Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Neurontin (Gabapentin)
Uploaded by
E100%(3)100% found this document useful (3 votes)
10K views1 pageGabapentin increases the synaptic concentration of GABA, enhances GABA responses at non-synaptic sites in neuronal tissues, and reduces the release of mono-amine neurotransmitters. Gabpentin has also been shown to bind and activate the adenosine A1 receptor. Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal medicines (ask patient specifically)
Original Description:
Original Title
Neurontin (gabapentin)
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGabapentin increases the synaptic concentration of GABA, enhances GABA responses at non-synaptic sites in neuronal tissues, and reduces the release of mono-amine neurotransmitters. Gabpentin has also been shown to bind and activate the adenosine A1 receptor. Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal medicines (ask patient specifically)
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(3)100% found this document useful (3 votes)
10K views1 pageNeurontin (Gabapentin)
Uploaded by
EGabapentin increases the synaptic concentration of GABA, enhances GABA responses at non-synaptic sites in neuronal tissues, and reduces the release of mono-amine neurotransmitters. Gabpentin has also been shown to bind and activate the adenosine A1 receptor. Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal medicines (ask patient specifically)
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
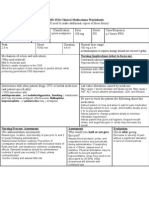
Clinical Medications Worksheets
Generic Name Trade Name Classification Dose Route Time/frequency
gabapentin Neurontin analgesic adjuncts, anticonvulsants 900 mg PO tid
Peak Onset Duration Normal dosage range
2-4 hr rapid 8 hr 300 mg 3 times daily initially. Titration may be continued until desired
(range is 900-1800 mg/day in 3 divided doses; doses should not be
more than 12 hr apart). Doses up to 2400-3600 mg/day have been well
tolerated.
Why is your patient getting this medication. For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or solutions
Partial seizures with and without secondary generalization N/A
(adjunct treatment). Neuropathy.
Mechanism of action and indications Nursing Implications (what to focus on)
(Why med ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactions
Gabapentin interacts with cortical neurons at auxillary subunits Hypersensitivity. Geriatric patients (because of age-related ↓ in renal
of voltage-sensitive calcium channels. Gabapentin increases function).
the synaptic concentration of GABA, enhances GABA
Common side effects
responses at non-synaptic sites in neuronal tissues, and reduces
Confusion, depression, drowsiness, ataxia.
the release of mono-amine neurotransmitters. One of the
mechanisms implicated in this effect of gabapentin is the
reduction of the axon excitability measured as an amplitude
change of the presynaptic fibre volley (FV) in the CA1 area of
the hippocampus. This is mediated through its binding to
presynaptic NMDA receptors. Other studies have shown that
the antihyperalgesic and antiallodynic effects of gabapentin are
mediated by the descending noradrenergic system, resulting in
the activation of spinal alpha2-adrenergic receptors.
Gabapentin has also been shown to bind and activate the
adenosine A1 receptor.
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal Lab value alterations caused by medicine
medicines (ask patient specifically) May cause false-positive readings when testing for urinary protein with
Seroquel: Central nervous system- and/or respiratory- Ames N-Multistix SG dipstick test; use sulfosalicylic acid precipitation
depressant effects may be additively or synergistically procedure. May cause leucopenia.
increased in patients taking multiple drugs that cause these Be sure to teach the patient the following about this medication
effects, especially in elderly or debilitated patients. Instruct patient to take medication exactly as directed. Take missed
Reglan: Central nervous system- and/or respiratory-depressant doses as soon as possible; if less than 2 hr until next dose, take dose
effects may be additively or synergistically increased in immediately and take next dose 1-2 hr later, then resume regular
patients taking multiple drugs that cause these effects, dosing schedule. Do not double doses. Advise patient not to take
especially in elderly or debilitated patients. gabapentin within 2 hr of an antacid. Gabapentin may cause dizziness
and drowsiness. Caution patient to avoid driving or activities requiring
alertness until response to medication is known. Instruct patient to
notify health care professional of medication regimen before treatment
or surgery. Advise patient to carry identification describing disease
process and medication regimen at all times.
Nursing Process- Assessment Assessment Evaluation
(Pre-administration assessment) Why would you hold or not give this med? Check after giving
Assess location, duration, and characteristics of Before surgery. Symptoms of overdose Decreased incidence of seizures.
seizure activity. Assess location, characteristics, include ataxia, labored breathing, ptosis,
and intensity of pain periodically during therapy. sedation, hypoactivity, and excitation.
You might also like
- Zoloft Sertraline Drug CardDocument1 pageZoloft Sertraline Drug CardSheri490100% (1)
- NeurontinDocument1 pageNeurontinAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Librium ChlordiazepoxideDocument2 pagesLibrium ChlordiazepoxideENo ratings yet
- Alprazolam Dosage, Uses, Side EffectsDocument2 pagesAlprazolam Dosage, Uses, Side EffectsKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- GabapentinDocument2 pagesGabapentinSar Patts100% (1)
- GabapentinDocument3 pagesGabapentinاحمد مفرح سالمNo ratings yet
- Drug SertralineDocument1 pageDrug SertralineSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug LexaproDocument1 pageDrug LexaproSrkocher100% (1)
- LorazepamDocument1 pageLorazepamMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Buspar (Buspirone)Document1 pageBuspar (Buspirone)ENo ratings yet
- DRUG SODIUM VALPROATE (Depakote, Epilim, Episenta)Document5 pagesDRUG SODIUM VALPROATE (Depakote, Epilim, Episenta)Pearl Princess Guerrero100% (2)
- Geodon (Ziprasidone)Document2 pagesGeodon (Ziprasidone)ENo ratings yet
- Prozac FluoxetineDocument2 pagesProzac FluoxetineENo ratings yet
- Zopiclone clinical worksheetDocument2 pagesZopiclone clinical worksheetMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- QuetiapineDocument3 pagesQuetiapineMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Aripiprazole Drug Study - Rhuby AbenojaDocument1 pageAripiprazole Drug Study - Rhuby AbenojaRHUBY ABENOJANo ratings yet
- RemeronDocument1 pageRemeronENo ratings yet
- Drug Card BenadrylDocument1 pageDrug Card BenadrylAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Venlafaxine XRDocument2 pagesVenlafaxine XRMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument27 pagesDrugspeterjongNo ratings yet
- AtivanDocument2 pagesAtivanNinoska Garcia-Ortiz100% (4)
- AMITRIPTYLINEDocument2 pagesAMITRIPTYLINERPh Krishna Chandra JagritNo ratings yet
- Docusate Sodium (Colace)Document2 pagesDocusate Sodium (Colace)E100% (1)
- Temazepam (Restoril)Document1 pageTemazepam (Restoril)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- AlprazolamDocument2 pagesAlprazolamGLen CaniedoNo ratings yet
- DesyrelDocument1 pageDesyrelKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- RamiprilDocument3 pagesRamiprilMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Xanax Drug CardDocument3 pagesXanax Drug Cardnasir khanNo ratings yet
- Naloxone (Narcan)Document2 pagesNaloxone (Narcan)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Fluticasone Flovent HFA asthma inhaler guideDocument1 pageFluticasone Flovent HFA asthma inhaler guideKevin Nelson0% (1)
- Benzodiazepines Drug StudyDocument4 pagesBenzodiazepines Drug Studyaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Atrovent (Ipratropium)Document1 pageAtrovent (Ipratropium)E100% (2)
- Drug Card ToradolDocument2 pagesDrug Card ToradolAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Drug Card LasixDocument2 pagesDrug Card LasixAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Aricept Donepezil Drug CardDocument1 pageAricept Donepezil Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Drug NeurontinDocument1 pageDrug NeurontinSrkocher100% (2)
- Managing Memantine Therapy for Alzheimer's PatientsDocument2 pagesManaging Memantine Therapy for Alzheimer's PatientsSNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Acetadote, Mucomyst MucolyticsDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Acetadote, Mucomyst MucolyticsMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FluvoxamineDocument2 pagesDrug Study FluvoxamineAngeline de Gala0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyRai D. MacapantonNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityLouie Danielle SegarraNo ratings yet
- CymbaltaDocument2 pagesCymbaltaENo ratings yet
- GuaifenesinDocument2 pagesGuaifenesinapi-379794150% (2)
- Tricyclic antidepressants overviewDocument2 pagesTricyclic antidepressants overviewAaLona RobinsonNo ratings yet
- NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsDocument1 pageNURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsCassieNo ratings yet
- Keppra (Levetiracetam)Document2 pagesKeppra (Levetiracetam)E100% (1)
- Percocet Drug CardDocument1 pagePercocet Drug CardSheri490100% (4)
- Lamictal (Lamotrigine)Document1 pageLamictal (Lamotrigine)E100% (1)
- Nalbuphine (Nubain)Document2 pagesNalbuphine (Nubain)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- ZofranDocument1 pageZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- TylenolDocument1 pageTylenolCassieNo ratings yet
- Morphine (Astramorph)Document1 pageMorphine (Astramorph)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Campral (Acamprosate Calcium)Document1 pageCampral (Acamprosate Calcium)E100% (1)
- Kemstro (Baclofen)Document1 pageKemstro (Baclofen)E100% (1)
- Drug Study: Adamson UniversityDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Adamson UniversityRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- DarvacetDocument1 pageDarvacetAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Morphine (Astramorph) PCADocument2 pagesMorphine (Astramorph) PCAAdrianne Bazo100% (3)
- NURS 2516 Clinical Medications Worksheets: Nursing Process-AssessmentDocument1 pageNURS 2516 Clinical Medications Worksheets: Nursing Process-AssessmentAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- AcetaminophenDocument1 pageAcetaminophenKatie McPeek100% (1)
- Drug TylenolDocument1 pageDrug TylenolSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency Anemia PathoDocument6 pagesIron Deficiency Anemia PathoENo ratings yet
- Left-Side CHF PathoDocument5 pagesLeft-Side CHF PathoENo ratings yet
- Influenza B PathoDocument4 pagesInfluenza B PathoENo ratings yet
- Pyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISDocument4 pagesPyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISENo ratings yet
- Hyperparathyroidism PathoDocument2 pagesHyperparathyroidism PathoENo ratings yet
- Chemical Burns PathoDocument2 pagesChemical Burns PathoENo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument4 pagesCongestive Heart FailureENo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure-ABDocument3 pagesCongestive Heart Failure-ABENo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Short PathoDocument2 pagesPneumonia Short PathoENo ratings yet
- Hyponatremic Dehydration PathoDocument4 pagesHyponatremic Dehydration PathoENo ratings yet
- Acute Pancreatitis PathoDocument5 pagesAcute Pancreatitis PathoENo ratings yet
- Bowel Resection PathoDocument7 pagesBowel Resection PathoENo ratings yet
- Autonomic DysreflexiaDocument2 pagesAutonomic DysreflexiaENo ratings yet
- Campral (Acamprosate Calcium)Document1 pageCampral (Acamprosate Calcium)E100% (1)
- Pancreatitis Short PathoDocument2 pagesPancreatitis Short PathoENo ratings yet
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocument1 pageClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENo ratings yet
- Theragran (Multiple Vitamins)Document3 pagesTheragran (Multiple Vitamins)ENo ratings yet
- Subluxation c6c7 Short PathoDocument1 pageSubluxation c6c7 Short PathoENo ratings yet
- Zosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)Document2 pagesZosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)E67% (3)
- Geodon (Ziprasidone)Document2 pagesGeodon (Ziprasidone)ENo ratings yet
- Buspar (Buspirone)Document1 pageBuspar (Buspirone)ENo ratings yet
- FiberCon (Polycarbophil)Document1 pageFiberCon (Polycarbophil)ENo ratings yet
- ZofranDocument1 pageZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- Prozac (Fluoxetine) 40mgDocument1 pageProzac (Fluoxetine) 40mgENo ratings yet
- Silvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)Document1 pageSilvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)ENo ratings yet
- Lexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)Document2 pagesLexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)ENo ratings yet
- Darvocet (Propoxyphene Napsylate/Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDarvocet (Propoxyphene Napsylate/Acetaminophen)ENo ratings yet
- Florinef (Fludrocortisone)Document3 pagesFlorinef (Fludrocortisone)E100% (1)
- Reglan (Metoclopramide)Document3 pagesReglan (Metoclopramide)E100% (1)
- Keppra (Levetiracetam)Document2 pagesKeppra (Levetiracetam)E100% (1)
- Case Study: Cushing and AddisonDocument4 pagesCase Study: Cushing and AddisonJeff ValdezNo ratings yet
- Jupiter EngDocument34 pagesJupiter EngakukauakuNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Diagnosis of A Third Root Canal in First and Second Maxillary Premolars A Challenge For The ClinicianDocument7 pagesPreoperative Diagnosis of A Third Root Canal in First and Second Maxillary Premolars A Challenge For The ClinicianS S Saad SaadNo ratings yet
- AllDocument48 pagesAllnanchieNo ratings yet
- Aapd Guidelines - Restorative DentistryDocument8 pagesAapd Guidelines - Restorative DentistrymahmoudNo ratings yet
- Clinical AssignmentDocument9 pagesClinical AssignmentkomalNo ratings yet
- Oman New Reimbursement Claim FormDocument3 pagesOman New Reimbursement Claim Formtoalok4723No ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Use of RH (D) Immunoglobulin (Anti D) (C Obs 6) Review November 2015Document11 pagesGuidelines For The Use of RH (D) Immunoglobulin (Anti D) (C Obs 6) Review November 2015vasanthNo ratings yet
- Exodus SMLXL Rem KoolhaasDocument11 pagesExodus SMLXL Rem Koolhaasjako60No ratings yet
- Salient Features - MPPRC DIARRHEA RevisedDocument12 pagesSalient Features - MPPRC DIARRHEA RevisedLui Yalong Jr.No ratings yet
- Newcastle Satisfaction With Nursing Scales AnDocument6 pagesNewcastle Satisfaction With Nursing Scales AnlemootpNo ratings yet
- Complication of PregnancyDocument55 pagesComplication of PregnancyQuolette Constante100% (1)
- Short Sightedness Vs Long SightDocument1 pageShort Sightedness Vs Long SightDevill DavajNo ratings yet
- AplDocument37 pagesApladitiya tegarNo ratings yet
- Chron Skin Allergy Oct 2010Document32 pagesChron Skin Allergy Oct 2010shannon3458No ratings yet
- Jurnal Kesehatan: Analisis Waste Dengan Model Lean Hospital Pada Pelayanan Poli Rawat JalanDocument10 pagesJurnal Kesehatan: Analisis Waste Dengan Model Lean Hospital Pada Pelayanan Poli Rawat JalanGuillermo Luis AcostaNo ratings yet
- Rectal ProlapseDocument2 pagesRectal ProlapseSalem ZoghbyNo ratings yet
- RN Viray ResumefinalDocument1 pageRN Viray Resumefinalapi-661315652No ratings yet
- Differentiating Physiologic vs Pathologic Jaundice in NewbornsDocument2 pagesDifferentiating Physiologic vs Pathologic Jaundice in Newbornscheem_porkeezNo ratings yet
- Bio Equivalence Study of Tizanidine HCL Tablets 4 MG of DR - Reddys Under Fasting Conditions - Full Text View - Clinical TrialsDocument4 pagesBio Equivalence Study of Tizanidine HCL Tablets 4 MG of DR - Reddys Under Fasting Conditions - Full Text View - Clinical TrialsMuhammad Hafeez ArainNo ratings yet
- Child With HematuriaDocument42 pagesChild With HematuriaalaaNo ratings yet
- Paraphrasing: How, Tips, ExamplesDocument9 pagesParaphrasing: How, Tips, ExamplesMahesh RamesNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Complications: Donald G. Camatura, RNDocument96 pagesPostpartum Complications: Donald G. Camatura, RNDonald Garcesa Camatura100% (4)
- Katsuura 2016Document6 pagesKatsuura 2016Wahyu InsanNo ratings yet
- Pulseless VT During Pediatric Dental AnesthesiaDocument4 pagesPulseless VT During Pediatric Dental AnesthesiaLjubomirErdoglijaNo ratings yet
- The Crusades and Ancient Medical TheoryDocument3 pagesThe Crusades and Ancient Medical TheoryJordan Tyler VoltzNo ratings yet
- Dental AssistantDocument19 pagesDental AssistantMelissa Forbes80% (5)
- Constrictive Pericarditis - UpToDateDocument26 pagesConstrictive Pericarditis - UpToDateSebastian CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Preimplantation Genetic DiagnosisDocument324 pagesAtlas of Preimplantation Genetic DiagnosisLaura Andrade100% (5)
- German Measles (Rubella) : Romena Salazar Monderondo Bs BiologyDocument10 pagesGerman Measles (Rubella) : Romena Salazar Monderondo Bs Biologycasandra moranteNo ratings yet