Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
SJ AbundaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
SJ AbundaCopyright:
Available Formats
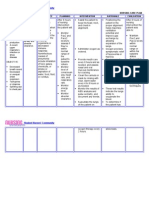
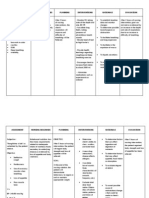
Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Impaired gas exchange r/t altered oxygen supply as manifested by dyspnea,
abnormal ABG results, Irritability/ restlessness, Abnormal rate, rhythm, depth of breathing and nasal flaring Analysis
Pneumonia develops when foreign matter such as viruses, bacteria, parasites, or fungus enters the lungs and causes inflammation. There are also chemicals that can enter the lungs and cause pneumonia. Additionally, an injury to the lungs may cause pneumonia, but it is much less common. Once this foreign matter enters the body, it provokes a response of the immune system. After that, the person's oxygen levels begin to deplete and he or she begins to breathe faster. The mucus production also begins to increase. As the mucus production increases, the fluid begins to fill the alveoli, which are the small pocket-like sacs in the lungs where gas exchange takes place. As the development of pneumonia progresses, the
Goal and objectives After 2 weeks of nursing intervention, the client will improve ventilation and adequate oxygen tissues by ABGs within clients normal limits and absence of symptoms of respiratory distress. Objectives: To increase the PO2 of the client To normalize the arterial pH of the client To decrease irritability and restlessness of
Interventions
Rationale
Evaluation
The client is irritable and cries continuously. Evident of difficulty of breathing. Increase RR85 bpm Increase HR150 bpm With nasal flaring With ABG results of: pH: 7.50 pO2: 70 pCO2: 28 pHCO3: 24 O2 sat: 87 %
Does the clients ventilation improved and he has adequate oxygen supply after 2 weeks of nursing intervention? __ Yes __ No WHY? Are the interventions safe? __ Yes __ No WHY? Are the interventions appropriate to the client? __ Yes __ No WHY?
- Maintain client airway. Place client in position of comfort with head of bed elevated 30 to 45 degrees. - Reposition the client frequently. Suction as
- These measures enhance lung expansion and reduce respiratory efforts.
- Good pulmonary toilet is
patient's white blood cell count begins to rise. Once the white blood cell count rises, the debris they leave behind also fill the alveoli. All of these things filling the alveoli is what causes pneumonia to become life-threatening very quickly if left untreated.
the client
needed.
To normalize the breathing pattern of the client.
necessary for reducing ventilation/perf usion imbalance and for mobilizing and facilitating removal of secretions to maximize gas exchange. - Prevents exhaustion and reduces oxygen consumption and demands to facilitate resolution of infection.
Are the interventions effective? __ Yes __ No WHY? Are the interventions efficient? __ Yes __ No WHY?
- Encourage the parents to let the patient to have adequate rest and limit activities to w/in client tolerance. Promote calm and restful environment. - Administer supplemental oxygen, as indicated via appropriate route: nasal cannula, mask, or high-flow rebreathing mask.
- Supplemental oxygen is necessary for correction of hypoxemia with failing respiratory effort.
- Keep environment allergen/ pollutant free.
- To reduce irritant effect of dust and chemicals on airway. - To treat the underlying condition. - Having good nutrition will improve stamina and reduce the work of breathing.
- Administer medications, as indicated. Emphasize to the SO about the importance of nutrition of the patient.
You might also like
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument7 pages1 Ineffective Breathing PatternKrisJane Ratilla Abiva100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanElijah S GomezNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan-AnemiaDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan-AnemiaAdrian Mallar100% (2)
- AEMT - Airway and Breathing Exam PracticeDocument26 pagesAEMT - Airway and Breathing Exam PracticeEMS DirectorNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanAl RizkyNo ratings yet
- Occupational Therapy Clinical Practice Guideline - Home Oxygen Therapy For Adult Patients - 3Document92 pagesOccupational Therapy Clinical Practice Guideline - Home Oxygen Therapy For Adult Patients - 3TWEH OCCNo ratings yet
- NCP & Prio!!!Document45 pagesNCP & Prio!!!Sj 斗力上100% (1)
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPEjie Boy Isaga67% (3)
- Ch50 NCP IneffAirClear 1395-1396Document2 pagesCh50 NCP IneffAirClear 1395-1396Caress Mae Gubaton CabudoyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanAdreanah Martin RañisesNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion NCPsDocument7 pagesPleural Effusion NCPsJaja Nagallo100% (2)
- Adult NursingDocument13 pagesAdult Nursing00060651No ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceBenly Grace Rebuyon MosquedaNo ratings yet
- What Is COPD? Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Signs and SymptomsDocument11 pagesWhat Is COPD? Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Signs and SymptomsCecil Bhang-i Cacay - PabloNo ratings yet
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNo ratings yet
- Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesAsthma Impaired Gas ExchangeAndrea Chua BuadoNo ratings yet
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Document6 pagesWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasNo ratings yet
- Oxy Act 2Document5 pagesOxy Act 2Joshua DauzNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 pageImpaired Gas ExchangeLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Bronchial AsthmaDocument21 pagesCase Analysis Bronchial AsthmaKim LladaNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Gas ExchangeRez ApegoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument11 pagesNCPRyan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab Questions:: Deep Breathing & Coughing Exercises Oxygen TherapyDocument3 pagesPre-Lab Questions:: Deep Breathing & Coughing Exercises Oxygen TherapyaliNo ratings yet
- Impaired Breathing PatternDocument1 pageImpaired Breathing PatternHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Competencymr McdougalcopdDocument17 pagesCompetencymr Mcdougalcopdmac_rymrt7569No ratings yet
- Activity Intolerance NCPDocument6 pagesActivity Intolerance NCPDoo NahNo ratings yet
- Asthma Nanda DiagnosesDocument4 pagesAsthma Nanda DiagnosesZinya RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Systems Plus College Foundation Macarthur Highway, Balibago, Angeles CityDocument13 pagesSystems Plus College Foundation Macarthur Highway, Balibago, Angeles CityLeanne Princess GamboaNo ratings yet
- Case Study COPDDocument6 pagesCase Study COPDpallavNo ratings yet
- 2 NCPDocument2 pages2 NCPJohn CenasNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument16 pagesNursing DiagnosisSi Bunga JonquilleNo ratings yet
- NCP Kochs2Document2 pagesNCP Kochs2Ava VierNo ratings yet
- Nursing ManagementDocument16 pagesNursing ManagementNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Gas ExchangeRez ApegoNo ratings yet
- Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesAsthma Impaired Gas ExchangeNedeve Ozned100% (5)
- NCP Proper 1Document6 pagesNCP Proper 1Noreen PinedaNo ratings yet
- CopdDocument47 pagesCopdNingshesil Ny HermantNo ratings yet
- EmphysemaDocument21 pagesEmphysemaEdmund RufinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 028.bridge To NCLEX Review Question AnswersDocument7 pagesChapter - 028.bridge To NCLEX Review Question AnswersJackie JuddNo ratings yet
- 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument8 pages1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceEsel Mae DinamlingNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Clients With COPD: - Initiate Infusion of Intravenous Antibiotic As PrescribedDocument3 pagesNursing Management of Clients With COPD: - Initiate Infusion of Intravenous Antibiotic As PrescribedNiña AngNo ratings yet
- NSG MGT Asthma (Autosaved)Document14 pagesNSG MGT Asthma (Autosaved)sarikaNo ratings yet
- NCP PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNCP PneumoniaChristian Apelo Serquillos100% (2)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument4 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeNuraini Hamzah100% (1)
- Tuberculosis Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesTuberculosis Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceCyrus De Asis86% (36)
- Nursing Care Plan For PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For PneumoniaJonas Galeos100% (2)
- Nursing Care Basic Concept of Emergency Nursing Nursing With Case of FailureDocument5 pagesNursing Care Basic Concept of Emergency Nursing Nursing With Case of Failurejamil aldasriNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Iniego Carlo Jay)Document9 pagesRespiratory Distress Syndrome (Iniego Carlo Jay)Carlojay IniegoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAbegail Abaygar100% (1)
- Copd CaseDocument36 pagesCopd Casejho_No ratings yet
- LUNGcancer NCPregieDocument1 pageLUNGcancer NCPregieShermay MortelNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPDidith AbanNo ratings yet
- Textbuk DiscussionDocument5 pagesTextbuk Discussionapi-3717941No ratings yet
- NCP (F&E Imb)Document2 pagesNCP (F&E Imb)Dustin JohnNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Oxygen Therapy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Oxygen Therapy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Nursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseFrom EverandNursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseNo ratings yet
- COPD Diet: A Beginner's 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide to Managing COPD Symptoms, With Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanFrom EverandCOPD Diet: A Beginner's 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide to Managing COPD Symptoms, With Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandRespiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsJian-Xin ZhouNo ratings yet
- Aspiration Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAspiration Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- C CCC C CC C C C C C C C CDocument6 pagesC CCC C CC C C C C C C C CSJ AbundaNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNcp-Impaired Gas ExchangeSJ Abunda0% (1)
- NCP QiDocument2 pagesNCP QiSJ AbundaNo ratings yet
- Assesing Lung SoundsDocument3 pagesAssesing Lung SoundsLisa TaylorNo ratings yet
- D V 5-l C o C: Service ManualDocument44 pagesD V 5-l C o C: Service ManualsylvainbdxNo ratings yet
- Clinical Trial Proposal PDFDocument6 pagesClinical Trial Proposal PDFRickgable100% (1)
- Advance Life Support Training Manual PDF 2022 PDFDocument128 pagesAdvance Life Support Training Manual PDF 2022 PDFMOHD HAFIZAL ARIFFINNo ratings yet
- AIGA 049 - 08 Guideline To Bulk Medical Oxygen Supply System For Healthcare FacilitiesDocument9 pagesAIGA 049 - 08 Guideline To Bulk Medical Oxygen Supply System For Healthcare Facilitiesnachiappan_rameshNo ratings yet
- Alexanders Care of The Patient in Surgery 16th Edition Rothrock Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument32 pagesAlexanders Care of The Patient in Surgery 16th Edition Rothrock Test Bank Full Chapter PDFwilliamboydnatcwzpofb100% (12)
- Oxygenation: Stikes Hafshawaty Pesantren Zainul Hasan Genggong Kel. 13Document5 pagesOxygenation: Stikes Hafshawaty Pesantren Zainul Hasan Genggong Kel. 13Al Adamie 87No ratings yet
- Literature Review On Oxygen TherapyDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On Oxygen Therapyjzneaqwgf100% (1)
- Meditech Oxygen ConcentratorDocument4 pagesMeditech Oxygen ConcentratorelmarwamedNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Skills First HitDocument1 pageNCM 112 Skills First HitShane Damian0% (1)
- Bts Guideline For Oxygen Use in Adults in Healthcare and Emergency SettingsDocument100 pagesBts Guideline For Oxygen Use in Adults in Healthcare and Emergency SettingsalbarkatNo ratings yet
- Ward RoutineDocument103 pagesWard Routinedarling ariwaNo ratings yet
- Domiciliary Oxygen Therapy - Summary of IndicationsDocument4 pagesDomiciliary Oxygen Therapy - Summary of IndicationsAdina BatajuNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Gawat DaruratDocument7 pagesJurnal Gawat DaruratFirzhan FharezNo ratings yet
- 1.e. Bronchiolitis Treatment & Management - Approach Considerations, Initial Management, Admission CriteriaDocument12 pages1.e. Bronchiolitis Treatment & Management - Approach Considerations, Initial Management, Admission CriteriaDavid CraigNo ratings yet
- Silenzio Tech ManualDocument24 pagesSilenzio Tech ManualsambadeeNo ratings yet
- Administering Oxygen Via Nasal Cannula (RLE)Document14 pagesAdministering Oxygen Via Nasal Cannula (RLE)Alliza LipaNo ratings yet
- SOP For Administration and Installation of Oxygen O2: Definition ?Document7 pagesSOP For Administration and Installation of Oxygen O2: Definition ?Yulia Mesy SyNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy GuidelinesDocument19 pagesOxygen Therapy GuidelinesAyuna Rahmani0% (1)
- Invacare Oxygen Equipment 5 PDFDocument68 pagesInvacare Oxygen Equipment 5 PDFJoel Enrique PerezNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy in Acute Care SettingsDocument96 pagesOxygen Therapy in Acute Care SettingsStacey SanchezNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Pricelist Booklet 2020Document17 pagesCatalogue Pricelist Booklet 2020charles kimeuNo ratings yet
- CONTEC21-X (220V 60Hz) 英文说明书Document34 pagesCONTEC21-X (220V 60Hz) 英文说明书dean HaroldNo ratings yet
- Oxygen TherapyDocument90 pagesOxygen TherapyharyatiNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy For NurseDocument46 pagesOxygen Therapy For NurseselviiNo ratings yet
- Nidek Mark 5 Plus Concentrator - User ManualDocument7 pagesNidek Mark 5 Plus Concentrator - User ManualΜοσχοβακος ΣωτηρηςNo ratings yet
- United States Patent: Rollins, IIIDocument13 pagesUnited States Patent: Rollins, IIIchicken curryNo ratings yet
- II. Modul 5 - Terapi OksigenDocument81 pagesII. Modul 5 - Terapi OksigenPerisha VeeraNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy Learning Module Cat 1and2Document62 pagesOxygen Therapy Learning Module Cat 1and2Baha'aeddin HammadNo ratings yet
- OptimDocument15 pagesOptimRashad Biomedical EngineerNo ratings yet