Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basics
Uploaded by
gopalraj2020Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basics
Uploaded by
gopalraj2020Copyright:
Available Formats
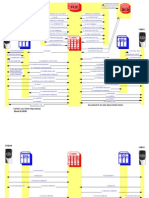
A reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (ROADM) is a form of optical add-drop multiplexer that adds the ability to remotely switch
traffic from a WDM system at the wavelength layer. This is achieved through the use of a Wavelength selective switching module. This allows individual or multiple wavelengths carrying data channels to be added and/or dropped from a transport fiber without the need to convert the signals on all of the WDM channels to electronic signals and back again to optical signals. The main advantages of the ROADM are: The planning of entire bandwidth assignment need not be carried out during initial deployment of a system. The configuration can be done as and when required without affecting traffic already passing the ROADM. ROADM allows for remote configuration and reconfiguration. In ROADM, as it is not clear beforehand where a signal can be potentially routed, there is a necessity of power balancing of these signals. ROADMs allow for automatic power balancing.
ROADM functionality originally appeared in long-haul DWDM equipment, but by 2005, it began to appear in metro optical systems because of the need to build out major metropolitan networks in order to deal with the traffic driven by the increasing demand for packet-based services. The switching or reconfiguration functions of a ROADM can be achieved using a variety of switching technologies including MEMS, Liquid crystal, thermo optic and beam-steering switches in planar waveguide circuits, and tunable optical filter technology. ** IN AMDs OEO should take place at each add & drop points. It introduces delay. ** To reduce this OADM has come into picture. Channels add/drop can be done from the same fiber without any OEO conversion at the demux/mux points in the network. **In OADM only one add/drop/pass thru can be done. In order to support the increase in bandwidth of metro, long haul networks ROADM is introduced. ** Main use of ROADM is using WSS it can direct the channels to different ways. (1X5 & 1X9). ** Using CMD44 cards we can accommodate total of 88 wave lengths. ** NO need of pre planed bandwidth allocation / hardware deployment like in TOADM/GOADM group CMD4 cards. ** WSS has the capacity to do Power balancing whenever there is new channel add/drop happens in the network. ** Optical Power monitoring on all channels & power equalization on input, output, add & drop channels. ** Some more Benefits Elimination of the OEO Pass-through tax Single Wavelength Granularity No stranded bandwidth Fully Automated Optical Layer Reduced human error, increased reliability, reduced OPEX
** Wave length steering, Selectivity & Directionality are the three main capabilities of a ROADM configuration.
**Granularity is the extent to which a system is broken down into small parts, either the system itself or its description or observation. It is the "extent to which a larger entity is subdivided. For example, a yard broken into inches has finer granularity than a yard broken into feet ** OSC is Optical Service Channel. **A ROADM network element typically includes: Transponders ROADM Subsystem Optical Service Channel Optical Power Monitoring Amplifiers (Pre-Amp & Post-Amp) Dispersion Compensation Module
Grating: Optical device consisting of a surface with many parallel grooves in it; disperses a beam of light (or other electromagnetic radiation) into its wavelengths to produce its spectrum
** Main part in WSS is Switch Engine which uses the following technologies LC (Liquid Crystal) MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical deviceS) PLC (Photonic Light guide Circuit / Planar Light-wave Circuit) LCoS (Liquid Crystal on Silicon)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- GSM Call Flow PDFDocument4 pagesGSM Call Flow PDFKiran Dhiman100% (1)
- An 613Document26 pagesAn 613krishnamohankola321No ratings yet
- MTL5042Document1 pageMTL5042julsaezNo ratings yet
- 4339 Midterm 01 Sem 011112Document3 pages4339 Midterm 01 Sem 011112xv2legionNo ratings yet
- Classification EssayDocument4 pagesClassification Essayapi-511995030No ratings yet
- Final Daze SeptemberDocument30 pagesFinal Daze SeptemberNeville AnimusicNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing: Figure 1: Concept of MultiplexingDocument4 pagesMultiplexing: Figure 1: Concept of MultiplexingMohammad Afiq AbidinNo ratings yet
- Rienzi: The Last of The Tribunes / by Richard Wagner English Translation of The Poem, Legend and Story of The Opera, by John P. JacksonDocument53 pagesRienzi: The Last of The Tribunes / by Richard Wagner English Translation of The Poem, Legend and Story of The Opera, by John P. JacksonEkashmanNo ratings yet
- Landslide Warning System Using Wireless Sensor NetworkDocument5 pagesLandslide Warning System Using Wireless Sensor NetworkInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Silent Hill Promise (Reprise) TabDocument1 pageSilent Hill Promise (Reprise) TabAdam Baylin100% (1)
- CG9812 V500R006C10 Feature DescriptionDocument79 pagesCG9812 V500R006C10 Feature Descriptionraj1978enatorNo ratings yet
- Seven Questions On Aristotelian Definitions of Tragedy and Comedy PDFDocument102 pagesSeven Questions On Aristotelian Definitions of Tragedy and Comedy PDFmarcusNo ratings yet
- Cheerdance (Guidelines & Mechanics)Document3 pagesCheerdance (Guidelines & Mechanics)Sugarleyne AdlawanNo ratings yet
- Review of Phasor Notation: Cos SinDocument15 pagesReview of Phasor Notation: Cos Siniordache0% (1)
- EssayDocument3 pagesEssayRohany AldefollaNo ratings yet
- Manual Radio West Marine VHF550 PDFDocument208 pagesManual Radio West Marine VHF550 PDFRdOx770% (1)
- Andre Waignein - Rhapsody PianoDocument39 pagesAndre Waignein - Rhapsody PianoАртём Бубнов100% (1)
- Art MakeupDocument209 pagesArt MakeupMilica MiMa Martic100% (4)
- k111, Square Wave GeneratorDocument2 pagesk111, Square Wave GeneratorYasir AliNo ratings yet
- Audiometry Procedures Manual: January 2009Document117 pagesAudiometry Procedures Manual: January 2009Victoria KusumoNo ratings yet
- Materi Sma Kelas X Introducing Ourself and OtherDocument3 pagesMateri Sma Kelas X Introducing Ourself and OtherNovita MulyawatiNo ratings yet
- 1 DistressDocument2 pages1 DistressAlin PieNo ratings yet
- Studio Sound 1988 08Document66 pagesStudio Sound 1988 08Hifi ShareNo ratings yet
- Lost All Seasons 720p Torrent PDFDocument2 pagesLost All Seasons 720p Torrent PDFHeroe Wsg CassaNo ratings yet
- Advanced VocabularyDocument10 pagesAdvanced VocabularyTrinity School, CarlisleNo ratings yet
- 7200 C30 5Document2 pages7200 C30 5Vasile Popescu0% (1)
- Kohaku No Ai, (Love of Amber)Document4 pagesKohaku No Ai, (Love of Amber)thieves11No ratings yet
- Essential Chords in Open G TuningDocument17 pagesEssential Chords in Open G TuningNail Bashirov100% (5)
- Bin Trac Install 09-15-09BWDocument21 pagesBin Trac Install 09-15-09BWRobinson SanchezNo ratings yet
- Christmas Bells FINAL-Score and PartsDocument64 pagesChristmas Bells FINAL-Score and PartsMatthew Peter ClareNo ratings yet