Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Previous Exam Questions
Uploaded by
sallyreffatOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Previous Exam Questions
Uploaded by
sallyreffatCopyright:
Available Formats
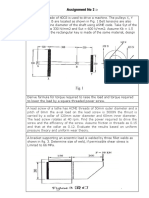
Section A: Answer the Following Question Question 1 (30%): June 2009 A bracket as shown in Figure 1 is to carry a load of 45 kN.
Determine: 1 (a) The diameter of the rivet if the maximum shear stress is 40 MPa assuming rivets of the same size. 2 (b) The bracket thickness if the maximum bending stress is 120 MPa and bearing stress is 200 MPa.
Figure 1: Riveted bracket Section B: Answer TWO of the Following Questions Question 2 (35%): June 2009 Power of 60 kW at 750 rpm is to be transmitted from an electric motor to compressor shaft at 300 rpm by V-belts. The approximate larger pulley diameter is 1500 mm. The approximate centre distance is 1650 mm, and overload factor is to be taken as 1.5. A belt with cross sectional area of 350 mm2 and density of 1000 kg/m3 and having an allowable tensile strength of 2 MPa is available for use. The coefficient of friction between the belt and the pulley may be taken as 0.28. The driven pulley is overhung to the extent of 300 mm from the nearest bearing and is mounted on a shaft having a permissible shear stress of 40 MPa with the help of a key. Determine: 1 (a) The number of belts and the belt length assuming a groove angle of 35o 2 (b) The shaft diameter 3 (c) The key dimensions, assuming a rectangular key with allowable shear stress of 40 MPa and bearing stress of 120 MPa.
Final 2009 Petroleum Assume any missing data and state your assumptions clearly Please attempt Five of the following questions. 7 questions were given and students were asked to attempt 5 1.Gears, 2.Threads, 3.Gears, 4.Shafts, 5.Pressure vessels, 6.Screw Jack-threads, 7. Fatigue failure Question 1 [20 Marks] Final 2009-Petroleum A conveyor drive involving heavy shock torsional loading is to be operated by an electric motor turning at a speed of 1600 rpm, as shown in Figure 1. The speed ratio of the spur gears connecting the motor and the conveyor or speed reducer is to be 1:2. Determine the maximum horsepower that the gear set can transmit, based on bending strength and applying the AGMA formulas. Both gears are made from Carburized and hardened steel Grade 1(Sall = 55 ksi), and have a face width of 1.5 in. The pinion has a diameteral pitch of 10 in-1 and 18 teeth.
Figure 1 Question 4 [20 Marks] Final 2009 Petroleum The gears in the shaft assembly shown in Figure 4 transmit 100 kW of power and rotate at 3600 rpm. Gear wheel 1 is loaded against another gear such that the force P1 acts in a 45o direction at a radius of 80 mm from the shaft centre. The force P2 acts vertically downward at a radius of 110 mm from the shaft centre. The distance from bearing A to gear 1 is 100 mm, that from gear 1 to gear 2 is 85 mm, and that from gear 2 to bearing B is 50 mm. Perform the following: a) Find values of force components as well as the resultant force at locations A and B. b) Find the transmitted torque. c) Draw a bending moment diagram in the x-y and x-z planes along with a torque diagram; also, indicate the maximum bending moment and the maximum torque. d) Find the safety factor according to the distortion-energy theory (DET) if the shaft has a diameter of 35 mm and is made of AISI 1080.
Figure 4 Question 7 [20 Marks] Final 2009 Petroleum Figure 7 shows the input shaft of the crane gear box, supported in the gear box by bearings A and B and driven by electric motor. Determine: 1 a) The factor of safety n guarding against fatigue failure of the shaft. For a hollow shaft, replace in the shaft design equations. 433 by 1dDdD 2 b) The stresses in the shaft key. The geometry and dimensions of the hollow shaft and square shaft key are: Ft = 206N, Fr = 75 N, T = 2.06 Nm, a = 66mm, b = 84mm, L = 150Nm, D = 12mm, d = 6 mm, dp = 20 mm, w = 2.4 mm, Lk = 25 mm, The shaft and shaft key are made of 1030 CD steel with machined surfaces: Sut = 520 MPa, Sy = 440 MPa. At the keyway, Kf = 2. The shaft rotates and carries steady loading at normal temperature with a survival rate of 99.9%. The factor of safety against shear of shaft key is n = 3.
Figure 7
Question 4 May2010 Mechanical In a horizontal belt drive for a centrifugal blower, the blower is belt driven at 600 rpm by a 15 kW, 1750 rpm electric motor. The centre distance is twice the diameter of the larger pulley. The density of the belt material is 1500 kg/m3; maximum allowable stress equals 4 MPa; friction coefficients between the belt and the motor pulley and the belt and the blower pulley are 0.5 and 0.4 respectively; and the peripheral velocity of the belt is 20 m/s. Determine the following: 1 (a) Pulley diameters and belt length, [8 Marks] 2 (b) Cross sectional area of the belt, [8 Marks] 3 (c) Minimum initial tension for operation without slip, [8 Marks] 4 (d) Resultant force in the plane of the blower when operating with an initial tension 50% greater than the minimum value, [6 Marks]
Figure 4
Question 1 Final 2007-2008 Petroleum The shaft shown in the figure below is supported on two bearings A and B, and rotates at 1150 rpm. The shaft carries a bending load of 44500 N. Identify the likely mode of failure and its location when d = 64 mm assuming the shaft is to be ground after machining and is to have 80000 cycles of life corresponding to 90 % reliability. The steel used has the following properties Sut= 827 MPa, and Sy= 620 MPa. Select suitable bearings to be used at A and B.
[20 marks]
Question 2 Final 2007-2008 Petroleum The shaft shown in the figure below supports two gears. The shaft is made from high carbon steel (AISI 1080), and is to be designed with a safety factor of 2.0. The gears transmit a constant torque caused by PA=2000 N acting vertically as shown. The shaft has a constant machined cross section. (a) What is the reaction force on Gear C (b) Where is the critical location in the shaft? Determine it using both shear force and bending moment diagrams. (c) Obtain the required shaft diameter assuming all endurance limit modification factors equal to 1.0 except for the surface finish factor. (d) Select suitable bearings to be used at 0 and B.
[20 marks]
Question 4 Fianl_Exam-package-2009-2010 Petroleum A 10x50 mm AISI 1080 cantilever bar supports a static load of 1.4 kN as shown in Figure 4. The bar is secured using two bolts size M12x1.75 grade 5.8. Determine: (a) The shear stress acting on each bolt and hence the safety factor guarding against bolts failure. [9 Marks] (b) The maximum bending stresses in the cantilever and its safety factor. [5 Marks] (c) The maximum bearing stresses in the cantilever and the corresponding safety factor if the allowable bearing stress is 380 MPa. [4 Marks] (d) Explain without calculations how to achieve the same shear stress in both bolts. [2 Marks]
Figure 4: Cantilever bar supports a static load. All dimensions in mm [Total 20 Marks]
Question 5 Fianl_Exam-package-2009-2010 Petroleum The shaft shown in Figure 5 supports two gears. The shaft is made from high carbon steel (AISI 1080), and is to be designed with a safety factor of 2.0. The gears transmit a constant torque caused by PA=2000 N acting vertically as shown. The shaft has a constant machined cross section. (a) What is the reaction force PC on Gear C [2 Marks] (b) Using both shear force and bending moment diagrams, determine the critical location on the shaft? [12 Marks] (c) Obtain the required shaft diameter assuming static loads and using both the distortion energy theory (DET) and maximum shear stress theory (MSST). [6 Marks]
Figure 5 [Total 20 Marks] Question 6 Fianl_Exam-package-2009-2010 Petroleum The tensile link shown in Figure 6 has a thickness of 15 mm and is made of steel with ultimate tensile strength of 700 MPa and yield strength of 500 MPa. Both fillets are 16 mm in radius and their surfaces are ground. Determine: (a) The maximum load Pmax that will cause static yielding. [5 Marks] (b) If the applied load fluctuates between Pmin = 90 kN and Pmax = 210 kN, determine the safety factor for infinite life. [10 Marks] (c) If the fillets surfaces were machines and not ground, what are the maximum forces for part (a) and the new safety factor for part (b)? [5 Marks]
Figure 6
[Total 20 Marks]
You might also like
- 4363 111 Machine Design IDocument6 pages4363 111 Machine Design Iyogesh_b_k100% (2)
- Dme Model Key 2019Document25 pagesDme Model Key 2019Siva RamanNo ratings yet
- 07a6ec05 Designofmachinemembers IIDocument11 pages07a6ec05 Designofmachinemembers IIzahid_polyNo ratings yet
- Dme Quest Ut-2Document9 pagesDme Quest Ut-2aadhithyarajasekaranNo ratings yet
- PMD ModelDocument8 pagesPMD ModelDamodara SatyaDeva MadhukarNo ratings yet
- 12ME5DCDM2Document3 pages12ME5DCDM2Abhyudaya SinghNo ratings yet
- DME Model QuesDocument3 pagesDME Model QuesSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements - IIDocument8 pagesDesign of Machine Elements - IIprasaad26No ratings yet
- Me 2303 - Design of Machine Elements December 2010Document3 pagesMe 2303 - Design of Machine Elements December 2010Ilaya Perumal K0% (1)
- Mech-nd-2020-Me 8593-Design of Machine Elements-334300796-X10703 (Me8593) Design of Machine ElementsDocument5 pagesMech-nd-2020-Me 8593-Design of Machine Elements-334300796-X10703 (Me8593) Design of Machine ElementsARIGARAN SNo ratings yet
- Design ProblemsDocument13 pagesDesign ProblemsAristotle RiveraNo ratings yet
- ME 331 - DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS EXAMDocument5 pagesME 331 - DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS EXAMarumugam_rNo ratings yet
- Design ExercisesDocument13 pagesDesign ExercisesBookieeNo ratings yet
- MDDocument5 pagesMDYogesh DanekarNo ratings yet
- MD II Machine Design AssignmentsDocument5 pagesMD II Machine Design Assignmentsrishabhk28995No ratings yet
- Question Bank All Units With VTU Old Questions With Front PageDocument11 pagesQuestion Bank All Units With VTU Old Questions With Front PageHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- Assignment No-01 MEPC-301Document6 pagesAssignment No-01 MEPC-301SANDEEP BUDANIANo ratings yet
- 12 Me 5dcdm2Document3 pages12 Me 5dcdm2Abhyudaya SinghNo ratings yet
- Machine Design II Question PaperDocument8 pagesMachine Design II Question PaperProf. Avinash MahaleNo ratings yet
- 9A14503 Principles of Machine DesignDocument8 pages9A14503 Principles of Machine DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Dme Model QPDocument3 pagesDme Model QPCody LeeNo ratings yet
- Supp Nov 2009Document10 pagesSupp Nov 2009prk74No ratings yet
- 12ME5DCDM2Document3 pages12ME5DCDM2Abhyudaya SinghNo ratings yet
- DMM Ii (2015)Document35 pagesDMM Ii (2015)gorijalaNo ratings yet
- Final Design Work SheetDocument7 pagesFinal Design Work SheetKINDUNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics exam with questions on control systems and PLC applicationsDocument62 pagesMechatronics exam with questions on control systems and PLC applicationshaptooorNo ratings yet
- Mech 325 Tutorials (Questions Only)Document54 pagesMech 325 Tutorials (Questions Only)Shahriar Norouzi ZadehNo ratings yet
- QB Unit-3,4,5Document7 pagesQB Unit-3,4,5Agranshu BhardwajNo ratings yet
- rr320305 Design of Machine Members IIDocument8 pagesrr320305 Design of Machine Members IISrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- 1 ST Assignment Section-A&B 3-1 Semester Dmm-2: Sir CR Reddy College of EngineeringDocument3 pages1 ST Assignment Section-A&B 3-1 Semester Dmm-2: Sir CR Reddy College of EngineeringChadaram JagadishNo ratings yet
- Dme Model 2Document6 pagesDme Model 2YashwanthI-StyleKuttiNo ratings yet
- Assignment QuestionDocument15 pagesAssignment QuestionPratik WalimbeNo ratings yet
- Dmm2 Mar2006Document8 pagesDmm2 Mar2006Abdul Saleem MohammedNo ratings yet
- 11.a.ii - ME03031 QA 1Document22 pages11.a.ii - ME03031 QA 1Bakkiya Raj100% (1)
- GATE - IES QuestionsDocument4 pagesGATE - IES QuestionsMahesh Chandrabhan ShindeNo ratings yet
- 05-04 Machine Design & Cad-II (Me)Document2 pages05-04 Machine Design & Cad-II (Me)Abdul AhadNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Element-IIDocument53 pagesDesign of Machine Element-IIPramod R Bidve100% (1)
- Final Exam MCT3214 Nov09Document6 pagesFinal Exam MCT3214 Nov09Deerah Aziz100% (1)
- 16mu315 - Machine Design Question Bank: Ut Yt B TDocument3 pages16mu315 - Machine Design Question Bank: Ut Yt B THarishNo ratings yet
- Me1302 Dme 2Document4 pagesMe1302 Dme 2sumikannu100% (1)
- B.Tech Degree S8 (S, FE) / S6 (PT) (S, FE) Examination June 2023 (2015 Scheme)Document3 pagesB.Tech Degree S8 (S, FE) / S6 (PT) (S, FE) Examination June 2023 (2015 Scheme)Venkitaraj K PNo ratings yet
- Machine Design-II Question BankDocument32 pagesMachine Design-II Question BankAbhishek SakatNo ratings yet
- Design of Curved Beams and SpringsDocument11 pagesDesign of Curved Beams and SpringsAnonymous utfuIcnNo ratings yet
- Makalah GTWDocument8 pagesMakalah GTWfaisalNo ratings yet
- 181505-181902-MD - IiDocument2 pages181505-181902-MD - IiSiddharth PanchalNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines & Machine DesignDocument3 pagesTheory of Machines & Machine DesignAvilash JainNo ratings yet
- dmm1 PDFDocument9 pagesdmm1 PDFmohan_rapaka6095No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (Unit 1 and 2)Document5 pagesAssignment 1 (Unit 1 and 2)Atharva ChoudhariNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Exam Design of Machine Members QuestionsDocument8 pagesB.Tech Exam Design of Machine Members Questionsprk74No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2sonawanepmsNo ratings yet
- 0326 Me 2303 Design of Machine ElementsDocument3 pages0326 Me 2303 Design of Machine ElementsSaravanan MathiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Shaft DesignDocument4 pagesAssignment Shaft DesignHasham Mehmood100% (1)
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: January 2015 Semester End Make Up ExaminationsDocument2 pagesBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: January 2015 Semester End Make Up ExaminationsAbhyudaya SinghNo ratings yet
- End Semester SY Question Paper MDD May 2021Document3 pagesEnd Semester SY Question Paper MDD May 2021FelishiaNo ratings yet
- 12me52 MQP-1Document3 pages12me52 MQP-1SumitKumarNo ratings yet
- MECHANICS (ME10001) : AluminumDocument2 pagesMECHANICS (ME10001) : AluminumRahulNo ratings yet
- ShaftsDocument1 pageShaftsNhlaka ZuluNo ratings yet
- 353 35435 ME357 2011 4 2 1 Sheet MD2Document10 pages353 35435 ME357 2011 4 2 1 Sheet MD2adel nabhanNo ratings yet
- Increased Adipose Tissue Expression of Hepcidin in Severe Obesity Is Independent From Diabetes and NASHDocument9 pagesIncreased Adipose Tissue Expression of Hepcidin in Severe Obesity Is Independent From Diabetes and NASHsallyreffatNo ratings yet
- MENG08I01 Final Exam 2010Document4 pagesMENG08I01 Final Exam 2010sallyreffatNo ratings yet
- Formula sheet with physics constants and equationsDocument1 pageFormula sheet with physics constants and equationssallyreffatNo ratings yet
- Alloys and Their Phase DiagramDocument45 pagesAlloys and Their Phase Diagramabskumar100% (1)
- Xs 04Document2 pagesXs 04sallyreffatNo ratings yet
- Foundations On Friction Creep Piles in Soft ClaysDocument11 pagesFoundations On Friction Creep Piles in Soft ClaysGhaith M. SalihNo ratings yet
- SAP Table BufferingDocument31 pagesSAP Table Bufferingashok_oleti100% (3)
- Transportation Installation R2000iC210FDocument25 pagesTransportation Installation R2000iC210FMeet PAtel100% (2)
- CADAM - Model Parameters: General InformationDocument4 pagesCADAM - Model Parameters: General InformationmyapmisNo ratings yet
- Foundation DetailsDocument29 pagesFoundation DetailsSUSOVAN BISWASNo ratings yet
- Movie Recommender System: Shekhar 20BCS9911 Sanya Pawar 20BCS9879 Tushar Mishra 20BCS9962Document27 pagesMovie Recommender System: Shekhar 20BCS9911 Sanya Pawar 20BCS9879 Tushar Mishra 20BCS9962Amrit SinghNo ratings yet
- MP Lab3Document4 pagesMP Lab3kawish420No ratings yet
- Line Tension and Pole StrengthDocument34 pagesLine Tension and Pole StrengthDon BunNo ratings yet
- Physics - Chapter 5 - Summary - G12 - ADV - 2022-2023Document11 pagesPhysics - Chapter 5 - Summary - G12 - ADV - 2022-2023alqanoonaseemNo ratings yet
- CBIP draft meter standardsDocument22 pagesCBIP draft meter standardslalit123indiaNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement Detailing in BeamsDocument9 pagesReinforcement Detailing in Beamssaheed tijaniNo ratings yet
- SCADADocument14 pagesSCADANunna BaskarNo ratings yet
- Openscape Business V2: How To Configure Sip Trunk For Netfone HungaryDocument14 pagesOpenscape Business V2: How To Configure Sip Trunk For Netfone HungaryBelahreche MohamedNo ratings yet
- Criteria Cogni+Ve Ap+Tude Style Free Test: AssessmentdayDocument15 pagesCriteria Cogni+Ve Ap+Tude Style Free Test: AssessmentdayRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sybase Basic & Advanced T-SQL ProgrammingDocument3 pagesSybase Basic & Advanced T-SQL Programmingmehukr0% (1)
- Emphatic Struct and InversionDocument11 pagesEmphatic Struct and InversionMaria Veronica BustosNo ratings yet
- EE - Revision Through Question - GATE - 2020 PDFDocument138 pagesEE - Revision Through Question - GATE - 2020 PDFRamesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Windows Firewall Netsh CommandsDocument4 pagesTop 10 Windows Firewall Netsh CommandsedsoncalleNo ratings yet
- Scan Path DesignDocument54 pagesScan Path DesignGowtham HariNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts: ProbabilityDocument32 pagesBasic Concepts: ProbabilityJhedzle Manuel BuenaluzNo ratings yet
- TOS in PRE-CALCULUSDocument2 pagesTOS in PRE-CALCULUSSerjohnRapsingNo ratings yet
- SQL Injection Attack Detection and Preve PDFDocument12 pagesSQL Injection Attack Detection and Preve PDFPramono PramonoNo ratings yet
- Science Clinic Gr10 Chemistry Questions 2016Document44 pagesScience Clinic Gr10 Chemistry Questions 2016BhekiNo ratings yet
- Cube Nets Non-Verbal Reasoning IntroductionDocument6 pagesCube Nets Non-Verbal Reasoning Introductionmirali74No ratings yet
- Queue PPTDocument19 pagesQueue PPTharshvardhanshinde.2504No ratings yet
- What Is Altimetry 1Document1 pageWhat Is Altimetry 1miguel rosasNo ratings yet
- Uefi Firmware Enabling Guide For The Intel Atom Processor E3900 Series 820238Document42 pagesUefi Firmware Enabling Guide For The Intel Atom Processor E3900 Series 820238賴翊翊No ratings yet
- SECTION 2-07 Fire Protection: Airplane Operations ManualDocument26 pagesSECTION 2-07 Fire Protection: Airplane Operations ManualAnish ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Junction boxes gas group IIC selectionDocument16 pagesJunction boxes gas group IIC selectionkskadryNo ratings yet