Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Graph To The Left Represents
Uploaded by
Douglas YoungOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Graph To The Left Represents
Uploaded by
Douglas YoungCopyright:
Available Formats
x
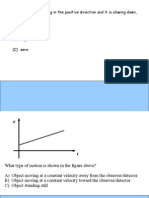
The graph to the left represents:
(A) constant (+) position (B) constant (+) velocity (C) constant (+) acceleration (D) standing still
(B) Constant Velocity (B) Constant Velocity
The graph to the left represents:
(A) constant (+) position (B) constant (+) velocity (C) constant (+) acceleration (D) standing still
(B) Constant Velocity (B) Constant Velocity
The graph to the left represents:
(A) constant (+) position (B) constant (+) velocity (C) constant (+) acceleration (D) standing still
(C) Constant Acceleration (C) Constant Acceleration
The graph to the left represents:
(A) constant velocity toward the detector (B) constant velocity away from the detector (C) constant acceleration toward the detector (D) constant acceleration away from the detector
(A) Constant Velocity (A) Constant Velocity toward the detector toward the detector
The graph to the left represents:
(A) constant velocity toward the detector (B) constant velocity away from the detector (C) constant acceleration toward the detector (D) constant acceleration away from the detector
(B) Constant Velocity (B) Constant Velocity away from detector away from detector
The graph to the left represents:
(A) constant velocity toward the detector (B) constant velocity away from the detector (C) constant acceleration toward the detector (D) constant acceleration away from the detector
(C) Constant (C) Constant acceleration toward acceleration toward the detector the detector
The graph to the left represents:
(A) constant velocity toward the detector (B) constant velocity away from the detector (C) constant acceleration toward the detector (D) constant acceleration away from the detector
(D) Constant (D) Constant acceleration away acceleration away from the detector from the detector
The graph to the left represents:
(A) constant velocity toward the detector (B) constant velocity away from the detector (C) constant acceleration toward the detector (D) constant acceleration away from the detector
(B) Constant velocity (B) Constant velocity away from the away from the detector detector
The graph to the left represents:
(A) constant velocity toward the detector (B) constant velocity away from the detector (C) constant acceleration toward the detector (D) constant acceleration away from the detector
(A) Constant Velocity (A) Constant Velocity toward the detector toward the detector
The graph to the left represents:
(A) constant velocity toward the detector (B) constant velocity away from the detector (C) constant acceleration toward the detector (D) constant acceleration away from the detector
(D) Constant (D) Constant acceleration away acceleration away from the detector from the detector
The graph to the left represents:
(A) constant velocity toward the detector (B) constant velocity away from the detector (C) constant acceleration toward the detector (D) constant acceleration away from the detector
(A) Constant Velocity (A) Constant Velocity toward the detector toward the detector
The graph to the left represents:
(A) constant velocity toward the detector (B) constant velocity away from the detector (C) constant acceleration toward the detector (D) constant acceleration away from the detector
(D) Constant (D) Constant acceleration away acceleration away from the detector from the detector
Which graph below matches the graph shown to the right:
v t (A )
v t (B ) v
a t (C )
a t (D )
(A )
Which graph below matches the graph shown to the right:
v t (A )
v t (B ) v
a t (C ) (B ) t
a t (D )
Which graph below matches the graph shown to the right:
v t (A )
v t (B )
a t (C )
a t (D )
v (A )
Which graph below matches the graph shown to the right:
v t (A )
v t (B )
a t (C )
a t (D )
v (A )
Which graph below matches the graph shown to the right:
x t (A )
x t (B )
a t (C ) (C ) t
a t (D )
Which graph below matches the graph shown to the right:
v t (A )
v t (B )
a t (C ) (B ) t
a t (D )
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Mechanics of Materials An Integrated Learning System 4th Edition Philpot Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesMechanics of Materials An Integrated Learning System 4th Edition Philpot Solutions ManualMarkManntjaid95% (20)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Liquid Nitrogen Safety TrainingDocument21 pagesLiquid Nitrogen Safety TrainingSteven James CapuanoNo ratings yet
- 2A016 Install Rev1972 1965Document40 pages2A016 Install Rev1972 1965Rich McDonaldNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's PrincipleDocument15 pagesBernoulli's PrincipleDedy KristiantoNo ratings yet
- Heat IIDocument14 pagesHeat IIDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Review Clicker QuestionDocument7 pagesProjectile Motion Review Clicker QuestionDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Heat Engines-Laws ThermoDocument19 pagesHeat Engines-Laws ThermoDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Heat ReviewDocument12 pagesHeat ReviewDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Test-I Review For District TestDocument5 pagesTest-I Review For District TestDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Heat IDocument31 pagesHeat IDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Heat IDocument31 pagesHeat IDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Heat IDocument31 pagesHeat IDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- LAb Safety-Clicker QuestionsDocument20 pagesLAb Safety-Clicker QuestionsDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Heat IIDocument14 pagesHeat IIDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Heat ReviewDocument12 pagesHeat ReviewDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Motion Diagram Clicker Questions-1Document5 pagesMotion Diagram Clicker Questions-1Douglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Heat IIDocument14 pagesHeat IIDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Heat Engines-Laws ThermoDocument19 pagesHeat Engines-Laws ThermoDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Heat ReviewDocument12 pagesHeat ReviewDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Heat Engines-Laws ThermoDocument19 pagesHeat Engines-Laws ThermoDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Gravity Clicker Questions 2Document16 pagesGravity Clicker Questions 2Douglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Review 1Document6 pagesKinematics Review 1Douglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Review Clicker QuestionDocument7 pagesProjectile Motion Review Clicker QuestionDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Gravity Clicker QuestionsDocument16 pagesGravity Clicker QuestionsDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Motion GraphsDocument18 pagesMotion GraphsDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Collisions MatrixDocument9 pagesCollisions MatrixDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Forces Train2Document12 pagesForces Train2Douglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Force Will It MoveDocument9 pagesForce Will It MoveDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Yoda Forces ProblemsDocument10 pagesYoda Forces ProblemsDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Misc Force ProblemsDocument7 pagesMisc Force ProblemsDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Forces ReviewDocument13 pagesForces ReviewDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Force Clicker Questions-JabbaDocument6 pagesForce Clicker Questions-JabbaDouglas YoungNo ratings yet
- Steel - WikipediaDocument16 pagesSteel - WikipediaaravindNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Solubility of Organic CompoundsDocument2 pagesExperiment 1 Solubility of Organic CompoundsJamica AmbionNo ratings yet
- Biaxial Bending of SFRC Slabs Is Conventional Reinforcement NecessaryDocument15 pagesBiaxial Bending of SFRC Slabs Is Conventional Reinforcement NecessaryDan MaceNo ratings yet
- Brief History of Remote SensingDocument16 pagesBrief History of Remote SensingFeyrisNo ratings yet
- PLC Simulation ReportDocument62 pagesPLC Simulation ReportAsraful Goni NirabNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Level 1: Temperature Scale and Work Done in Different ProcessesDocument7 pagesThermodynamics Level 1: Temperature Scale and Work Done in Different ProcessesViren Patel50% (2)
- Free Fall: Objective: The Purpose of This Experiment Is To Prove ThatDocument5 pagesFree Fall: Objective: The Purpose of This Experiment Is To Prove ThatSunday Glo M. Cabuyao100% (1)
- Research Paper in MicrowavesDocument10 pagesResearch Paper in MicrowavesManoling PanopioNo ratings yet
- EE593Document4 pagesEE593hassanNo ratings yet
- Role of Energy Loss On Discharge Characteristics of Sluice GatesDocument25 pagesRole of Energy Loss On Discharge Characteristics of Sluice GatesBabak mahmoudiNo ratings yet
- Production Drawings & Process ModelsDocument15 pagesProduction Drawings & Process ModelsnotonectalNo ratings yet
- V Dy DT A DV DT: Indian Language School GR Xi Physics Worksheet-1 2022-23 Chapter: Motion in A Straight Line SolutionsDocument3 pagesV Dy DT A DV DT: Indian Language School GR Xi Physics Worksheet-1 2022-23 Chapter: Motion in A Straight Line SolutionsRudra RoshanNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Report 5Document8 pagesPhysics Practical Report 5NatashaAnneNo ratings yet
- Vernacular ArchitectureDocument33 pagesVernacular ArchitectureShyam Sekhar MenonNo ratings yet
- Trapezoidal Rule and Simpson's RuleDocument5 pagesTrapezoidal Rule and Simpson's RuleSai VandanaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Seismic Reservoir CharacterizationDocument30 pagesBasics of Seismic Reservoir Characterizationgodfrey edezuNo ratings yet
- Current Mode Pi ControllerDocument19 pagesCurrent Mode Pi ControllersunitaNo ratings yet
- Performance of HT & LT Catalyst: Amit Kumar Jha MT (Chemical) # 0247/7161Document25 pagesPerformance of HT & LT Catalyst: Amit Kumar Jha MT (Chemical) # 0247/7161sb1984_hithaldiaNo ratings yet
- Maths Take Home Pack Gr.7 T3 W6Document24 pagesMaths Take Home Pack Gr.7 T3 W6Muhammed ChopdatNo ratings yet
- Alat Ukur Ketebalan Besi - Jual Ultrasonick Thickness Gauge Mitech MT 180 0812 9595 8196Document2 pagesAlat Ukur Ketebalan Besi - Jual Ultrasonick Thickness Gauge Mitech MT 180 0812 9595 8196Regi EgiNo ratings yet
- Exploration Archaeology (John M. Stanley)Document4 pagesExploration Archaeology (John M. Stanley)henarroNo ratings yet
- Definition of Elements 1-20Document2 pagesDefinition of Elements 1-20War ThunderNo ratings yet
- B D Khosla Practical ChemistryDocument6 pagesB D Khosla Practical ChemistryJaswinder Sidhu18% (11)
- Sales Bulletin American Meter 4510Document12 pagesSales Bulletin American Meter 4510rieza_fNo ratings yet
- Ee 303 Pti Version 34 Power Flow Project Fall 2018Document2 pagesEe 303 Pti Version 34 Power Flow Project Fall 2018api-458050099No ratings yet
- Contrasts Between Finite and Infinite Dimensional Spaces and Between Normed and Inner Product SpacesDocument5 pagesContrasts Between Finite and Infinite Dimensional Spaces and Between Normed and Inner Product SpacesQuinton WestrichNo ratings yet