Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Downloads Course Info Award UMTS302 Mastering UMTS Core Networks R99 To R7
Uploaded by
Shiva KumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Downloads Course Info Award UMTS302 Mastering UMTS Core Networks R99 To R7
Uploaded by
Shiva KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Mastering UMTS Core Networks (R99 to R7)
Instructor Led | Duration: 3 Days | Course Number: UMTS302
UMTS (WCDMA), an evolution of GSM and GPRS, created a platform to converge the worlds of speech, data services and the Internet, to create a global market for mobile multimedia. This course contains an overview of the evolved core networks in different releases of UMTS from Release 4 to Release 7. Release 4 is considered a stepping stone to an All-IP network with a separation of the MSC into an MSC-server and a media gateway. An overview of UMTS and its vision for the next generation all-IP multimedia networks known as IP Multimedia Subsystems (IMS) and the various concepts used in IMS architecture, functions, components and interfaces are covered. Enabling technologies such as SIP, MEGACO and IPv6 and the use of these technologies within the IMS architecture will be studied. A discussion of Quality of Service (QoS) follows, with a presentation of key protocols and the scenarios associated with QoS.
Intended Audience
This course is intended for those in design, development, engineering and product management on UMTS core networks.
Course Outline
1. R99 UMTS Architecture
1.1. UMTS network architecture 1.2. UMTS releases and their goals 1.3. UMTS circuit and packet switched domains
7. Services Architecture
7.1. Services architecture and role of application servers 7.2. Subscriber profiles and triggers
Learning Objectives
After completing this course, the student will be able to: Identify the driving forces, requirements and goals of the UMTS evolved core networks Describe the building blocks used to construct Release 5 List the functions of the UMTS Release 5, Release 6 and Release 7 architecture Explain the signaling and transport protocols like SIP, BICC, Megaco and RTP Step through end-to-end service establishment flows in the Release 5, Release 6 and Release 7 architectures Explain the scenarios that illustrate interworking with the PSTN and legacy wireless networks Identify various services that are supported in Release 6 Describe how session border controller enables access of a common IMS network with different access technologies like cdma2000, WiMAX, etc. Explain Voice Call Continuity (VCC) which enables an IMS subscriber on a VoIP call to continue the call into a circuit switched environment Describe reduction of latency in Release 7 with a simplified architecture
8. R6 Enhancements to IMS
8.1. 8.2. 8.3. 8.4. New services Group management QoS enhancements Session border controller
2. R4 Bearer Independent CS Core Network
2.1. Motivation of Release 4 2.2. Reference architecture 2.3. Signaling and transport
9. R7 One Tunnel Architecture
9.1. Different options 9.2. Interface changes 9.3. Scenarios
3. R5 IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) Architecture
3.1. Motivation for Release 5 3.2. Architecture, components and functions 3.3. Interfaces and protocols
10. Voice Call Continuity
10.1. Architecture 10.2. Scenarios
4. IMS Signaling and Transport Protocols
4.1. SIP, SDP and MEGACO 4.2. Use of SIP and MEGACO in UMTS 4.3. RTP and RTCP
5. IMS Scenarios
5.1. 5.2. 5.3. 5.4. Registration Call origination and termination Roaming and handovers PSTN and UMTS IMS
6. Quality of Service
6.1. QoS techniques (IntServ, DiffServ) 6.2. End-to-end QoS architecture 6.3. QoS allocation scenarios
v1.0
Suggested Prerequisites
Exploring UMTS (WCDMA) (Instructor Led)
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Configure BIND As A Private Network DNS Server On Ubuntu 14Document17 pagesConfigure BIND As A Private Network DNS Server On Ubuntu 14ashblessNo ratings yet
- Az 700Document323 pagesAz 700Thilina Android100% (1)
- How To Setup A Routed IPSEC VPN Tunnel From Juniper SRX UTM Firewall To Draytek 2820 ADSL Firewall RouterDocument7 pagesHow To Setup A Routed IPSEC VPN Tunnel From Juniper SRX UTM Firewall To Draytek 2820 ADSL Firewall Routeraahoo86No ratings yet
- Instructor Materials Chapter 7: IP Addressing: CCNA Routing and Switching Introduction To Networks v6.0Document21 pagesInstructor Materials Chapter 7: IP Addressing: CCNA Routing and Switching Introduction To Networks v6.0Honey ShineNo ratings yet
- ATN905 Data SheetDocument4 pagesATN905 Data SheetCHENOINo ratings yet
- Cse C NW MCQDocument11 pagesCse C NW MCQbasualok@rediffmail.comNo ratings yet
- Lab 10.2 - Configure IPv6 Addresses On Network DevicesDocument4 pagesLab 10.2 - Configure IPv6 Addresses On Network DevicesRecky JimmyNo ratings yet
- 2.wirelessdatagramprotocol PDFDocument9 pages2.wirelessdatagramprotocol PDFPillarisetty PremsaiNo ratings yet
- Networking Essentials - DHCPv4 ConfigurationDocument1 pageNetworking Essentials - DHCPv4 ConfigurationРахат ЕрежеповNo ratings yet
- 124MCAVSDocument368 pages124MCAVSvr0ssi46No ratings yet
- Manual ZyXEL P-660R-T1 v3.40.Pdf1Document302 pagesManual ZyXEL P-660R-T1 v3.40.Pdf1Juan Sampertegui MoralesNo ratings yet
- Hows To Set Up SSH ServerDocument72 pagesHows To Set Up SSH Serversignup101No ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Routing and Switching - Introduction To Networks Final Exam - CisacadDocument27 pagesCCNA 1 Routing and Switching - Introduction To Networks Final Exam - CisacadplayonteamNo ratings yet
- 11 XX SM61 AAM61Document57 pages11 XX SM61 AAM61belle1405No ratings yet
- Virtual Chassis Fabric Best Practices Guide: Modified: 2018-07-03Document36 pagesVirtual Chassis Fabric Best Practices Guide: Modified: 2018-07-03itnewclassNo ratings yet
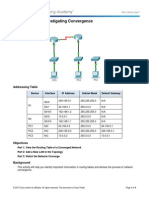
- 3.1.3.6 Packet Tracer - Investigating Convergence InstructionsDocument4 pages3.1.3.6 Packet Tracer - Investigating Convergence InstructionsJosCarr1497No ratings yet
- Solved - Connected To - Ip Address - But Connection Died. (#4.4.2) - Experts ExchangeDocument12 pagesSolved - Connected To - Ip Address - But Connection Died. (#4.4.2) - Experts ExchangeIndopalsNo ratings yet
- Distance Vector Routing ExampleDocument24 pagesDistance Vector Routing ExampleAbhiram SayaniNo ratings yet
- 2.3.2.7 Lab - Configuring Basic PPP With AuthenticationDocument17 pages2.3.2.7 Lab - Configuring Basic PPP With AuthenticationTony Blanco100% (1)
- How To Forward GRE Traffic Over IPSec VPN TunnelDocument5 pagesHow To Forward GRE Traffic Over IPSec VPN TunnelAdrian MafteiNo ratings yet
- Campus Network For High Availability Design Guide PDFDocument62 pagesCampus Network For High Availability Design Guide PDFguesieroNo ratings yet
- Foot PrintingDocument16 pagesFoot PrintingadmingandaNo ratings yet
- FortigateDocument234 pagesFortigaterkgraman86No ratings yet
- Net StatDocument32 pagesNet Statemil1970No ratings yet
- Voip 2 GSMDocument46 pagesVoip 2 GSMmotaz_omar9651No ratings yet
- Roll - No:43358 - Batch: BE-IT 11-S11Document47 pagesRoll - No:43358 - Batch: BE-IT 11-S11pooja PatilNo ratings yet
- Iscom2900 Series Configuration Guide (Rel 10) PDFDocument526 pagesIscom2900 Series Configuration Guide (Rel 10) PDFLavin DevnaniNo ratings yet
- Tutorial SubnettingDocument6 pagesTutorial SubnettingOttou EmmanNo ratings yet
- Subnetting Class C AddressesDocument6 pagesSubnetting Class C Addresseschowsaj9No ratings yet
- Assignment 5 Slides - 1Document12 pagesAssignment 5 Slides - 1Alex TengNo ratings yet