Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Disc 2 Chp9 Weep Now
Uploaded by
Brian LinerOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Disc 2 Chp9 Weep Now
Uploaded by
Brian LinerCopyright:
Available Formats
Discovery 2 Chapter 9
Created: November 7, 2011 9.1.1.1 1. What do many technicians use to help isolate the cause of a problem when troubleshooting? 9.1.1.2 2. What do the upper layers (5-7) of the OSI model deal with? 3. Problems isolated to these layers can frequently be caused by what? 4. What do the lower layers (1-4) of the OSI model handle? 5. What type of errors account for many problems isolated to these layers? 6. What types of errors occur at Lay 3? 7. What causes most Layer 1 and Layer 2 problems? Complete the activity on 9.1.1.3 Complete the Lab Activity on 9.1.1.4 9.1.2.1 8. List the three main troubleshooting approaches when using network models. 9. Where does the Top-Down troubleshooting method start? It looks at the problem from what point-of-view? 10. Where does the Bottom Up troubleshooting method start? What is the Physical Layer concerned with? A user can access any web page on the Internet but cannot access e-mail. What troubleshooting method would be most efficient for troubleshooting this issue? 11. Where does the Divide-and Conquer troubleshooting method start? Complete the activity on 9.1.2.2 9.1.3.1 12. What does a physical network topology show? 13. List the six things that are typically included in a physical network topology. They use the OSI and TCP/IP net models Specific application functionality and implemented only in software End system software configuration Data-transport issues 3-4 are software errors on end systems. Ip addy errors on Layer3. Layer1-2 are both hardware and software Ip addy errors Cabling issues also hardware problems and incompatibility 1. Top-down 2. Bottom up 3. Divide and conquer Starts at the application layer and works down. It looks from the users point of view -Starts at the physical layer and works up. Concerned with hardware and wire connections - A top down method would work best for that
In the middle and works its way up or down depending on the IT hypothesis The physical layout of the devices connected to the network. 1.Device types 2.Models and manufacturers mark 3.Locations 4.OS versions
14. What does a logical network topology show? 15. List the seven things that are typically included in a logical network topology.
9.1.3.2 16. List three ways that CiscoWorks can be helpful. 17. What are four examples of commonly used network management tools? Used to check performance 18. What does a protocol analyzer decode?
9.1.3.4 19. What can cable testers detect? 20. What can time-domain reflectometers (TDR) pinpoint? 21. What do Digital multimeters (DMMs) directly measure? 22. What do most multimeter tests involve in network troubleshooting? 23. By plugging a network analyzer into a switch anywhere on the network, what can a network engineer see? 9.1.3.4 24. What can network analyzers also be used to do? 25. When are network analyzers useful? 9.2.1.1 26. What is the Physical Layer, or Layer 1, is responsible for? 27. On an Ethernet network, what happens when two devices to begin sending at the exact same time? 28. When a collision occurs, what do all devices do? 29. Cables that exceed maximum length and that exhibit poor
5.Cable types 6.Cable end points Shows how data is transferred on the net. Symbols used to represent different elements. 1.Device id 2.Ip addy and subnet masks 3.Interface identifiers 4.Routing protocal 5. Static and default routes 6. data-link prot 7.WAN tech 1.Draw network diagrams 2.keep network software and hardware documentation 3.Measure baseline bandwidth 1.CiscoView, and 2. HP Openview 3. SolarWinds 4. WhatsUpGold It decodes the various prot layers in a recorded frame and presents them in a readable format. It captures network traffic and can filter it easily and view specific types or to and from different sources Specialized hand held devices designed for testing the various communication cables The distance to a cable break as well as total length Electric values of voltage, current, and resistance Checking power supply voltage The avg and peak utilization of the segment. Can also see device using the most traffic and verify interface details. Useful for diagnosing malware and DoS attack 1.Diagnosising malware 2.Diagnosising DoS attacks 3.Find who is using the most traffic See 23-24 The physical and electrical specs or transmission (Wired or wirless) A collision occurs and all devices stop transmitting for a random amount of time till the wire clears See 27 Layer 1 (Issues are based off medium used. Fiber and wireless
terminations would be identified as a problem at what layer? 30. List six symptoms of Layer 1 errors. (Look at the buttons in the graphic.) 9.2.1.2 31. What does the Data Link Layer, or Layer 2, specify? 32. What are a couple of possible errors if a host can ping the local loopback address, 127.0.0.1, but cannot access any services over the network? 33. List four symptoms of Layer 2 errors. (Look at the buttons in the graphic.) Complete the activity on 9.2.1.3 9.2.2.1 34. What are the three stages of the bootup process? 35. Where will a router look for the IOS first? Where will a router look for the IOS second? (Look at Step 2 on graphic.) 36. Where will a router look for a config file first? Where will a router look for a config file second? If a config file is not found in either location, what will the router enter? (Look at Step 3 on graphic.) 37. What does show version command display? 38. What does show flash command display? 39. What does show ip interfaces brief display? 40. What do the show runningconfiguration and show startupconfiguration commands verify? 9.2.2.2 41. When a device fails POST what output appears? What happens to the system LEDs? A cable from a new PC is plugged into a switch port and the switchs LED for that port changes to solid green. Why
have their own L1 issues)(Carrier Sense Multi Acces w/ Collision Detection CSMA/CD) Console error messages, Loss of connectivity, high collisions, performance lower then baseline, network bottlenecks, high CPU utilizations Specifies how data is formatted for transmission as well as regulated network access It may be framing issues or a misconfigured NIC card. Check your Layer 2 components 1. More console error msgs 2. Excessive broadcasts 3.Network operating below baseline 4. No connection at Network Layer (NIC or NIC drivers) 1.Perform POST 2.Load IOS 3. Locate/Load startup config or enter setup mode Flash Memory and then a TFTP server??
NVRAM first, then TFTP server, and then console mode if it cant find what its looking for??
Displays the version of the OS and whether all interface hardware is recognized. Displays the contents of the Flash memory including the IOS image. All shows mem used and available Operational status of the device interfaces and IP addies assigned. That all the config commands were recognized during the reload. No output appears. They may change color or blink Port is operational and ready to transmit
9.2.2.3 9.2.2.3
9.2.3.1
9.2.3.1
might be the meaning of the solid green LED? 42. If a router completes the POST The interface module. successfully without the interface modules installed, what probably failed? 43. What is a boothelper? An image designed to load if no IOS file can load. It has limited functionality, but can be used to bring the IOS back online or copy one from a TFTP server 44. What will the device enter if there ROMmon mode is no boothelper? 45. What will the device do if there is Scroll error msgs rapidly or constantly reboot not enough memory to decompress the image? 46. How can the device be forced to Crtl + Break boot into ROMmon mode? 47. What will have to be done to the Replaced or upgraded memory for the device to function normally? 48. How do you know if faulty or Show version command improperly seated interface modules are not recognized during the POST and when the Cisco IOS is loaded? 49. If a valid startup configuration file It broadcasts a TFTP request for a config file. It will cannot be found, what is the purpose of swap to setup mode if none respond after 5 tries and it the autoinstall utility? has an autoinstall ability built in 50. How can the configuration be Either by doing it manually or copying an image from a reloaded or recreated? TFTP server. No traffic till it is set up 51. What commands can troubleshoot Show interfaces and show ip interface brief. router interface errors by examining the statistics recorded on the problematic interface? 52. What does each output for the Up/up status: normal operations and both the media and show ip interface brief command layer 2 prot are functional indicate? (List three) Down/down status: indicates that a connectivity or Also shows device interfaces w/ IP media problem exists addy and interface status Up/Down Status: media is connected properly but the Layer 2 is not functioning or misconfiged What is the meaning of administratively down? Means the no shutdown cmd was never applied 53. What are four common cable or -Loose cables or too much tension media issues that can cause a -Incorrect termination down/down output? -Damaged serial interface connector -Break or short in the cable. 54. What are two common Layer 2 Encapsulation is improperly configured issues that can cause an up/down No keepalives are received on the interface output?
9.2.3.2 55. If the output from the command show interfaces is excessive noise, what type of error is present? What are three causes for these types of errors? 56. If the output from the command show interfaces is excessive collisions, collisions occur on what type of connection? What can cause collisions? 57. If the output from the command show interfaces is excessive runt frames, what is the usual cause for runt frames? 58. If the output from the command show interfaces is late collisions, what are two causes for late collisions? Complete the Lab Activity on 9.2.3.3 9.2.4.1 59. What is the first step in troubleshooting LAN connectivity issues on switches? 60. If the port LED is red or orange, what does it indicate? 61. If no link light is present, what should be ensured? 62. After checking power and swapping patch cables and there is still no link light, what should be verified? 63. What will the command show running-config interface display? 9.2.4.2 64. What does it mean if a port flaps? 65. What command will get a quick view of switch port error statistics? 66. When are duplex mismatches more common? 67. If one device on a link is configured to autonegotiate and the other side is manually configured with speed and duplex settings, what will happen? What will this lead to? 68. What will the command show interface port status view? 9.2.4.2 69. What can be done to correct duplex mismatch errors? Complete the PacketTracer on 9.2.4.3 Complete the Lab Activity on 9.2.4.4 9.2.5.1 70. What command can be used to gather information about most serial
CRC errors. Electrical interference, loose/dmged connectors, or incorrect cable type Half duplex or shared Ethernet. Dmged cables can cause collisions
Malfunctioning NICs are usually the cause (can also be caused in a high collision environment, ex: sharted Ethernet) Excessive cable lengths or possibly duplex mismatches
Make sure that the switch port the user is connected to is active and the LED is lit. Error condition That cables are connected to proper ports on both ends Make sure that the port is not admin down. Shows the parameters configured for that switch port. It loses and regains a link Show interface port counters error On switches more than routers There will be collisions and packets will be lost. Cisco Discovery Prot (CDP) can be loaded onto devices and can be used to help detect errors on local or near machines It will show whether the port is set to auto negotiate speed or if its manually set Set both devices to auto negotiate
Show interfaces serial command
interface and line problems? 71. What are four reasons for problems on serial connections? 72. In order to successfully troubleshoot serial WAN connectivity problems, what is important to know? 9.2.5.2 73. What are the possible problems for the following output of the show interfaces serial command: Serial x is down, line protocol is down (DTE mode) - Use Graphic 74. What are the possible problems for the following output of the show interfaces serial command: Serial x is up, line protocol is down (DTE mode) - Use Graphic 75. What are the possible problems for the following output of the show interfaces serial command: Serial x is up, line protocol is down (DCE mode) - Use Graphic 76. What are the possible problems for the following output of the show interfaces serial command: Serial x is up, line protocol is down (looped) - Use Graphic 77. What are the possible problems for the following output of the show interfaces serial command: Serial x is up, line protocol is down (disabled) - Use Graphic 78. What are the possible problems for the following output of the show interfaces serial command: Serial x is administratively down, line protocol is down - Use Graphic Complete the PacketTracer on 9.2.5.3 Complete the Lab Activity on 9.2.5.4 9.3.1.1 79. What are the primary functions implemented at Layer 3 of the OSI model? 80. Why are Layer 3 networks referred to as logical networks? 81. Where is most of the focus of 1.packet errors 2.config errors 3.mismatched encapsulation 4.timing The type of modem or CSU/DSU unit being used Router not sensing carrier detect signal??
Local or remote router is misconfigured. Keepalives not being sent by remote router. Failed remote or local CSU/DSU Missing clockrate interface config command Failed local/remote CSU/DSU Failed or incorrect cable Router hardware failure A loop exists in circuit. The sequence number in the keepalive packet changes to a random number when the loop is detected initially. If the same random number is returned over the link, a loop exists. High error rate due to TS provider problem. CSU/DSU hardware problem Bad router hardware Routerconfig includes shutdown interface config commands Duplicate IP addy
Network addressing and routing They exist only in software and can pass over any physical medium IP addy errors or routing prot operations
troubleshooting Layer 3 problems concentrated on? 9.3.1.2 82. How are Layer 3 network boundaries determined? 83. What is a simple rule to remember about the network prefix? Complete the Activity on 9.3.1.3 Complete the PacketTracer on 9.3.1.4 9.3.2.1 84. What are some advantages that hierarchical IP addressing schemes offer? 85. What are two conditions that account for many IP addressing and routing issues within networks? 86. How do overlapping subnets occur? 9.3.2.2 87. Although Cisco IOS software does permit you to configure an IP address from overlapping subnets on two different interfaces, what does the router do to the second interface? 88. What will happen if there is an attempt to enable an overlapped interface with the no shutdown command? What happens to the traffic on this interface? 89. What is indicated when an interface that remains administratively down after the no shutdown command is issued? 9.3.2.3 90. What can poorly configured subnet masks cause? Complete the Activity on 9.3.2.4 9.3.3.1 91. What does an administrator often underestimate when designing subnets? 92. What is one indication of a subnet having too many hosts? 9.3.3.1 93. What will a host do when running Microsoft Windows and it does not receive an address from a DHCP server? 94. What will the show ip dhcp binding command check? 95. What is another indication of not enough IP addresses? Complete the Activity on 9.3.3.2
By the number of bites contained in the network prefix of the addy. The longer the network prefix the smaller the range of IP addies for hosts Smaller routing tables to make it easier to process. Its also more structured so its easier to document 1.overlapping subnets 2.incorrectly configured subnet masks When the addy range of 2 subnets include the same ranges It does not activate it.
A second error msg is displayed and no traffic is forwarded
That there is an overlap in the IP assignments.
Hosts will lose access to network resources. The potential for growth DHCP cant give out an IP addy Give itself a 169.254.0.0 link local addy
It will check and see if the DHCP has available addies to give Error message state duplicate IP addies exist
Complete the Lab Activity on 9.3.3.3 9.3.4.1 96. What will the command ipconfig /all verify? 97. What is always the first step in troubleshooting? 98. What will the command show interfaces confirm? 99. How can address conflicts occur even if there are available addresses within the DHCP pool? 100. What will the command show ip dhcp conflict display? 9.3.4.2 101. What does it mean that DHCP is a broadcast protocol? 102. What will the command ip helper-address do on a router? 103. Once this command is configured, what will happen to all broadcast packets? 104. When a router forwards address requests, what is it acting as? If this is not operational, what affect will it have on hosts? 9.3.4.3 105. What is usually the first indication that there is a NAT problem? 106. What are the three types of address translations? 107. What are two common types of configuration errors that affect all three translation methods? 9.3.4.3 108. What does the inside interface connect to? What does the outside interface connect to? 109. What should be configured if external users must be able to reach specific servers on the internal network? 9.3.4.4 110. What is one of the most useful commands when verifying that NAT is operational? 111. What command can be used to clear existing NAT translations? 112. What utility can be used to determine the path that the translated packets are taking and verify that the Verify what IP addies are assigned to windows hosts if any. Check the physical connectivity It will confirm that the interfaces are operational If a host is statically configured within the DHCP pool range All addy conflicts recorded in the DHCP server It must be reachable through a broadcast msg. It will make the router forward DHCP server request broadcast, but turns it into a unicast signal Turned into unicast message with a specific addy DHCP relay agent. If the relay fails no host can get an IP addy Hosts cant reach internet sites Static, dynamic, and PAT Incorrect Designation of Inside and Outside Interfaces Incorrect Assignment of Interface IP addy or Pool Addy Inside connects to the LAN the outside connects to the public network, usually the ISP Static translations are needed.
Show ip nat translation Clear ip nat translation * traceroute
route is correct? Complete the PacketTracer on 9.3.4.5 9.4.1.1 113. List the four issues that typically cause Layer 3 routing problems. 9.4.1.2 114. What are four reasons why the status of a network can change frequently? 115. What is a primary tool to use when troubleshooting Layer 3 routing problems? What will this command display? 116. A routing table consists of route entries from which three sources? Manual route entry errors, routing prot configs, operation errors, or failure at lower layers -Interface fails -A service provider drops connection -available bandwidth is overloaded -Admin enter incorrect config Show ip route Shows all the routes the router uses to forward traffic.
Directly connected networks Static routes Dynamic routing prots 117. How do routing protocols choose Routing prots that chose based on metrics. (Damn which routes are preferred? those metrics) 118. What is the default metric of static Default metric value for directly connected and static routes and directly connected routes? routes are = 0 119. If there is more than one route to a The one with the lowest AD (Administrative distance) specific destination network, which based on the metric used. route is installed into the routing table? 9.4.1.2 120. Any time a routing problem is That the expected routes (the ones with the lowest AD) suspected, what will the show ip route are installed on the table. command ensure? 9.4.1.3 121. When are directly connected Directly connected routes are auto installed when an IP routes automatically installed in the addy is configed on the interface w/ a no shutdown routing table? command. 122. If a directly connected route does It will verify that the addy is assigned and that the not appear in the table, what will the interface is in an up/up state. show interfaces or show ip interface brief commands verify? 123. What is most likely the problem A config error when a static or default route does not appear in the routing table? 124. Why do static routing errors The next hop addy is not the correct IP addy range of sometimes occur? any directly connected network. 125. What could a missing route be Misconfig of on one or more routers on the path to the caused by? destination. Complete the PacketTracer on 9.4.1.4 *** Be able to do simple class C subnetting *** 9.4.2.1 126. When do routing table updates When a new network is configed or an already configed usually occur? one becomes unreachable 127. When does a router access and Anytime a change is reported by a neighbor router or if change its own routing table? the static/default route are manually changed (includes exit interface)
9.4.2.1 132. What can happen when there is a missing or incorrect network statement? 9.4.2.2 133. What TCP/IP utilities are used to verify connectivity? What show command would be helpful? 134. What TCP/IP utility verifies connectivity and make configuration changes? 135. What kind of information do debug commands provide? 136. What kind of information does the debug ip rip command display? 137. Why should debug commands be used to isolate problems, not to monitor normal network operation? Complete the PacketTracer on 9.4.2.3 Complete the Lab Activity on 9.4.2.4 9.5.1.1 138. What is Layer 4 responsible for? 139. Where can Layer 4 network problems arise? 140. What protocols are supported for Layer 4 traffic? 141. What is necessary when denying traffic based on the port number? 142. How do filtering problems occur in firewalls? 143. What is a common indication of Layer 4 problems? Complete the Activity on 9.5.1.2 9.5.2.1 144. The upper layer protocols provide user services that are typically used for what? 145. Protocols at these layers are often referred to as what? Review and know the functionality and responsibility of each of the TCP/IP Application Layer protocols!
128. What type of networks typically use RIP as a routing protocol? 129. What does RIPv1 not support? 130. What does RIPv1 not listen for? 131. What two things does the network statement accomplish?
Small and med sized LANs Classless routing or VLSM Does not listen for RIPv2 updates -Enables routing prot to send/receive updated on any local interfaces that belong to that network. -It includes that network in its routing updates to others. Inaccurate routing updates and can prevent an interface from sending/receiving updates. Ping and traceroute Cisco show commands like show IP route Telnet Real-time info on traffic movement and the interaction of prot The exchange of RIP routing updates and packets as they occur. It uses a high amount of CPU resources
Transporting data packets and specific port numbers for specific apps. (Most issues from fire walls) At the network edge where security tech examines and modifies traffic TCP and UDP You must specify the transport protocol used Denying access to programs that should be allowed due to statements in firewall exceptions Users saying services are not reachable Network management, file transfer, distributed file services, terminal emulation, and email TCP/IP Application Layer Prots
9.5.2.2 146. List the five steps using the "divide and conquer" method of troubleshooting, when verifying Layer 3 connectivity. 147. If all these steps above are completed successfully, and it is verified that the end-to-end connectivity is not the issue, but the end device is still not operating as expected, where is the problem? 9.5.2.3 148. What accounts for the majority of upper layer network problems? 149. What Windows command will verify that DNS is functioning correctly and can resolve server addresses? 150. If DNS is not working as expected what should be ensured? 151. When hosts receive DNS server information from a DHCP server, what should be verified? 152. List four symptoms of Upper Layer Problems. (Use graphic) 9.5.2.4 153. What kind of mismatch can cause applications to not function or to function poorly? 154. What must be done to browser plug-in programs, such as Adobe Reader, in order to function properly? 9.5.3.1 155. What does Telnet enable a technician to do when accessing networking devices? 156. Since Telnet is an unsecure protocol, what other protocol can be used that offers security? Complete the Lab Activity on 9.5.3.2 9.6.1.1 157. What does the Cisco Certified Entry Networking Technician (CCENT) certification validate? 158. What does the CCNA certification (Cisco Certified Network Associate) cover? 159. What must be passed to obtain CCENT certification?
1.Ping the host default gateway 2.Verify end-to-end connectivity 3.Verify the routing config 4.Ensure that NAT is working 5.Check for firewall filter rules The upper layers
Services being unreachable?? NSlookup
Make sure the correct DNS server info is configured in the host. That the DHCP server has the correct IP addy for the DNS server 1.User complains of slow application performance 2.Application error msg 3.Unable to access apps like FTP 4.Unable to access web services Encryption or compression of data Updated constantly Enables the tech to enter commands to devices as if they were locally attached SSH or Secure Shell prot
That you have the skills for entry level network support positions. Med sized enterprise branch networks. The ICND1 exam
9.6.1.2 160. What are Cisco certification examinations designed to measure? 9.6.2.1 161. While there may be a few questions on the exam that require the basic factual answers, more often the factual knowledge is needed for what purpose? 9.6.2.2 162. What are the Lab and Packet Tracer activities designed to provide? 163. Many exam tasks require the interpretation of output from what type of Cisco IOS commands? 9.6.2.3 164. What do scenario-based tasks or simulation tasks require an individual to apply? 165. What is one of the best ways to develop troubleshooting abilities? Complete the Activity on 9.6.2.4 Complete the Lab Activity on 9.6.2.5 9.6.3.1 166. List the three smaller steps that make exam preparation more successful. 9.6.3.2 167. What is the first step to obtaining a Cisco certification? 168. In addition to taking time, what else is required when preparing for a certification exam? 9.6.4.1 169. After you have made the commitment to dedicate the time necessary to prepare to take the ICND1 examination, what is the next step? 170. What are the two ways to approach studying for a certification exam? 9.6.4.2 171. What can be used from Cisco Press to structure a schedule for CCENT certification? 9.6.4.2 172. What does the book contain? 9.6.4.3 173. What is critical to successful preparation for CCENT? 9.6.5.1 174. What should be done before taking the exam? 175. What should you find out before taking the exam? 176. List four differences between certification exams that are given
The ability to install, operate, and troubleshoot a small branch office network Needed to diagnose or solve a networking problem.
A structured practice environment for learners. Show commands (Damn it all its the truth) You must apply facts and skills to solve a problem Analyze what knowledge and skills are needed in order to perform specific networking tasks. 1.Make a commitment 2.Creating a plan 3.Practice testing taking Making a commitment to take the time to prep Concentration (And lets not forget luck) Create a plan on how to prepare and schedules to do so. Also include resources. 1.Individually 2.Group 31 days to the CCENT References to the sections and topics in the CCNA curriculum Access to the online curriculum, labs, and Packet Tracer activities is critical to successful preparation Visit the testing center and see how the test is done. What you can and cant bring. 1.Survey questions may be present 2.Cert exams are timed
online compared to the Networking Academy assessments that are delivered. 177. What is the best thing to do if you do not know the answer to a question on a certification exam? 9.6.5.2 178. List the seven different formats of test questions that are included in the Cisco certification exams. 179. What can you do to be comfortable with the format and operation of each type of question and task on a certification exam? Complete the Lab Activity on 9.6.5.3 9.6.5.4 180. What else is often helpful to do to prepare for the ICND1 exam? 181. What else is recommended that you do in preparation for the ICND1 exam? 182. What are many of the scenario questions and tasks on the ICND1 exam are based on? Problem The four IP addresses listed below are assigned to the interfaces on a router. Are there any problems using these 4 addresses on the router interfaces?
3.Varity of questions or tasks 4.You cant go back to a previous question Skip it and mark it for later. Move on. 1.Multi choice single answer 2.multi choice multi answer 3.drag and drop 4.fill in the blank 5.testlet 6.Simlet 7.Simulations Practice the exam tutorial found on the Cisco Learning Network website
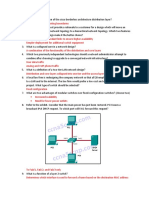
Take practice exams. Create your own practice questions and share them with others. Based on troubleshooting network problems. 192.206.115.121/224 and 193.206.115.113/252 are both trying to subnet in the same space. The range is hosts 96-127
E0: 193.206.115.121/224 S0: 193.206.115.19/252 E1: 193.206.115.94/224 S1: 193.206.115.113/252 Problem Under what circumstance can the PCs Never or hosts on a network or sub-network segment be in a different network or sub-network than their associated default gateway? Problem Explain the difference between total Cant use first or last host address in a subnet to hosts and useable or assignable hosts. assign to hosts Complete the PacketTracer on 9.6.5.5 Complete the Quiz on 9.8.1.1 Addition problem left out on our copy of the guide: If the line in Addy to a switch from a router is 194.102.113.8/29 what are the assignable IP addies Answer: 9-15
You might also like
- Cisco Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesCisco Interview QuestionsssprudhviNo ratings yet
- Troubleshoot TipsDocument22 pagesTroubleshoot TipsRaheel ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Assessment System: Take Assessment - EWAN Chapter 8 - CCNA Exploration: Accessing The WAN (Version 4.0)Document9 pagesAssessment System: Take Assessment - EWAN Chapter 8 - CCNA Exploration: Accessing The WAN (Version 4.0)asceric4363No ratings yet
- Network engineer interview questions and answersDocument29 pagesNetwork engineer interview questions and answersmohamedalihashNo ratings yet
- Steps To Clean A ComputerDocument9 pagesSteps To Clean A Computerchawla_tarunNo ratings yet
- 2 Lab Manual 2 CNDocument5 pages2 Lab Manual 2 CN70131127No ratings yet
- CCNA4 V 4.0 Exam Chapter 8 Network TroubleshootingDocument4 pagesCCNA4 V 4.0 Exam Chapter 8 Network TroubleshootingNathan SmithNo ratings yet
- Test CcnaDocument19 pagesTest CcnaMohita PandeyNo ratings yet
- Fudamentos de Redes Final ExamDocument11 pagesFudamentos de Redes Final ExamEnriqueNo ratings yet
- EWAN Chapter 8 1Document8 pagesEWAN Chapter 8 1anujgitNo ratings yet
- NDocument8 pagesNRaja GhoshNo ratings yet
- Network Engineer Interview QuestionsDocument34 pagesNetwork Engineer Interview QuestionsMir Farhan Ali Abedi100% (5)
- Networking Essentials Exam NotesDocument5 pagesNetworking Essentials Exam NotesKevin H PhamNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting TCP IPDocument13 pagesTroubleshooting TCP IPSuman RathoreNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Chapter 2 Exam Answer v5 & v5.02 2015 (100%) : March 21, 2015 byDocument14 pagesCCNA 1 Chapter 2 Exam Answer v5 & v5.02 2015 (100%) : March 21, 2015 byAmine MaacheNo ratings yet
- Diorey Practice ExamDocument22 pagesDiorey Practice ExamYeroid Diorey PotestasNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 2017Document18 pagesLab Manual 2017Gebruu HagossNo ratings yet
- Ccna1 V7 Cap 1-3Document6 pagesCcna1 V7 Cap 1-3ask_gaby100% (1)
- Vittore Zen - Theory, Laboratories and Exercises For Mikrotik RouterOS-Vittore Zen (2021)Document196 pagesVittore Zen - Theory, Laboratories and Exercises For Mikrotik RouterOS-Vittore Zen (2021)nhandhaayeNo ratings yet
- Akku 75Document7 pagesAkku 75sonupawar8883No ratings yet
- Identifying and ResolvingDocument48 pagesIdentifying and Resolvingyami adiNo ratings yet
- Ali CCNab8 ReportDocument7 pagesAli CCNab8 ReportMuhammad Ali RajarNo ratings yet
- q4 Module1 2 g9 Css San Jacinto NhsDocument8 pagesq4 Module1 2 g9 Css San Jacinto NhsAimee Joy L HermosoraNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 Subiecte Cisco CorectateDocument127 pagesModul 1 Subiecte Cisco CorectateMorar CameliaNo ratings yet
- Rift Valley University Bishoftu CampusDocument58 pagesRift Valley University Bishoftu CampusAyansa TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 Subiecte Cisco (Nerezolvate)Document125 pagesModul 1 Subiecte Cisco (Nerezolvate)Morar CameliaNo ratings yet
- Application layer protocols, UDP preferred for lossy data, ARP maps IPv4 addressesDocument28 pagesApplication layer protocols, UDP preferred for lossy data, ARP maps IPv4 addressesSaba AslamazishviliNo ratings yet
- Ccna 4 Module 8 v4Document4 pagesCcna 4 Module 8 v4montillaeNo ratings yet
- Find switch IP address and VLAN configuration stepsDocument9 pagesFind switch IP address and VLAN configuration stepshatfied862No ratings yet
- Top of FormDocument26 pagesTop of FormAditya ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment 2018-2019Document15 pagesLab Assignment 2018-2019tuyambaze jean claudeNo ratings yet
- Assessment System: Take Assessment - Enetwork Final Exam - Ccna Exploration: Network Fundamentals (Version 4.0)Document24 pagesAssessment System: Take Assessment - Enetwork Final Exam - Ccna Exploration: Network Fundamentals (Version 4.0)mr_mwad3No ratings yet
- INTERVIEW QUESTIONSDocument12 pagesINTERVIEW QUESTIONSINFATUATIONNo ratings yet
- CCNA InterviewDocument3 pagesCCNA Interviewapi-3747051No ratings yet
- Online Test AnswersDocument28 pagesOnline Test AnswersBlake MatthewsNo ratings yet
- CCNA1 Final ExamDocument74 pagesCCNA1 Final ExamDidi SunardiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document6 pagesChapter 7Indio CarlosNo ratings yet
- Cisco 123Document18 pagesCisco 123ElaineNo ratings yet
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionFrom EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Manual Laboratorio LaunchpadDocument54 pagesManual Laboratorio LaunchpadAnthony ACNo ratings yet
- Networking Questions PDFDocument38 pagesNetworking Questions PDFAdam DanielNo ratings yet
- G12 Q2 Activity Sheets 1Document7 pagesG12 Q2 Activity Sheets 1Rose Anne Patrimonio0% (1)
- QuestionDocument4 pagesQuestionkaushal.mdb85No ratings yet
- Network Lab Mid RevisionDocument36 pagesNetwork Lab Mid RevisionMohammed MadanyNo ratings yet
- Dovetail Dumps Latest Phase2Document47 pagesDovetail Dumps Latest Phase2Arun Tez Marata50% (2)
- Oed Net1234Document13 pagesOed Net1234roy EncarnadoNo ratings yet
- These Interview Questions With Answers Will Test Your Basic Knowledge of PC and NetworkingDocument4 pagesThese Interview Questions With Answers Will Test Your Basic Knowledge of PC and NetworkingAnonymous LYPs0TATwVNo ratings yet
- Cisco 1 Exams 1-6Document24 pagesCisco 1 Exams 1-6Andreas PitziolisNo ratings yet
- LTE Troubleshoot TipsDocument17 pagesLTE Troubleshoot TipsRao Dheeru63% (8)
- DCN Manual 2019Document73 pagesDCN Manual 2019Suhani SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- DCN Manual 2019Document74 pagesDCN Manual 2019Suhani SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Verify Connectivity and Configure IP AddressesDocument94 pagesVerify Connectivity and Configure IP AddressesvivekNo ratings yet
- CCNANOTESDocument86 pagesCCNANOTESSunkadahalli Govindaiah Bhanu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Understanding Network Devices and Wireless LabDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Network Devices and Wireless LabramanshankarNo ratings yet
- Becoming a Hacker Part 1: TCP/IP Basics ExplainedDocument59 pagesBecoming a Hacker Part 1: TCP/IP Basics Explainedleo_valenNo ratings yet
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Manual WkhtmltopdfDocument5 pagesManual WkhtmltopdfGeorge DiazNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Swashplate-Less HelicopterDocument68 pagesDesign and Development of Swashplate-Less HelicopterNsv DineshNo ratings yet
- Ci-2001 Ab OmDocument30 pagesCi-2001 Ab OmEnrique FlowersNo ratings yet
- Hdpe Alathon H5520 EquistarDocument2 pagesHdpe Alathon H5520 EquistarEric Mahonri PereidaNo ratings yet
- BYG Опросный лист на режущую кромкуDocument51 pagesBYG Опросный лист на режущую кромкуMMM-MMMNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument7 pagesLab 3 - Series and Parallel CircuitsHảo PhùngNo ratings yet
- Coal Drying Technology and Plant DesignDocument12 pagesCoal Drying Technology and Plant DesignJigar M. UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Rocket Icluster V8.1Document16 pagesRocket Icluster V8.1Felipe Cervantes EspinosaNo ratings yet
- K1 RootingDocument20 pagesK1 RootingHassan BallouzNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Faculty Hydraulics Division: HydrologyDocument2 pagesCivil Engineering Faculty Hydraulics Division: HydrologyENA CO LTD100% (1)
- Kali Linux For BeginnersDocument13 pagesKali Linux For Beginnersnihal0% (1)
- Pfaff 360 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualDocument55 pagesPfaff 360 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualiliiexpugnansNo ratings yet
- Cable Memebres ProfiledirectoryDocument5 pagesCable Memebres ProfiledirectoryMigration Solution100% (1)
- 02 - MEE10603 - Fourier Series and Power Computations in Nonsinusoidally Driven CircuitsDocument33 pages02 - MEE10603 - Fourier Series and Power Computations in Nonsinusoidally Driven CircuitsMohammad HayazieNo ratings yet
- Hardness Vs TextureDocument5 pagesHardness Vs TextureShofa R HaqNo ratings yet
- JIMCO Filter Catalog with Products and SpecificationsDocument8 pagesJIMCO Filter Catalog with Products and SpecificationsDedy CjNo ratings yet
- QlikView Business Intelligence Tool OverviewDocument11 pagesQlikView Business Intelligence Tool OverviewMithun LayekNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Vivek PatilDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Vivek PatilVivek PatilNo ratings yet
- Sublimation of CaffeineDocument3 pagesSublimation of CaffeineNabil ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Haffmans DPT: Dew Point TesterDocument2 pagesHaffmans DPT: Dew Point TesterLaura Elianne QuirogaNo ratings yet
- 2.ARC - ARC Binh Duong ASRS - Quotation For PK2 - Panel and Refrigeration System - Phase 2 - 2020 10 28Document12 pages2.ARC - ARC Binh Duong ASRS - Quotation For PK2 - Panel and Refrigeration System - Phase 2 - 2020 10 28vu nguyen ngocNo ratings yet
- Autocad 2010 Tutorial Series Autocad Mechanical 2010 Tutorial SeriesDocument4 pagesAutocad 2010 Tutorial Series Autocad Mechanical 2010 Tutorial Seriesbdi_roNo ratings yet
- MIT OCW Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II Lecture on Octahedral ML6 Sigma ComplexesDocument7 pagesMIT OCW Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II Lecture on Octahedral ML6 Sigma Complexessanskarid94No ratings yet
- Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage For Firewall Traversal Deployment Guide X12 5Document60 pagesCisco Expressway IP Port Usage For Firewall Traversal Deployment Guide X12 5JodieNo ratings yet
- Bioethanol From CornDocument13 pagesBioethanol From Cornpricett100% (1)
- Francis Turbines PDFDocument12 pagesFrancis Turbines PDFabbas bilal100% (1)
- Making Your Chain Run For Longer: Effective Chain Maintenance Advice From Renold JeffreyDocument2 pagesMaking Your Chain Run For Longer: Effective Chain Maintenance Advice From Renold JeffreyCương Phạm NgọcNo ratings yet
- Xlpe - Ls243Nta: - 1 Technical Data Sheet Crosslinkable Polyethylene CompoundDocument3 pagesXlpe - Ls243Nta: - 1 Technical Data Sheet Crosslinkable Polyethylene CompoundLe MinhNo ratings yet
- HYDRO VesselsDocument5 pagesHYDRO VesselsMarvinPatricioNarca0% (1)
- Evolution of Oilfield BatteriesDocument16 pagesEvolution of Oilfield BatteriesPasquale CutriNo ratings yet