Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Malformations Summary G.Ponce
Uploaded by
teethexpertiseOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Malformations Summary G.Ponce
Uploaded by
teethexpertiseCopyright:
Available Formats
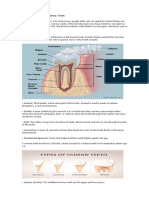
Condition NatalTooth RigaFedeApathae
Classification AbnormalEruption AbnormalEruption
Definition&Etiology Anytoothpresentatbirth. Asmallulcerationontheundersurfaceofthetongue.Occurs duetocontactofenonatalornatalteethwiththetongue, typicallyduringsucking/feeding. Crooked,stagnated,oranglederuptionofteeth. Tissuetag;tissuelayingoverdentition
MostCommonlySeen
Comments Observedwithwhoopingcoughanddiphtheria,butnot explainedwhy.
EctopicEruption Operculum EruptionHematoma
AbnormalEruption AbnormalEruption AbnormalEruption
Maxillarycanines(palpableat910years) Fromtheretromollarpads,especiallyontopof wisdomteethorsecondmolars.
Canoftenleadtodamageandstagnation.
Ankylosis
AbnormalEruption
Ared,bloodfilledblisteroftheoralgingiva,oftencontaininga toothbud(ie.Astagnantbloodpoolaroundthedevelopmentof atooth). Whenteethbecomestuck.Causedbythefusionoftherootto Deciduousmolars thebone,withnoresoptionoccurings.
Couldbereferedtoas'bloodblisters'.
Toothcannotmove,andtheheightitstopsatisthe heightitachieves.Txforchildrenrequiresmonitoring andpossibleextractionofthetoothtopermit permenantdentitionerruption.Txforadultsmayalso involvesurgeryifconditionleadstocomplications. Comments
Condition Microdontia
Classification NaturallyOccuringVariation
Definition&Etiology
MostCommonlySeen
Teeththatareundersizedcomparedtotheircontralateraltooth PrimarilyseenasapeglateralSecondmostcommon Geneticallyinheritedinmostcases(familialtrait).It formiswithinthe3rdmolars. couldbesaidthatisolatedtypeisamerepresenceof oropposingtooth,oftenbilateral(ie.Atoothdoesnot"fill"its spaceinthedentalarch).Itcouldbeuniformtothearchesor anundersizedtoothinthedentition,whilegeneralized isolated. type(truetype)iswhenthejawisregularilysizedwith smallteeth.Truegeneralizedcasesoccuronlywith dwarfismandcancertreatmentduring morphodifferentiation. Coneshapedlateralincisor(conicalandpossiblytapered). Seeninmicrodontia Truegeneralizedcasesmayresultfrompituitary gigantismduringmorphodifferentiation. Conditionfoundin'ElephantMan'.
PegLaterals Macrodontia
NaturallyOccuringVariation NaturallyOccuringVariation
Teeththatareoversizedcomparedtotheircontralateraltoothor Incisorsandmadibular3rdmolars. opposingtooth. Theoccuranceofmacrodontiaononesideofthedentalarch, withtheothersideofthearchcontainingnormalteeth (unaffected). Overproductionofcementum(toomuchcementum).Associated Permenantmolars withtrauma,localorsytemicmetabolicdisturbancesand commonlywithchronicinflammationofpulp. Unusuallongpulpchamberthatmayextendintotherootareaof anormalsizedtooth. Asnamedescribes. Anextracusponananteriortooth. Mainlyfoundonmaxillarylaterals,followedby maxillarycentrals.Rarelyfoundonprimary dentition. Commonlyseenonthe3rdmolars.
Hemihypertrophy
NaturallyOccuringVariation
Hypercementoses
NaturallyOccuringVariation
Occursaftereruption.
Taurodontisum ExcessiveEnamel TalonCusps
NaturallyOccuringVariation NaturallyOccuringVariation NaturallyOccuringVariation
Alsoknownasbullorprisimteeth.Cancauseproblem forendodonics andtooth extractions.
AccessoryCusp EnamelPearls
NaturallyOccuringVariation NaturallyOccuringVariation
Extracuspsonatooth. Enameldepositsonareasenameldoesnotnaturallyoccur(ex. Onarootsurface).
CouldincludeTalonCusps,CuspofCarbabelli,orDens evaginatus. Notcommoninteethwithasingleroot.
Condition PulpPolyps
Classification CausesofAcquiredVariations
Definition&Etiology Soft,red,nonpainfulpolypsonthegingiva.Itisahyperplastic inflammatoryresponseofanopenpulpchambertochronic bacterialinfection. Severedecayofdeciduousteethofachild.Causedbyfeeding childbeveragesandfoodhighinfermentatablecarbohydrates. Carieswithinthepit&fissuresofatooth.Unroughingtheenamel willrevealsoftdentinaldecay.If>30%decaycouldeatthrough tothepulp. Abrokentooth,oftenduetoseverephysicaltrauma. Causeofdentitiondamage.
MostCommonlySeen
Comments
EarlyChildhoodCaries(ECC)
CausesofAcquiredVariations
Commonlyseenoncaseswhereextensivecariesare Txofapulppolypinmanycasescaninvolveeitherroot presentondeciduousteethand6yearmolars.Can canaltherapyorextractionofthetooth. affectpermenantdentition. Worthnotingthatfacialcariesneedssignificant attentionastheyarethelastsurfacesformingcaries.
Pit&FissureCaries
CausesofAcquiredVariations
FracturedTeeth Trauma Attrition
CausesofAcquiredVariations CausesofAcquiredVariations CausesofAcquiredVariations
Asymmetryintraumaishardtospeculateacausefor. Acceleratedbybruxism(grindingoftheteeth)ororal habbits. Commonlycausedbythirdpartyinstrumentssuchas toothbrushes,pipes,clamps,etc.
Abrasion
CausesofAcquiredVariations
Physiologicalconditioncausedbychronictoothfriction.Caused Commonlyseeninyoungchildrenortheelderly bynormalwearandtear.Leadstolossoftheocclusalorincisal population. toothstructure. Lossoftoothstructureduetoabnormalmechanicalwear.Itisa slowandchronicprocess.Commonlycausedbytoothbrush abrasionatthecervicalportionofthefacialaspect. Lossoftoothstructurecausedbychemicalaction(typicallya loweringofthepH). Excessivevomitingduetoexternalfactors.Causeserosionof teethduetotheacidity/lowpHofstomachcontents. Buccalandlingualsurfacesarecommonlyaffected.
Erosion ChronicRegurgiataion
CausesofAcquiredVariations CausesofAcquiredVariations
Patternoferrosionoftenindicatesthecausativeagent.
Condition Anodontia
Classification AnomaliesinNumbers
Definition&Etiology Thecompleteabsenceofteeth.Arareconditionthatisoftensex linked.
Patientssufferingfrombulimia,anorexia,pregnancy, Worthnotingthatmandibularteethareoftennot hiatalhernias,etc. errodedastheyareshieldedbythetongueduring regurgitation(tongueoftencoversmandibularsand alsodirectsstomachcontentstowardsmaxillaryteeth instead). MostCommonlySeen Comments Associatedwithectodermdefects,resultingin loss/defectsonotherstructuressuchashair,sebaceous glands,andsweatglands).Thetermpartialanodontia isincorrect. Commonlyoccursinthepermenantteeth,butalso Approx.5%ofthepopulationisaffectedwiththisasa withintheprimarydentition.Seeorderofoccurance hereditaryfactor.Txcommonlyinvolvesorthodontic forteethunderoligodontia (below). treatmentandinsomecasesusedof implants/bridges/etc. Mostcommonlyoccursinthepermanent3rd molars,permanentmaxillarylaterals,and permentantmandiubular2ndpremolars(more mostoccuringtoleast,respectively).Rarelyoccursin primarydentition,butcanoccurontheprimary mandibularcentralincisor.
Hypodontia
AnomaliesinNumbers
Congenitalabsenceofoneorafewteeth(3orlessteeth).
Oligodontia
AnomaliesinNumbers
Congenitalabsenceof4ormoreteeth.
Hyperdontia
AnomaliesinNumbers
Presenceyofsupernumeracyteeth,thatistosay,extrateeththat Frequnetlyaffectsthepermenantdentition.Inrarer Aka.Supernumeracyteeth.Commonlyoccursas mediodems.Teethmaybeeruptedorimpacted.Tx wouldnotbepresentinthenormaldentition. casesaffectstheprimarydentition.Itis8times morepresentinthemaxillaryarch. commonlyincludesoralsurgeryforremovalof supernumeracyteeth,andsometimesorthodontic workduetocommoncrowdingcausedbyextrateeth. Amalformed,peglikestructurethatoccursbetweenthe maxillarycentralincisors. Oftenoccursincasesofhyperdontia.
Mesiodems
AnomaliesinNumbers
EctodermalDysplasia
AnomaliesinNumbers
Agroupofconditionsinwhichthereisabnormaldevelopmentof theskin,hair,nails,teeth,orsweatglands. Definition&Etiology MostCommonlySeen
Thesearethestructurestypicallydevelopedlastin development. Comments Aka.Toothwithinatooth.Canclincallyappearasa deepcreviceoraccentuatedlingualpit.Txtypically includesendodonicintervention.
Condition DensinDente
Classification AnomaliesinShape
Dilaceration
AnomaliesinShape
Flexion
AnomaliesinShape
Maxillarilylaterals. Enamelanddentinofacrowninvaginateorfoldonitselfinan apicaldirectiontowardsthepulpchamberonthelingualaspect ofthetooth.Oftenbilateral. Developmentdisturbancesintheshapeoftheteeth,often Oftenseeninsupernumeracyteeth(hyperdontia) angulationorasharpcurveintherootorcrownofthetooth(not andinteethwithaccessoryroots. linear).Causedbytraumaand/orpressuretothedeveloping tooth. Distortionofonlytherootstructure.Likedilaceration,thisisalso causedbypressureand/ortraumatothetoothbutoccurslaterin development,causingsharpbends. Anincompletelydivided(bifid)crown,withtheaffectedtooth Oftenseenintheprimarymandibularincisorsand stillhavingasinglerootandacommonpulpcavity.Canappear permenantmaxillaryincisors. 'fused'. Affectsprimarymorethanpermenantdentition, Unionoftwoadjacentteeth,whereintworootsandtwopulp cavitiesarepresent.Teethappear'fused'.Thoughttobecaused withtheanteriorteethmostcommonlyaffected. bypressureorforce. Twoormoreteethjoinedthroughthecementumonly.Causedby Commonlyseeninthepermenantmolars,especially excessivecementumdeposition. themaxillarymolars. Asignofcongenitalsyphilis,teetharesmallerandmorewidely spacedthannormal,withnotchesontheirbitingsurfaces. Rootswhichareabnormallyshort(whilecrownsremainnormal size). Extracuspsonthesurfaceofatooth. Extrarootsonatooth.Canleadtodilaceration. Theabsenceofanormallypresentcusponatooth. Commonlyseenonanteriorteeth,especially maxillarycentrals. Commonlyseenonthe3rdmolars. Commonlyseenonthe3rdmolars,butcanalso occuronotherteeth. Oftenseenforthelingualcuspofthemandibular firstmolar,thedistolingualcuspofthemaxillary molars,andthedistalcuspofthemandibular1st molars.
Notcommonlyrecognizedasadentalterm.Itisworth notingthatflexioncancausetraumato underlining/adjacentdevelopingteeth. Donotconfusewithfusion(onevs.tworoot/chamber).
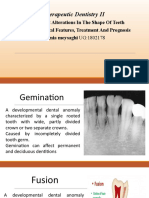
Gernination
AnomaliesinShape
Fusion
AnomaliesinShape
Donotconfusewithfusion(twovs.once root/chamber). Ifonetoothofthetwo(ormore)needstobeextracted, surgicalseperationoftheteethmayberequired. Onanteriors,incisaledgeappearsnotched,whileon posteriorteeth,occlusalsurfaceappearsgnarled,with poorlydevelopedcusps. Thoughttobehereditary.Shortrootsmayleadto shortenedclinicallifeforaffectedteeth. CouldincludeTalonCusps,CuspofCarbabelli,orDens evaginatus.
Concresence
AnomaliesinShape
Hutchinson'sTeeth
AnomaliesinShape
DwarfedRoots AccessoryCusps(Tubercles) AccessoryRoots MissingCusps
AnomaliesinShape AnomaliesinShape AnomaliesinShape AnomaliesinShape
EnamelPearls Condition EnamelDysplasia
AnomaliesinShape Classification AnomaliesinStructure
Enameldepositsonareasenameldoesnotnaturallyoccur(ex. Onarootsurface). Definition&Etiology Abnormalenamelformation,characterizedbybands,ridges,or pittedareasofdicoloredenamel.Thoughttobehereditary, causedsystemically(drugs,infection,nutirition)orlocally (trauma,periapicalinfections). Anenameldefectthatcausessoft,undercalcifiedenamel. Appearsopaque,softandchalky.Canbecausedbydefective maturationofameloblasts. Enamelhypoplasia/underdevelopedenamelofapermenant tooth.Typicallycausedbyinjuryofadevelopingtoothbud throughtraumaoraperiapicalinfectionaroundadecidious tooth.
Notcommoninteethwithasingleroot. MostCommonlySeen Comments
Hypocalcification
AnomaliesinStructure
Canoccuronbothprimaryandpermenant dentitions.
Turner'sTooth
AnomaliesinStructure
Surfacescanwearrapidlyandaremoresusceptableto caries.Affectedteeth(white,chalkybands)canindicate atwhatpointindevelopmenthypocalcification occurred. Aside:Usuallyonlyaffectsonetooth.
DentalFluorosis
AnomaliesinStructure
AmeleogenesisImperfecta
AnomaliesinStructure
Causedbyexcessivefluorideintakeduringenamelcalcification (manytimesgreaterthan1ppm/levelsfoundinwatersupply). Usuallyinvolvesallteeth.Canleadtodiscolourationoftheteeth. Chalkyisamildcase,andmoderatecasesleadtobrown spots/bands. Completetopartialabsenceofenamelthatdoesnotmature. Crownsappearastrongshadeofwhite,yellowbrown,pitted,or grooved.Thisconditionishereditary.
Causedbyflourideionincorperationratherthan hydroxylion,causingformationoffluorapatiterather thanhydroxyapetite.Fluorapatiteislesssolublein acidicenviornment,preventingdentalcaries. Ararecondition.Withnoenamel,thedentinisaquick targetforattrition,abrassion,orboth.Alsosuspectable torampantcariesandsensitivity.
DentinalDysplasia
AnomaliesinStructure
DentinogenesisImperfecta
AnomaliesinStructure
Abnormaldentinformation.Thoughttobehereditary,caused systemically(drugs,infection,nutirition)orlocally(trauma, periapicalinfections). Lackofdentinogenesis.Causescrownoftoothtoappearbluish Affectsallorsomeoftheteeth,beitpermenantor Patientissubjecttogreaterchanceofattrition. brownincolour(opalescence).Enamelisnormalbutbreaksapart primarydentition. easily.Pulpchambercanbecomebrittleduetoobliteration, leadingthestructuretobemorebrittleduetolackofnutrition. Theenameltendstoseperatefromthedentin.Conditionis hereditary. Stainingoftheteethcausedbytheuseoftheantibioticdrug tetracyclineduringprimaryorpermenanttoothdevelopment. Seenasadarkgrayshadeinareasexposedduringdevelopment (discolouredbyexposuretoUVlight). Definition&Etiology MostCommonlySeen Tetracyclinecanbeusedlongorshorttermon individualswhenrequired,buttheissueiswhenthisis donebeforetheageof8.
TetracyclineStaining
AnomaliesinStructure
Condition
Classification
Comments
You might also like
- Developmental Anomalies of TeethDocument78 pagesDevelopmental Anomalies of TeethPauline Joy Cayago CastilloNo ratings yet
- Fissured TongueDocument0 pagesFissured Tonguepink_grcq_sssttt4836No ratings yet
- Anatomic Anomalies - LectureDocument10 pagesAnatomic Anomalies - LectureKhalid BhatNo ratings yet
- Dr. O.M Ogundana Dept of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology/BiologyDocument62 pagesDr. O.M Ogundana Dept of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology/BiologyoladunniNo ratings yet
- CURS 5 Teething Problems and Their ManagementDocument61 pagesCURS 5 Teething Problems and Their Managementtaliya. shvetzNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic IIDocument11 pagesTherapeutic IIkimiaNo ratings yet
- Developmental TeethDocument53 pagesDevelopmental Teethlyli Star AngeloNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disorders: Dr. Chakshu Aggarwal (MDS) SNR Lecturer Oral PathologyDocument38 pagesDevelopmental Disorders: Dr. Chakshu Aggarwal (MDS) SNR Lecturer Oral PathologydrchakshuaggarwalNo ratings yet
- Pedo2013 14Document189 pagesPedo2013 14Vladimir Argirovic100% (4)
- Oral Cavity: PartsDocument10 pagesOral Cavity: Partsnanda adiNo ratings yet
- Oral PathologyDocument184 pagesOral Pathologyyalahopa100% (1)
- Non-Caries Dental DiseaseDocument61 pagesNon-Caries Dental Diseaseapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Armin HedayatDocument2 pagesArmin HedayatarminhedayatnetNo ratings yet
- Malocclusion (2nd Concept Map)Document4 pagesMalocclusion (2nd Concept Map)Stephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- DentalDocument7 pagesDentalLatifaNo ratings yet
- 174 Anatomy Teeth and GumsDocument20 pages174 Anatomy Teeth and GumsMehri Aisha ShanavasNo ratings yet
- Structure of Teeth: Khushi Desai III BDS 808Document36 pagesStructure of Teeth: Khushi Desai III BDS 808Khushi DesaiNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Dental Anomalies on RadiographsDocument52 pagesInterpreting Dental Anomalies on RadiographsyongkyNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of TeethDocument24 pagesAbnormalities of TeethRoshni ButalaNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of Teeth Eruption, Structure, Form, Number, and SizeDocument48 pagesAbnormalities of Teeth Eruption, Structure, Form, Number, and SizeNoor AlsanouriNo ratings yet
- Enamel and Dentine Maria BarraganDocument19 pagesEnamel and Dentine Maria Barraganjobar60No ratings yet
- Sakeena Assad PresentationDocument93 pagesSakeena Assad Presentationjenny girlNo ratings yet
- Dental Issues and Treatments in AnimalsDocument38 pagesDental Issues and Treatments in AnimalsAdarshBijapurNo ratings yet
- APznzabu1Ci9p9yRpxFqJSukJAe2 6rzeDQRKy GGsZNB1jUFPKmnLhAb3H17ZdDocument24 pagesAPznzabu1Ci9p9yRpxFqJSukJAe2 6rzeDQRKy GGsZNB1jUFPKmnLhAb3H17Zdclassybrands0No ratings yet
- Naim Oral CareDocument34 pagesNaim Oral Carenaim157No ratings yet
- $pediatric Dentistry dd2011-2012 DR GhadeerDocument96 pages$pediatric Dentistry dd2011-2012 DR GhadeerGhadeerHassaanNo ratings yet
- Teething: Krishna Chauhan 55 3 YearDocument29 pagesTeething: Krishna Chauhan 55 3 YearkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Teeth Developmental DisturbancesDocument97 pagesTeeth Developmental DisturbancesEmad AlriashyNo ratings yet
- Variation in Tooth Morphology Anatomy PDFDocument9 pagesVariation in Tooth Morphology Anatomy PDFadriiianaiiioanaNo ratings yet
- Regressive Alterations of TeethDocument3 pagesRegressive Alterations of TeethBhaveshNo ratings yet
- Oral Path PDFDocument367 pagesOral Path PDFAashka Desai100% (2)
- Developmental Disorders of TeethDocument64 pagesDevelopmental Disorders of TeethPatterson MachariaNo ratings yet
- Dental AnomaliesDocument62 pagesDental AnomaliesRanjanNo ratings yet
- Etiologic Factors of MalocclusionDocument25 pagesEtiologic Factors of MalocclusionBibek RajNo ratings yet
- PEDIATRIC PATHOLOGY TITLEDocument27 pagesPEDIATRIC PATHOLOGY TITLERayne GelleNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disturbances of TeethDocument65 pagesDevelopmental Disturbances of Teethisraa0dentist100% (4)
- Classification of Anomaly2Document213 pagesClassification of Anomaly2samar yousif mohamed100% (1)
- 10 - Nose, Mouth, and ThroatDocument25 pages10 - Nose, Mouth, and ThroatArka Ogeh100% (1)
- Dental Anomalies Related To Shape of TeethDocument54 pagesDental Anomalies Related To Shape of TeethFasina AbubackerNo ratings yet
- Dental Plaque: Dental Diseases and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease and MortalityDocument54 pagesDental Plaque: Dental Diseases and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease and MortalityNabilah ZulkiflyNo ratings yet
- Anamolies of Formation and Eruption For Class 22Document76 pagesAnamolies of Formation and Eruption For Class 22Nihaz 72No ratings yet
- About Oral Health.Document1 pageAbout Oral Health.nicolelo418bbNo ratings yet
- مصطلحات طب الاسنان dental termsDocument15 pagesمصطلحات طب الاسنان dental termsAyedAlfalah100% (1)
- Armin HedayatDocument1 pageArmin HedayatarminhedayatNo ratings yet
- Common Equine Dental IssuesDocument11 pagesCommon Equine Dental IssuesdwataNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Basic of Dentistry: TeethDocument2 pagesWeek 5 - Basic of Dentistry: Teethnoelah salcedoNo ratings yet
- Principle of Maxillary Impacted Teeth: Done By: Yamamh Emad Hadeel Luay Yaseen TareqDocument26 pagesPrinciple of Maxillary Impacted Teeth: Done By: Yamamh Emad Hadeel Luay Yaseen TareqB AlhashimiNo ratings yet
- OM3 Skenario 2Document15 pagesOM3 Skenario 2Jennifer Abella BrownNo ratings yet
- Careis Dentis 2Document3 pagesCareis Dentis 2zayNo ratings yet
- Enamel Defects and Clinical ConsiderationsDocument51 pagesEnamel Defects and Clinical ConsiderationsBarnali Misra50% (6)
- What Is Malocclusion?Document24 pagesWhat Is Malocclusion?Bibek RajNo ratings yet
- 174 Anatomy Teeth and GumsDocument20 pages174 Anatomy Teeth and GumsRhona AngelaNo ratings yet
- Equine / Horse Dental Problems: Sharp EdgesDocument13 pagesEquine / Horse Dental Problems: Sharp EdgesdwataNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disturbances of TeethDocument45 pagesDevelopmental Disturbances of TeethAmritha JamesNo ratings yet
- Classification of Tooth Discolouration Causes and MechanismsDocument14 pagesClassification of Tooth Discolouration Causes and MechanismsSARINAHNo ratings yet
- Neurofisiologia Oclusion Dental: PictureDocument10 pagesNeurofisiologia Oclusion Dental: Picturefegi dwiyantiroNo ratings yet
- Impacted Wisdom Tooth, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandImpacted Wisdom Tooth, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Absen Metod!!!Document4 pagesAbsen Metod!!!Haris Pratama RebornNo ratings yet
- HerpesDocument9 pagesHerpesTilak ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cultivation of Super Food Spirulina Blue-Green Algae An AgribusinessDocument8 pagesCultivation of Super Food Spirulina Blue-Green Algae An AgribusinessRupesh Kumar100% (1)
- Tissue RepairDocument9 pagesTissue RepairSakidu LegionNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis SchizophreniaDocument2 pagesCase Analysis Schizophreniamark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Heaven & Earth Spa Treatments Under 40Document2 pagesHeaven & Earth Spa Treatments Under 40Janhavi SoniNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance in Radiation Therapy: Simulators & Ancillary EquipmentDocument82 pagesQuality Assurance in Radiation Therapy: Simulators & Ancillary EquipmentnefziNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical: Phytochemicals As Candidate NutrientsDocument3 pagesPhytochemical: Phytochemicals As Candidate Nutrientssempreaprender3701No ratings yet
- Rol HPNDocument5 pagesRol HPNOamaga NajlaNo ratings yet
- Classification Criteria For SLE PDFDocument4 pagesClassification Criteria For SLE PDFCocea MihaiNo ratings yet
- Category-Wise Opening & Closing Rank-Ayur - BHU Int.Document5 pagesCategory-Wise Opening & Closing Rank-Ayur - BHU Int.srikanth PosaNo ratings yet
- What Is Malnutrition?: WastingDocument6 pagesWhat Is Malnutrition?: WastingĐoan VõNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of A Anxiety Disorder PDFDocument7 pagesPathophysiology of A Anxiety Disorder PDFpragna novaNo ratings yet
- CPC PowerpointDocument36 pagesCPC Powerpointapi-277377339No ratings yet
- MMPI-2 Validity ScalesDocument7 pagesMMPI-2 Validity ScalesEspíritu Ciudadano50% (2)
- Interpersonal PsychotherapyDocument21 pagesInterpersonal PsychotherapyDr. Jayesh PatidarNo ratings yet
- 250 Medical Office Procedures R 2014Document6 pages250 Medical Office Procedures R 2014api-250674550No ratings yet
- Course Plan MSNDocument27 pagesCourse Plan MSNSanthosh.S.UNo ratings yet
- Emergency Psychiatry Other Than Suicide: Dr. Pooja Singh, MD Assistant ProfessorDocument45 pagesEmergency Psychiatry Other Than Suicide: Dr. Pooja Singh, MD Assistant Professorpooja singhNo ratings yet
- Full Mouth Reconstruction - by John UtamaDocument11 pagesFull Mouth Reconstruction - by John Utamajutama8289No ratings yet
- Sop Icu H & FW 12725 28.04.2018Document20 pagesSop Icu H & FW 12725 28.04.2018shah007zaadNo ratings yet
- HNS 107Document95 pagesHNS 107claudette1882No ratings yet
- Bladder StonesDocument20 pagesBladder StonesRiean AuliaNo ratings yet
- A2z Company ProfileDocument90 pagesA2z Company ProfileChandan Srivastava100% (1)
- Yakima Co (WA) Protocols 2010Document117 pagesYakima Co (WA) Protocols 2010Anthony James-Hartwell100% (1)
- DisolusiDocument47 pagesDisolusiNoonaNuzha Lestary NuzhaAyuNo ratings yet
- For Older People, Medications Are Common AGS Beers Criteria Aims To Make Them Appropriate, TooDocument3 pagesFor Older People, Medications Are Common AGS Beers Criteria Aims To Make Them Appropriate, TooindriNo ratings yet
- Events Prevented Calculator OverviewDocument5 pagesEvents Prevented Calculator OverviewAlvaro MuñozNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Waste ManagementDocument14 pagesBiomedical Waste ManagementdivyeshkpatelNo ratings yet
- IndianJPain3341-1062069 025700Document10 pagesIndianJPain3341-1062069 025700docbinNo ratings yet