Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Mammalian Heart PP Worksheet
Uploaded by
nremeckiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Mammalian Heart PP Worksheet
Uploaded by
nremeckiCopyright:
Available Formats
THE MAMMALIAN HEART
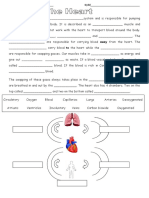
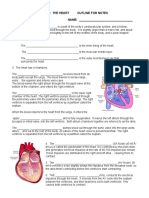
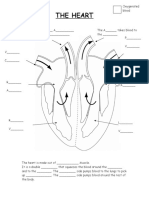
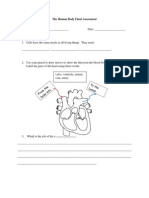
The heart consist of ______________________ separated by the septum Both sides beat ________________(at the same time) _________________ circulation takes blood to and from the lungs ________________ circulation takes blood to and from the body tissues The ______________________takes blood from the body and pumps it to the __________ The _____________________takes blood from the lungs and pumps it to the body
ONE WAY BLOOD FLOW
Veins carry blood _____________________ _______________ are the largest veins in the body Arteries carry blood ______________________ The ___________ is the largest artery in the body ________________ pumped from the atria to ventricles is prevented by ________________________ (AV) valves Back flow of blood pumped from the ___________________ is prevented by _____________________ valves
Heart Blood Supply
_______________ arteries branch off the aorta and supply the muscle cells of the heart with oxygen and nutrients Blockage in these arteries can cause chest pain called ___________ Clogged arteries may be treated with drugs or ______________________surgery An alternative to a bypass is called _____________________ where a tube is inserted into the blocked artery and inflated to clear the blockage
REVIEW
Describe pulmonary circulation. Which side of the heart carries oxygenated blood? What vessels supply the heart with oxygen and nutrients? Give the order of structures that blood flows past starting with the vena cava until it reaches the aorta
HEART RATE AND CONTROL
Your heart beats about ________________ (108,000/day or 2.96 x 109 / lifetime)
each beat must be __________________ cardiac (________________) muscle can beat without stimulation but the 4 heart chambers must contract in a specific sequence the _______________________located in the right atrium acts as the pacemaker and sends impulses that radiate across the atria The _____________ signal causes the atria to contract downwards and eventually reaches the AV (________________________) second signal is sent from AV node through special fibres (__________________) in a structure called _________________________ the signal sent to the base of the ventricles will spread upward causing _________________ ____________ SA node is linked to nerves that make the heart rate increase (______________nerves) or decrease (___________________________ nerves)
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHS
An ___________ (EKG) detects changes in electrical current during the cardiac cycle _________________ - atrial contraction _________________ - ventricular contraction _________________ - ventricle recovery ECGs may reveal disorders of the heart _____________ - relaxation of the heart _____________- contraction of the heart
HEART SOUNDS
Heart sounds are caused by ____________________ as the heart beats contraction of ventricles forces AV valves shut ________ sound relaxation of ventricles lowers pressure in ventricle so semilunar valves snap shut to prevent backflow from arteries _____________ incomplete closure of valve results in different sound (_________________) and may indicate a faulty heart valve
REVIEW
What is the pacemaker and where is it located in the heart? What represents ventricular contraction on an ECG? What is the relaxation phase of the heart beat called? What makes the lubb-dubb heart sound? When you run a race, what nerves tell the pacemaker to speed up? What causes heart murmurs?
You might also like
- Epilepsy PresentationDocument10 pagesEpilepsy Presentationapi-346838508No ratings yet
- Human Body System NotesDocument5 pagesHuman Body System NotesShannon BandyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Unit 10 Test Review KEYDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Unit 10 Test Review KEYsenjicsNo ratings yet
- 3j Cuci - The Circulatory System WorksheetDocument6 pages3j Cuci - The Circulatory System Worksheetcharmaine nwankwoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory ClozeDocument1 pageCirculatory Clozemikemaia82No ratings yet
- Medical Prioritization ProcessDocument20 pagesMedical Prioritization ProcessIGDNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System ExplainedDocument4 pagesThe Circulatory System ExplainedshearmureighNo ratings yet
- Systems BookletDocument8 pagesSystems Bookletapi-383568582No ratings yet
- Closed Tibia and Fibula Fractures in 44-Year-Old Male PatientDocument25 pagesClosed Tibia and Fibula Fractures in 44-Year-Old Male Patientleonard0% (1)
- The circulatory system transports oxygen and nutrientsDocument2 pagesThe circulatory system transports oxygen and nutrientsAmarpreet Kaur100% (1)
- Heart Muscle Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHeart Muscle Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemAlba CubilloNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Guided NoteDocument2 pagesCirculatory System Guided Noteapi-251528487No ratings yet
- A Standard Procedure For DeviationDocument2 pagesA Standard Procedure For DeviationGAURAV SHARMA100% (1)
- UG Curriculum Vol II PDFDocument247 pagesUG Curriculum Vol II PDFRavi Meher67% (3)
- NCP: Labor Stage 1 Latent PhaseDocument9 pagesNCP: Labor Stage 1 Latent PhaseJavieNo ratings yet
- 2021 Guided Study Notes - CardioRespiratory Unit - Part 1Document33 pages2021 Guided Study Notes - CardioRespiratory Unit - Part 1CarsonNo ratings yet
- Circulation in Humans ExplainedDocument2 pagesCirculation in Humans ExplainedKliemmah PeltierNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: The Heart Outline For Notes Health Care Careers NAMEDocument2 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: The Heart Outline For Notes Health Care Careers NAMEEvi DousiaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Blood VesselsDocument7 pagesCardiovascular System Blood VesselsRocío RosabalNo ratings yet
- PLM Screening ActivityDocument8 pagesPLM Screening Activityjamie mutucNo ratings yet
- Edmodo Quiz As Biology Topic 1 Cardiac Cycle1Document2 pagesEdmodo Quiz As Biology Topic 1 Cardiac Cycle1Arun NandhaNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System BookletDocument30 pagesThe Circulatory System BookletTroy CampbellNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System StoryDocument3 pagesCirculatory System StoryportnoymichNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory and Respiratory SystemsDocument6 pagesThe Circulatory and Respiratory SystemsColtonNo ratings yet
- 3 HeartDocument2 pages3 HearthomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Physiol Wkst 7 The HeartDocument5 pagesPhysiol Wkst 7 The HeartritomNo ratings yet
- Platelets Are Pieces of Cells That Form A Plug orDocument1 pagePlatelets Are Pieces of Cells That Form A Plug orF3DENo ratings yet
- How Does Your Heart Work WorksheetDocument7 pagesHow Does Your Heart Work WorksheetJessica SkeffreyNo ratings yet
- The circulatory systemDocument1 pageThe circulatory systemTharanga HewabuhageNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Word Definition - 21.03Document1 pageUnit 2 - Word Definition - 21.03Kieu AnhNo ratings yet
- CH 13 ActivityDocument4 pagesCH 13 Activityash vldnbrNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Biology Blood-Vessels and LymphDocument9 pagesYear 10 Biology Blood-Vessels and LymphMNSB Year 04No ratings yet
- Latin Roots and Cardiovascular TermsDocument5 pagesLatin Roots and Cardiovascular TermsAmber DavisNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Unit Booklet sm20Document17 pagesCardiovascular System Unit Booklet sm20api-383568582No ratings yet
- AJ Lesson 2: B4.3 The Heart: Mammalian Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesAJ Lesson 2: B4.3 The Heart: Mammalian Circulatory SystemIntelaNo ratings yet
- Gross - ScalpDocument3 pagesGross - ScalpIsaac OnigbindeNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument23 pagesCirculatory Systemhellwakeisbored12No ratings yet
- Human HeartDocument11 pagesHuman HeartManav KohliNo ratings yet
- Exercises On The Cardiovascular SystemDocument2 pagesExercises On The Cardiovascular SystemNguyễn Thị Hương Y.K53HNo ratings yet
- 12.1 The Function of Circulation - Cont - Student SheetDocument5 pages12.1 The Function of Circulation - Cont - Student Sheeteshaaljamal27No ratings yet
- Organ Systems Guided NotesDocument3 pagesOrgan Systems Guided Noteslavanya.pervelaNo ratings yet
- Cow's HeartDocument10 pagesCow's HeartAllyzha AguilarNo ratings yet
- Act 12Document3 pagesAct 12Rose CostaNo ratings yet
- The circulatory system in 30 secondsDocument11 pagesThe circulatory system in 30 secondsRentika SiahaanNo ratings yet
- B05.Transport SummaryDocument1 pageB05.Transport Summaryshin99000No ratings yet
- Macie Joyner - Copy of Lymphatic & Immune Systems - NotesDocument3 pagesMacie Joyner - Copy of Lymphatic & Immune Systems - NotesMacie JoynerNo ratings yet
- Heart, Blood Vessesls and Blood WorksheetDocument4 pagesHeart, Blood Vessesls and Blood WorksheetJoanne MullengerNo ratings yet
- Modul - Transport 10.1 The Importance of Transport SystemDocument4 pagesModul - Transport 10.1 The Importance of Transport SystemROSMALIANA BINTI MOHAMAD MoeNo ratings yet
- Blood FlowDocument1 pageBlood Flownikinagy1No ratings yet
- Blood Vessels Notesheet: Characteristics of ArteriesDocument2 pagesBlood Vessels Notesheet: Characteristics of ArteriesTanya GrantNo ratings yet
- C1-Human HeartDocument3 pagesC1-Human HeartNursuzela Abd MalekNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System IntroductionDocument3 pagesCardiovascular System IntroductionMartina KlanjcicNo ratings yet
- BIO 202 Circulation I Lab 22S PDFDocument2 pagesBIO 202 Circulation I Lab 22S PDFTraci GardnerNo ratings yet
- Heartlesson-Guidednotes 1Document2 pagesHeartlesson-Guidednotes 1api-298312370No ratings yet
- Repaso Sistema Circulatorio y ExcretorDocument2 pagesRepaso Sistema Circulatorio y ExcretorRocío Madolell100% (1)
- Ex-F3 2nd UT RevisionDocument3 pagesEx-F3 2nd UT RevisionTsz BigbangNo ratings yet
- Block 2 - The Heart Note CDocument6 pagesBlock 2 - The Heart Note Capi-352801580No ratings yet
- Health TestDocument2 pagesHealth Testapi-373839745No ratings yet
- Bio 202 - Exam 1 (Part 2)Document6 pagesBio 202 - Exam 1 (Part 2)GretchenNo ratings yet
- Heart WorksheetDocument4 pagesHeart Worksheetmim3112No ratings yet
- Keeping Healthy Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesKeeping Healthy Circulatory Systemsama ahmedNo ratings yet
- The Human Body AssessmentDocument5 pagesThe Human Body AssessmentJessie OlsonNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Circulatory System WorksheetKliemmah PeltierNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology Vascular System Blood VesselsDocument14 pagesAnatomy Physiology Vascular System Blood VesselsJustine May Balinggan DelmasNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Blood - Body BitsDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Blood - Body BitsJohnny Miller60% (5)
- ActonelDocument42 pagesActonelSimon JonatanNo ratings yet
- Association of Voiding Dysfunction With Functional ConstipationDocument3 pagesAssociation of Voiding Dysfunction With Functional ConstipationSisca Dwi AgustinaNo ratings yet
- Jcthe Role of Abutment-Attachment Selection in Resolving Inadequate Interarch Distance: A Clinical ReportdDocument7 pagesJcthe Role of Abutment-Attachment Selection in Resolving Inadequate Interarch Distance: A Clinical ReportdSyed Noorani100% (1)
- Nle Exam SamplesDocument6 pagesNle Exam SamplesAldrich ArquizaNo ratings yet
- Disc Bulge Recovery LikelyDocument4 pagesDisc Bulge Recovery LikelyItai IzhakNo ratings yet
- Question Excerpt From 96Document5 pagesQuestion Excerpt From 96Lorainne FernandezNo ratings yet
- OXFORD CARDIOTHORACIC SURGERY ST1Document10 pagesOXFORD CARDIOTHORACIC SURGERY ST1Javier Nicolas Pena DazaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument37 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseHikmah Ilyas El-LuthanyNo ratings yet
- Improving Patient Safety in Radiotherapy by Learning From Near Misses, Incidents and ErrorsDocument5 pagesImproving Patient Safety in Radiotherapy by Learning From Near Misses, Incidents and ErrorsrosanaNo ratings yet
- Smile Journey With 32 Watts Clear Journey - Alignwise Smile TechnologiesDocument7 pagesSmile Journey With 32 Watts Clear Journey - Alignwise Smile TechnologiesAlignwise Smile TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- APLS Scenario OSCE PDFDocument5 pagesAPLS Scenario OSCE PDFNikita JacobsNo ratings yet
- The Babinski Sign and The Pyramidal SyndromeDocument9 pagesThe Babinski Sign and The Pyramidal SyndromeEstela Beatríz Mora GarcíaNo ratings yet
- 0315 DVTDocument28 pages0315 DVTEloisa TardioNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome Treatment & Management - Approach Considerations, Acute NephroDocument5 pagesNephrotic Syndrome Treatment & Management - Approach Considerations, Acute NephroErvirson Jair Cañon AbrilNo ratings yet
- ERCP ExplainedDocument4 pagesERCP ExplainedMichelle TamorNo ratings yet
- Toxic and Metabolic Disorders of The Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesToxic and Metabolic Disorders of The Nervous SystemBenj Ricafrente IIINo ratings yet
- IVMS ICM-Heart MurmursDocument22 pagesIVMS ICM-Heart MurmursMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- A Soft-Tissue Cephalometric Analysis and Its Use in Orthodontic Treatment Planning. Part IDocument28 pagesA Soft-Tissue Cephalometric Analysis and Its Use in Orthodontic Treatment Planning. Part IJorge Ramírez100% (1)
- Worldwide Trends in Diabetes Since 1980Document484 pagesWorldwide Trends in Diabetes Since 1980L P Lozada MartinezNo ratings yet
- Or-Indicator Measure Profile-Kpi-6.4 Day Surgery Conversion To AdmissionDocument2 pagesOr-Indicator Measure Profile-Kpi-6.4 Day Surgery Conversion To Admissionangeli punoNo ratings yet
- Beltran, Justin KyleDocument4 pagesBeltran, Justin KyleKYLENo ratings yet
- A+P CHP 15 QuizDocument8 pagesA+P CHP 15 QuizGennaroNo ratings yet
- Anamnesis SampleDocument7 pagesAnamnesis SampleKaloy Kamao100% (2)
- Twin Block 3Document2 pagesTwin Block 3GisselaMaldonadoNo ratings yet