Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Histo Kidney Intro
Uploaded by
ameerabestCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Histo Kidney Intro
Uploaded by
ameerabestCopyright:
Available Formats
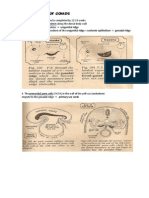
KIDNEY
Mixed gland Exocrine (Compound tubular gland) Uriniferous Tubule = Glomeruli + Renal tubules Urine Structural Organization CORTEX outer, dark layer granular appearance - dt : presence of highly vascular renal corpuscles * difference in colour between the cortex and medulla reflects the distribution of intrarenal vasculature - 90-95% of blood passes through the cortex - only 5-50% passes through medulla MEDULLA inner, pale layer striated appearance - dt: presence of renal tubules and surrounding vasculature
composed of : 8-12 medullary pyramids - their bases form = cortico-medullary junction - apices (renal papillae) protrude into minor calyces - tips of papillae are perforated by the openings of collecting duct hence, called area of cribrosa
Endocrine Juxta-glomerular apparatus + Renal Interstitium Control of A.B.P
Lobulation of Kidney (no true CT septa!)
Kidney represents compound tubular gland divided into lobes & lobules but is lacking of CT septa Lobulation is based on: subdivisions of renal artery within renal parenchyma/distribution of blood vessels drainage of the unit structures of the kidney (uriniferous tubules) Renal Lobe 1 medullary pyramid + mass of cortical tissue surrounding its base & sides ( renal column on each side of a pyramid) Renal Lobule 1 medullary ray + mass of cortical tissue surrounding it *all nephrons in each lobules are drained by a single collecting duct in its centre
Medullary rays Renal columns
extensions from medulla into the cortex extensions from cortex into the medulla
contain straight tubules & collecting ducts contain interlobar blood vessels
1 ureter 2 renal column 3 renal pyramid 4 cortex 5 medulla 6 renal pelvis 7 renal papillae
Histological Components of the Kidney parenchyma functional unit : uriniferous tubule capsule Outer fibrous layer Inner cellular layer dense regular CT dense irregular CT - myofibroblast stroma renal interstitium
Nephrons Renal corpuscle - Bowmans capsule - glomerulus -mesangium
Collecting tubules
Proximal convoluted tubule Loop of Henle Distal convoluted tubule
Classification of nephrons
- CT filling the spaces between the parenchyma - in medulla > cortex - composed of : 1. delicate network of reticular fibers (supporting parenchyma) + small collagen bundles (around BV) 2. highly hydrated matrix of mucopolysaccharides 3. CT cells : -macrophages -fibroblasts - medullary fibroblasts (myofibroblasts) Oriented perpendicular to the axis of tubules Their processes are closely attached to tubules Supportive + secretory function secrete PG + medullipin peptide (control ABP)
Subcapsular nephrons Intermediate nephrons Juxtamedullary nephrons
Zonation of the MEDULLA
position of renal corpuscles lying under the capsule in the midregion of cortex deep in the cortex, near the medulla
length of Loop of Henle very short intermediate length very long
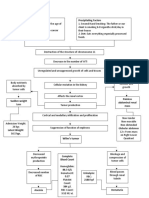
longitudinal organization of the renal tubules forming the nephrons is responsible for - the striated appearance of renal medulla - its morphological divisions into zones Intrarenal vasculature Arterial supply renal artery (on entering the hilum, through renal column) interlobar arteries (at corticomedullary junctions) arcuate arteries interlobular arteries (between adjacent medullary rays, end as capsular arteries) afferent arterioles (intralobular branches) glomerular capillaries ( 1st capillary network from 10-20 capillary loops) efferent arterioles (portal) 2nd capillary network
(according to position of corpuscular glomeruli from which they originate)
corpuscles subcapsular & intermediate juxtamedullary corpuscles
2 capillary network peritubular capillaries - surround nearby renal tubules vasa recta - descending vessels - ascending vessels
nd
endothelium + fx fenestrated transport of reabsorbed substance from renal tubules into blood continuous trap urea fenestrated water transport from collecting tubule to blood
Structural features of renal vasculature creating high glomerular pressure: 1. Short course of renal artery ( arise directly from abdominal aorta) 2. Coiled course of glomerular tuft of capillaries 3. well developed internal elastic lamina of afferent arterioles
Venous drainage outer zone of cortex deep zone of cortex medulla
superficial cortical veins stellate veins interlobular veins arcuate veins interlobar veins deep cortical veins interlobular arcuate interlobar veins poor directly in interlobar veins renal veins IVC
You might also like
- Cme Bronchial AsthmaDocument28 pagesCme Bronchial AsthmaameerabestNo ratings yet
- Burn Injuries GuideDocument53 pagesBurn Injuries GuideHusna NadiaNo ratings yet
- @acute Nephritic SyndromeDocument3 pages@acute Nephritic Syndromeameerabest100% (1)
- E.coli, Klebsiella, Proteus EtcDocument3 pagesE.coli, Klebsiella, Proteus EtcameerabestNo ratings yet
- @ovary Cyst ComparisonDocument2 pages@ovary Cyst ComparisonameerabestNo ratings yet
- @hypothalamic HormonesDocument1 page@hypothalamic HormonesameerabestNo ratings yet
- @drugs Acting On Uterus and Erectile DysfunctionDocument2 pages@drugs Acting On Uterus and Erectile DysfunctionameerabestNo ratings yet
- @acute Nephrotic SyndromeDocument1 page@acute Nephrotic SyndromeameerabestNo ratings yet
- @ductal CarcinomaDocument1 page@ductal CarcinomaameerabestNo ratings yet
- @contraceptives DrugsDocument1 page@contraceptives DrugsameerabestNo ratings yet
- @sex SteroidsDocument2 pages@sex SteroidsameerabestNo ratings yet
- @ovarian Tumors ComparisonDocument6 pages@ovarian Tumors ComparisonameerabestNo ratings yet
- @ovary Cyst ComparisonDocument2 pages@ovary Cyst ComparisonameerabestNo ratings yet
- @tumors of The Breast 1Document2 pages@tumors of The Breast 1ameerabestNo ratings yet
- @histology of Male Genital SystemDocument6 pages@histology of Male Genital SystemameerabestNo ratings yet
- Genitourinarybacteria Comparisons PDFDocument7 pagesGenitourinarybacteria Comparisons PDFameerabest100% (1)
- Semen AnalysisDocument3 pagesSemen Analysisameerabest80% (5)
- @non Neoplastic Non Inflammatory Lesions of The BreastDocument2 pages@non Neoplastic Non Inflammatory Lesions of The BreastameerabestNo ratings yet
- @male PathoDocument8 pages@male Pathoameerabest100% (2)
- Histology Female PDFDocument5 pagesHistology Female PDFameerabestNo ratings yet
- Patho Male BreastDocument1 pagePatho Male BreastameerabestNo ratings yet
- Nota Patho PDFDocument8 pagesNota Patho PDFameerabestNo ratings yet
- Genitourinarybacteria Comparisons PDFDocument7 pagesGenitourinarybacteria Comparisons PDFameerabest100% (1)
- Anatomy of Male GenitaliaDocument4 pagesAnatomy of Male GenitaliaameerabestNo ratings yet
- Virology of Hepatitis ADocument33 pagesVirology of Hepatitis AameerabestNo ratings yet
- OSCE DermaDocument8 pagesOSCE DermaameerabestNo ratings yet
- Genital EmbryologyDocument6 pagesGenital EmbryologyameerabestNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ExamDocument7 pagesCardiac ExamameerabestNo ratings yet
- #Chest TraumasDocument4 pages#Chest Traumasameerabest100% (3)
- PleuraDocument6 pagesPleuraameerabest100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- PhysioEx Exercise 9Document13 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 9patricia ankarNo ratings yet
- RenalDocument1 pageRenalYezin Shamoon100% (1)
- Staghorn CalculiDocument29 pagesStaghorn CalculiLiza M. PurocNo ratings yet
- Regulasi CA, MG and PO4Document16 pagesRegulasi CA, MG and PO4siskaNo ratings yet
- Week 7. Medical Terminology: NAMA: Novianti Nur Rahmah Ramadhani Kelas: 2A Nim:2110035032Document3 pagesWeek 7. Medical Terminology: NAMA: Novianti Nur Rahmah Ramadhani Kelas: 2A Nim:2110035032novianti nurNo ratings yet
- 16-12th Full Book Bio MCQsDocument8 pages16-12th Full Book Bio MCQsRaees Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- mcq renalفاطمه جاسم محمدDocument4 pagesmcq renalفاطمه جاسم محمدFatema Al-KananiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Study GuideDocument61 pagesPharmacology Study Guide32bballgoNo ratings yet
- Renal Blood Flow Until Regulation of RBF and GFRDocument5 pagesRenal Blood Flow Until Regulation of RBF and GFRDoogie ReynaldoNo ratings yet
- The Kidneys Are A Pair of Purplish-Brown Organs Is Located Below The Ribs Toward The Middle ofDocument6 pagesThe Kidneys Are A Pair of Purplish-Brown Organs Is Located Below The Ribs Toward The Middle ofJoana Bless PereyNo ratings yet
- K10 Kuliah NefrourologiDocument170 pagesK10 Kuliah NefrourologimarinanananaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE ExcretionDocument17 pagesIGCSE ExcretionClayesmoreBiologyNo ratings yet
- MDCAT BIOLOGY TITLEDocument22 pagesMDCAT BIOLOGY TITLESalam FatimaNo ratings yet
- Ingles StudyDocument23 pagesIngles StudyMatiasUrraNo ratings yet
- Urine Formation: Mohamad Ashraf IsmailDocument13 pagesUrine Formation: Mohamad Ashraf IsmailAshraf MobyNo ratings yet
- Wilm's Tumor Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument1 pageWilm's Tumor Pa Tho Physiologya_yeLNo ratings yet
- Study Material - 2Document5 pagesStudy Material - 2rohitsonkarrohit15No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Life Process Gaurav SutharDocument29 pagesChapter 6 Life Process Gaurav SutharRaunik Motwani100% (5)
- Unit 7 TransDocument5 pagesUnit 7 TransGrace FernandoNo ratings yet
- ESRD Management and TreatmentDocument39 pagesESRD Management and TreatmentsiarahNo ratings yet
- Physiology Passmrcog 2016Document73 pagesPhysiology Passmrcog 2016Mona HelouNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 PhysioEx 9 2022Document4 pagesAssignment 4 PhysioEx 9 2022Lydia DuncanNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Balance: A Review of Normal Physiology: February 2002Document5 pagesAcid-Base Balance: A Review of Normal Physiology: February 2002Tee bagNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure RegulationDocument11 pagesBlood Pressure RegulationManuNo ratings yet
- CCDocument4 pagesCCJaymih Santos AbasoloNo ratings yet
- 01 FLP-1 by Doctor Biology 03333354576Document14 pages01 FLP-1 by Doctor Biology 03333354576Aashir Ali AyubNo ratings yet
- +1 Bio Zoo em Vol 2Document38 pages+1 Bio Zoo em Vol 2Ameena BegumNo ratings yet
- Class X Biology QN BankDocument74 pagesClass X Biology QN BankSankalp PariharNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biochemistry Past PaperDocument7 pagesClinical Biochemistry Past PaperAnonymous WkIfo0P100% (1)
- CSEC Biology MCQ - Answer KeyDocument54 pagesCSEC Biology MCQ - Answer KeyDark PlaceNo ratings yet