Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Analysis-Med Forbes
Uploaded by
Justine Mark SoberanoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Analysis-Med Forbes
Uploaded by
Justine Mark SoberanoCopyright:
Available Formats
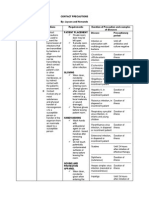
DRUG ANALYSIS Jennica Celine S.
Ponce II-8 RLE 2 Patient s Name: Remedios Castillo Room: 209B CC: dyspnea Medical Dx: ASHD CAD NSTEMI Class IV-D, DM Type 2 right foot, HPN Stage 2
GENERIC NAME TRIMETAZIDINE
BRAND NAMES Vastarel MR, Vastarel LM, Vastarel LP, Flavedon MR, Vestar
CLASSIFICATION Anti-ischemic / Anti-anginal
INDICATION - Ischemic heart disease (angina pectoris, sequelae of infarction - Adjuvant symptomatic treatment of vertigo and tinnitus - Adjuvant treatment of decreased visual acuity *taken because patient is a known case of ASHD CAD NSTEMI Class IV-D to prevent any anginal/ stroke attacks
CONTRAINDICATION Hypersensitivity to Trimetazidine, pregnancy
MODE OF ACTION Improves myocardial glucose utilization through inhibition of fatty acid metabolism
SIDE EFFECTS GI discomfort, nausea, vomiting, headache, vertigo
ADVERSE EFFECTS Parkinsonism, gait disorders, tremors, visual hallucinations
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES - Assess location, duration and intensity of anginal pain - Monitor BP and PR before and after administering the drug - Notify prescribing signs of heart failure such as swelling of the hands and feet or shortness of breath - Instruct to avoid strenuous or hazardous activities requiring alertness to prevent risks of falls and injury
ATORVASTATIN
Lipitor, Xarator
Antihyperlipide mic/ HMG CoA reductase inhibitor
Hypercholesterolem ia, Type III hyperlipoproteinem ia, elevated serum triglycerides *taken by patient to reduce her cholesterol and lipoprotein levels which contributes to increased
Pregnancy (category X), hypersensitivity, active liver disease, breastfeeding or of childbearing potential who do not use adequate contraceptive measures
Selectively inhibits HMGCoA reductase, which converts HMG-CoA to mevalonate, a precursor of sterols; lowers cholesterol
Headache, myalgia, athralgia, nausea, abdominal cramps, flatulence
Rhabdomyolysis with acute renal failure; liver failure
- Obtain LFT s as baseline; discontinue if AST or ALT levels increase to 3x than normal - Ensure patient has tried cholesterollowering diet regimen for 3-6 months before beginning therapy - Administer without
deposits and accumulation of both in the blood vessel walls thereby reducing severity of ASHD condition.
and lipoprotein levels
regard to food, but at same time each day, preferably in the evening. Do not take with grapefruit juice - Do not combine with other HMGCoA reductase inhibitors or fibrates Increased volume and frequency of urination, dizziness, confusion, drowsiness, increased thirst Gynecomastia, agranulocytosis, postmenopausal bleeding, hyperkalemia, hyponatremia - Give daily doses early so that increased urination does not interfere with sleep - Measure and record regular weight to monitor mobilization of edema fluid - Avoid giving food rich in potassium - Arrange for regular evaluation of serum electrolytes and BUN
SPIRINOLACTONE
Aldactone, Novospiroto n
Aldosterone antagonist / Potassiumsparing diuretic
Short-term preop treatment of primary hyperaldosteronism , long-term maintenance for idiopathic hyperaldosteronism ; essential HPN, edematous CHF, hypokalemia, liver cirrhosis and nephritic syndrome *patient is on IC and bladder training; taken to prevent any urinary retention and accumulation of fluid which may lead to bladder distention; also to increase excretion of sodium and water to prevent edema
Pregnancy (category D), acute renal insufficiency, anuria, hyperkalemia
antagonizes aldosterone in the distal tubules, increasing sodium and water excretion
ESOMEPRAZOLE
Nexium, Nexium IV
Antisecretory / Proton pump inhibitor
Erosive reflux esophagitis. Prevents relapse of healse esophagitis, symptomatic treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Helicobacter pylori associated ulcer disease *patient is on NGT and is not allowed to take any other food except for scheduled meals; taken to prevent occurrences of gastric acidity which may lead to GI discomfort and increased gastric acid secretion that may lead to gastric acid reflux (heart burns)
Known hypersensitivity to esomeprazole, substituted benzimidazoles or any other constituents of the formulation; children
Inhibits the H-K-ATPase pump (proton pump) in gastric parietal cells effectively blocking the final step in acid production, thereby reducing gastric acidity
Dizziness, headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, symptoms of URTI, cough
Asthenia, dream abnormalities, insomnia, inflammation, alopecia, epistaxis
- If administering antacid, they may be administered concominantly with esomeprazole - Administer IV for maximum of 10 days; switch to oral form as soon as possible - Instruct not to crush or chew oral forms - Obtain baseline liver function tests and monitor periodically during therapy - Maintain supportive treatment - Comfort measures - Safety precautions (side rails)
ISOSORBIDE MONONITRATE (ISMN)
Angistad, Angistad SR, Elantad, Elantad Long, Imdur Durules, Isomonit, Monosorb, Schwarz ISMN 60
Antianginal / Nitrate / Vasodilator
Preventive and long-term treatment of angina pectoris/ post myocardial infarction angina; severe CHF; pulmonary HPN *patient has ASHD which blocks the flow of blood to her body due to accumulation of deposits in the vessel wall; taken to
Allergy to nitrates, severe anemia, head trauma, cerebral hemorrhage, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, narrow-angle glaucoma, orthostatic hypotension
Increases supply of oxygen to the heart by dilating both the arteries and veins which supply the heart itself
Dizziness, lightheadedness, headache, flushing of the neck or face
Syncope, blurred vision, persistent or severe headache, rash, more persistent or more severe angina attacks, fainting
- Discourage swallowing in sublingual administration - Create a nitrate-free period to minimize tolerance - Give oral preparations on an empty stomach, 1 hr before or 2 hrs after meals; take with meals if severe uncontrollable headache occurs - Keep life support
dilate the blood vessels and increase oxygen supply
equipment readily available if overdose occurs - Gradually reduce dose if angina treatment is being terminated to prevent withdrawal Hypersensitivity, acute intoxication with alcohol, hynotics, centrally acting analgesics, opioids or psychotropic agents Centrally acting analegesic not chemically related to opioids but binds to muopioid receptors and inhibits reuptake of norepinephri ne and serotonin Dizziness, sedation, drowsiness, impaired visual acuity, nausea, loss of appetite Seizures, anaphylactoid reactions, - Control environment (lighting, temperature) if sweating or CNS effects occur - Limit use in patients with past or present history of addiction to or dependence on opioids - Avoid alcohol - Instruct patient to change positions slowly to prevent orthostatic hypotension - Instruct to refrain from performing activities that require alertness - Instruct to avoid driving or other hazardous activities until stabilized on medication - Avoid alcohol and other CNS depressants so as not to enhance sedative effect of the drug - Avoid smoking / smoke-filled
TRAMADOL
Dolotral, Euro-Med Tramadol HCl, Gesidol, Milador, Peptrad, Siverol, TDL, Tradonal, Tramal
Analgesic (centrally-acting) / Opioid analgesic
Moderate to severe pain
ERDOSTEINE
Erdotin, Dostin, Mucotec
Mucolytic
Acute and chronic respiratory disease; acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis; productive cough *patient has productive cough with clear, watery sputum; taken to liquefy and aid in expectoration of
Active peptic ulcer
contains two sulfhydryl groups, which are freed after metabolic transformatio n in the liver. The liberated sulfhydryl groups break the disulphide
Nausea, vomiting, headache, loose stools
Epigastralgia, spasmodic colitis
sputum
bonds, which hold the glycoprotein fibers of mucus together making the bronchial secretions more fluid and enhances elimination hypersensitivity to penicillins, history of gastrointestinal disease, particularly colitis, renal impairment Inhibits cell wall synthesis during bacterial multiplication Agitation, constipation, diarrhea, dizziness, headache, indigestion, nausea, pain, swelling, or redness at the injection site, sleeplessness , vomiting Phlebitis, thrombophlebiti s, edema, syncope, cardiac failure, mycordial infarction, convulsions, ulcerative stomatitis, tinnitus, pseudomembra nous colitis, photophobia, symptomatic hypoglycemia
environment
PIPTAZO (PIPERACILLINTAZOBACTAM)
Zosyn, Tazocin
Antibacterials (beta-lactamase inhibitors)
Moderate to severe nosocomial pneumonia; for beta-lactamase producing strains in appendicitis or peritonitis; complicated and uncomplicated UTI; ischemia / diabetic foot infection *patient is a known case of DM Type 2 on right foot; taken to decrease risk of infection on the affected foot. (there is elevated neutrophil and WBC levels = 0.92 mg/dl and 13.30 mg/dl respectively Feb. 16, 2010)
- Ask patient if there is penicillin allergy - Monitor hematologic and coagulative parameters - Monitor sodium intake because drug contains 2.35 mEq sodium/g of piperacillin - Instruct to report adverse reactions promptly - Instruct to notify nurse about IV site discomfort
PARACETAMOL
Aldep, Alvedon, Biogesic, Calpol, Dolexpel, Medgenol, Naprex, Tempra, Tylenol
Analgesic
Relief of mild to moderate pain; treatment of fever *patient sometimes experiences febrile episodes and is taken to reduce fever (last Wednesday, Feb. 17, 2010 at around 11:30am, Temp = 37.8 C)
Hypersensitivity; intolerance to tartrazine (yellow dye #5), alcohol, table sugar, saccharin
Decreases fever by inhibiting the effects of pyrogens on the hypothalamic heat regulating centers and by a hypothalamic action leading to sweating and vasodilation. Relieves pain by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis at the CNS
Stimulation, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain
Hepatotoxicity, hepatic seizures, renal failure, leukopenia, neutropenia, hemolytic anemia, delirium followed by vascular collapse, convulsions, coma, death
- Monitor liver and renal functions - Check input and output ratio - Advise patient to avoid taking more than one product containing paracetamol at one time to avoid toxicity - Avoid alcohol to prevent acute poisoning with liver damage - Inform patient that urine may become dark brown as a result of phenacetin (metabolite of paracetamol) - Teach patient to recognize signs of chronic overdose ( bleeding, bruising, malaise, fever, sore throat) - Monitor fasting blood glucose 2 hrs after meals and glycosylated Hgb - Monitor body weight periodically - Assess for hypoglycemic reaction that may occur during peak time - Observe injection sites for signs and symptoms of local hypersensitivity such as redness,
INSULIN
Humalin N & Humalin R
Anti-diabetic
Management of type 1 DM or insulin-dependent DM (IDDM) and type 2 DM or noninsulin-dependent DM (NIDDM) which cannot be controlled by diet, exercise and weight reduction alone *patient is a DM Type 2 case and takes insulin to regulate/ decrease
Hypoglycemia, insulinoma, hypersensitivity reactions, IV administration of insulin suspension, diabetic coma
Decreases blood glucose; by transport of glucose into cells and the conversion of glucose to glycogen indirectly increases blood pyruvate and lactate, decreases phosphate
Redness, swelling, itching, or mild pain at the injection site.
Lipodystrophy, insulin resistance, severe allergic reactions, hypoglycemia, visual impairment, edema and refraction anomalies
blood glucose during elevated levels
and potassium
itching or burning - If via SQ route, give after warming to room temperature by rotating palms to prevent injecting cold insulin - Advice patient to avoid vigorous exercise immediately after injection to prevent risk of high glucose level - Instruct not to smoke within 30 mins because it decreases insulin absorption - Avoid alcohol because it lowers glucose level Nausea, vomiting, headache, palpitations Irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, swelling of hands and feet, pronounced dizziness, constipation - Monitor patient s BP, cardiac rhythm and output carefully; may develop increased frequency, duration or severity of angina in acute MI after initiation of therapy - Administer drug without regard to meals; take with meals if GI upset occurs - Advice patient to avoid hazardous activities until stabilized on drug and dizziness is no longer a problem - Instruct to comply
AMLODIPINE
Amcal, Amvasc, Lopicard, Norvasc, Pharex Amlodipine besylate, Vasalat
Antihypertensive/ Antianginal / Calcium channel blocker
HPN; chronic stable angina; vasospastic (Prinzmetal or variant) angina *patient is known case of HPN Stage 2 and takes this drug to decrease BP to at least 120/80 (usual high BP is 160/80); also taken as maintenance
Sick sinus syndrome; second- or thirddegree atrioventricular block, except with a functioning pacemaker
Inhibits influx of calcium ion across cell membranes to produce relaxation of coronary vascular smooth muscle, decrease peripheral vascular resistance of smooth muscle and increases myocardial oxygen delivery in
patients with vasospastic angina
with the drug regimen - Do not withdraw abruptly; may case frequency and duration of chest pain; taper dose gradually
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVderic81% (16)
- C Post Concussion ChecklistDocument1 pageC Post Concussion Checklistalston96No ratings yet
- Folic AcidDocument1 pageFolic Acidhazelnutski88% (8)
- Chap11 SolutionDocument29 pagesChap11 SolutionJustine Mark Soberano100% (1)
- Pathology Outlines - Papillary Carcinoma - GeneralDocument6 pagesPathology Outlines - Papillary Carcinoma - Generalpatka1rNo ratings yet
- Depression and Anxiety Among College StudentsDocument2 pagesDepression and Anxiety Among College StudentsAnonymous 5WUUQijWNo ratings yet
- PSA and Psoriasis Exam ChecklistDocument2 pagesPSA and Psoriasis Exam ChecklistChaken ManiyanNo ratings yet
- Activation Method For 2010, 2011, 2012Document2 pagesActivation Method For 2010, 2011, 2012Justine Mark SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology On Liver CirrhosisDocument38 pagesPathophysiology On Liver Cirrhosisတမန္ေတာ္ တမန္ေတာ္100% (30)
- Marginal Zone Lymphomas: Subtypes: MALT (Extranodal), Nodal, SplenicDocument2 pagesMarginal Zone Lymphomas: Subtypes: MALT (Extranodal), Nodal, SplenicwwxxmmNo ratings yet
- Contact PrecautionsDocument2 pagesContact PrecautionsCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- Tnkhetp LBLDocument2 pagesTnkhetp LBLvijayabhavani.sNo ratings yet
- Patient Anita NCPDocument15 pagesPatient Anita NCPJoshoua MalanaNo ratings yet
- Psych EnhancementDocument4 pagesPsych EnhancementRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- Indications To Administer Special Tests: (1) Cochlear PathologyDocument11 pagesIndications To Administer Special Tests: (1) Cochlear PathologyASMAA NOORUDHEENNo ratings yet
- Cicatricial Atelectasis - Print Friendly - STATdxDocument2 pagesCicatricial Atelectasis - Print Friendly - STATdxmihaelaNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Failure For StudentDocument41 pagesAcute Respiratory Failure For Studentapi-379952350% (4)
- Perioperative Fluid Management in ChildrenDocument31 pagesPerioperative Fluid Management in ChildrenRashmi SahaNo ratings yet
- Resume Ahmad AkbariDocument3 pagesResume Ahmad AkbariSepideh MirzaeiNo ratings yet
- 01 NGT Procedure With RationaleDocument4 pages01 NGT Procedure With RationaleAryaj SulitNo ratings yet
- Celluar and Neural Regulation StudentDocument52 pagesCelluar and Neural Regulation StudentCruz YrNo ratings yet
- Chlamydia InfectionDocument5 pagesChlamydia InfectionYogesh PhadtareNo ratings yet
- CHN Rle Midterm Exam ReviewerDocument3 pagesCHN Rle Midterm Exam Reviewercassy SadieNo ratings yet
- Acne (Causes and Symptoms)Document4 pagesAcne (Causes and Symptoms)Siddharth ChoudheryNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Health Programs in Barangay Quezon, Arevalo, Iloilo CityDocument30 pagesThe Effectiveness of Health Programs in Barangay Quezon, Arevalo, Iloilo CityuhrlizNo ratings yet
- Guia Idsa Pie Diabetico PDFDocument42 pagesGuia Idsa Pie Diabetico PDFAliciaNo ratings yet
- Hematology Topics Objectives References: Our Lady of Fatima University Department of Internal MedicineDocument7 pagesHematology Topics Objectives References: Our Lady of Fatima University Department of Internal MedicineAlmar NuñezNo ratings yet
- Is A Traditional Colonoscopy or A Virtual Colonoscopy BetterDocument1 pageIs A Traditional Colonoscopy or A Virtual Colonoscopy BetterPaul JensenNo ratings yet
- Oral Manifestations of Thyroid Disorders and Its MDocument4 pagesOral Manifestations of Thyroid Disorders and Its MNike WijayaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Patterns and Antibiotic Resistance in Grade Two Diabetic UlcersDocument15 pagesBacterial Patterns and Antibiotic Resistance in Grade Two Diabetic UlcersNadya AbigailNo ratings yet
- LoperamideDocument1 pageLoperamidekimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Perioral DermatitisDocument6 pagesPerioral DermatitisYeni OktaviaNo ratings yet
- 2020-68 Annex B - Health Declaration Form110320Document4 pages2020-68 Annex B - Health Declaration Form110320Aileen MayaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease in ChildrenDocument7 pagesRheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease in ChildrenSurya MahardikaNo ratings yet