Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP
Uploaded by
Didith AbanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP
Uploaded by
Didith AbanCopyright:
Available Formats
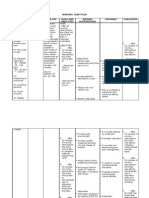
ASSESSMENT Subjective: nahihirapan akong huminga as verbalized.
NURSING DIAGNOSIS Impaired gas exchange r/t ventilation perfusion imbalance.
Objective: RR26cpm PR88bpm DOB/ dyspnea Irritable Weak in appearan ce Tachycar dia Diaphore tic Use of accessor y muscles
SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION Reduced myocardial contractility Increased cardiac workload Obstruction of left arterial emptying Pressure of blood into the pulmonary capillary bed increases Fluid shifts into the intraalveolar spaces Pulmonary congestion Impaired gas exchange
NURSING GOAL SHORT TERM GOAL Within 8 hours of rendering nursing interventions the patient will complh to the planned interventions as evidenced by: Demonstrate improve ventilation and adequate oxygenation. Verbalized understanding of causative factors and appropriate interventions. Cooperate in the treatment regimen.
NURSING INTERVENTION Independent: Note rate/ depth of respiration, use of accessory muscles, increased work of breathing, presence of dyspnea, and cyanosis.
RATIONALE
EVALUATION SHORT TERM GOAL After rendering 2-3 hors of nursing intervention goal was met aeb: Demonstration on how to improve ventilation and adequate oxygenation . -elevating head of bed -coughing and deep breathing technique -turning of position atleast every 2 hours Verbalized underst of causative factors and appropriate interventions anding Cooperation in the treatment regimen
It suggest need need for increased surveillance/ medical intervention
Assess change in Level of consciousness .
LONG TERM GOAL Throughout hospitalization the patient will -relieve from DOB/ dyspnea
Elevate head of bed. Have client turn , cough, deep breathing technique Allow adequate to rest periods between care activities. Collaborative: Provide humidified supplemental oxygen.
Hypoxemia can result in changes ranging anxiety and confusion to unresponsiveness. Promotes optimal pulmonary functionand reduces incidence of aspiration. Reduces oxygen consumption.
LONG TERM GOAL Throughout hospitalization goal was met aeb: - patient was relieved from DOB/ dyspnea.
Maintains effective ventilation/ oxygenation to prevent/ or correct respiratory crisis.
ASSESSMENT Subjective: nanghihina yung buong katawan ko as verbalized by the patient.
NURSING DIAGNOSIS Activity in tolerance r/t imbalance between oxygen supply and demand secondary to MI.
Objectives: Generalized weakness Fatigue PR-88bpm Increased BP Tachycardia Pale in appearance With minimal assistance in performing ADLs
SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION Deficient oxygen in the coronary arteries Use of anaerobic pathway to for ATP production Decreased oxygen supply to the myocardium Inadequate amounts of oxygen to the tissues
NURSING GOAL SHORT TERM GOAL Within 8 hours of rendering nursing intervention the patient will comply/ adhere to the planned interventions as evidenced by: Use identified techniques to enhance activity intolerance. Participate willingly in the desired activities. Report measurable increase in activity tolerance Demonstrate a decrease in physiological signs of intolerance. LONG TERM GOAL Throughout the hospitalization period the patient will: tolerate ADLs
NURSING INTERVENTION Independent -Assess clints ability to perform ADLs noting reports of weakness, fatigue, and difficulty accomplishing task. -Monitor BP, PR,RR before and after activity.
RATIONALE
EVALUATION SHORT TERM GOAL Within 8 hours of rendering nursing intervention goal was met as evidenced by: Use identified techniques to enhance activity intolerance -conserving energy (sitting while performing task) -alterating rest periods Participation in the desired activities Repoted measureable increased in activity tolerance Demonstrated a decrease in physiological signs of intolerance -BP-130/80mmHg -PR- 88bpm
-Influences choice of interventions/ needed assistance
-Elevate head of bed as tolerated. -Suggest to change position slowly, monitor for dizziness. -Encourage rest periods between care activities.
-Cardiopulmo-nary manifestations result from attempts by the heart and lungs to supply adequate amounts of oxygen to the tissues -Enhances lung expansion to maximize oxygenation for cellular uptake -Postural hypotension/ cerebral hypoxia may cause dizziness, fainting, and increased risk of injury -Promotes rest and maintains energy level and alleviates strain on the cardiac and resp. systems. -encourages client to do as much as possible while conservimg limited energy and preventing fatigue.
-Provide assistance during activities, allowing to do as much as possible -Identify energysaving techniques (eg. sitting to perform tasks.)
You might also like
- Impaired Liver FunctionDocument1 pageImpaired Liver FunctionShop Dzubiri Here100% (3)
- Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesTissue PerfusionMichael John LeandichoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions for Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument1 pageNursing Interventions for Ineffective Breathing PatternnikkilyceeNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPJ. ishtelleNo ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument1 pageNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAnn AquinoNo ratings yet
- Learning About Pediatric Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument2 pagesLearning About Pediatric Urinary Tract InfectionsNickaela CalalangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan #1Document6 pagesNursing Care Plan #1Yamete KudasaiNo ratings yet
- NCP - Acute Pain Related To EdemaDocument2 pagesNCP - Acute Pain Related To EdemaChenime Añana0% (1)
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPTracy Camille EscobarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care Planruggero07100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523No ratings yet
- NCP For CHDDocument2 pagesNCP For CHDMonica Rivera100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation for Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation for Impaired Gas ExchangeCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Document1 pageNursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Adhf NCPDocument3 pagesAdhf NCPkristine keen buanNo ratings yet
- NCP Epidural HemDocument32 pagesNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument2 pagesImpaired Urinary EliminationMatty-b AskalaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationJhevilin RM100% (1)
- BPN NCPDocument6 pagesBPN NCPJoart EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresNo ratings yet
- Actual NCPDocument2 pagesActual NCPbaki0146No ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesKarl Lourenz DeysolongNo ratings yet
- NCP Fluid Vol Excess AgnDocument3 pagesNCP Fluid Vol Excess AgnArbie JacintoNo ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument2 pagesNCP For CTTKay D. BeredoNo ratings yet
- NCP SEIZURE DISORDERDocument2 pagesNCP SEIZURE DISORDERPatricia FaraonNo ratings yet
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Document6 pagesRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Acute Pain ManagementDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Acute Pain ManagementSheene Lysethea Sioteco AguilosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 2Isabel Barredo Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Biperiden Generic and Brand Names, Uses, Side EffectsDocument1 pageBiperiden Generic and Brand Names, Uses, Side EffectsMFQ.RN100% (2)
- NCP HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP HypertensionCharisse VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Managing Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesAssessing and Managing Ineffective Airway ClearanceNelle Agni100% (1)
- Impaired mobility assessmentDocument2 pagesImpaired mobility assessmentVhin Lim100% (2)
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Document3 pagesNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- NCP Ch31 p991-992Document2 pagesNCP Ch31 p991-992Ala'a Abd Mansor100% (2)
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPAbbie TantengcoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Priorities for Hemodialysis PatientsDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan Priorities for Hemodialysis PatientsPauling FrezNo ratings yet
- NCP DobDocument3 pagesNCP DobLester BuhayNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionMitsika AnadiaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKath RubioNo ratings yet
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan ADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care to Prevent Suffocation in BabiesDocument2 pagesNursing Care to Prevent Suffocation in BabiesKimberly Subade Mandilag100% (2)
- NCP DizzinessDocument2 pagesNCP Dizzinesschristine mercadoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Dianosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Dianosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationkyaw100% (1)
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument3 pagesImpaired Urinary EliminationAgcopra MtchNo ratings yet
- NCP PSHDocument17 pagesNCP PSHMargareth OrtizNo ratings yet
- NCP For CipDocument22 pagesNCP For CipBing DayaoNo ratings yet
- Activity Intolerance NCPDocument6 pagesActivity Intolerance NCPDoo NahNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ComplicationDocument12 pagesCardiac ComplicationResa ShotsNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument6 pagesNCP PTBJay Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanmariasomorayNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument6 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivebanyenye25No ratings yet
- Causes and Nursing Care of Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesCauses and Nursing Care of Pleural EffusionHania Polangi100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationJharene BasbañoNo ratings yet
- Activity2 Mba 302Document2 pagesActivity2 Mba 302Juan PasyalanNo ratings yet
- Project On International BusinessDocument18 pagesProject On International BusinessAmrita Bharaj100% (1)
- Hercules SegersDocument15 pagesHercules SegerssuneelaamjadNo ratings yet
- BWT Septron Line 31-61 Rev01!08!05-18 Opm enDocument56 pagesBWT Septron Line 31-61 Rev01!08!05-18 Opm enDavide Grioni100% (1)
- Skype Sex - Date of Birth - Nationality: Curriculum VitaeDocument4 pagesSkype Sex - Date of Birth - Nationality: Curriculum VitaeSasa DjurasNo ratings yet
- John Williams - WikipediaDocument2 pagesJohn Williams - Wikipedia三木和代No ratings yet
- COP2251 Syllabus - Ellis 0525Document9 pagesCOP2251 Syllabus - Ellis 0525Satish PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Manuais - 727312 - manuais-Raios-X AXR - 77000001249Document72 pagesManuais - 727312 - manuais-Raios-X AXR - 77000001249Hosam Ahmed HashimNo ratings yet
- CGL Flame - Proof - MotorsDocument15 pagesCGL Flame - Proof - MotorspriteshNo ratings yet
- Pathways-Childrens Ministry LeaderDocument16 pagesPathways-Childrens Ministry LeaderNeil AtwoodNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1Nor-man KusainNo ratings yet
- Afrah Summer ProjectDocument11 pagesAfrah Summer Projectاشفاق احمدNo ratings yet
- Heads of Departments - 13102021Document2 pagesHeads of Departments - 13102021Indian LawyerNo ratings yet
- List of StateDocument5 pagesList of StatedrpauliNo ratings yet
- Cypress Enable Basic Rer Erence ManualDocument2 pagesCypress Enable Basic Rer Erence ManualCarlos RodasNo ratings yet
- PCG Master Consultancy Services AgreementDocument12 pagesPCG Master Consultancy Services Agreementawscobie100% (1)
- Cost Systems: TermsDocument19 pagesCost Systems: TermsJames BarzoNo ratings yet
- METRIC_ENGLISHDocument14 pagesMETRIC_ENGLISHKehinde AdebayoNo ratings yet
- 10CV54 Unit 05 PDFDocument21 pages10CV54 Unit 05 PDFvinodh159No ratings yet
- C++ Programmierung (Benjamin Buch, Wikibooks - Org)Document257 pagesC++ Programmierung (Benjamin Buch, Wikibooks - Org)stefano rossiNo ratings yet
- p2 - Guerrero Ch13Document40 pagesp2 - Guerrero Ch13JerichoPedragosa88% (17)
- JTIL Purchase Requisition for Plasma Machine SparesDocument3 pagesJTIL Purchase Requisition for Plasma Machine Sparesshivam soniNo ratings yet
- CAM TOOL Solidworks PDFDocument6 pagesCAM TOOL Solidworks PDFHussein ZeinNo ratings yet
- Roll Covering Letter LathiaDocument6 pagesRoll Covering Letter LathiaPankaj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Priming An Airplane EngineDocument6 pagesPriming An Airplane Enginejmoore4678No ratings yet
- Study Quran Online - The Online Quran Teaching Academy UK - QutorDocument9 pagesStudy Quran Online - The Online Quran Teaching Academy UK - QutorQutor co ukNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing Eighth Edition Philip Kotler and Gary ArmstrongDocument17 pagesPrinciples of Marketing Eighth Edition Philip Kotler and Gary ArmstrongJunaid KhalidNo ratings yet
- Illegal FishingDocument1 pageIllegal FishingDita DwynNo ratings yet
- 1 Univalent Functions The Elementary Theory 2018Document12 pages1 Univalent Functions The Elementary Theory 2018smpopadeNo ratings yet
- Bonding in coordination compoundsDocument65 pagesBonding in coordination compoundsHitesh vadherNo ratings yet