Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Psych Final Study Guide
Uploaded by
ekf71Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Psych Final Study Guide
Uploaded by
ekf71Copyright:
Available Formats
PSYCHOLOGY FINAL STUDYGUIDE: Psychological approaches: Psychoanalytical/psychodynamic- Unconscious drives and urges motive your behavior.
. Everything that happens in your childhood matters and affects you as an adult. (Freud) Behavioral- you behave the way you do because you learned to behave that way and you were rewarded for behaving that way. (Skinner and Watson) Humanistic- you have the way you do because you choose to. You are the captain of your own shop. All people have the ability to reach their full potential. Cognitive- your behavior is motivated by your memories and experiences and how you think. Social cultural- ethnicity, gender, and culture affect your behavior. Research Techniques: Naturalistic observation- observing behavior in a natural environment Case study- following a single case, typically over an extended period of time. Involves naturalistic observations and include psychological testing. Survey- questionnaires often used to gather opinions. Correlation studies- relationships and purpose of correlation study to determine if a relationship exists. *Does not mean causation*. Father of Psychology: Freud, discovered psychoanalysis and discovered how the mind works. Watsons contributions to the field of psychology: Explained behaviors ie. Reward and punishment, behaviorally shaping human beings. Milgram Experiment: Torturing okay when instructed by an adult, assumed it was okay because an authority figure told them to do so. Behavior, nature and nurture, we are brought up to trust and obey authority. Correlation v. Causation: Correlation- extent of two factors vary together, thus how well either factor predicts the other. To measure relationship. Causation- the sole provider for the effect. Key component of liability. Measures of Central Tendency: Mode- the most frequently occurring score. Mean- arithmetic average Median- the middle score Range-difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution. Perception: Grouping: Proximity- group nearby figures together. Similarity- group figures that are similar. Continuity- perceives continuous patterns. Closure- fill in gaps Connectedness-spots, lines, and areas are seen as unit when connected. Functions of the limbic system: Associated with emotions such as fear and aggression. Hippocampus- in charge of memory and the correlation with the emotion experienced at that time. Amygdala- linked with emotion, fear and aggression. Hypothalamus- lies below the thalamus, linked to emotion, directs maintenance activities ie. Eating, drinking, and body temp. and helps govern endocrine system via
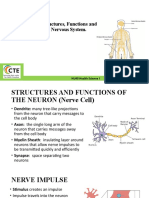
pituitary gland. Central Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Brain. Neural pathways governing our reflexes. Its the automatic response to stimulus. Simple spinal relax pathway is composed of a single sensory neuron and a single motor neuron. Peripheral Nervous System: Two components- Somatic and Autonomic. Somatic Nervous System- controls movements of our muscles. Autonomic Nervous System- controls the glands and muscles of our internal organs. Is broken down into two additional parts. o Sympathetic Nervous System- arouses us for defensive action, accelerating our heartbeat, arousing body (fight-or-flight) o Parasympathetic Nervous System- conserves energy and decreases hearbeat and calms the body. Functions of the Lobes: Frontal lobes- involves speaking and muscle movement and planning and judgment. (behind forehead) Parietal lobes- involves the sensory cortex. (at the top of the head/middle) Occipital lobes- includes visual areas receiving visual info from opposite visual field. (back of the head) Temporal lobes- includes auditory areas receiving auditory info primarily from the opposite ear. (above the ears) Sleep Disorders: Insomnia- difficulty in getting to sleep. Sleep apnea- person stops breathing and is awakened when blood levels rise. Causes lack of REM sleep, so feels like not a good nights rest. Narcolepsy- sleep appears at odd times Nightmares- anxiety-arousing dreams generally occur in REM sleep. Night Terrors- abrupt awakenings from deep sleep stages, accompanied by intense psychological arousal and panic. Stages of Sleep: Awake and Relaxed- Alpha waves and relaxation Stage 1 Sleep- hallucinations Stage 2 Sleep- bursts of activities, (spindles) Stage 3 Sleep- deep sleep Stage 4 Sleep- Delta waves and deep sleep REM Sleep- eye movement phase Bobo doll experiment: Experiment run by Albert Bandura, showed that children changed their actions without reward or punishment. Children modeled after what they saw. Introduced insight learningthe first moment you know how to do something.Mirror Neurons enable us perform certain actions when observing others doing so. Parapsychology: The study of paranormal phenomena such as ESP and Psychokinesis. Types of ESP: Telepathy- move things with mind Clairvoyance- the power to see objects or events that cannot be perceived by the senses. Precognition- predicting future
Behaviorism: Classical conditioningPavlov, automatic stimulus response Operant conditioningSkinner and Watson, reward and enforcement. VOCAB: Standard Deviation- A computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean. Hindsight bias- tendency to believe, after learning the outcome that one would have foreseen. (I-knew-it-all-along phenomenon) Placebo effect-a change in a participants behavior that results from a belief that the treatment will have an effect, rather than the actual treatment. Empiricism- knowledge comes from experience via the senses, science flourishes through observation and experiment. Structuralism- Wilhelm Wundt, introspection to explore the elemental structure of the human mind. HOW the mind WORKED. IntrospectionStructuralismFocus on mind. Functionalism-Focused on behavioral function, how they enable organisms to adapt, survive and learn. William James. Absolute threshold- fifty percent minimum stimulus to notice/detect change. Learning- a relatively permanent change in an organisms behavior due to experience. Intrinsic Motivation- a desire to do something for your own sake and to be effective. (doing things when people are not looking) Extrinsic Motivation- a desire to do something for a reward or threat of punishment. (only doing something for a reward) Neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine (Ach)- enables muscle action, learning and memory. Dopamine- Influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion. Serotonin- affects mood, hunger, sleep and arousal Norepinephrine- helps control alertness and arousal. GABA- a major inhibitory neurotransmitter Glutamate- excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory. Drugs: Psychoactive Drugs- 3 categories o Depressants- downers, calm neural activity and slow body functions. Alcohol, Opiates (heroin and morphine), and Barbiturates (tranquilizers) o Stimulants- temporarily excite neural activity and arouse body functions. Cocaine, Ecstasy (MDMA), Caffeine, Nicotine, and Meth. Ecstasy is an amphetamine that triggers the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Its major affect is to release stored serotonin and block its reabsorption. o Hallucinogens-distort perceptions and evoke sensory images LSD and Marijuana Main ingredient in marijuana is THC
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Biochemistry QuizDocument28 pagesBiochemistry Quizsanjviews100% (3)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Phylum Arthropoda - Why such abundance and diversityDocument4 pagesPhylum Arthropoda - Why such abundance and diversitySHILNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hematology Analyzers, Coagulation Systems Product GuideDocument4 pagesHematology Analyzers, Coagulation Systems Product GuideElvan Dwi WidyadiNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Biology Chapter 8 - Cell CommunicationDocument8 pagesBiology Chapter 8 - Cell CommunicationDonnabelle VaronaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- CP On AmoebiasisDocument77 pagesCP On Amoebiasiskathy100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Biology Mcqs Part IDocument17 pagesBiology Mcqs Part IUsama NiaziNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Science (Digestion) Notes/ActivityDocument4 pagesScience (Digestion) Notes/ActivityHi HelloNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Activity 1what A Bunch of GrapesDocument3 pagesActivity 1what A Bunch of GrapesLesly Santillan100% (4)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- 3.03 Understand Structures, Functions and Disorders of The Nervous SystemDocument38 pages3.03 Understand Structures, Functions and Disorders of The Nervous SystemLoriwinchesterNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Francisco Aboitiz (Auth.) - A Brain For Speech - A View From Evolutionary Neuroanatomy-Palgrave Macmillan UK (2017)Document515 pagesFrancisco Aboitiz (Auth.) - A Brain For Speech - A View From Evolutionary Neuroanatomy-Palgrave Macmillan UK (2017)TecuitlatlNo ratings yet
- Nanosep 1Document5 pagesNanosep 1MomNo ratings yet
- Mobilization NotesDocument239 pagesMobilization NotesSuganya Balachandran100% (6)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- q3 Sci10 Unit1 Feedback MechanismsDocument125 pagesq3 Sci10 Unit1 Feedback MechanismsIvann EboraNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Effects of Electromagnetic Forces of Earth On HumansDocument6 pagesEffects of Electromagnetic Forces of Earth On HumansArtist MetuNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Modul Anatomi Blok 7Document27 pagesModul Anatomi Blok 7Dewandaru I A BNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Management of Clients With Disturbances in OxygenationDocument13 pagesManagement of Clients With Disturbances in OxygenationClyde CapadnganNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Toxic and Nontoxic GoiterDocument2 pagesThe Difference Between Toxic and Nontoxic GoiterJawad Rehman100% (1)
- IlizarovDocument62 pagesIlizarovAsh Moaveni100% (2)
- Anesthesia For The Pet Practitioner (2011 3rd Edition)Document216 pagesAnesthesia For The Pet Practitioner (2011 3rd Edition)Amela Dolittle Halilbašić100% (5)
- Circulatory System: Heart, Blood Vessels & Their FunctionsDocument17 pagesCirculatory System: Heart, Blood Vessels & Their FunctionskangaanushkaNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- GEC General Studies Part 1Document42 pagesGEC General Studies Part 1daisyNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Focusing Instruction ManualDocument15 pagesFocusing Instruction Manualplan2222100% (1)
- 3 9 1 bMSDS-Reagen-LaboratoriumDocument4 pages3 9 1 bMSDS-Reagen-Laboratoriumswahyulisah100% (1)
- Shah Et Al-2016-Frontiers in Plant ScienceDocument28 pagesShah Et Al-2016-Frontiers in Plant ScienceJamie SamuelNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Refeeding SyndromeDocument4 pagesRefeeding SyndromeallyNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of AtherosclerosisDocument21 pagesPathogenesis of Atherosclerosishakky gamyNo ratings yet
- M 371Document14 pagesM 371Anonymous h0DxuJTNo ratings yet
- Amniodarone (Norvasc) Drug SummDocument1 pageAmniodarone (Norvasc) Drug SummWarrenNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Integumentary SystemDocument11 pagesThe Integumentary SystemHamdy Pagilit DimaporoNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)