Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Levis Final
Uploaded by
shahmeerbilalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Levis Final
Uploaded by
shahmeerbilalCopyright:
Available Formats
Contents
Acknowledgement .......................................................................................................................... 2 Introduction ..................................................................................................................................... 3 History............................................................................................................................................. 5 SWOT Analysis .............................................................................................................................. 7 Strengths ..................................................................................................................................... 7 Weaknesses ................................................................................................................................. 7 Opportunities............................................................................................................................... 8 Threats......................................................................................................................................... 8 Strategic Marketing Management Objectives ................................................................................. 9 Objective 1: ................................................................................................................................. 9 Objective 2: ............................................................................................................................... 12 Objective 3 ................................................................................................................................ 13 Product Strategy ............................................................................................................................ 16 Branding Strategy ......................................................................................................................... 19 Pricing Strategy............................................................................................................................. 24 Channel Strategy ........................................................................................................................... 25 Promotion Strategy ....................................................................................................................... 26 Recommendations ......................................................................................................................... 29 Attachments .................................................................................................................................. 31
1|Page
Acknowledgement
I am grateful to Almighty Allah, who gave me the vision and ability to work on this report and collect relevant research data. I owe special gratitude to Mr. Muhammad Ahmed Butt who enlightened and guides me pertaining to the preparation of this report without which it would not be as smooth as it had been.
2|Page
Introduction
Levi Strauss & Co. (LS&CO.) is one of the world's largest brand-name apparel marketers with sales in more than 110 countries. There is no other company with a comparable global presence in the jeans and casual pants markets. Today, the Levi's trademark is one of the most recognized in the world and is registered in more than 160 countries. The company is privately held by descendants of the family of Levi Strauss. Shares of company stock are not publicly traded. After experiencing more than a century of positive sales trends and market growth, Levis began to lose market share in 1996.There were several reasons that set off the downward trend which lasted for more than a decade, including a lack of innovation, failure to anticipate consumer trends and an influx of fashion forward competitors willing to do what Levis either couldnt or wouldnt. In the 1990s the jeans market changed dramatically and Levis faced stronger competition than it had in the past. The new entrants into the market were two types: high-end designer jeans manufacturers and retail chains (Perman). The designer jeans came from fashion houses such as Donna Karan, Tommy Hilfiger, Ralph Lauren and Versace and other edgy upstarts. These style-conscious rivals stole sales from Levis and had stylish jeans models that followedand sometimes even setfashion trends; something that Levis jeans and models did not. Many consumers were willing to pay a premium price to obtain a pair of these much hipper jeans. Around the same time period, retail stores like Gap Inc., J.C. Penney and Sears started offering affordable jeans, cheaper than Levis, which attracted the younger population and chipped away at even more of Levis share of the jeans market. Levis was confronted by competition from two different directions and they were stuck in the middle between their new rivalsrivals who went after niche customer segments and were able to earn profits from them. As a result, both fashion and price conscious consumers abandoned the Levis brand. In 1999 Levis Strauss brought new CEO, Philip Marineau, from Pepsi Co. and he established new strategies. As Levis faced increasing competition from designer brands and retail stores 3|Page
they finally decided to counter their rivals by providing Levis products at select discounters and specialty chains (Lee). Levis approach to turn the tide of lost market share and consumer loyalty was to develop new product lines to be distributed in different types of stores. In 2003, the company launched their new Signature line, which Levis website describes as a brand that offers high-quality, fashionable jeans at affordable prices to value-conscious consumers at [discount] stores like Walmart, Target and Kmart. According to Jenny Strasburgs article in The San Francisco Chronicle, titled Levi's treats itself to an image makeover / Once-workaday jeans to challenge designer lines, Levis also made their way into high-end specialty chains such as Saks Fifth Avenue, Neiman Marcus, Bloomingdale's and Nordstrom with their premium product lines. More than offering their jeans at discount and specialty stores, Levis also tried to make themselves more attractive to younger consumers by making their jeans available at Pacific Sunwear of California Inc. and other stores frequented by younger shoppers (Lee). An important, and risky, move in Levis reinvention was to become more obtainable and offer something to different market segments. Rather than worry about the risk of thinning out the brand by spreading themselves too thin, Levis saw the benefit of diversifying their products to engage with customers who had varying needs and expectations. Creating a line for selected retail stores was a bold move because Levis could have tarnished their brand in the minds of consumers and degraded their legacy of good quality. The same could have happened with regard to more upscale stores had patrons of those establishments perceived Levis jeans as lacking sophistication. Yet Levis understood that if executed well, they could expand their range of product lines, increase their availability, and by doing so be seen as consumer focused and as a result become profitable once again.
4|Page
History
Today, the Levis brand is an authentic American icon, known the world over. Levi Strauss started it 150 years ago & forever earned a place in history. In 1847, Levi Strauss, his two sisters & mother sailed for America where they joined half-brothers Jonas & Louis in New York. Levi joined their dry goods business. In 1853, Levi sailed to San Francisco to join dry goods business and started selling clothing, bedding & linen to small stores in California. In 1902, Levi died and his two nephews inherited the business. In 1910s, LS&CO. received Blue Ribbon highest award for waist overalls in Panama. One-piece garment for women was introduced to work and play. In 1930s, the Great Depression stroke & demand for Levis jeans, shirts and jackets declined. In 1991, the first original Levis store was opened in United States. In 1994, Dockers brand was introduced in Europe. It launched its first website in 1995.In 1996; it introduced its Slates brand, a new style for men wearing. In 1999, classic 5 pocket pants were reinvented. In 2000, LS&CO. introduced Levis engineered jeans TM, the reinvention of jeans for the new generation. It named No. 2 for Americas best companies for minorities. In 2003, it celebrated its 150th anniversary of its founding and 130th anniversary of invention of blue jeans. MISSION STATEMENT The mission of Levis Strauss & Co. is to sustain responsible commercial; success as a global marketing company of branded apparel. We must balance goals of superior profitability and return on investment, leadership market positions, and superior products and services. We will conduct our business ethically and demonstrate leader ship in satisfying our responsibilities to our communities and to society. Our work environment will be safe and productive and characterized by fair treatment, teamwork, open communications, personal accountability and opportunities for growth and development.
5|Page
VISION STATEMENT: When LS & Co. describe the future of Levi they are talking about a building on the foundation they have inherited: affirming best of their Companys tradition, closing gaps that may exist between principles and practices and updating some of their values to reflect contemporary circumstances. ASPIRATION STATEMENT: They want a company that make them proud of and committed to, where all employees have an opportunity to contribute, learn, grow and advanced based on merit, not politics or background. They want their people to feel respected, treated fairly, listened to and involved. Above all, they want satisfaction from accomplishments and friendships, balanced personal and professional lives, and to have fun in our endeavors.
6|Page
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
Customers are brand loyal and are maintaining high level of awareness and association. Levis is maintaining formidable position against competitors. Company is maintaining cordial relationship with management Company is maintaining good relationship with suppliers. Levis needs significant improvement in defining vision and formulating corporate strategies. The company financial position is stable. Production system procedure reflects consistency with industry standards. Levis enjoys high brand equity. People all around the world recognize the brand name. Levis products are unique and innovative in the style. A lot of variety is offered by Levis ranging from sunglasses to skirts and shirts. The products are renowned and are considered as the most durable i.e. the long lasting products. Levis follows a high standard of quality.
Weaknesses
Customers have become more saver and value conscious.
In jeans segment Levis is facing an increased competition. HRM needs improvements. Marketing management is apparently mismanaged. Levis products are considered as very expensive. Therefore a large percentage of people are reluctant to buy the products. As no discounts are present and products are sold at fixed prices many customers are lost. Levis does not provide any services like free delivery etc.
7|Page
Opportunities
Economic conditions are relatively stable. Levis is taking care of the new trends in the society related to social shift. Levis is including the whole industry is enjoying consistent policies given by the government. Levis is equipped with latest technology International environment demonstrate friendly environment. Levis can do more well in the women section. This section is give less importance as compared to the men section. The kids section, which has been started from few years, should also be given proper attention to gain customers. Sales promotion can be increased by increasing the advertisements expenses so as to enjoy a large number of customers.
Threats
US is experiencing social shift and society has become more value seeking and saving money .They are following hedonism. Technological apparel industry is facing challenges.
8|Page
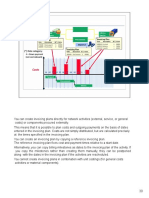
Strategic Marketing Management Objectives
Objective 1:
Using the Brand Management Process for the repositioning the Levis brand.
Mental maps Competitive frame of reference Point-of-parity and point-ofdifference Core brand associations Brand mantra Mixing and matching of brand elements Integrating brand marketing activities Leveraging secondary association
Identify and Establish Identify and Establish Brand Positioning and Values Brand Positioning and Values
Plan and Implement Plan and Implement Brand Marketing Programs Brand Marketing Programs
Measure and interpret Measure and interpret Brand Performance Brand Performance
Brand Value Chain Brand audits Brand tracking Brand equity management system Brand-product matrix Brand portfolios and hierarchies Brand expansion strategies Brand reinforcement and revitalization
Grow and Sustain Grow and Sustain Brand Equity Brand Equity
FIGURE 1-11 Strategic Brand Management Process
Identifying and Establishing Brand Positioning The Strategic brand management process starts with a clear understanding of what the brand is to represent and how it should be positioned with respect to competitors.
Planning and Implementing Brand Marketing Programs In general, this knowledgebuilding process will depend on three factors: The initial choices of the brand elements or identities making up the brand and how they are mixed and matched. 9|Page
The marketing activities and supporting marketing program and the way the brand is integrated into them. Other associations indirectly transferred to or leveraged by the brand as a result of linking it to some other entity (such as the company, country of origin, channel of distribution, or another brand) Choosing Brand Elements. The most common brand elements are brand names, URLS, logos,
symbols, characters, packaging, and slogans. A number of options and criteria are relevant for choosing them to enhance brand awareness or facilitate the formation of strong, favorable, and unique brand associations. Integrating the Brand into Marketing Activities and the Supporting Program Although the judicious choice of brand elements can make some contribution to building brand equity, the biggest contribution comes from marketing activities related to the brand. Marketing programs can create strong, favorable, and unique brand associations in a variety of different ways. Leveraging Secondary Associations The third and final way to build brand equity is to leverage secondary associations. Brand associations may themselves be linked to other entities that have their own associations, creating secondary associations.
Measuring and Interpreting Brand Performance A brand audit is a comprehensive examination of a brand to assess its health, uncover its sources of equity, and suggest ways to improve and leverage that equity. The brand value chain is a means to trace the value creation process for brands, to better understand the financial impact of brand marketing expenditures and investments. A brand equity measurement system is a set of research procedures designed to provide timely, accurate, and actionable information for marketers so that they can make the best possible tactical decisions in the short run and the best strategic decisions in the long run.
10 | P a g e
Growing and Sustaining Brand Equity Maintaining and expanding on brand equity can be quite challenging. Brand equity management activities take a broader and more diverse perspective of the brands equity understanding how branding strategies should reflect corporate concerns, and be adjusted, if at all, over time or over geographical boundaries or market segments. Defining the Branding Strategy The brand-product matrix is a graphical representation of all the brands and products sold by the firm. The brand hierarchy displays the number and nature of common and distinctive brand components across the firms products. The brand portfolio is the set of all brands and brand lines that a particular firm offers for sale to buyers in a particular category.
Managing Brand Equity over Time Effective brand management also requires taking a long-term view of marketing decisions. Managing Brand Equity over Geographic Boundaries, Cultures, and Market Segments. Another important consideration in managing brand equity is recognizing and accounting for different types of consumers in developing branding and marketing programs.
Repositioning of Levis After seeing sales decrease in the 1990s and 2000s due to their failure to respond to market trends, Levis also chose to reposition themselves. They began to be seen as being out of style and out of touch with current trends. In order to prevent further loss of market share and counter these perceptions, Levis took the innovative step of shipping in staffers from its more fashionoriented European division and holding brainstorming sessions to dig out what consumers wanted in their clothes . As a result, the new product lines were in vogue and Levis enjoyed a triumph with new, trendier products such as their low-rise jeans. The company became better at 11 | P a g e
responding to trends and once again gained popularity among younger consumers. Levis also became better at teasing out trends, not just in the apparel industry, but in society. As pointed out in the online article Dressed to impress? at CMDGlobal.com, Levis created the Eco jean, made with organically farmed cotton that responded well to the environmental movement taking place in our society in the last decade. Levis also uses technology to connect and communicate with younger consumers. Products have been designed to meet their needs, e.g. some models have pockets for iPods, and Levis also interacts with their younger customers through the web (CMDGlobal.com). As stated in Sara Ins Calderns article Levis Uses New Facebook Plugins to Reach Potential Jeans Purchasers in Inside Network, Levis [] was one of the first web sites to debut Facebooks new social plugins [in April of 2010]. When asked why Levis was one of the first companies asked by Facebook to integrate with the new plugins, Megan OConnor, Levis director of digital and social marketing, explained that Facebook [] approached us because they knew we had a reputation as being a pioneer not just in the social space, but also with technology. Levis managed to lure consumers back by positioning themselves as a brand that is up to date; not only when it comes to their products, but also when it came to grasping trends in society such as social and environmental movements and technology.
Objective 2:
Using the four steps of Brand Building, Levis have to build a strong Brand and Customer Based Equity. The steps are as following: 1. Ensure identification of the brand with customers and an association of the brand in customers minds with a specific product class or customer need. 2. Firmly establish the totality of brand meaning in the minds of customers by strategically linking a host of tangible and intangible brand associations with certain properties. 3. Elicit the proper customer responses to this brand identification and brand meaning.
12 | P a g e
4. Convert brand response to create an intense, active loyalty relationship between customers and the brand. The four questions (with corresponding brand steps in parentheses) are: 1. Who are you? (brand identity) 2. What are you? (brand meaning) 3. What about you? What do I think or feel about you? (brand responses) 4. What about you and me? What kind of association and how much of a connection would I like to have with you? (brand relationships)
Objective 3
Using Segmentation Strategy to convince retailer to keep Levis. Market Segmentation Market segmentation is the selection of groups of people who will be most receptive to a product. The most frequent methods of segmenting include demographic variables such as age, sex, race, income, occupation, education, household status, and geographic location; psychographic variables such as life-style, activities, interests, and opinions; product use patterns; and product benefits. Much segmentation involves combinations of these methods. No matter how segments are defined, however, they are characterized by considerable change over time. The readings in this section exemplify areas of rapid change.
Basis of Market Segmentation Demographic Segmentation Geographic Segmentation Psychographic Segmentation Behavioral Segmentation 13 | P a g e
Target Market Levis JEANS targets its market by evaluating the wants of customers. Mostly Levis targets its market among the following classes: Upper Class Upper Middle Class Middle Class Lower Middle Class Target Market Strategy: Target market strategy adopted by Levis is basically on having long-term relations with their customers and to provide them with better product.
Benefits of Segmentation: Levis has got customer oriented approach by segmentation. Company is promoting its products effectively within segments by print media as well as electronic media, e.g. Newspapers, Signboards, Television commercials, Internet, etc. Company is providing their customers with stylish better quality and different product keeping
in view its cost.
Conditions for effective segmentation: Levis JEANS is fulfilling the conditions for effective segmentation. Segments are strong enough to make profit.
14 | P a g e
Segments of company are measurable.
Limitation of Segmentation: Because of segmentation, Levis faces some limitations. Lack of awareness in middle class. Company has to pay extra cost for multi-advertisement. Face several Cultural Barriers.
15 | P a g e
Product Strategy
Product means set of tangible and intangible attributes which may include packaging, color, price, quality and brand plus the sellers services and reputation. A product may be a place, service, good or promotion. The product itself is the primary influence on what consumers experience with a brand, what they hear about a brand from others, and what the firm can tell customers as about the brand.
LEVIS Invented in 1853, Levi's jeans are the original, authentic jeans. They are the most successful, widely recognized and often imitated clothing products in the history of apparel. Levi's jeans have captured the attention, imagination and loyalty of generations of diverse individuals. As the inventor of the category, the Levis brand continues to define jeans wear with widest range of products available from quintessential classics, such as the famous Levi's501 Original jean to favorite fits and styles in our Red Tab and Levi's Premium collections.
DOCKERS Launched in 1986 in the United States, Dockers brand products and marketing played a major role in the creation of a new apparel category for men's pants and the shift to casual clothing in the workplace. Dockers Khakisquickly became the No. 1 khaki pant brand in the United States. In 1988, the brand launched Dockers for Women, a feminine interpretation of Dockers brand apparel. The line offers fashionable tops, dress and casual pants and a full range of accessories designed to fit a variety of different body types and sizes. Today, the Dockers brand has expanded to more than 50 countries in every region of the world with a complete assortment of stylish and innovative products including a full line of tops, footwear, outerwear and accessories for a broad range of consumers 16 | P a g e
LEVIS STRAUSS SIGNATURE The Levi Strauss Signature brand was launched in 2003 exclusively for consumers who shop in the mass channel. The brand gives value-conscious consumers access to high-quality, affordable and fashionable jeans wear from a company and name they trust. The Levi Strauss Signature brand includes a collection of denim and non-denim pants, shirts, skirts and jackets for men, women and children all designed with the high quality.
Product Attributes Products are usually considered to be the No.1 factor contributing towards building goodwill of a firm. A product should be unique, durable, reliable, comfortable and economical. Following are some of the basic attributes of LS&CO.S products Variety Features Design Color Size
Variety Levis products today are perceived by many as a symbol of youth, freedom, confidence, individualism, independence & comfort. LS & CO. provides a wide variety of products including:
Jeans Baby clothing Bags Wallets Mens Khaki
17 | P a g e
Features Features are competitive tools that differentiate the companys products from its competitors products. Following are some of the main and distinctive features of Levis products. Comfort: Levis jeans and other products are comfortable enough to be worn even at the times of protest, war, cultural revolution, relative peace and pure fun. Durability: The two figures on the patch of Levis jeans with whips in hand pulling in opposite directions, yet the jeans remain intact; symbolize the strength and durability of the Patent riveted clothing. Style: Clothing means more than just fabric, thread and rivets. To clothe oneself means to put on something that symbolizes who you are. Levis jeans are available in different styles for men and women.
18 | P a g e
Branding Strategy
Levis need to build a strong brand by using Brand Building Blocks
FIGURE 2-5 Customer-Based Brand Equity Pyramid
Stages of Brand Development 4. Relationships 4. Relationships
What about you and me? What about you and me?
Branding Objectives at Each Stage
Resonance
Intense, Intense, Active loyalty Active loyalty
3. Response 3. Response What about you? What about you?
Judgments
Feelings
Positive, Positive, Accessible reactions Accessible reactions
2. Meaning 2. Meaning What are you? What are you?
Performance
Imagery
Points of parity Points of parity and difference and difference
1. Identity 1. Identity Who are you? Who are you?
Salience
Deep, broad Deep, broad Brand awareness Brand awareness
Brand Salience Brand salience measures awareness of the brand, for example, how often and easily the brand is evoked under various situations or circumstances. Breadth and Depth of Awareness. The depth of brand awareness measures how likely it is for a brand element to come to mind, and the ease with it does so. The breadth of brand awareness measures the range of purchase and usage situations in which the brand element comes to mind and depends to a large extent on the organization of brand and product knowledge in memory.
19 | P a g e
Brand Performance The product itself is at the heart of brand equity, because it is the primary influence on what consumers experience with a brand, what they hear about a brand from others, and what the firm can tell customers about the brand in their communication. Brand performance describes how well the product or service meets customers more functional needs. Five important types of attributes and benefits often underlie brand performance, as follows: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Primary ingredient and supplementary features Product reliability, durability, and serviceability Service effectiveness, efficiency, and empathy Style and design Price
How do customers view performance? Reliability measures the consistency of performance over time and from purchase to purchase. Durability is the expected economic life of the product, and serviceability the ease of repairing the product if needed. Service effectiveness measures how well the brand satisfies customers service requirements. Service efficiency describes the speed and responsiveness of service. Finally, service empathy is the extent to which service providers are seen as trusting, caring, and having the customers interests in mind.
Brand Imagery The other main type of brand meaning brand imagery. Brand imagery depends on the extrinsic properties of the product or service, including the ways in which the brand attempts to meet customers psychological or social needs. Many kinds of intangibles can be linked to a brand, but four main ones are: User profiles Purchase and usage situations 20 | P a g e
Personality and values History, heritage, and experiences Demographic factors might include the following: Gender. Age. Race. Income.
Psychographic factors might include attitudes towards life, careers, possessions, social issues, or political institutions; for example, a brand user might be seen as iconoclastic or as more traditional and conservative.
Brand Judgments Brand judgments are customers personal opinions and evaluations of the brand, which consumers form by putting together all the different performance and imagery associations. Brand Quality. Brand attitudes are consumers overall evaluations of a brand and often form the basis for brand choice. Brand Credibility. Brand credibility describes the extent to which customers see the brand as credible in terms of three dimensions: perceived expertise, trustworthiness, and likeability. Brand Consideration. Favorable brand attitudes and perceptions of credibility are important but not enough if customers dont actually consider the brand for possible purchase or use. Brand Superiority. Superiority measures the extent to which customers view the brand as unique and better than other brands.
Brand Feelings Brand feelings are customers emotional responses and reactions to the brand. Brand feelings also relate to the social currency evoked by the brand.
21 | P a g e
Researchers have defined transformational advertising as advertising designed to change consumers perceptions of the actual usage experience with the product. The following are six important types of brand-building feelings. Warmth: The brand evokes soothing types of feelings and makes consumers feel a sense of calm or peacefulness. Fun: Upbeat types of feelings make consumers feel amused, lighthearted, joyous, playful, cheerful, and so on. Excitement: The brand makes consumers feel energized and that they are experiencing something special. Security: The brand produces a feeling of safety, comfort, and self-assurance. Social approval: Consumers feel that others look favorably on their appearance, behavior, and so on. Self-respect: The brand makes consumers feel better about themselves; consumers feel a sense of pride, accomplishment, or fulfillment.
Brand Resource Brand resonance describes the nature of this relationship and the extent to which customers feel that they are in sync with the brand. We can break down these two dimensions of brand resonance into four categories: Behavioral loyalty Attitudinal attachment Sense of community Active engagement
We can gauge behavioral loyalty in terms of repeat purchases and the amount or share of category volume attributed to the brand, that is, the share of category requirements.
22 | P a g e
Resonance, however, requires a strong personal attachment. The brand may also take on broader meaning to the customer by conveying a sense of community. Finally, perhaps the strongest affirmation of brand loyalty occurs when customers are engaged, or willing to invest time, energy, money, or other resources in the brand beyond those expended during purchase or consumption of the brand. In summary, brand resonance and the relationships consumers have with brands have two dimensions: Intensity and activity. Intensity measures the strength of the attitudinal attachment and sense of community. Activity tells us how frequently the consumer buys and uses the brand, as well as engages in other activities not related to purchase and consumption.
23 | P a g e
Pricing Strategy
Price is the one revenue-generating element of the traditional marketing mix, and price premiums are among the most important brand equity benefits of building a strong brand. Levis set the prices of its different product to build the brand equity and levis adopted ValuePricing strategy so that it could satisfy its customer from different market segment.
Setting Prices to Build Brand Equity Choosing a pricing strategy to build brand equity means determining the following: A method for setting current prices A policy for choosing the depth and duration of promotions and discounts
Value Pricing The objective of value pricing is to uncover the right blend of product quality, product costs, and product prices that fully satisfies the needs and wants of consumers and the profit targets of the firm. In general, an effective value-pricing strategy should strike the proper balance among the following: Product design and delivery Product costs Product prices
Product design and delivery The first key is the proper design and delivery of the product.
24 | P a g e
Product Costs The second key to a successful value-pricing strategy is to lower costs as much as possible. Product Prices The final key to a successful value-pricing strategy it to understand exactly how much value consumers perceive in the brand and thus to what extent they will pay a premium over product costs.
Channel Strategy
Marketing channels are defined as set of interdependent organizations involved in the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption. Channel Design Direct channels means selling through personal contacts from the company to prospective customers by mail, phone, electronic means, in-person visits, and so forth. Indirect channels sell through third-party intermediaries such as agents or broker representatives, wholesalers or distributors, and retailers or dealers. Levis uses both direct and Indirect Channels for selling its products. In Direct channel Levis sell its products through its retail outlets while in Indirect Channel Levis have other retailers like J C Penney CO, SEARS, Wal- Mart, Bloomingdale and Barneys New York through which it sell its products.
25 | P a g e
Promotion Strategy
Levis Promotion objectives: To inform, persuade and remind the potential customers about its products Increase awareness and build primary demand To build strong brand equity. Build Companys image as innovator. To create bonds between public and Levi Strauss by helping the people. To create the importance of its products
Sales promotion For the promotion of sales Levi Strauss & Co. adopt a very effective but comprehensive strategy. Levis pays attention to the publicity of its products. The major source of promotion of levis is done by creating public relations. The sales promotion of LEVIS targets the end consumers. Since the Levis JEANS are in growth stage in Pakistan, therefore, the promotional strategy is based on persuading of prospective buyers. Levis uses the following promotional strategies to promote its product. Personal selling Personal selling by the representative of the organization takes place face to face with final consumers. Mass Selling Levis does mass selling to inform a bulk of persons by advertising. Advertising The type of advertising used by LEVIS.
26 | P a g e
Competitive advertising The advertisement given by the LEVIS stresses on the demand of the product and enhancement of its features. Institutional advertising Levis uses institutional advertising to promote companys image by saying Many Copy the Red Tab No One can copy the Original Advertising mediums The advertising media used by the company are Television Fashion Magazines , Newspapers Internet. Bill boards ,banners etc
Television & Radio: Advertisements of Levi Strauss & Co. are very innovative and eye-catching. Buyers are
attracted towards the product. The advertisements are placed at the international level. Fashion Magazines & Newspapers: For fashion magazines and newspapers LS&Co. is a target due to its grand brand equity ,it has become a benchmark for all the others to follow. The newspaper gives a coverage to the social events in which LS &Co takes part with great interest. Whereas fashion magazines are always dealing with the gorgeous models working with LS& Co and the unique outfits of the models Internet: Levis provides up-to-date information to their customers through electronic media i.e. from their website
27 | P a g e
Billboards & banners: Billboards and banners are also used for the advertisement purpose. Sales force: Levis holds a very big sales department as it is working in many countries.
28 | P a g e
Recommendations
After a little more than a decade of losing consumers, Levis was eventually able to get back on their feet and in early 2007 the company could announce that profits were finally increasing again. After being successful most of the 20th century Levis had some dark years at the end of the century and what led them there was their inability to anticipate or even meet fashion trends as well as the entrance of rivals into the jeans market. Levis could not offer stylish jeans models and the consumers abandoned them for their competitors. By making some bold moves and utilizing smart business strategies Levis was able to turn itself around and is today no longer thought of as a baby boomer brand and has gained popularity among younger consumers. Levis effectively developed more product lines and increased their availability to meet the needs of more market segments. In order to interact with and maintain an ongoing relationship with their young buyers, the organization makes huge efforts to remain technologically up-to-date and responsive to societal trends. Levis has learned their lesson to not take success for granted. Upholding a relationship with consumers and keeping them loyal to their brand is a continuous task and Levis needs to be innovative and create new ways to maintain these relationships. Different ways to do so could be: 1.Strategic alliances and licensing: Levis has often teamed up with different organizations to give back to society, e.g. the White Knot and Goodwill, but could take it further and join forces with other parties to create more Levis products than just clothes. Levis logo could be seen on products such as furniture and home accessories such as sheets, blankets etc. Since Levis sponsors music festivals, camping gear could also be part of their product range. 2. Fast Fashion: Levis could meet trends faster and enjoy higher consumer satisfaction by speeding up the process of spotting trends, manufacturing and distribution. Similar to Zara, Levis could engage in Fast Fashion and would develop products quicker and have them in stores more rapidly. 29 | P a g e
3. Customization: Levis offered the Personal Pair program to consumers from 1994 to 2003. People got measured at Original Levis stores and could a few weeks later enjoy their own customized jeans. Levis decided to discontinue the program to put efforts into restrengthening the brand. Now that Levis has improved their brand, the program could be relaunched.
30 | P a g e
Attachments
References Book: Strategic Brand Management, 3rd Edition. By Kevin Lane Keller Website: http://www.levistrauss.com/sites/default/files/librarydocument/2010/6/lvisf2009arc.pdf http://www.levistrauss.com http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Levi_Strauss_%26_Co. http://www.ibscdc.org/Case_Studies/Strategy/Restructuring%20Turnaround%20S trategies/RTS0112B.htm>. http://www.levistrauss.com/sites/default/files/librarydocument/2010/4/HistoryDenim.pdf http://www.cmdglobal.com/analysis/brand_experts/levis http://www.businessweek.com/magazine/content/02_29/b3792068.htm http://articles.latimes.com/2007/apr/11/business/fi-levi11 http://www.businessweek.com/1999/99_07/b3616001.htm http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,987368-1,00.html http://www.levistrauss.com/brands/signature-by-levistrauss http://articles.sfgate.com/2002-08-15/business/17556016_1_levi-straussneimanmarcus-saks
31 | P a g e
32 | P a g e
You might also like
- Marketing Project On LevisDocument6 pagesMarketing Project On LevisHelpdeskNo ratings yet
- Levis Strauss Power Point PresentationDocument25 pagesLevis Strauss Power Point PresentationPurva BhandariNo ratings yet
- LevisDocument14 pagesLevisMishika WadhwaniNo ratings yet
- Levi's PakistanDocument31 pagesLevi's Pakistanpandeyjdeepak100% (1)
- Brand Equity PyramidDocument8 pagesBrand Equity PyramidBhushan GoyalNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy Levis Strauss & Co.Document18 pagesMarketing Strategy Levis Strauss & Co.Sayeed Ahmed89% (19)
- Levis ReportDocument49 pagesLevis Reportsimra mehar67% (3)
- Levi S Final Project UpdatedDocument32 pagesLevi S Final Project UpdatedIsmail Fakhar0% (1)
- WranglerDocument34 pagesWrangleraman_suneja123100% (1)
- Strategic Management of LevisDocument23 pagesStrategic Management of LevisAnns AhmadNo ratings yet
- Marketing :questionnaireDocument3 pagesMarketing :questionnairerahul vatsyayan67% (3)
- ProvogueDocument27 pagesProvogueAnurag MishraNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Levis Wrangler & LeeDocument10 pagesComparative Analysis of Levis Wrangler & LeeNeelakshi srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Mix WranglerDocument2 pagesMarketing Mix WranglerSakshi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Levis Case StudyDocument10 pagesLevis Case StudyRagini VyasNo ratings yet
- Levis Final ReportDocument27 pagesLevis Final ReportOsama RiazNo ratings yet
- Advanced Marketing 2007/2008: HomeworkDocument40 pagesAdvanced Marketing 2007/2008: HomeworkJyoti PathrejaNo ratings yet
- Future of Luxury Brands in IndiaDocument76 pagesFuture of Luxury Brands in IndiaHemanshu Pandita100% (1)
- UCB & LEVIsDocument26 pagesUCB & LEVIsKhyati DhabaliaNo ratings yet
- Zara Company Project ReportDocument24 pagesZara Company Project Reportabhishek2006No ratings yet
- Nike PPT ON BUSINESS ETHICSDocument13 pagesNike PPT ON BUSINESS ETHICSSachin NagargojeNo ratings yet
- ArrowDocument72 pagesArrowVandana AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Benetton Group ProjectDocument15 pagesBenetton Group ProjectSonu DhangarNo ratings yet
- Arvind LTDDocument52 pagesArvind LTDabhi96410% (1)
- HR Policy of Aditya Birla GroupDocument3 pagesHR Policy of Aditya Birla GroupMd Minhaj100% (1)
- Zara and HMDocument19 pagesZara and HMYing SuvannachiveNo ratings yet
- Allen SollyDocument38 pagesAllen SollyVarun KannanNo ratings yet
- Levi's (Eom) Submitted by Kanika and UrvashiDocument40 pagesLevi's (Eom) Submitted by Kanika and UrvashiKomal ShreeNo ratings yet
- Fab IndiaDocument24 pagesFab IndiaSuvo Saha100% (1)
- Presentation On Levis Wrangler & LeeDocument24 pagesPresentation On Levis Wrangler & LeeNeelakshi srivastava100% (1)
- Marketing LevisDocument48 pagesMarketing Levisgumsum100% (9)
- United Colors of BenettonDocument16 pagesUnited Colors of BenettonShiv ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 'A Comparative Analysis For Customer Satisfaction Level of Levi's & Wrangler JeansDocument50 pages'A Comparative Analysis For Customer Satisfaction Level of Levi's & Wrangler JeansDigvijay Singh Chauhan80% (10)
- Brand RepositioningDocument2 pagesBrand Repositioningamitpriyashankar100% (1)
- Comparative Study Between Fila and ReebokDocument56 pagesComparative Study Between Fila and ReebokAniket MoreNo ratings yet
- PEPE JEANS mm2 ProjectDocument25 pagesPEPE JEANS mm2 ProjectDivya50% (2)
- Consumer Behaviour of Allen SollyDocument8 pagesConsumer Behaviour of Allen SollyViveek RulesNo ratings yet
- Target Corporation Supply ChainDocument3 pagesTarget Corporation Supply ChainJanine OnealNo ratings yet
- Management Discussion and Analysis: Economic BackdropDocument47 pagesManagement Discussion and Analysis: Economic BackdropSumeer BeriNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain of ArrowDocument26 pagesSupply Chain of ArrowNamanJainNo ratings yet
- Arvind MillsDocument111 pagesArvind Millsfun_madurai100% (3)
- LevisDocument15 pagesLevisAzhar Shaikh100% (6)
- Gini and Jony FinalDocument13 pagesGini and Jony Finalria0% (1)
- H&M Integrated AssignmentDocument38 pagesH&M Integrated AssignmentKARISHMA RAJNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Hypercity ProjectDocument93 pagesSummer Internship Hypercity ProjectArunesh Singh100% (2)
- Levi's Brand AuditDocument21 pagesLevi's Brand Auditjamie71% (7)
- Case Levi Strauss-UKDocument10 pagesCase Levi Strauss-UKa_chanNo ratings yet
- Levi Strauss: An Iconic American Company Attempts To Reinvent ItselfDocument9 pagesLevi Strauss: An Iconic American Company Attempts To Reinvent Itselfomgan1042No ratings yet
- Levis AssgnDocument4 pagesLevis Assgninstantshikhar222No ratings yet
- Levi's Case StudyDocument6 pagesLevi's Case StudyFlori May CasakitNo ratings yet
- Levis Strauss & Co MM ProjectDocument16 pagesLevis Strauss & Co MM ProjectVaibhav DayalNo ratings yet
- Levi's Strauss & CompanyDocument17 pagesLevi's Strauss & CompanyQurat Ul AinNo ratings yet
- Levis: Aiming at The Echo BoomersDocument8 pagesLevis: Aiming at The Echo BoomersJamil HussainNo ratings yet
- Manegerial Economics Assignment: National Institute of Fashion TechnologyDocument12 pagesManegerial Economics Assignment: National Institute of Fashion Technologyomgan1042No ratings yet
- Levis Marketing CaseDocument6 pagesLevis Marketing Casen.govindarajanNo ratings yet
- Levi StraussDocument4 pagesLevi StraussArshman ChNo ratings yet
- LevismarketingprojectDocument7 pagesLevismarketingprojectJamil HussainNo ratings yet
- LevisDocument3 pagesLevisKin Fai LeungNo ratings yet
- Levis: Aiming at The Echo BoomersDocument7 pagesLevis: Aiming at The Echo BoomersJamil HussainNo ratings yet
- 01 SGDockers VFDocument26 pages01 SGDockers VFbajracharyasandeepNo ratings yet
- EFE of Pak SuzukiDocument4 pagesEFE of Pak SuzukishahmeerbilalNo ratings yet
- Nishat SWOT AnalysisDocument7 pagesNishat SWOT Analysisshahmeerbilal71% (7)
- Competitive Profile Matrix (PSO)Document3 pagesCompetitive Profile Matrix (PSO)shahmeerbilalNo ratings yet
- Zara Case Analysis Operations Management MBM1110Document8 pagesZara Case Analysis Operations Management MBM1110MacMehtaNo ratings yet
- Energy Starvation in Pakistan: Mr. Hafeez-ur-Rehman Obaidullah Masood Syed Muhammad BilalDocument23 pagesEnergy Starvation in Pakistan: Mr. Hafeez-ur-Rehman Obaidullah Masood Syed Muhammad BilalshahmeerbilalNo ratings yet
- Beckman Coulter B2B Marketing StrategyDocument47 pagesBeckman Coulter B2B Marketing Strategyshahmeerbilal100% (2)
- Reed Solomen RSDocument8 pagesReed Solomen RSshahmeerbilalNo ratings yet
- MisDocument3 pagesMisshahmeerbilalNo ratings yet
- Recycling of BagasseDocument4 pagesRecycling of BagasseshahmeerbilalNo ratings yet
- Indirect Pattern For Bad News MessagesDocument27 pagesIndirect Pattern For Bad News MessagesshahmeerbilalNo ratings yet
- Energy Crisis in PakistanDocument14 pagesEnergy Crisis in PakistanshahmeerbilalNo ratings yet
- Null Modem Hand ShakingDocument3 pagesNull Modem Hand ShakingshahmeerbilalNo ratings yet
- Hospital Equipments PrecurmentDocument10 pagesHospital Equipments PrecurmentRashid UmerNo ratings yet
- Gri 202 Market Presence 2016Document10 pagesGri 202 Market Presence 2016Pablo MalgesiniNo ratings yet
- History Nestle Pakistan LTDDocument20 pagesHistory Nestle Pakistan LTDMuhammad Khurram Waheed RajaNo ratings yet
- RBI FAQ of FDI in IndiaDocument53 pagesRBI FAQ of FDI in Indiaaironderon1No ratings yet
- Cultural Norms, Fair & Lovely & Advertising FinalDocument24 pagesCultural Norms, Fair & Lovely & Advertising FinalChirag Bhuva100% (2)
- Khushboo Kukreja Front PageDocument4 pagesKhushboo Kukreja Front Pagejassi7nishadNo ratings yet
- Dispute Form - Bilingual 2019Document2 pagesDispute Form - Bilingual 2019Kxng MindCtrl OrevaNo ratings yet
- A KariozenDocument4 pagesA Kariozenjoseyamil77No ratings yet
- SAP InvoiceDocument86 pagesSAP InvoicefatherNo ratings yet
- Kuis PDFDocument4 pagesKuis PDFZhay Anty0% (1)
- Number Correct Answer ExplanationDocument20 pagesNumber Correct Answer Explanationshmally1No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accounting II AssignmentDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Accounting II Assignmentbirukandualem946No ratings yet
- MARK977 Research For Marketing Decisions Autumn Semester, 2017 Week 8Document54 pagesMARK977 Research For Marketing Decisions Autumn Semester, 2017 Week 8Soumia HandouNo ratings yet
- Guide To Importing in ZimbabweDocument22 pagesGuide To Importing in ZimbabweMandla DubeNo ratings yet
- CH 07Document41 pagesCH 07Mrk KhanNo ratings yet
- Clementi TownDocument3 pagesClementi TownjuronglakesideNo ratings yet
- The Implications of Globalisation For Consumer AttitudesDocument2 pagesThe Implications of Globalisation For Consumer AttitudesIvan Luis100% (1)
- Lean Production SystemDocument8 pagesLean Production SystemRoni Komarul HayatNo ratings yet
- GeM Bidding 2401209Document4 pagesGeM Bidding 2401209SRARNo ratings yet
- Annotated Glossary of Terms Used in The Economic Analysis of Agricultural ProjectsDocument140 pagesAnnotated Glossary of Terms Used in The Economic Analysis of Agricultural ProjectsMaria Ines Castelluccio100% (1)
- Leonardo Roth, FLDocument2 pagesLeonardo Roth, FLleonardorotharothNo ratings yet
- An 09034Document16 pagesAn 09034lejigeNo ratings yet
- Aqua Health PDFDocument1 pageAqua Health PDFJoseph Gavier M. FrancoNo ratings yet
- 2012 Towers Watson Global Workforce StudyDocument24 pages2012 Towers Watson Global Workforce StudySumit RoyNo ratings yet
- أثر السياسة النقدية على سوق الأوراق المالية في الجزائرDocument21 pagesأثر السياسة النقدية على سوق الأوراق المالية في الجزائرTedjani Ahmed DzaitNo ratings yet
- Report On Credit Appraisal in PNBDocument76 pagesReport On Credit Appraisal in PNBSanchit GoyalNo ratings yet
- DSE Assignment SummaryDocument14 pagesDSE Assignment SummaryDipongkorPaulNo ratings yet
- PARCOR-SIMILARITIESDocument2 pagesPARCOR-SIMILARITIESHoney Lizette SunthornNo ratings yet
- State Bank of India (SBI) Personal Loan: Eligibility Criteria Loan Amount Documents RequiredDocument3 pagesState Bank of India (SBI) Personal Loan: Eligibility Criteria Loan Amount Documents RequiredMojahed AhmarNo ratings yet
- $100M Offers: How to Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying NoFrom Everand$100M Offers: How to Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying NoRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (21)
- How to Read People: The Complete Psychology Guide to Analyzing People, Reading Body Language, and Persuading, Manipulating and Understanding How to Influence Human BehaviorFrom EverandHow to Read People: The Complete Psychology Guide to Analyzing People, Reading Body Language, and Persuading, Manipulating and Understanding How to Influence Human BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (33)
- Fascinate: How to Make Your Brand Impossible to ResistFrom EverandFascinate: How to Make Your Brand Impossible to ResistRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Obviously Awesome: How to Nail Product Positioning so Customers Get It, Buy It, Love ItFrom EverandObviously Awesome: How to Nail Product Positioning so Customers Get It, Buy It, Love ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (152)
- $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffFrom Everand$100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (18)
- Summary: Range: Why Generalists Triumph in a Specialized World by David Epstein: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: Range: Why Generalists Triumph in a Specialized World by David Epstein: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- The Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindFrom EverandThe Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (273)
- Ca$hvertising: How to Use More than 100 Secrets of Ad-Agency Psychology to Make Big Money Selling Anything to AnyoneFrom EverandCa$hvertising: How to Use More than 100 Secrets of Ad-Agency Psychology to Make Big Money Selling Anything to AnyoneRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (114)
- Pre-Suasion: Channeling Attention for ChangeFrom EverandPre-Suasion: Channeling Attention for ChangeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (277)
- Dealers of Lightning: Xerox PARC and the Dawn of the Computer AgeFrom EverandDealers of Lightning: Xerox PARC and the Dawn of the Computer AgeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (88)
- Jab, Jab, Jab, Right Hook: How to Tell Your Story in a Noisy Social WorldFrom EverandJab, Jab, Jab, Right Hook: How to Tell Your Story in a Noisy Social WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessFrom EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessNo ratings yet
- Summary: Traction: Get a Grip on Your Business: by Gino Wickman: Key Takeaways, Summary, and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Traction: Get a Grip on Your Business: by Gino Wickman: Key Takeaways, Summary, and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (10)
- Summary: Dotcom Secrets: The Underground Playbook for Growing Your Company Online with Sales Funnels by Russell Brunson: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: Dotcom Secrets: The Underground Playbook for Growing Your Company Online with Sales Funnels by Russell Brunson: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Brand Identity Breakthrough: How to Craft Your Company's Unique Story to Make Your Products IrresistibleFrom EverandBrand Identity Breakthrough: How to Craft Your Company's Unique Story to Make Your Products IrresistibleRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Scientific Advertising: "Master of Effective Advertising"From EverandScientific Advertising: "Master of Effective Advertising"Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (163)
- Create Once, Distribute Forever: How Great Creators Spread Their Ideas and How You Can TooFrom EverandCreate Once, Distribute Forever: How Great Creators Spread Their Ideas and How You Can TooNo ratings yet
- Summary: $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your Stuff by Alex Hormozi: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your Stuff by Alex Hormozi: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (6)
- Marketing Made Simple: A Step-by-Step StoryBrand Guide for Any BusinessFrom EverandMarketing Made Simple: A Step-by-Step StoryBrand Guide for Any BusinessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (203)
- Blue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantFrom EverandBlue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (387)
- How To Win Customers And Keep Them For Life: An Action-Ready Blueprint for Achieving the Winner's Edge!From EverandHow To Win Customers And Keep Them For Life: An Action-Ready Blueprint for Achieving the Winner's Edge!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Invisible Influence: The Hidden Forces that Shape BehaviorFrom EverandInvisible Influence: The Hidden Forces that Shape BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (131)
- Understanding Digital Marketing: Marketing Strategies for Engaging the Digital GenerationFrom EverandUnderstanding Digital Marketing: Marketing Strategies for Engaging the Digital GenerationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (22)
- How to Get a Meeting with Anyone: The Untapped Selling Power of Contact MarketingFrom EverandHow to Get a Meeting with Anyone: The Untapped Selling Power of Contact MarketingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (28)
- Yes!: 50 Scientifically Proven Ways to Be PersuasiveFrom EverandYes!: 50 Scientifically Proven Ways to Be PersuasiveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (153)
- Summary: Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion by Robert B. Cialdini Ph.D.: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion by Robert B. Cialdini Ph.D.: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Summary: The 1-Page Marketing Plan: Get New Customers, Make More Money, And Stand Out From The Crowd by Allan Dib: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The 1-Page Marketing Plan: Get New Customers, Make More Money, And Stand Out From The Crowd by Allan Dib: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- The Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetFrom EverandThe Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetNo ratings yet