Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sys Unit
Uploaded by
btbaylasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sys Unit
Uploaded by
btbaylasCopyright:
Available Formats
SYSTEM UNIT
SYSTEM UNIT
A case that contains electronic components of the computer used to process data Sometimes called the chassis
SYSTEM UNIT: COMPONENTS
Motherboard Power supply Processor Memory modules Drives Expansion cards Ports and connectors
MOTHERBOARD
the main circuit board of the system unit Contains chips, integrated circuits, and transistors Also called system board
MOTHERBOARD
POWER SUPPLY
Converts standard electrical power to a form a computer can use
PROCESSOR
also called the central processing unit (CPU), interprets and carries out the basic instructions that operate a computer Contain a control unit and an arithmetic logic unit (ALU)
PROCESSOR: CU and ALU
The control unit is the component of the processor that directs and coordinates most of the operations in the computer
The arithmetic logic unit (ALU) performs arithmetic, comparison, and other operations
PROCESSOR: CU and ALU
PROCESSOR: Clock Speed
Clock speed measures how fast a processor performs an activity. Clock speed rates are shown in Gigahertz (GHz), which means billions of cycles per second. 1 gigabyte = 1000 MHz = 1 GHz
PROCESSOR: Cores and Threads
Pipelining Processor begins fetching a second instruction before it completes the machine cycle for the first instruction Parallel Processing - the ability to carry out multiple operations or tasks simultaneously.
Threads - the smallest unit of processing
SINGLE CORE DUAL CORE MULTICORE
MEMORY
consists of electronic components that store instructions waiting to be executed by the processor, data needed by those instructions, and the results of processing the data measured in kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), or terabytes (TB)
MEMORY: Volatile and Non-volatile
Volatile memory Loses its contents when power is turned off Random Access Memory (RAM)
Non volatile memory Does not lose contents when power is removed Read-only memory (ROM)
MEMORY: RAM
temporary storage and working space for the operating system and its applications Resides in memory slots.
MEMORY: RAM
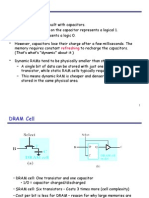
Static RAM: does not need to be periodically refreshed, as SRAM uses bistable latching circuitry to store each bit. Dynamic RAM: stores each bit of data in a separate capacitor within an integrated circuit. refreshed periodically. Magnetoresistive RAM: retains its information when power is turned off
MEMORY: RAM
MEMORY: RAM
It takes 200ns (nanoseconds) for the CPU to access RAM compared to 12,000,000ns to access the hard drive The more peripherals you add to a computer, or the more advanced applications you ask it to perform, the more RAM it needs to operate smoothly.
DRIVES
Hard Disk - a non-volatile, random access digital magnetic data storage device A bay is an opening inside the system unit in which you can install additional equipment
A drive bay typically holds disk drives
EXPANSION CARDS
Connects peripheral devices and add functionality to the system. Also called adapter cards
Interface adapter cards, including parallel port cards, serial port cards, multi-I/O cards, USB port cards, and proprietary interface cards. Sound and Video Cards Network cards Host adapters such as SCSI and RAID controllers. Etc. etc. etc. :)
EXPANSION CARDS
PORTS AND CONNECTORS
A port is the point at which a peripheral attaches to or communicates with a system unit (sometimes referred to as a jack) A connector joins a cable to a port
PORTS AND CONNECTORS
PORTS AND CONNECTORS
A USB port can connect up to 127 different peripherals together with a single connector
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- 8086 Hardware 2 MEMORY and IO IntefaceDocument46 pages8086 Hardware 2 MEMORY and IO IntefaceНемања БорићNo ratings yet
- Manuals Electric Jaw Crusher and Reciprocating Plate FeedersDocument771 pagesManuals Electric Jaw Crusher and Reciprocating Plate FeedersKatherine Nicole Miranda Godoy100% (1)
- Lesson01 FT125 Overview SiemensDocument10 pagesLesson01 FT125 Overview SiemensใบบอนสิชลNo ratings yet
- CST232 Tutorial2Document2 pagesCST232 Tutorial2VortexProYeoNo ratings yet
- CPU Stability Test: Rev.011: ProcedureDocument10 pagesCPU Stability Test: Rev.011: ProcedureDelwar HossainNo ratings yet
- hw02 SolsDocument24 pageshw02 SolsMuhammad Fahad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Son-CA - Lec1 - 1 - Computer Abstraction and TechnologyDocument31 pagesSon-CA - Lec1 - 1 - Computer Abstraction and TechnologyVăn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- SKhynix Computing DDR2 Part Numbering PDFDocument2 pagesSKhynix Computing DDR2 Part Numbering PDFlinkNo ratings yet
- Qualified Vendors List (QVL), Model Name: X570 AORUS PRO (1.1)Document7 pagesQualified Vendors List (QVL), Model Name: X570 AORUS PRO (1.1)elmiNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8085Document66 pagesMicroprocessor 8085BoradPritesh50% (2)
- Design and Development of A Smart Shopping Cart SystemDocument5 pagesDesign and Development of A Smart Shopping Cart SystemNihed JebaliNo ratings yet
- AHTN2022 CHAPTER85 wNOTESDocument41 pagesAHTN2022 CHAPTER85 wNOTESdoookaNo ratings yet
- 14-RAM&ROM - Dynamic Memory Is Built With Capacitors. A Stored Charge On The Capacitor Represents A Logical 1. No Charge Represents A Logic 0.Document8 pages14-RAM&ROM - Dynamic Memory Is Built With Capacitors. A Stored Charge On The Capacitor Represents A Logical 1. No Charge Represents A Logic 0.Nava KrishnanNo ratings yet
- CS-208 Stack and Related Instructions in 8085 Microprocessor by B R MALI GPC JODHPURDocument7 pagesCS-208 Stack and Related Instructions in 8085 Microprocessor by B R MALI GPC JODHPURINFINITY GAmErNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor UNIT-6Document15 pagesMicroprocessor UNIT-6pravin2275767No ratings yet
- If You Plan To Transfer The Shader Cache To A Different PC or Cemu Installation You Only Need To Copy The 'Transferable' DirectoryDocument1 pageIf You Plan To Transfer The Shader Cache To A Different PC or Cemu Installation You Only Need To Copy The 'Transferable' DirectorysheoNo ratings yet
- Types of MemoryDocument3 pagesTypes of MemoryVenkatareddy Mula0% (1)
- QUAN-Digital BSCIT DescriptiveDocument31 pagesQUAN-Digital BSCIT DescriptiveDebanjan PatraNo ratings yet
- Ca Ipcc - ItDocument82 pagesCa Ipcc - ItIQBAL MAHMUDNo ratings yet
- Memory Validation List ExternalDocument135 pagesMemory Validation List ExternalVlad CasuneanuNo ratings yet
- Accident Detection System Using Android ApplicatioDocument4 pagesAccident Detection System Using Android ApplicatioGarena Free fireNo ratings yet
- H5GQ1H24AFR (Rev1 0)Document173 pagesH5GQ1H24AFR (Rev1 0)tszampanoNo ratings yet
- Accelerating ML Recommendation With Over A Thousand Risc-V/Tensor Processors On Esperanto'S Et-Soc-1 ChipDocument23 pagesAccelerating ML Recommendation With Over A Thousand Risc-V/Tensor Processors On Esperanto'S Et-Soc-1 ChipddscribeNo ratings yet
- Cr10X Measurement and Control Module Operator'S Manual: REVISION: 2/03Document0 pagesCr10X Measurement and Control Module Operator'S Manual: REVISION: 2/03Bruce BarrosNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 MemoryDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 MemoryIslahNo ratings yet
- Answer: SolutionDocument9 pagesAnswer: Solutionars rahmanNo ratings yet
- Page ReplacementDocument8 pagesPage ReplacementPrabavathiNo ratings yet
- Page Replace Ment Algo PrintDocument5 pagesPage Replace Ment Algo PrintSK ANARULNo ratings yet
- P5GPL DDR400 QVLDocument1 pageP5GPL DDR400 QVLStefan MitrescuNo ratings yet
- True USB GQ Universal Programmer Supported Device List (Re. 7.23)Document73 pagesTrue USB GQ Universal Programmer Supported Device List (Re. 7.23)ecutronicssNo ratings yet