Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NEEM2
Uploaded by
Mani KandanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NEEM2
Uploaded by
Mani KandanCopyright:
Available Formats
NEEM
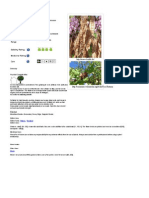
Botanical name : Azadirachta indica A.Juss Family : Meliaceae Distribution Neem is a versatile multipurpose tree native of dry forest areas of India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand, Myanmar and Africa. In India it occurs throughout the drier parts including the states of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Orissa, Maharastra, Gujrarat, Rajasthan, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu. Environmental Requirements Neem is a sturdy tree and can adapt to a-wide range of climatic, edaphic and topographical conditions. Climate Temperature Being a tropical / sub-tropical plant, it is found in areas with annual mean maximum temperature upto32.5 to 42.5Cand minimum temperature of 4 to 21C. Temperatures below 4C and frost are unfavorable. Rainfall Neem comes up well in areas with an average annual rainfall of 450 - 1200 mm. Soil Neem grows well on almost all kinds of soils which are well drained. It grows well in loamy, clayey and black cotton soil. It also thrives better than other species on dry, stony, clayey and shallow soils. It can also come up on soil, where there is
hard calcareous or clay pan just below the soil surface. It does not grow well on sodic soil and grows moderately on alkaline soil. The optimum pH is 6.2 and above and can also grow well at pH 5.0 and helps in increasing the pH through the addition of calcium rich leaf litter. Water logging and poorly drained soils are unsuitable for Neem. Phenology Neem is an evergreen tree, but in dry locations, it sheds its leaf during February to March leaves appear during March to April. Flowering varies with climate of the locality. Flower from January to March. Fruit ripen from June to August. Silvicultural Characters Light - Neem is a light demander but tolerates fairly heavy shade during the early ye; Frost - It is frost tender species and cannot withstand excessive cold, especially in se and sapling stages. Drought - Well extensive root system makes neem drought hardy Waterlogging - Neem cannot withstand waterlogging Fire - Fire tender species Coppice - It can coppice well Root suckers - Produces root suckers Pollarding - It can withstand pollarding Silviculture Natural regeneration - Though self sown seeds and through seeds from birds dropi neem reproduce naturally. It establishes well in thorny bushes, along field bunds, wire fence "telegraph wires. It requires protection from grazing during early stages. Natural regene from coppice and root suckers' is also common. Artificial Regeneration Neem seeds are collected from June to August. Fresh seeds collected should be usi sowing. Fruits on collection should be depulped and shade dried and then treated with fungi like Agrason or Cerason and than used for sowing. Artificial regeneration could be ach though direct sowing or out planting nursery raised seedling.
You might also like
- Gardener's Guide to Succulents: A Handbook of Over 125 Exquisite Varieties of Succulents and CactiFrom EverandGardener's Guide to Succulents: A Handbook of Over 125 Exquisite Varieties of Succulents and CactiRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Maximum Yield USA January 2019 PDFDocument84 pagesMaximum Yield USA January 2019 PDFYogeish H. MayekarNo ratings yet
- Neem Cultivation Techniques and UsesDocument9 pagesNeem Cultivation Techniques and UsesmandaremNo ratings yet
- Acacia ModestaDocument13 pagesAcacia ModestaAkshay BoobathiNo ratings yet
- Forestry Wasteland - NeemDocument8 pagesForestry Wasteland - NeemVipul SuranaNo ratings yet
- Tamarind Production GuideDocument9 pagesTamarind Production GuideSubhash BoseNo ratings yet
- Narra Information PaperDocument2 pagesNarra Information PaperKhaelNo ratings yet
- Forest & Envionment SpeciesDocument156 pagesForest & Envionment Specieslitrakhan100% (1)
- Growing Hardy Soft Cane Dendrobium OrchidsDocument2 pagesGrowing Hardy Soft Cane Dendrobium OrchidsDheemanth BhandarkarNo ratings yet
- Jamun Production GuideDocument9 pagesJamun Production GuideHall OwnNo ratings yet
- Leaflet Callophyllum InophyllumDocument2 pagesLeaflet Callophyllum InophyllumSuci Desriana RSNo ratings yet
- CloveDocument3 pagesCloveheenaNo ratings yet
- DeodaraDocument12 pagesDeodaraNE e-SportsNo ratings yet
- Hands-on Training for Quality PlantingDocument30 pagesHands-on Training for Quality PlantingKanchanNo ratings yet
- Tamarind tree usesDocument6 pagesTamarind tree usesZhafronsya Alfarij NurzainNo ratings yet
- Fast-Growing Commercial and Native Philippine Tree SpeciesDocument25 pagesFast-Growing Commercial and Native Philippine Tree SpeciesEvelyn VergaraNo ratings yet
- Indian Kino Tree UsesDocument14 pagesIndian Kino Tree UsespandithuraiNo ratings yet
- Bael fruit to Java almond guideDocument24 pagesBael fruit to Java almond guideAlarm GuardiansNo ratings yet
- Organic Production of Medicinal and Aromatic Crops in Andhra PradeshDocument34 pagesOrganic Production of Medicinal and Aromatic Crops in Andhra PradeshRohith GandhiNo ratings yet
- Forest Plantation ManagementDocument11 pagesForest Plantation ManagementYOGA SHURUTHI A/P YESUDASS BP21160619No ratings yet
- Versatile Neem Tree GuideDocument4 pagesVersatile Neem Tree Guidedcollot8026No ratings yet
- Temperate ForagesDocument3 pagesTemperate ForagesAnanda PreethiNo ratings yet
- Citrus Crops PDFDocument15 pagesCitrus Crops PDFLucky TraderNo ratings yet
- Moringa Oleifera MoringaDocument2 pagesMoringa Oleifera Moringagemni7No ratings yet
- Homework - SOFT AND HARD LANDSCAPING MATERIALS IN THE PHILIPPINESDocument19 pagesHomework - SOFT AND HARD LANDSCAPING MATERIALS IN THE PHILIPPINESmissey liwanagNo ratings yet
- White Jasmine: Care and MaintenanceDocument6 pagesWhite Jasmine: Care and Maintenancejurilyn estilleroNo ratings yet
- Biology Report G6Document24 pagesBiology Report G6Allen JangcaNo ratings yet
- Silvan FeatureDocument12 pagesSilvan FeatureAkash 9liNo ratings yet
- Jasmine Flower Cultivation GuideDocument24 pagesJasmine Flower Cultivation GuideHumaira YmNo ratings yet
- Moringa OleiferaDocument13 pagesMoringa OleiferaEmcee WaterNo ratings yet
- Allied 07Document12 pagesAllied 07Neha DasNo ratings yet
- Philippine Native TreesDocument12 pagesPhilippine Native TreesMaiko Gil Hiwatig100% (1)
- Omafra Growing Raspberries For Home Gardens 22 037 en 2023 03 22Document7 pagesOmafra Growing Raspberries For Home Gardens 22 037 en 2023 03 22Fairyland Daycare WestNo ratings yet
- Acrocarpus fraxinifolius Species ProfileDocument5 pagesAcrocarpus fraxinifolius Species ProfileCarolina GeblerNo ratings yet
- Growing Guide for Brightly Colored Marigold FlowersDocument20 pagesGrowing Guide for Brightly Colored Marigold FlowersPrajakt RaulNo ratings yet
- Acacia polyacantha subsp. campylacanthaDocument2 pagesAcacia polyacantha subsp. campylacanthaLunília Inês CaniveteNo ratings yet
- Aloe Vera Uses and BenefitsDocument7 pagesAloe Vera Uses and Benefitsscribd4SkdNo ratings yet
- Andropogon GayanusDocument10 pagesAndropogon GayanusSophia Mitz Aya-ayNo ratings yet
- 12-3 PlumDocument98 pages12-3 PlumZeshan mukhtarNo ratings yet
- Cedrus Deodara: Pinaceae (D. Don.) G. DonDocument5 pagesCedrus Deodara: Pinaceae (D. Don.) G. DonTanveer Ahmad AfridiNo ratings yet
- LegumesDocument3 pagesLegumeszerk4000No ratings yet
- Forest and Environmental Species PDFDocument156 pagesForest and Environmental Species PDFAhsanHashmiNo ratings yet
- Maesopsis EminiiDocument5 pagesMaesopsis EminiiRizki Ersa HeryanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document3 pagesChapter 17KavieswarNo ratings yet
- Sandal: Santalum Album LinnDocument7 pagesSandal: Santalum Album LinnRaNo ratings yet
- Individual Task Management of Grazing Land For Small Holder FarmsDocument9 pagesIndividual Task Management of Grazing Land For Small Holder FarmsSelvira HasanNo ratings yet
- Flaky Juniper (Blue Star) : 1-2feet Indoor PurposeDocument26 pagesFlaky Juniper (Blue Star) : 1-2feet Indoor PurposePrakhar SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Delonix RegiaDocument6 pagesDelonix RegiaJesus MiguelNo ratings yet
- Notes On Eucalypts PDFDocument7 pagesNotes On Eucalypts PDFDragana SekulicNo ratings yet
- Cercis Siliquastrum L.: Common Name Family Synonyms Known Hazards HabitatsDocument1 pageCercis Siliquastrum L.: Common Name Family Synonyms Known Hazards HabitatsxlikoNo ratings yet
- Growing Figs Guide for Home Gardens in the SouthDocument13 pagesGrowing Figs Guide for Home Gardens in the SouthkathrynbaxNo ratings yet
- Desert Rose ProductionDocument2 pagesDesert Rose ProductionBenito Neto0% (1)
- Site Analysis2Document19 pagesSite Analysis2Ehab HaddadNo ratings yet
- Cryptomeria JaponicaDocument5 pagesCryptomeria JaponicaFitzgerald BillyNo ratings yet
- Crown of Thorns ProductionDocument2 pagesCrown of Thorns ProductionDdoa TandlianwalaNo ratings yet
- Kigelia Africana IntDocument2 pagesKigelia Africana IntMia Audina MiyanoshitaNo ratings yet
- IxoraDocument2 pagesIxoraRudient De VriendschapNo ratings yet
- Flemingia MacrophyllaDocument2 pagesFlemingia MacrophyllaTravisNo ratings yet
- Areca Palm (Small) - PlantDocument21 pagesAreca Palm (Small) - PlantHarsimran ChadhaNo ratings yet
- L14. Hort181 - GuavaDocument4 pagesL14. Hort181 - GuavaAmit Goenka100% (1)
- Growing the Stone Fruits - With Information on Growing Cherries, Peaches and PlumsFrom EverandGrowing the Stone Fruits - With Information on Growing Cherries, Peaches and PlumsNo ratings yet
- Creed Rice Market Report, November 15, 2023Document13 pagesCreed Rice Market Report, November 15, 2023asociacion de caficultores de la amazonia peruanaNo ratings yet
- Research MolluscicideDocument11 pagesResearch MolluscicideLaureah ParNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra Village's Groundwater Projects Under Anna HazareDocument4 pagesMaharashtra Village's Groundwater Projects Under Anna HazareMitashi SinhaNo ratings yet
- Landscaping With Native Plants: A Gardener's Guide For MissouriDocument38 pagesLandscaping With Native Plants: A Gardener's Guide For MissouriMaryland Native Plant ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Organic Farm Business Plan SummaryDocument6 pagesOrganic Farm Business Plan Summaryharishini venkatesan100% (1)
- The Role of The Private Sector in Agriculture Extension in PakistanDocument8 pagesThe Role of The Private Sector in Agriculture Extension in Pakistanshahidmrd100% (2)
- FREE Diet Profile Sample Meal Plan Success Stories Print Report CardDocument3 pagesFREE Diet Profile Sample Meal Plan Success Stories Print Report CardGabriel Esteban Rodríguez EscandónNo ratings yet
- Propagating and marketing treesDocument8 pagesPropagating and marketing treesSarah Sierra HernandezNo ratings yet
- Geography Optional Paper II Previous Year's Questions Topic Wise ListingDocument42 pagesGeography Optional Paper II Previous Year's Questions Topic Wise ListingSubh sNo ratings yet
- Hypophthalmus) in Rupandehi and Nawalparasi Districts of NepalDocument10 pagesHypophthalmus) in Rupandehi and Nawalparasi Districts of NepalShailesh GurungNo ratings yet
- PM Fasal Bima YojnaDocument6 pagesPM Fasal Bima YojnaSunilNo ratings yet
- DeforestationDocument27 pagesDeforestationRabi'atul Adawiyah Ismail100% (1)
- Unido-Gti Tors Pomegranate ProgramDocument4 pagesUnido-Gti Tors Pomegranate Programapi-304173542No ratings yet
- Efsrp Awpb Format 2016Document53 pagesEfsrp Awpb Format 2016Dereje AyimeloNo ratings yet
- Articles of Incorporation-Non Stock Corp - AGLALOMADocument5 pagesArticles of Incorporation-Non Stock Corp - AGLALOMAcharles bautistaNo ratings yet
- Managing Floods for Agriculture in Spate Irrigation SystemsDocument10 pagesManaging Floods for Agriculture in Spate Irrigation SystemsSharmarke Mohamed AhmedNo ratings yet
- WestHighSchoolSLC AoPa Aff University of Michigan HS Debate Tournament OctasDocument67 pagesWestHighSchoolSLC AoPa Aff University of Michigan HS Debate Tournament OctasEmronNo ratings yet
- Manitou MLT 634 (EN)Document20 pagesManitou MLT 634 (EN)ManitouNo ratings yet
- Horizontal and Vertical Soilless Growing Systems Under Cyprus ConditionsDocument5 pagesHorizontal and Vertical Soilless Growing Systems Under Cyprus ConditionsShailendra RajanNo ratings yet
- Agro-Ecologicalzones of Ethiopia - PdfabbyyyDocument136 pagesAgro-Ecologicalzones of Ethiopia - PdfabbyyyHenok HenokNo ratings yet
- Adp 2014 15 PDFDocument251 pagesAdp 2014 15 PDFHayat Ali ShawNo ratings yet
- Kurukshetra Mcqs August 2021Document38 pagesKurukshetra Mcqs August 2021abhay thakurNo ratings yet
- The History of DEKALB Poultry Research, Inc.Document4 pagesThe History of DEKALB Poultry Research, Inc.rockfakeyNo ratings yet
- Industry and CommerceDocument20 pagesIndustry and CommerceanishNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan Afa 10Document3 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan Afa 10Khey Delos Reyes DorimanNo ratings yet
- Business: Presentation On My PlanDocument12 pagesBusiness: Presentation On My PlanGOPALAKRISHNAN KNo ratings yet
- Papaya Breeding in IndiaDocument8 pagesPapaya Breeding in Indiachauhan1234100% (1)
- Deforestation: Causes & Concequences: by - Sahit DevganDocument20 pagesDeforestation: Causes & Concequences: by - Sahit DevgansahitNo ratings yet
- Kaveri SeedsDocument13 pagesKaveri Seedsdeepak palNo ratings yet