissues
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING IMPLICATIONS BEFORE: Check results of C & S and real function; assess V/S (BP, PR, R) DURING: Have the pt state his name, explain the importance of giving the medication and administer cautiously AFTER: Instruct pt to report signs of adverse effects (severe headache, loss of hearing, DOB).
Dizziness Headache Numbness Paresthesia Muscle twitching Palpitations HPN Hypotension Pain fever
NAME OF DRUG Penicillin G
DATE ORDERED CLASSIFICATION DOSE FREQUENCY ROUTE 01-24-12 Antibiotic 500U IVTT q6
MECHANISM OF ACTION Bactericidal: inhibits synthesis of cell wall of sensitive organism, causing cell death.
SPECIFIC INDICATION Severe infections caused by sensitive organisms (streptococci)
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING IMPLICATIONS BEFORE: Obtain history of hypersensitivity to cephalosporins and other allergies; renal disorder; culture infection; assess V/S (R) ; normal output. DURING: Have the pt state his name, explain the importance of giving the medication and administer cautiously. AFTER: Monitor serum electrolytes and cardiac status ( Na/K preparations have been assoc. with severe electrolyte
Lethargy Abdominal pain Rash Fever Pain phlebitis
imbalances); keep epinephrine, IVF,vasopressors, bronchodilators, O2 and E equipment readily available in case of serious hypersensitivity reaction; notify physician id A/E occurs.
NAME OF DRUG Tramadol
DATE ORDERED
01-24-12
CLASSIFICATION DOSE FREQUENCY ROUTE Centrally acting 50mg analgesic q8 IVTT
MECHANISM OF ACTION Binds to muopioid receptors and inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin; causes many effects similar to opioidsdizziness, somnolence, nausea, constipationbut does not have the
SPECIFIC INDICATION Relief of moderate to severe pain
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING IMPLICATIONS BEFORE: Obtain history of hypersensitivity to tramadol and opioid addiction; assess V/S (BP, R) and PS. DURING: Have the pt state his name, explain the importance of giving the medication and
Sedation Dizziness Headache Confusion Sweating Anxiety Hypotension Pruritus Rash Urticaria Nausea vomiting
respiratory depressant effects.
administer cautiously. AFTER: Instruct pt to report if he experience severe nausea/ dizziness/ constipation.
NAME OF DRUG Parecoxib
DATE ORDERED
01-24-12
CLASSIFICATION DOSE FREQUENCY ROUTE NSAIDs 40 mg IVTT q 12
MECHANISM OF ACTION
SPECIFIC INDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING IMPLICATIONS BEFORE: Assess for presence of GI lesions and bleeding disorders; check results of renal functions, liver studies and platelet. DURING: Have the pt state his name, explain the importance of giving the medication and administer cautiously. AFTER:
Parecoxib is a Management selective antiof postinflammatory, operative pain. meaning that it blocks the enzyme cyclooxygenase2 (COX-2), responsible for prostaglandin (chemicals that play a role in pain and inflammation) synthesis, without affecting the enzyme COX-1, involved in the production of
Indigestion Flatulence Mild swelling Rash
prostaglandins that protect the lining of the stomach against stomach ulcers.
Educate pt about the side effects and report for any adverse effects ( GI bleeding/pain).
NAME OF DRUG Ranitidine
DATE ORDERED
01-24-12
CLASSIFICATION DOSE FREQUENCY ROUTE Histamine2 50 mg (H2) antagonist q 8 once NPO IVTT
MECHANISM OF ACTION Ranitidine blocks histamine H2receptors in the stomach and prevents histaminemediated gastric acid secretion. It does not affect pepsin secretion, pentagastrinstimulated factor secretion or serum gastrin.
SPECIFIC INDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING IMPLICATIONS BEFORE: Assess history of allergy to ranitidine; check renal or hepatic function. DURING: Have the pt state his name, explain the importance of giving the medication; Administer oral drug with meals. AFTER: Educate pt
constipation diarrhea fatigue headache insomnia muscle pain nausea vomiting
about the side effects of drug; Report sore throat, fever, unusual bruising or bleeding, tarry stools, confusion, hallucinations, dizziness, severe headache, muscle or joint pain.
NAME OF DRUG Clindamycin
DATE ORDERED 01-25-12
CLASSIFICATION DOSE FREQUENCY ROUTE Lincosamide 600 mg antibiotic q8 IVTT
MECHANISM OF ACTION Inhibits protein synthesis in susceptible bacteria, causing cell death.
SPECIFIC INDICATION It is used to o treat o infections and o anaerobic o bacteria o
o
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING IMPLICATIONS BEFORE: Assess history of allergy to clindamycin and others: check results of renal function and C & S. DURING: Have the pt state his name, explain the importance of giving the
o o o o o
Abdominal pain Nausea Vomiting Diarrhea Dry scaly skin Phlebitis thrombophlebitis with IV administration urticaria pruritus Headache dizziness
medication and administer cautiously. AFTER: Educate pt about the side effects; report severe or watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, inflamed mouth, skin rash or lesions.
NAME OF DRUG Paracetamol
DATE ORDERED 01-26-12
CLASSIFICATION DOSE FREQUENCY ROUTE Antipyretics 300 mg >37.5 prn IVTT
MECHANISM OF ACTION Paracetamol exhibits analgesic action by peripheral blockage of pain impulse generation. It produces antipyresis by inhibiting the hypothalamic heat-regulating centre. Its weak anti-
SPECIFIC INDICATION fever.
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING IMPLICATIONS BEFORE: Assess temperature, administer if >37.5; check for renal function. DURING: Have the pt state his name, explain the importance of giving the medication and administer
Side effects from paracetamol are rare but can include: -a rash; -blood disorders, such as thrombocytopenia (low platelet count) and leukopenia (low number
inflammatory activity is related to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis in the CNS.
of white blood cells); -hypotension (low blood pressure) when given in hospital by infusion (a continuous drip of medicine into a vein in your arm) ; -liver and kidney damage, when taken at higher-thanrecommended doses.
cautiously. AFTER: Educate pt about the side effects and report to physician if it worsens.
NAME OF DRUG Ceftriaxone
DATE ORDERED
02-02-12
CLASSIFICATION DOSE FREQUENCY ROUTE Antibiotic 1 gm q8 IVTT
MECHANISM OF ACTION Bactericidal: inhibits synthesis of bacterial cell wall, causing cell death.
SPECIFIC INDICATION Skin and skin structure infections caused by P. Mirabilis
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING IMPLICATIONS BEFORE: Check C & S test before therapy. DURING: Have the pt state his name, explain the importance of
Headache Dizziness Nausea Vomiting Diarrhea Anorexia Flatulence Pain Inflammation
at IV site
giving the medication and administer cautiously; administer slowly. AFTER: Educate pt about the side effects; report severe diarrhea, DOB, unusual tiredness or fatigue.
NAME OF DRUG Ciprofloxacin
DATE ORDERED
02-02-12
CLASSIFICATION DOSE FREQUENCY ROUTE Antibacterial 1 gm OD if not on NPO P.O
MECHANISM OF ACTION Bactericidal: interferes with DNA replication in susceptible bacteria preventing cell reproduction.
SPECIFIC INDICATION For the treatment of infections caused by susceptible gram-negative bacteria, including proteus mirabilis.
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING IMPLICATIONS BEFORE: Assess history of allergy to ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin or other Quinolones; check C & S result. DURING: Have the pt state his name, explain the importance of
Headache Dizziness Fatigue Insomnia Nausea Vomiting Dry mouth diarrhea
giving the medication and administer cautiously; Instruct pt not to crush, cut/ chew the tablet. AFTER: Educate pt about the side effects; report rash, visual changes, severe GI problems, weakness, and tremors.
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Drug Study: Medication Indication Contraindicati0N Side Effects Use Caution inDocument17 pagesDrug Study: Medication Indication Contraindicati0N Side Effects Use Caution inAngely Dianne Santiago II100% (2)
- Volume 42, Issue 34 - August 26, 2011Document56 pagesVolume 42, Issue 34 - August 26, 2011BladeNo ratings yet
- Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis GuidelinesDocument9 pagesStress Ulcer Prophylaxis GuidelinesHAIDAR RACHMANNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Practice Questions 2010Document4 pagesPharmacology Practice Questions 2010Khairul IzzatNo ratings yet
- The PDR Family Guide To Nutritional Supplements An Authoritative A To Z Resource On The 100 Most Popular Nutritional Therapies and Nutraceuticals PDDocument353 pagesThe PDR Family Guide To Nutritional Supplements An Authoritative A To Z Resource On The 100 Most Popular Nutritional Therapies and Nutraceuticals PDtfashourNo ratings yet
- Drug Administration ScheduleDocument4 pagesDrug Administration ScheduleMichael VillavertNo ratings yet
- Monitor for signs of fluid overload: increasing dyspnea, rales, edema, weight gain. Notify physician if presentDocument3 pagesMonitor for signs of fluid overload: increasing dyspnea, rales, edema, weight gain. Notify physician if presentmakyofrancis20No ratings yet
- Ranitidine (Zantac)Document3 pagesRanitidine (Zantac)sshah56No ratings yet
- Pharmacy & Medical Store Procedure.Document22 pagesPharmacy & Medical Store Procedure.Google BdNo ratings yet
- A Mini-Atlas of Ear-Drum Pathology PDFDocument7 pagesA Mini-Atlas of Ear-Drum Pathology PDFalexandra_i_nitaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Common IV DrugsDocument6 pagesNursing Management of Common IV DrugsStephanie Dellera AgdanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Name of Patient: Mr. DG U Date: January 12, 201Document2 pagesDrug Study: Name of Patient: Mr. DG U Date: January 12, 201ceian230% (1)
- Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database 2010Document26 pagesNatural Medicines Comprehensive Database 2010PsineticNo ratings yet
- Ranitidine Injection SDSDocument7 pagesRanitidine Injection SDSNur AlfiahNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument10 pagesEmergency DrugsnieacatleyaNo ratings yet
- DRUGS and DOSAGES for Pediatric Analgesics and AntimicrobialsDocument4 pagesDRUGS and DOSAGES for Pediatric Analgesics and Antimicrobialssharmee sarmientaNo ratings yet
- PHarma GiDocument28 pagesPHarma GiShahd KhatibNo ratings yet
- Elbert A. Mutuc Drug Study BSN III - 1 Group 2Document4 pagesElbert A. Mutuc Drug Study BSN III - 1 Group 2Elbert Aquitania Mutuc RNNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RanitidineDocument2 pagesDrug Study RanitidineTipey SegismundoNo ratings yet
- Medications Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesMedications Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Histamine and Anti HistaminesDocument12 pagesHistamine and Anti HistaminesshrikantNo ratings yet
- C-Gastointestinal agent; Antisecretory (H2-receptor antagonist) adverse reactionsDocument10 pagesC-Gastointestinal agent; Antisecretory (H2-receptor antagonist) adverse reactionsSitti Zhainab0% (1)
- Drug Study DMDocument8 pagesDrug Study DMJana Ross Serranilla100% (2)
- Chapter 57 - Drugs Affecting Gastrointestinal SecretionsDocument11 pagesChapter 57 - Drugs Affecting Gastrointestinal SecretionsJonathonNo ratings yet
- Case Study - CholecystitisDocument26 pagesCase Study - Cholecystitismeed02100% (2)
- Peptic Ulcer Drugs and Pharmcotherapy - DrdhritiDocument60 pagesPeptic Ulcer Drugs and Pharmcotherapy - Drdhritidbrahma100% (2)
- MidtermDocument53 pagesMidtermwriter topNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer - Causes, Treatment, and PreventionDocument24 pagesPeptic Ulcer - Causes, Treatment, and PreventionAmfo Baffoe FrederickNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyFirst SnowNo ratings yet
- Upper GI BleedDocument4 pagesUpper GI BleedAdela SusanNo ratings yet